面试的时候经常被问到锁、JUC工具包等相关内容,其中CAS机制是必问题目,以下简单总结CAS的机制、CAS产生的ABA现象、CAS产生的ABA现象解决思路
1.什么是CAS?
CAS(Compare and Swap)是一种多线程同步的原子操作,用于解决并发环境下的数据竞争和线程安全问题。像我们平时使用到的JUC并发包下的AtomicInteger、AtomicLong、AtomicLong、AtomicBoolean等等底层都是基于CAS实现的,另外ReentrantLock、ConcurrentHashMap这些底层也是采用CAS机制实现。
2.CAS的原理?
CAS需要有3个操作数:内存地址V,旧的预期值A,即将要更新的目标值B,首先比较某个内存位置的值与预期值是否相等,如果相等,则将新值写入该内存位置;如果不相等,则表示其他线程已经修改了该内存位置的值,操作失败。这样子就能保证原子性。
如AtomicInteger 类中compareAndSet方法如下,expectedValue是指内存中期望的值,newValue是指新值,VALUE是在类中的偏移量,用于后面CAS操作时使用
public final boolean compareAndSet(int expect, int update) {return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, valueOffset, expect, update);
}
注: jdk17和jdk8实现有很大的不同
其属性如下
// 获取Unsafe的实例
private static final Unsafe U = Unsafe.getUnsafe();
// 标识value字段的偏移量
private static final long VALUE= U.objectFieldOffset(AtomicInteger.class, "value");
// 存储int类型值的地方,使用volatile修饰
private volatile int value;static {try {valueOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(AtomicInteger.class.getDeclaredField("value"));} catch (Exception ex) { throw new Error(ex); }}
这里使用volatile的作用是为了保证可见性( 内存屏障),即一个线程的修改另一个线程可见,线程修改数据后往主存更新数据,另一个线程也从主存读取数据,从而保证可见性。
compareAndSet()方法底层调用Unsafe类的compareAndSwapInt()方法实现,这个方法有四个参数:
- this:当前对象;
- VALUE:对象中字段的偏移量;
- expectedValue:内存中的旧值;
- newValue:新的期望值;
public final native boolean compareAndSwapInt(Object var1, long var2, int var4, int var5);
Unsafe类的compareAndSwapInt()方法是一个本地方法,底层是使用C/C++写的,主要是调用CPU的CAS指令来实现。
再来看一个AtomicInteger 类中的核心方法,getAndIncrement()
public final int getAndIncrement() {return U.getAndAddInt(this, VALUE, 1);
}
getAndIncrement()方法底层是调用的Unsafe的getAndAddInt()方法,这个方法有三个参数分别表示,当前操作对象、对象中字段的偏移量、要增加的值
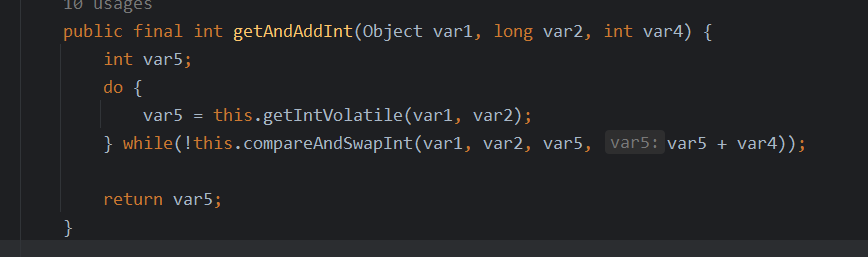
getAndAddInt()方法底层会调用Unsafe类的compareAndSwapInt()方法
public final native boolean compareAndSwapInt(Object var1, long var2, int var4, int var5);
3.ABA现象产生分析
为了方便演示,采用AtomicReference实现一个CAS机制导致的ABA现象,如下
public class CASCostABADemo {private static AtomicReference<Integer> sharedVariable = new AtomicReference<>(10);public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> {int oldValue = sharedVariable.get();System.out.println("Thread 1 - Old value: " + oldValue);sleep(2000); // 线程1暂停1秒,给线程2足够的时间执行// 尝试修改共享变量的值boolean success = sharedVariable.compareAndSet(oldValue, 20);System.out.println("Thread 1 - Value changed: " + success);});Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> {sleep(500); // 线程2暂停0.5秒// 修改共享变量的值为30,然后再修改回10sharedVariable.set(30);System.out.println("Thread 2 - Value changed to 30");sleep(500); // 线程2暂停0.5秒sharedVariable.set(10);System.out.println("Thread 2 - Value changed to 10");});thread1.start();thread2.start();Thread.sleep(3000);System.out.println("Final value: " + sharedVariable.get());}private static void sleep(long milliseconds) {try {Thread.sleep(milliseconds);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}
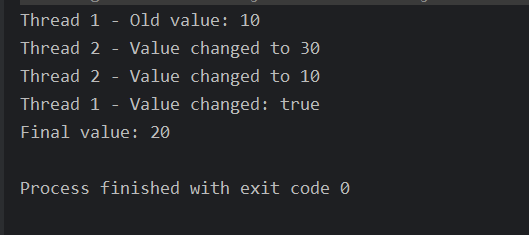
运行结果如下:
具体的说
- 线程1旧值是10,线程2旧值也是10,线程1休眠1秒,线程2得到CPU时间片,进入执行状态;
- 线程2采用CAS机制,内存旧值是10,新值是30,发现不一致,则把10改成30,此时内存值是30;
- 线程2继续执行把30改成10;
- 线程1此时开始执行,发现内存值是10,旧的内存值也是10,因此把10改成20;
以上就是CAS可能会产生的ABA问题。
4.ABA问题解决
为了解决CAS的ABA现象,引入了AtomicStampedReference。我的个人理解CAS的 ABA现象,不能看成是设计的缺陷,可以理解为不同业务场景的选型问题,如果我要实现一个类似于倒计时的功能使用AtomicInteger 就能实现这样的需求。
public class CASABASolveDemo {private static AtomicStampedReference<Integer> sharedVariable = new AtomicStampedReference<>(10, 0);public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> {//当前共享变量的值int oldValue = sharedVariable.getReference();//当前共享变量的版本号int oldStamp = sharedVariable.getStamp();System.out.println("Thread 1 - Old value: " + oldValue + ", Stamp: " + oldStamp);sleep(1000);// 尝试修改共享变量的值int newStamp = oldStamp + 1;boolean success = sharedVariable.compareAndSet(oldValue, 20, oldStamp, newStamp);System.out.println("Thread 1 - Value changed: " + success + ", New Stamp: " + newStamp);});Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> {sleep(500);int[] stampHolder = new int[1];//获取当前共享变量的值,并且把版本号存储在stampHolder 数组中。int currentValue = sharedVariable.get(stampHolder);int stamp = stampHolder[0];System.out.println("Thread 2 - Old value: " + currentValue + ", Stamp: " + stamp);// 修改共享变量的值为30int newStamp = stamp + 1;sharedVariable.compareAndSet(currentValue, 30, stamp, newStamp);System.out.println("Thread 2 - Value changed to 30, New Stamp: " + newStamp);sleep(500);// 修改共享变量的值回10boolean success = sharedVariable.compareAndSet(30, 10, newStamp, newStamp + 1);System.out.println("Thread 2 - Value changed to 10: " + success + ", New Stamp: " + (newStamp + 1));});thread1.start();thread2.start();Thread.sleep(3000);System.out.println("Final value: " + sharedVariable.getReference() + ", Stamp: " + sharedVariable.getStamp());}private static void sleep(long milliseconds) {try {Thread.sleep(milliseconds);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}
ry {
Thread.sleep(milliseconds);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
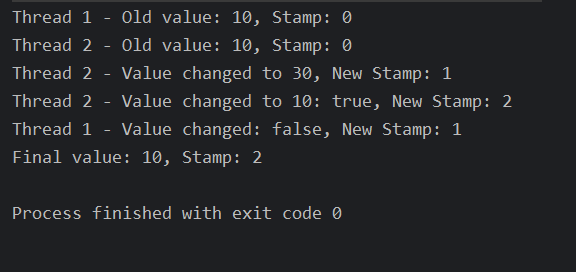
[外链图片转存中...(img-eJfEZdNk-1700280126493)]运行结果如上,最终的结果是10,是由线程2计算得到的最终结果,线程1操作失败。