单链表
- 1,单链表的概念及结构
- 2,单链表的实现
- 2.1初始化内容(所需文件,接口)
- 2.2申请结点
- 2.3打印单链表
- 2.4尾插
- 2.5头插
- 2.6尾删
- 2.7头删
- 2.8查找
- 2.9在pos位置之后插入
- 2.10在pos位置前面插入
- 2.11删除pos之后的值
- 2.12删除pos位置的值
- 2.13销毁链表
- 3.全部码源
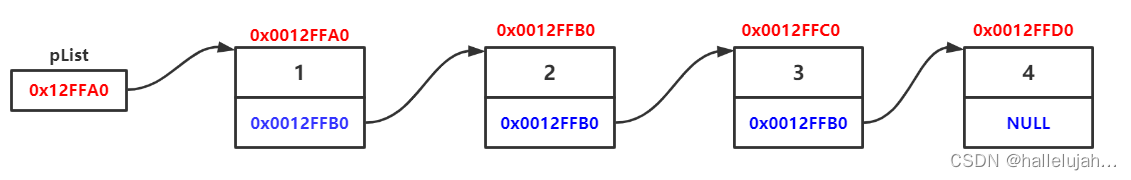
1,单链表的概念及结构
概念:链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的 。
现实中 数据结构中
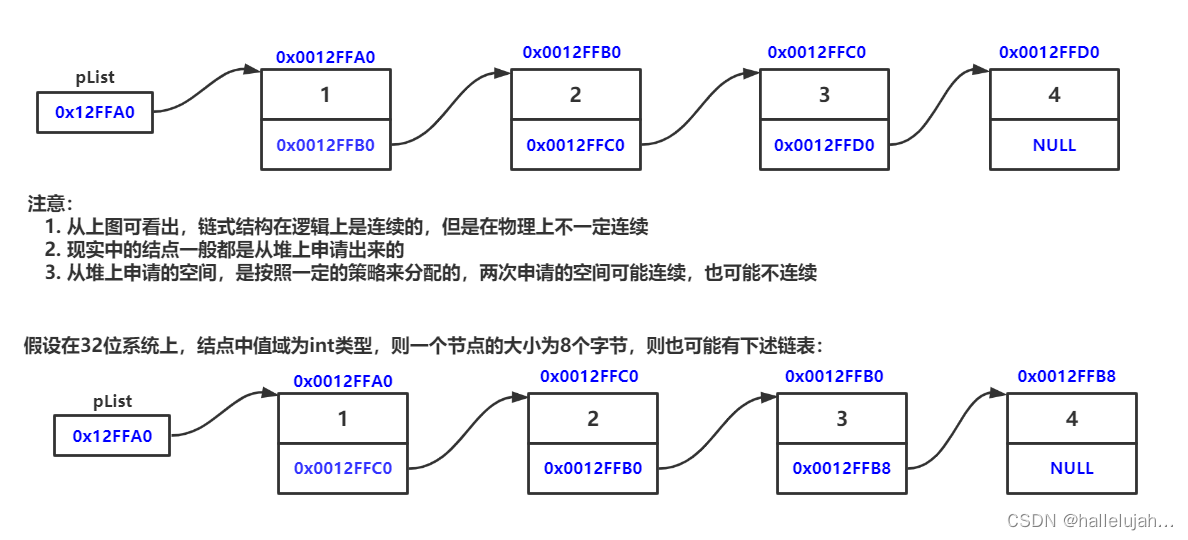
2,单链表的实现
2.1初始化内容(所需文件,接口)
所需文件
头文件->SList.h
源文件->test.c
源文件->SList.c
接口(SList.h中)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>typedef int SLTDataType;typedef struct SListNode
{SLTDataType data;struct SListNode* next;
}SLTNode;void SLTPrint(SLTNode* phead);SLTNode* BuySListNode(SLTDataType x);
void SLTPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x);
void SLTPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x);void SLTPopBack(SLTNode** pphead);
void SLTPopFront(SLTNode** pphead);SLTNode* SLTFind(SLTNode* phead, SLTDataType x);// 在pos之前插入x
void SLTInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x);// 在pos以后插入x
void SLTInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x);// 删除pos位置
void SLTErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos);// 删除pos的后一个位置
void SLTInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos);
2.2申请结点
SLTNode* BuySListNode(SLTDateType x)
{SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode*));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}else{newnode->date = x;newnode->next = NULL;}return newnode;
}
2.3打印单链表
void SLTPrint(SLTNode* phead)
{SLTNode* cur = phead;while (cur){printf("%d->", cur->date);cur = cur->next;}printf("NULL\n");
}
2.4尾插
void SLTPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDateType x)
{assert(pphead);//pphead不能为空,pphead为空说明里面没有存指向头节点指针的地址,那就说明没有链表SLTNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);//由于在头插和随机插入的过程中也会涉及到节点的创建,所以这里把节点的创建单独封装了一个函数if (*pphead == NULL){*pphead = newnode;}else{SLTNode* tail = *pphead;while (tail->next != NULL)//假如链表为空这里就非法访问了,因此要先判断{tail = tail->next;}tail->next = newnode;}
}
2.5头插
头插显然是要改变头指针存放的地址,因此形参也需要传递二级指针。头插无需单独考虑空链表的情况
void SLTPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDateType x)
{SLTNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);newnode->next = *pphead;*pphead = newnode;
}
2.6尾删
尾删先要遍历一遍链表找到最后一个节点将其释放掉,还要找到倒数第二个节点将它的指针域中存的地址改为NULL。所以定义两个指针让他们同时去遍历链表,一个找尾,另一个找倒数第二个节点。需要注意的是空链表和只有一个节点的链表的情况,空链表无法进行尾删,而只有一个节点的链表在尾删后会变成一个空链表,这意味着要改变头指针里面存放的地址,所以尾删形参也要传递二级指针。
void SLTPopBack(SLTNode** pphead)
{assert(pphead);assert(*pphead);//暴力检查是否为空链表,空链表不能删数据/*if (*pphead == NULL)//温柔的进行检查{return;}*///只有一个节点if ((*pphead)->next == NULL){free(*pphead);*pphead = NULL;}//有多个节点else{/*SLTNode* tailPrev = NULL;SLTNode* tail = *pphead;while (tail->next != NULL){tailPrev = tail;tail = tail->next;}free(tail);tailPrev = NULL;*/SLTNode* tail = *pphead;while (tail->next->next){tail = tail->next;}free(tail->next);tail->next = NULL;}
}
2.7头删
头删很明显需要改变头指针中存放的地址,所以形参仍然需要传递二级指针。头删只需要注意链表是否为空,空链表无法进行删除。此外在进行头删的时候记得将原来的头节点释放掉,因此在改变头节点之前需要先保留原来头结点的地址,否则在更换完新的头节点后就找不到原来的头节点了。
void SLTPopFront(SLTNode** pphead)
{assert(pphead);assert(*pphead);SLTNode* newnode = (*pphead)->next;//假如链表为空,这里就会发生越界,因此要判断链表是否为空free(*pphead);*pphead = newnode;
}
2.8查找
其实就是遍历一遍链表,但是只能返回第一次出现的地址。查找可以当修改来使用,我们查找到节点的地址后就可以通过地址去修改数据域中存储的数据。
SLTNode* SLTFind(SLTNode* phead, SLTDateType x)
{SLTNode* cur = phead;while (cur){if (cur->date == x){return cur;}cur = cur->next;}return NULL;
}
2.9在pos位置之后插入
先让newnode的指针域存储pos后一个节点的地址,再让pos的指针域存newnode的地址
void SLTInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDateType x)
{assert(pos);SLTNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);newnode->next = pos->next;pos->next = newnode;
}
2.10在pos位置前面插入
和尾插类似,但此时只需要遍历链表找到pos位置的前一个节点即可,同样需要注意pos是头结点的情况,此时就成头插了,需要改变头指针中存的地址,因此函数的形参需要传二级指针。
void SLTInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDateType x)
{assert(pphead);assert(pos);if (pos == *pphead){SLTPushFront(pphead, x);}else{SLTNode* prev = *pphead;if (prev->next != pos){prev = prev->next;}SLTNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);prev->next = newnode;newnode->next = pos;}
}
2.11删除pos之后的值
注意不能写成后面这样:pos->next = pos->next->next。这样写虽然把pos位置后面的节点从链表中剔除出去了,但并没有真正意义上的实现删除,因为每一个节点都是通过malloc在堆上申请的,不使用的时候要主动的去释放掉,也就是free掉,把这块空间归还给操作系统,否则会导致内存泄漏。而上面那样写,就会导致pos后面的节点丢失,无法进行释放,正确的做法是在执行这条语句之前把pos后边节点的地址先保存起来。
void SLTEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos)
{assert(pos);//检查pos是不是尾结点assert(pos->next);SLTNode* posNext = pos->next;pos->next = posNext->next;free(posNext);posNext = NULL;
}
2.12删除pos位置的值
pos可能是头结点的地址,因此形参要用二级指针。
void SLTErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos)
{assert(pphead);assert(pos);if (pos == *pphead){SLTPopFront(pphead);}else{SLTNode* prev = *pphead;while (prev->next != pos){prev = prev->next;}prev->next = pos->next;free(pos);}
}
2.13销毁链表
void SListDestroy(SLTNode* plist)
{assert(plist);SLTNode* cur = plist;while (cur){SLTNode* pur = cur;cur = cur->next;free(pur);}
}
3.全部码源
SList.c
#include"SList.h"void SLTPrint(SLTNode* phead)
{SLTNode* cur = phead;//while (cur != NULL)while (cur){printf("%d->", cur->data);cur = cur->next;}printf("NULL\n");
}SLTNode* BuySListNode(SLTDataType x)
{SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;return newnode;
}void SLTPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{SLTNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);if (*pphead == NULL){// 改变的结构体的指针,所以要用二级指针*pphead = newnode;}else{SLTNode* tail = *pphead;while (tail->next != NULL){tail = tail->next;}// 改变的结构体,用结构体的指针即可tail->next = newnode;}
}void SLTPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{SLTNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);newnode->next = *pphead;*pphead = newnode;
}void SLTPopBack(SLTNode** pphead)
{// 1、空assert(*pphead);// 2、一个节点// 3、一个以上节点if ((*pphead)->next == NULL){free(*pphead);*pphead = NULL;}else{//SLTNode* tailPrev = NULL;//SLTNode* tail = *pphead;//while (tail->next)//{// tailPrev = tail;// tail = tail->next;//}//free(tail);tail = NULL;//tailPrev->next = NULL;SLTNode* tail = *pphead;while (tail->next->next){tail = tail->next;}free(tail->next);tail->next = NULL;}
}void SLTPopFront(SLTNode** pphead)
{assert(pphead);// 空assert(*pphead);// 非空SLTNode* newhead = (*pphead)->next;free(*pphead);*pphead = newhead;
}SLTNode* SLTFind(SLTNode* phead, SLTDataType x)
{SLTNode* cur = phead;while (cur){if (cur->data == x){return cur;}cur = cur->next;}return NULL;
}void SLTInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
{assert(pphead);assert(pos);if (pos == *pphead){SLTPushFront(pphead, x);}else{SLTNode* prev = *pphead;while (prev->next != pos){prev = prev->next;}SLTNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);prev->next = newnode;newnode->next = pos;}
}// 在pos以后插入x
void SLTInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
{assert(pos);SLTNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);pos->next = newnode;newnode->next = pos->next;
}// 删除pos位置
void SLTErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos)
{assert(pphead);assert(pos);if (pos == *pphead){SLTPopFront(pphead);}else{SLTNode* prev = *pphead;while (prev->next != pos){prev = prev->next;}prev->next = pos->next;free(pos);//pos = NULL;}
}// 删除pos的后一个位置
void SLTEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos)
{assert(pos);// 检查pos是否是尾节点assert(pos->next);SLTNode* posNext = pos->next;pos->next = posNext->next;free(posNext);posNext = NULL;
}
SList.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>typedef int SLTDataType;typedef struct SListNode
{SLTDataType data;struct SListNode* next;
}SLTNode;void SLTPrint(SLTNode* phead);SLTNode* BuySListNode(SLTDataType x);
void SLTPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x);
void SLTPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x);void SLTPopBack(SLTNode** pphead);
void SLTPopFront(SLTNode** pphead);SLTNode* SLTFind(SLTNode* phead, SLTDataType x);// 在pos之前插入x
void SLTInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x);// 在pos以后插入x
void SLTInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x);// 删除pos位置
void SLTErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos);// 删除pos的后一个位置
void SLTInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos);
test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"SList.h"void TestSList1()
{int n;printf("请输入链表的长度:");scanf("%d", &n);printf("\n请依次输入每个节点的值:");SLTNode* plist = NULL;for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++){int val;scanf("%d", &val);SLTNode* newnode = BuySListNode(val);// 头插newnode->next = plist;plist = newnode;}SLTPrint(plist);SLTPushBack(&plist, 10000);SLTPrint(plist);
}void TestSList2()
{SLTNode* plist = NULL;SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);SLTPushBack(&plist, 5);SLTPrint(plist);SLTPushFront(&plist, 10);SLTPushFront(&plist, 20);SLTPushFront(&plist, 30);SLTPushFront(&plist, 40);SLTPrint(plist);
}void TestSList3()
{SLTNode* plist = NULL;SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);SLTPushBack(&plist, 5);SLTPrint(plist);SLTPopBack(&plist);SLTPrint(plist);SLTPopBack(&plist);SLTPrint(plist);SLTPopBack(&plist);SLTPrint(plist);SLTPopBack(&plist);SLTPrint(plist);SLTPopBack(&plist);SLTPrint(plist);// SLTPopBack(&plist);// SLTPrint(plist);
}void TestSList4()
{SLTNode* plist = NULL;SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);SLTPushBack(&plist, 5);SLTPrint(plist);SLTPopFront(&plist);SLTPrint(plist);SLTPopFront(&plist);SLTPrint(plist);SLTPopFront(&plist);SLTPrint(plist);SLTPopFront(&plist);SLTPrint(plist);SLTPopFront(&plist);//SLTPopFront(&plist);SLTPrint(plist);
}void TestSList5()
{SLTNode* plist = NULL;SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);SLTPushBack(&plist, 5);SLTPrint(plist);SLTNode* pos = SLTFind(plist, 3);SLTInsert(&plist, pos, 30);
}void TestSList6()
{SLTNode* plist = NULL;SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);SLTPushBack(&plist, 5);SLTPrint(plist);int x;scanf("%d", &x);SLTNode* pos = SLTFind(plist, x);if (pos){SLTInsertAfter(pos, x * 10);}SLTPrint(plist);
}void TestSList7()
{SLTNode* plist = NULL;SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);SLTPushBack(&plist, 5);SLTPrint(plist);int x;scanf("%d", &x);SLTNode* pos = SLTFind(plist, x);if (pos){//SLTErase(&plist, pos);SLTEraseAfter(pos);pos = NULL;}SLTPrint(plist);SLTPopFront(&plist);SLTPrint(plist);SLTPopFront(&plist);SLTPrint(plist);SLTPopFront(&plist);SLTPrint(plist);SLTPopFront(&plist);SLTPrint(plist);}
int main()
{TestSList4();return
💘不知不觉,【数据结构初阶】单链表以告一段落。通读全文的你肯定收获满满,让我们继续为数据结构学习共同奋进!!!