目录
一、背景
二、硬件拓扑
三、概述
四、PHY控制器驱动
五、PHY驱动解析
1、相关结构体
2、网口和mdio总线设备树配置
3、MAC驱动和mdio控制器注册
4、PHY设备驱动
5、PHY 设备驱动注册和加载
6、以太网卡 PHY 和 MAC 的协作
7、网络操作命令解析
8、设备驱动与控制驱动之间的框图
一、背景
CPU:IMX6ULL
内核版本:Linux-6.3.5
二、硬件拓扑

上图来自 瑞昱半导体 (RealTek) 的 RTL8201F 系列网卡 PHY 芯片手册。按OSI 7层网络模型划分,网卡PHY 芯片(图中的RTL8201F)位于物理层,对应的软件层就是本文讨论的 PHY 驱动层;而 MAC 位于 数据链路层,也是通常软件上所说的网卡驱动层,它不是本文的重点,不做展开。另外,可通过 MDIO 接口对 PHY 芯片进行配置(如PHY芯片寄存器读写),而 PHY 和 MAC 通过 MII/RMII 进行数据传输。
值得一提的是,Linux的网络子系统,只取了OSI 7层网络模型的 前4层:物理层、数据链路层、网络层(IP协议等)、传输层(TPC/UDP协议等)。在内核代码注释里,我们经常看到用 L2 指代 物理层, L3 指代 网络层。
三、概述
PHY芯片为OSI最底层 —— 物理层,通过MII/GMII/RMII/SGMII/XGMII等多种媒体独立接口(介质无关接口)与数据链路层的MAC芯片相连,并通过MDIO接口实现对PHY 状态的监控、配置和管理。
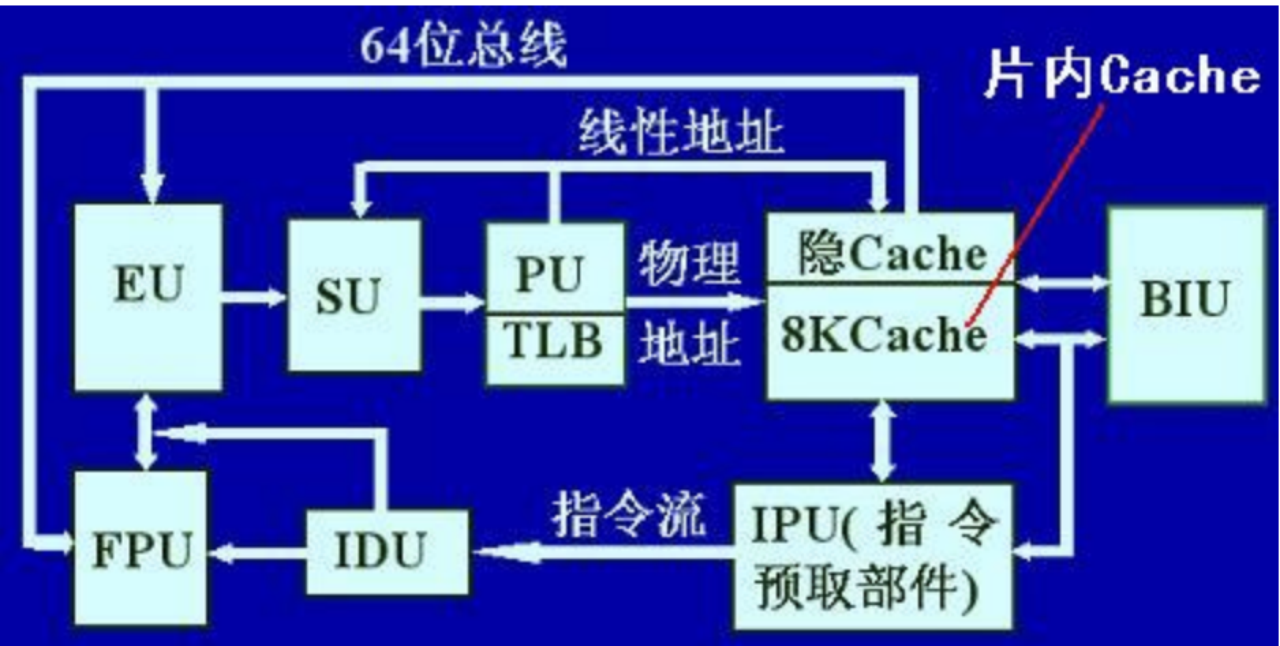
PHY与MAC整体的连接框图:
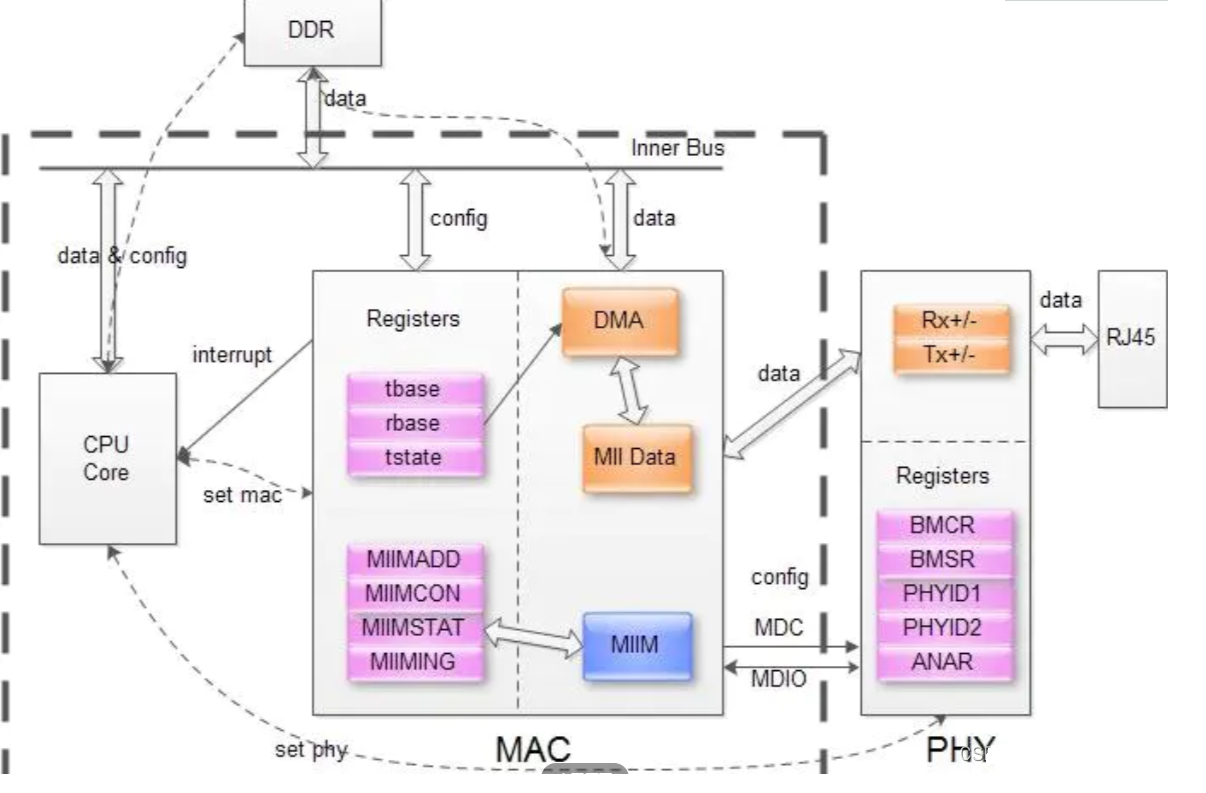
注:MII是走网络数据的
四、PHY控制器驱动
PHY控制器驱动和SPI/I2C类似,控制器功能是实现具体的读写功能。实现方法有两种(与I2C类似):
-
直接调用CPU的MDIO控制器(直接调用CPU对应的寄存器)
-
通过GPIO/外围soc模拟MDIO时序的方式
PHY的控制器一般被描述为mdio_bus平台
注:这是一个设备,等同于SPI/I2C中的master设备;和总线、驱动、设备中的bus不一样。既然是平台设备,那么设备树中有可以被解析为平台的设备节点,也有对应的平台设备驱动。
五、PHY驱动解析
1、相关结构体
// 平台结构体
struct platform_driver {int (*probe)(struct platform_device *); int (*remove)(struct platform_device *);void (*shutdown)(struct platform_device *);int (*suspend)(struct platform_device *, pm_message_t state);int (*resume)(struct platform_device *);struct device_driver driver;const struct platform_device_id *id_table;bool prevent_deferred_probe;
};/* 在dts文件里,每个大括号{}代表一个节点,比如根节点里有个大括号,对应一个device_node结构体;memory也是一个大括号,也是对应一个device_node结构体* 节点里面有各种属性,也有可能里面还有子节点,所以它们还有一些父子关系* 根节点下的memory、chosen、led等节点是并列关系* 对于父子关系、兄弟关系,在device_node结构体里面肯定有成员来描述这些关系*/
// 设备节点结构体
struct device_node {const char *name; /* node的名称,取最后一次"/"和"@"之间字符串 */const char *type; /* device_type的属性名称,没有为<NULL> */phandle phandle; /* phandle属性值 */const char *full_name; /* 指向该结构体结束位置,存放node的路径全名 */struct fwnode_handle fwnode;struct property *properties; /* 指向该节点下的第一个属性,其他属性与该属性链表相接 */struct property *deadprops; /* removed properties */struct device_node *parent; /* 父节点 */struct device_node *child; /* 子节点 */struct device_node *sibling; /* 与自己同等级的node */struct kobject kobj; /* sysfs文件系统目录体现 */unsigned long _flags; /* 当前node状态标志位 */ void *data;
};struct net_device {char name[IFNAMSIZ]; /* 用于存放网络设备的设备名称 */char *ifalias; /* 网络设备的别名 */int ifindex; /* 网络设备的接口索引值,独一无二的网络设备标识符 */struct hlist_node name_hlist; /* 这个字段用于构建网络设备名的哈希散列表,而struct net中的name_hlist就指向每个哈希散列表的链表头 */struct hlist_node index_hlist; /* 用于构建网络设备的接口索引值哈希散列表,在struct net中的index_hlist用于指向接口索引值哈希散列表的链表头 */struct list_head dev_list; /* 用于将每一个网络设备加入到一个网络命名空间中的网络设备双链表中 */unsigned int flags; /* 网络设备接口的标识符 */unsigned int priv_flags; /* 网络设备接口的标识符,但对用户空间不可见;*/unsigned short type; /* 接口硬件类型 */unsigned int mtu; /* 网络设备接口的最大传输单元 */unsigned short hard_header_len; /* 硬件接口头长度 */unsigned char *dev_addr; /* 网络设备接口的MAC地址 */bool uc_promisc; /* 网络设备接口的单播模式 */unsigned int promiscuity; /* 网络设备接口的混杂模式 */unsigned int allmulti; /* 网络设备接口的全组播模式 */struct netdev_hw_addr_list uc; /* 辅助单播MAC地址列表 */struct netdev_hw_addr_list mc; /* 主mac地址列表 */struct netdev_hw_addr_list dev_addrs; /* hw设备地址列表 */unsigned char broadcast[MAX_ADDR_LEN]; /* hw广播地址 */struct netdev_rx_queue *_rx; /* 网络设备接口的数据包接收队列 */struct netdev_queue *_tx /* 网络设备接口的数据包发送队列 */unsigned int num_tx_queues; /* TX队列数 */unsigned int real_num_tx_queues; /* 当前设备活动的TX队列数 */unsigned long tx_queue_len; /* 每个队列允许的最大帧 */unsigned long state; /* 网络设备接口的状态 */struct net_device_stats stats; /* 网络设备接口的统计情况 */possible_net_t nd_net; /* 用于执行网络设备所在的命名空间 */
}; struct mii_bus {const char *name; // 总线名字char id[MII_BUS_ID_SIZE]; // ID MII_BUS_ID_SIZE=61void *priv; // 私有数据int (*read)(struct mii_bus *bus, int phy_id, int regnum); // 读方式int (*write)(struct mii_bus *bus, int phy_id, int regnum, u16 val); // 写方式int (*reset)(struct mii_bus *bus); // 复位struct mutex mdio_lock;struct device *parent; // 父设备enum {MDIOBUS_ALLOCATED = 1,MDIOBUS_REGISTERED,MDIOBUS_UNREGISTERED,MDIOBUS_RELEASED,} state; // 总线状态struct device dev; // 设备文件struct phy_device *phy_map[PHY_MAX_ADDR]; // PHY设备数组u32 phy_mask;int *irq; // 中断
};// PHY设备结构体
struct phy_device {struct phy_driver *drv; // PHY设备驱动 struct mii_bus *bus; // 对应的MII总线 struct device dev; // 设备文件 u32 phy_id; // PHY ID struct phy_c45_device_ids c45_ids; bool is_c45;bool is_internal;bool has_fixups;bool suspended;enum phy_state state; // PHY状态u32 dev_flags;phy_interface_t interface; // PHY接口 int addr; // PHY 总线地址(0~31) int speed; // 速度 int duplex; // 双工模式 int pause; // 停止 int asym_pause;int link;u32 interrupts; // 中断使能标志 u32 supported;u32 advertising;u32 lp_advertising;int autoneg;int link_timeout;int irq; // 中断号 void *priv; // 私有数据 struct work_struct phy_queue; // PHY工作队列 struct delayed_work state_queue; // PHY延时工作队列 atomic_t irq_disable;struct mutex lock;struct net_device *attached_dev; // 网络设备 void (*adjust_link)(struct net_device *dev);
};// PHY驱动结构体
struct phy_driver {struct mdio_driver_common mdiodrv;u32 phy_id;char *name;u32 phy_id_mask;u32 features;u32 flags;const void *driver_data;int (*soft_reset)(struct phy_device *phydev);int (*config_init)(struct phy_device *phydev);int (*probe)(struct phy_device *phydev);int (*suspend)(struct phy_device *phydev);int (*resume)(struct phy_device *phydev);int (*config_aneg)(struct phy_device *phydev);int (*aneg_done)(struct phy_device *phydev);int (*read_status)(struct phy_device *phydev);int (*ack_interrupt)(struct phy_device *phydev);int (*config_intr)(struct phy_device *phydev);int (*did_interrupt)(struct phy_device *phydev);void (*remove)(struct phy_device *phydev);int (*match_phy_device)(struct phy_device *phydev);int (*ts_info)(struct phy_device *phydev, struct ethtool_ts_info *ti);int (*hwtstamp)(struct phy_device *phydev, struct ifreq *ifr);bool (*rxtstamp)(struct phy_device *dev, struct sk_buff *skb, int type);void (*txtstamp)(struct phy_device *dev, struct sk_buff *skb, int type);int (*set_wol)(struct phy_device *dev, struct ethtool_wolinfo *wol);void (*get_wol)(struct phy_device *dev, struct ethtool_wolinfo *wol);void (*link_change_notify)(struct phy_device *dev);int (*read_mmd)(struct phy_device *dev, int devnum, u16 regnum);int (*write_mmd)(struct phy_device *dev, int devnum, u16 regnum,u16 val);int (*read_page)(struct phy_device *dev);int (*write_page)(struct phy_device *dev, int page)int (*module_info)(struct phy_device *dev,struct ethtool_modinfo *modinfo);int (*module_eeprom)(struct phy_device *dev,struct ethtool_eeprom *ee, u8 *data);int (*get_sset_count)(struct phy_device *dev);void (*get_strings)(struct phy_device *dev, u8 *data);void (*get_stats)(struct phy_device *dev,struct ethtool_stats *stats, u64 *data);int (*get_tunable)(struct phy_device *dev,struct ethtool_tunable *tuna, void *data);int (*set_tunable)(struct phy_device *dev,struct ethtool_tunable *tuna,const void *data);int (*set_loopback)(struct phy_device *dev, bool enable);ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(1);ANDROID_KABI_RESERVE(2);
};
2、网口和mdio总线设备树配置
// imx6ull设备树配置
fec1: ethernet@2188000 {compatible = "fsl,imx6ul-fec", "fsl,imx6q-fec";reg = <0x02188000 0x4000>;interrupt-names = "int0", "pps";interrupts = <GIC_SPI 118 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>,<GIC_SPI 119 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>;clocks = <&clks IMX6UL_CLK_ENET>,<&clks IMX6UL_CLK_ENET_AHB>,<&clks IMX6UL_CLK_ENET_PTP>,<&clks IMX6UL_CLK_ENET_REF>,<&clks IMX6UL_CLK_ENET_REF>;clock-names = "ipg", "ahb", "ptp","enet_clk_ref", "enet_out";fsl,num-tx-queues = <1>;fsl,num-rx-queues = <1>;fsl,stop-mode = <&gpr 0x10 3>;fsl,magic-packet;status = "disabled";
};
fec2: ethernet@20b4000 {compatible = "fsl,imx6ul-fec", "fsl,imx6q-fec";reg = <0x020b4000 0x4000>;interrupt-names = "int0", "pps";interrupts = <GIC_SPI 120 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>,<GIC_SPI 121 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>;clocks = <&clks IMX6UL_CLK_ENET>,<&clks IMX6UL_CLK_ENET_AHB>,<&clks IMX6UL_CLK_ENET_PTP>,<&clks IMX6UL_CLK_ENET2_REF_125M>,<&clks IMX6UL_CLK_ENET2_REF_125M>;clock-names = "ipg", "ahb", "ptp","enet_clk_ref", "enet_out";fsl,num-tx-queues = <1>;fsl,num-rx-queues = <1>;fsl,stop-mode = <&gpr 0x10 4>;fsl,magic-packet;status = "disabled";
};&fec1 {pinctrl-names = "default";pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_enet1>;phy-mode = "rmii";phy-handle = <ðphy0>;phy-supply = <®_peri_3v3>;phy-reset-duration = <200>;phy-reset-gpios = <&gpio5 7 GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW>; //phy复位管脚status = "okay";
};&fec2 {pinctrl-names = "default";pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_enet2>;phy-mode = "rmii";phy-handle = <ðphy1>;phy-supply = <®_peri_3v3>;phy-reset-duration = <200>;phy-reset-gpios = <&gpio5 8 GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW>; //phy复位管脚status = "okay";mdio { // mdio总线设备节点#address-cells = <1>;#size-cells = <0>;ethphy0: ethernet-phy@0 { // 设备fec1,地址为0compatible = "ethernet-phy-ieee802.3-c22";reg = <0>;smsc,disable-energy-detect;clocks = <&clks IMX6UL_CLK_ENET_REF>;clock-names = "rmii-ref";};ethphy1: ethernet-phy@1 { // 设备fec2,地址为1compatible = "ethernet-phy-ieee802.3-c22";reg = <1>;smsc,disable-energy-detect;clocks = <&clks IMX6UL_CLK_ENET2_REF>;clock-names = "rmii-ref";};};};
3、MAC驱动和mdio控制器注册
static const struct of_device_id fec_dt_ids[] = {{ .compatible = "fsl,imx25-fec", .data = &fec_devtype[IMX25_FEC], },{ .compatible = "fsl,imx27-fec", .data = &fec_devtype[IMX27_FEC], },{ .compatible = "fsl,imx28-fec", .data = &fec_devtype[IMX28_FEC], },{ .compatible = "fsl,imx6q-fec", .data = &fec_devtype[IMX6Q_FEC], },{ .compatible = "fsl,mvf600-fec", .data = &fec_devtype[MVF600_FEC], },{ .compatible = "fsl,imx6sx-fec", .data = &fec_devtype[IMX6SX_FEC], },{ .compatible = "fsl,imx6ul-fec", .data = &fec_devtype[IMX6UL_FEC], },{ .compatible = "fsl,imx8mq-fec", .data = &fec_devtype[IMX8MQ_FEC], },{ .compatible = "fsl,imx8qm-fec", .data = &fec_devtype[IMX8QM_FEC], },{ .compatible = "fsl,s32v234-fec", .data = &fec_devtype[S32V234_FEC], },{ /* sentinel */ }
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of, fec_dt_ids);static struct platform_driver fec_driver = {.driver = {.name = DRIVER_NAME,.pm = &fec_pm_ops,.of_match_table = fec_dt_ids,.suppress_bind_attrs = true,},.id_table = fec_devtype,.probe = fec_probe,.remove = fec_drv_remove,
};module_platform_driver(fec_driver); //向platform注册mac驱动
设备树的compatible和驱动的compatible匹配成功之后,会调用fec_probe函数,此为mac驱动的真正入口。
-
注册网络设备net_device
-
申请队列和DMA
-
申请MDIO总线
-
创建并注册PHY设备
fec_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)-> struct device_node *np = pdev->dev.of_node, *phy_node; // 获取设备树节点句柄,并创建一个phy的设备树节点句柄-> fec_enet_get_queue_num(pdev, &num_tx_qs, &num_rx_qs); // 从设备树获取fsl,num-tx-queues和fsl,num-rx-queues的属性值-> ndev = alloc_etherdev_mqs // 申请net_device-> netdev_priv(ndev) // 获取私有数据空间首地址
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------> of_parse_phandle(np, "phy-handle", 0) // 从mac的设备树节点中获取phy子节点-> of_get_phy_mode(pdev->dev.of_node) // 从设备树节点中获取phy模式,phy-mode = "rmii";-> fec_reset_phy(pdev); // 复位phy-> fec_enet_init(ndev) // 申请队列和DMA,设置MAC地址-> of_property_read_u32(np, "fsl,wakeup_irq", &irq) // 唤醒中断-> fec_enet_mii_init(pdev); // 注册MDIO总线、注册phy_device-> fep->mii_bus = mdiobus_alloc() //申请MDIO总线-> fep->mii_bus->name = "fec_enet_mii_bus"; // 总线名字-> fep->mii_bus->read = fec_enet_mdio_read; // 总线的读函数-> fep->mii_bus->write = fec_enet_mdio_write; // 总线的写函数-> snprintf(fep->mii_bus->id, MII_BUS_ID_SIZE, "%s-%x",
pdev->name, fep->dev_id + 1); // 总线id -> of_get_child_by_name(pdev->dev.of_node, "mdio"); // 获取phy节点句柄-> of_mdiobus_register // 注册mii_bus设备,并通过设备树子节点创建PHY设备 drivers/of/of_mdio.c of_mdiobus_register(struct mii_bus *mdio, struct device_node *np) -> mdio->phy_mask = ~0; // 屏蔽所有PHY,防止自动探测。相反,设备树中列出的phy将在总线注册后填充-> mdio->dev.of_node = np;-> mdio->reset_delay_us = DEFAULT_GPIO_RESET_DELAY;-> mdiobus_register(mdio) // 注册MDIO总线设备-> bus->dev.parent = bus->parent;-> bus->dev.class = &mdio_bus_class; // 总线设备类“/sys/bus/mdio_bus”/*-----------------------------------------static struct class mdio_bus_class = {.name = "mdio_bus",.dev_release = mdiobus_release,};-------------------------------------------*/-> bus->dev.groups = NULL;-> dev_set_name(&bus->dev, "%s", bus->id); //设置总线设备的名称-> device_register(&bus->dev); // 注册总线设备-> if (bus->reset) bus->reset(bus); // 总线复位
---------------------------------------另一条分支解析(可忽略)---------------------------------------------------------> phydev = mdiobus_scan(bus, i); // 扫描phy设备-> phydev = get_phy_device(bus, addr); //获取创建phy设备->err = phy_device_register(phydev); //注册phy设备
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------> for_each_available_child_of_node(np, child) { // 遍历这个平台设备的子节点并为每个phy注册一个phy_device-> addr = of_mdio_parse_addr(&mdio->dev, child) // 从子节点的"reg"属性中获得PHY设备的地址 -> of_property_read_u32(np, "reg", &addr)-> if (addr < 0) scanphys = true; continue; // 如果未获得子节点的"reg"属性,则在后面再启用扫描可能存在的PHY的,然后注册-> of_mdiobus_register_phy(mdio, child, addr) } // 创建并注册PHY设备-> is_c45 = of_device_is_compatible(child,"ethernet-phy-ieee802.3-c45") //判断设备树中的PHY的属性是否指定45号条款-> if (!is_c45 && !of_get_phy_id(child, &phy_id)) //如果设备树中的PHY的属性未指定45号条款 且未通过"ethernet-phy-id%4x.%4x"属性指定PHY的ID-> phy = phy_device_create(mdio, addr, phy_id, 0, NULL);-> else phy = get_phy_device(mdio, addr, is_c45); //用这个分支-> get_phy_id(bus, addr, &phy_id, is_c45, &c45_ids);//通过mdio得到PHY的ID-> mdiobus_read(bus, addr, MII_PHYSID1)-> __mdiobus_read(bus, addr, regnum);-> bus->read(bus, addr, regnum)-> mdiobus_read(bus, addr, MII_PHYSID2)-> phy_device_create(bus, addr, phy_id, is_c45, &c45_ids) // 创建PHY设备-> struct phy_device *dev;-> dev = kzalloc(sizeof(*dev), GFP_KERNEL);dev->dev.release = phy_device_release;dev->speed = 0;dev->duplex = -1;dev->pause = 0;dev->asym_pause = 0;dev->link = 1;dev->interface = PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_GMII;dev->autoneg = AUTONEG_ENABLE; // 默认支持自协商(自动使能)dev->is_c45 = is_c45;dev->addr = addr;dev->phy_id = phy_id;if (c45_ids)dev->c45_ids = *c45_ids;dev->bus = bus;dev->dev.parent = bus->parent;dev->dev.bus = &mdio_bus_type; //PHY设备和驱动都会挂在mdio_bus下,匹配时会调用对应的match函数 -- /*----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------struct bus_type mdio_bus_type = {.name = "mdio_bus", //总线名称.match = mdio_bus_match, //用来匹配总线上设备和驱动的函数.pm = MDIO_BUS_PM_OPS,.dev_groups = mdio_dev_groups,};----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/dev->irq = bus->irq != NULL ? bus->irq[addr] : PHY_POLL;dev_set_name(&dev->dev, PHY_ID_FMT, bus->id, addr);dev->state = PHY_DOWN; //指示PHY设备和驱动程序尚未准备就绪,在PHY驱动的probe函数中会更改为READY-> INIT_DELAYED_WORK(&dev->state_queue, phy_state_machine); //PHY的状态机(核心WORK)后续解析-> INIT_WORK(&dev->phy_queue, phy_change); // 由phy_interrupt / timer调度以处理PHY状态的更改-> request_module(MDIO_MODULE_PREFIX MDIO_ID_FMT, MDIO_ID_ARGS(phy_id)); // 加载内核模块-> device_initialize(&dev->dev); //设备模型中的一些设备,主要是kset、kobject、ktype的设置-> irq_of_parse_and_map(child, 0); //将中断解析并映射到linux virq空间(-> of_node_get(child); //将OF节点与设备结构相关联-> phy->dev.of_node = child;-> phy_device_register(phy) // 注册phy设备-> if (phydev->bus->phy_map[phydev->addr]) //判断PHY是否已经注册了 -> phydev->bus->phy_map[phydev->addr] = phydev; //添加PHY到总线的phy_map里-> phy_scan_fixups(phydev); //执行匹配的fixups -> device_add(&phydev->dev); // 注册到linux设备模型框架中-> if (!scanphys) return 0; // 如果从子节点的"reg"属性中获得PHY设备的地址,scanphys=false,这里就直接返回了,因为不需要再扫描了
------------一般来说只要设备树种指定了PHY设备的"reg"属性,后面的流程可以自动忽略 -------------> register_netdev(ndev) // 向内核注册net_device
注:PHY的状态机(核心WORK)后续解析 PHY状态机以及网络相关操作命令解析
4、PHY设备驱动
PHY设备驱动是基于device、driver、bus的连接方式。
-
总线 ——— struct mii_bus
-
设备 ——— struct phy_device
-
驱动 ——— struct phy_driver
注:phy设备不像i2c和spi有一个board_info函数进行设备的添加,而是直接读取phy中的寄存器。
<根据IEEE的规定,PHY芯片的前16个寄存器的内容必须是固定的>
路径:kernel/drivers/net/phy/phy_device.c
static int __init phy_init(void)
{int rc;rc = mdio_bus_init(); // mdio_bus总线注册if (rc)return rc;ethtool_set_ethtool_phy_ops(&phy_ethtool_phy_ops);features_init();rc = phy_driver_register(&genphy_c45_driver, THIS_MODULE); if (rc)goto err_c45;rc = phy_driver_register(&genphy_driver, THIS_MODULE); // 注册通用的PHY设备驱动if (rc) {phy_driver_unregister(&genphy_c45_driver);
err_c45:mdio_bus_exit();}return rc;
}static void __exit phy_exit(void)
{phy_driver_unregister(&genphy_c45_driver);phy_driver_unregister(&genphy_driver);mdio_bus_exit();ethtool_set_ethtool_phy_ops(NULL);
}subsys_initcall(phy_init);
module_exit(phy_exit);
// 注:subsys_initcall(phy_init) 这行的作用非常重要,这一行就决定了内核在启动的时候会调用该函数,注册完了之后紧接着又注册一个通用的PHY驱动。
static struct class mdio_bus_class = {.name = "mdio_bus",.dev_release = mdiobus_release,.dev_groups = mdio_bus_groups,
};// 设备和驱动的匹配函数
/*** mdio_bus_match - determine if given MDIO driver supports the given* MDIO device* @dev: target MDIO device* @drv: given MDIO driver** Description: Given a MDIO device, and a MDIO driver, return 1 if* the driver supports the device. Otherwise, return 0. This may* require calling the devices own match function, since different classes* of MDIO devices have different match criteria.*/
static int mdio_bus_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{struct mdio_driver *mdiodrv = to_mdio_driver(drv); // 获取PHY驱动struct mdio_device *mdio = to_mdio_device(dev); // 获取PHY设备/* Both the driver and device must type-match */if (!(mdiodrv->mdiodrv.flags & MDIO_DEVICE_IS_PHY) !=!(mdio->flags & MDIO_DEVICE_FLAG_PHY))return 0;if (of_driver_match_device(dev, drv))return 1;if (mdio->bus_match)return mdio->bus_match(dev, drv);return 0;
}struct bus_type mdio_bus_type = {.name = "mdio_bus", //总线名称.dev_groups = mdio_bus_dev_groups, .match = mdio_bus_match, //用来匹配总线上设备和驱动的函数.uevent = mdio_uevent,
};
EXPORT_SYMBOL(mdio_bus_type);int __init mdio_bus_init(void)
{int ret;ret = class_register(&mdio_bus_class); //注册设备类 /sys/class/mdio_busif (!ret) {ret = bus_register(&mdio_bus_type); //总线注册 /sys/bus/mdio_busif (ret)class_unregister(&mdio_bus_class);}return ret;
}
注:在phy_init函数中不仅注册了mdio_bus总线,还注册了一个通用的PHY驱动作为缺省的内核PHY驱动,但是如果PHY芯片的内部寄存器和802.3定义的并不一样或者需要特殊的功能配置以实现更强的功能,这就需要专有的驱动。
一般在内核源码 drivers\net\phy目录下都有对应的驱动,以lan8720为例
static struct phy_driver smsc_phy_driver[] = {
{.phy_id = 0x0007c0a0, /* OUI=0x00800f, Model#=0x0a */ /* PHY ID */.phy_id_mask = 0xfffffff0, /* PHY ID 掩码 */.name = "SMSC LAN83C185",/* PHY 驱动接口 *//* PHY_BASIC_FEATURES */.probe = smsc_phy_probe,/* basic functions */.config_init = smsc_phy_config_init,.soft_reset = smsc_phy_reset,/* IRQ related */.config_intr = smsc_phy_config_intr,.handle_interrupt = smsc_phy_handle_interrupt,.suspend = genphy_suspend,.resume = genphy_resume,
}, {.phy_id = 0x0007c0b0, /* OUI=0x00800f, Model#=0x0b */.phy_id_mask = 0xfffffff0,.name = "SMSC LAN8187",/* PHY_BASIC_FEATURES */.probe = smsc_phy_probe,/* basic functions */.config_init = smsc_phy_config_init,.soft_reset = smsc_phy_reset,/* IRQ related */.config_intr = smsc_phy_config_intr,.handle_interrupt = smsc_phy_handle_interrupt,/* Statistics */.get_sset_count = smsc_get_sset_count,.get_strings = smsc_get_strings,.get_stats = smsc_get_stats,.suspend = genphy_suspend,.resume = genphy_resume,
}, {/* This covers internal PHY (phy_id: 0x0007C0C3) for* LAN9500 (PID: 0x9500), LAN9514 (PID: 0xec00), LAN9505 (PID: 0x9505)*/.phy_id = 0x0007c0c0, /* OUI=0x00800f, Model#=0x0c */.phy_id_mask = 0xfffffff0,.name = "SMSC LAN8700",/* PHY_BASIC_FEATURES */.probe = smsc_phy_probe,/* basic functions */.read_status = lan87xx_read_status,.config_init = smsc_phy_config_init,.soft_reset = smsc_phy_reset,.config_aneg = lan87xx_config_aneg,/* IRQ related */.config_intr = smsc_phy_config_intr,.handle_interrupt = smsc_phy_handle_interrupt,/* Statistics */.get_sset_count = smsc_get_sset_count,.get_strings = smsc_get_strings,.get_stats = smsc_get_stats,.suspend = genphy_suspend,.resume = genphy_resume,
}, {.phy_id = 0x0007c0d0, /* OUI=0x00800f, Model#=0x0d */.phy_id_mask = 0xfffffff0,.name = "SMSC LAN911x Internal PHY",/* PHY_BASIC_FEATURES */.probe = smsc_phy_probe,/* IRQ related */.config_intr = smsc_phy_config_intr,.handle_interrupt = smsc_phy_handle_interrupt,.suspend = genphy_suspend,.resume = genphy_resume,
}, {/* This covers internal PHY (phy_id: 0x0007C0F0) for* LAN9500A (PID: 0x9E00), LAN9505A (PID: 0x9E01)*/.phy_id = 0x0007c0f0, /* OUI=0x00800f, Model#=0x0f */.phy_id_mask = 0xfffffff0,.name = "SMSC LAN8710/LAN8720",/* PHY_BASIC_FEATURES */.probe = smsc_phy_probe,.remove = smsc_phy_remove,/* basic functions */.read_status = lan87xx_read_status,.config_init = smsc_phy_config_init,.soft_reset = smsc_phy_reset,.config_aneg = lan95xx_config_aneg_ext,/* IRQ related */.config_intr = smsc_phy_config_intr,.handle_interrupt = smsc_phy_handle_interrupt,/* Statistics */.get_sset_count = smsc_get_sset_count,.get_strings = smsc_get_strings,.get_stats = smsc_get_stats,.suspend = genphy_suspend,.resume = genphy_resume,
}, {.phy_id = 0x0007c110,.phy_id_mask = 0xfffffff0,.name = "SMSC LAN8740",/* PHY_BASIC_FEATURES */.flags = PHY_RST_AFTER_CLK_EN,.probe = smsc_phy_probe,/* basic functions */.read_status = lan87xx_read_status,.config_init = smsc_phy_config_init,.soft_reset = smsc_phy_reset,/* IRQ related */.config_intr = smsc_phy_config_intr,.handle_interrupt = smsc_phy_handle_interrupt,/* Statistics */.get_sset_count = smsc_get_sset_count,.get_strings = smsc_get_strings,.get_stats = smsc_get_stats,.suspend = genphy_suspend,.resume = genphy_resume,
}, {.phy_id = 0x0007c130, /* 0x0007c130 and 0x0007c131 *//* This mask (0xfffffff2) is to differentiate from* LAN88xx (phy_id 0x0007c132)* and allows future phy_id revisions.*/.phy_id_mask = 0xfffffff2,.name = "Microchip LAN8742",/* PHY_BASIC_FEATURES */.flags = PHY_RST_AFTER_CLK_EN,.probe = smsc_phy_probe,/* basic functions */.read_status = lan87xx_read_status,.config_init = smsc_phy_config_init,.soft_reset = smsc_phy_reset,/* IRQ related */.config_intr = smsc_phy_config_intr,.handle_interrupt = smsc_phy_handle_interrupt,/* Statistics */.get_sset_count = smsc_get_sset_count,.get_strings = smsc_get_strings,.get_stats = smsc_get_stats,.suspend = genphy_suspend,.resume = genphy_resume,
} };module_phy_driver(smsc_phy_driver); /* 模块 加载、卸载 时分别 注册、注销 PHY 驱动 */static struct mdio_device_id __maybe_unused smsc_tbl[] = {{ 0x0007c0a0, 0xfffffff0 }, /* PHY ID 和 PHY ID 掩码 */{ 0x0007c0b0, 0xfffffff0 },{ 0x0007c0c0, 0xfffffff0 },{ 0x0007c0d0, 0xfffffff0 },{ 0x0007c0f0, 0xfffffff0 },{ 0x0007c110, 0xfffffff0 },{ 0x0007c130, 0xfffffff2 },{ }
};// 生成一个名为__mod_mdio__smsc_tbl_device_table,
// 内核构建时,depmod程序会在所有模块中搜索符号__mod_mdio__smsc_tbl_device_table
// 把数据(设备列表)从模块中抽出,添加到映射文件 /lib/modules/KERNEL_VERSION/modules.mdiomap 中
// 当depmod结束之后,所有的MDIO设备连同他们的模块名字都被该文件列出。
// 在需要驱动的时候,由modules.mdiomap 文件来找寻恰当的驱动程序。
// 模块加载时候可以研究下。。。。。。。
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(mdio, smsc_tbl);
5、PHY 设备驱动注册和加载
同一品牌的PHY设备有多种不同的型号,内核为了支持一次可以注册多个型号的PHY的驱动,在include\linux\phy.h中提供了用于注册PHY驱动的宏module_phy_driver。
#define phy_module_driver(__phy_drivers, __count) \
static int __init phy_module_init(void) \
{ \return phy_drivers_register(__phy_drivers, __count, THIS_MODULE); \
} \
module_init(phy_module_init); \
static void __exit phy_module_exit(void) \
{ \phy_drivers_unregister(__phy_drivers, __count); \
} \
module_exit(phy_module_exit)#define module_phy_driver(__phy_drivers) \phy_module_driver(__phy_drivers, ARRAY_SIZE(__phy_drivers))
phy_driver_register定义
/*** phy_driver_register - register a phy_driver with the PHY layer* @new_driver: new phy_driver to register* @owner: module owning this PHY*/
int phy_driver_register(struct phy_driver *new_driver, struct module *owner)
{int retval;/* Either the features are hard coded, or dynamically* determined. It cannot be both.*/if (WARN_ON(new_driver->features && new_driver->get_features)) {pr_err("%s: features and get_features must not both be set\n",new_driver->name);return -EINVAL;}/* PHYLIB device drivers must not match using a DT compatible table* as this bypasses our checks that the mdiodev that is being matched* is backed by a struct phy_device. If such a case happens, we will* make out-of-bounds accesses and lockup in phydev->lock.*/if (WARN(new_driver->mdiodrv.driver.of_match_table,"%s: driver must not provide a DT match table\n",new_driver->name))return -EINVAL;new_driver->mdiodrv.flags |= MDIO_DEVICE_IS_PHY;new_driver->mdiodrv.driver.name = new_driver->name; // 驱动名称new_driver->mdiodrv.driver.bus = &mdio_bus_type; // 驱动挂载的总线new_driver->mdiodrv.driver.probe = phy_probe; // PHY设备和驱动匹配后调用的probe函数new_driver->mdiodrv.driver.remove = phy_remove; // PHY设备卸载new_driver->mdiodrv.driver.shutdown = phy_shutdown;new_driver->mdiodrv.driver.owner = owner;new_driver->mdiodrv.driver.probe_type = PROBE_FORCE_SYNCHRONOUS;/* * 注册 PHY 驱动到 driver core 。* 如果 PHY 设备已经注册,可触发此驱动加载过程。*/retval = driver_register(&new_driver->mdiodrv.driver); // 向linux设备模型框架中注册device_driver驱动if (retval) {pr_err("%s: Error %d in registering driver\n",new_driver->name, retval);return retval;}pr_debug("%s: Registered new driver\n", new_driver->name);return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(phy_driver_register);int phy_drivers_register(struct phy_driver *new_driver, int n,struct module *owner)
{int i, ret = 0;for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {ret = phy_driver_register(new_driver + i, owner); // 注册数组中所有的phy驱动if (ret) {while (i-- > 0)phy_driver_unregister(new_driver + i);break;}}return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(phy_drivers_register);
假设 PHY 设备已经先注册到 driver core (先后关系是无所谓的,不管是哪种顺序,最终都会触发驱动的加载),注册 PHY 驱动将触发驱动加载过程:
phy_driver_register()driver_register(&new_driver->mdiodrv.driver)bus_add_driver(drv)driver_attach(drv)bus_for_each_dev(drv->bus, NULL, drv, __driver_attach)while ((dev = next_device(&i)) && !error)/* 循环到注册的 PHY 设备时 */fn(dev, data) = __driver_attach()/* 匹配设备和驱动 */driver_match_device(drv, dev)mdio_bus_match(dev, drv)phy_bus_match(dev, drv)/* 按 phy_id & phy_id_mask 匹配 */return (phydrv->phy_id & phydrv->phy_id_mask) == (phydev->phy_id & phydrv->phy_id_mask);/* 匹配到设备和驱动,加载驱动 */driver_probe_device(drv, dev)really_probe(dev, drv)dev->driver = drv; /* 绑定设备的驱动 */drv->probe(dev) = phy_probe()
设备和驱动通过phy_id匹配后,调用phy_probe
/*** phy_probe - probe and init a PHY device* @dev: device to probe and init** Description: Take care of setting up the phy_device structure,* set the state to READY (the driver's init function should* set it to STARTING if needed).*/
static int phy_probe(struct device *dev)
{struct phy_device *phydev = to_phy_device(dev); // 获取PHY设备struct device_driver *drv = phydev->mdio.dev.driver;struct phy_driver *phydrv = to_phy_driver(drv); // 获取PHY驱动int err = 0;phydev->drv = phydrv; /* 绑定 phy_device 和 phy_driver *//* Disable the interrupt if the PHY doesn't support it* but the interrupt is still a valid one*//* PHY 中断模式最终配置 */if (!phy_drv_supports_irq(phydrv) && phy_interrupt_is_valid(phydev)) // 设置中断方式phydev->irq = PHY_POLL;if (phydrv->flags & PHY_IS_INTERNAL)phydev->is_internal = true;/* Deassert the reset signal */phy_device_reset(phydev, 0);if (phydev->drv->probe) { // 判断驱动有probe方式err = phydev->drv->probe(phydev); /* PHY 驱动的 probe */if (err)goto out;}/* Start out supporting everything. Eventually,* a controller will attach, and may modify one* or both of these values*/if (phydrv->features) {linkmode_copy(phydev->supported, phydrv->features);}else if (phydrv->get_features)err = phydrv->get_features(phydev);else if (phydev->is_c45)err = genphy_c45_pma_read_abilities(phydev);elseerr = genphy_read_abilities(phydev);if (err)goto out;if (!linkmode_test_bit(ETHTOOL_LINK_MODE_Autoneg_BIT,phydev->supported))phydev->autoneg = 0;if (linkmode_test_bit(ETHTOOL_LINK_MODE_1000baseT_Half_BIT,phydev->supported))phydev->is_gigabit_capable = 1;if (linkmode_test_bit(ETHTOOL_LINK_MODE_1000baseT_Full_BIT,phydev->supported))phydev->is_gigabit_capable = 1;/* PHY 功能特性配置 */of_set_phy_supported(phydev);phy_advertise_supported(phydev);/* Get the EEE modes we want to prohibit. We will ask* the PHY stop advertising these mode later on*/of_set_phy_eee_broken(phydev);/* The Pause Frame bits indicate that the PHY can support passing* pause frames. During autonegotiation, the PHYs will determine if* they should allow pause frames to pass. The MAC driver should then* use that result to determine whether to enable flow control via* pause frames.** Normally, PHY drivers should not set the Pause bits, and instead* allow phylib to do that. However, there may be some situations* (e.g. hardware erratum) where the driver wants to set only one* of these bits.*/if (!test_bit(ETHTOOL_LINK_MODE_Pause_BIT, phydev->supported) &&!test_bit(ETHTOOL_LINK_MODE_Asym_Pause_BIT, phydev->supported)) {linkmode_set_bit(ETHTOOL_LINK_MODE_Pause_BIT,phydev->supported);linkmode_set_bit(ETHTOOL_LINK_MODE_Asym_Pause_BIT,phydev->supported);}/* Set the state to READY by default */phydev->state = PHY_READY; /* 标记 PHY 设备已经就绪 */out:/* Re-assert the reset signal on error */if (err)phy_device_reset(phydev, 1);return err;
}
到此,以太网 PHY 设备的驱动也已经加载,看起来似乎一切都已经结束了,是这样吗?事实上,我们还差一步,就是在软件层面绑定 MAC 和 PHY,让它们一起协作 ,这样才组成了一张完整的以太网卡。
6、以太网卡 PHY 和 MAC 的协作
以太网卡 PHY 管理了 连接状态、和对端通信速度的自动协商 等工作,作为一个网卡内外部沟通的桥梁:对外连接了网线,对内连接着 MAC。我们来看 PHY 是如何工作的。现在我们知道 PHY 工作在状态机 work 函数 phy_state_machine() 中:
/*** rivers/net/phy/phy.c* 注册phy_device后,状态机就开始启动,监测phy状态*/
/*** phy_state_machine - Handle the state machine* @work: work_struct that describes the work to be done*/
void phy_state_machine(struct work_struct *work)
{struct delayed_work *dwork = to_delayed_work(work);struct phy_device *phydev =container_of(dwork, struct phy_device, state_queue);struct net_device *dev = phydev->attached_dev;bool needs_aneg = false, do_suspend = false;enum phy_state old_state;bool finished = false;int err = 0;mutex_lock(&phydev->lock);old_state = phydev->state;switch (phydev->state) {case PHY_DOWN: // 关闭((ifconfig eth0 down)case PHY_READY: // 准备好break;case PHY_UP: // 开启(ifconfig eth0 up)needs_aneg = true;break;case PHY_NOLINK: // 开启 未连接case PHY_RUNNING: //运行err = phy_check_link_status(phydev);break;case PHY_CABLETEST:err = phydev->drv->cable_test_get_status(phydev, &finished);if (err) {phy_abort_cable_test(phydev);netif_testing_off(dev);needs_aneg = true;phydev->state = PHY_UP;break;}if (finished) {ethnl_cable_test_finished(phydev);netif_testing_off(dev);needs_aneg = true;phydev->state = PHY_UP;}break;case PHY_HALTED: // 停止if (phydev->link) {phydev->link = 0;phy_link_down(phydev);}do_suspend = true;break;}mutex_unlock(&phydev->lock);if (needs_aneg) /* 需要自动协商 */err = phy_start_aneg(phydev); /* 自动协商处理 */else if (do_suspend)phy_suspend(phydev);if (err == -ENODEV)return;if (err < 0)phy_error(phydev);phy_process_state_change(phydev, old_state);/* Only re-schedule a PHY state machine change if we are polling the* PHY, if PHY_MAC_INTERRUPT is set, then we will be moving* between states from phy_mac_interrupt().** In state PHY_HALTED the PHY gets suspended, so rescheduling the* state machine would be pointless and possibly error prone when* called from phy_disconnect() synchronously.*/mutex_lock(&phydev->lock);if (phy_polling_mode(phydev) && phy_is_started(phydev))phy_queue_state_machine(phydev, PHY_STATE_TIME);mutex_unlock(&phydev->lock);
}
7、网络操作命令解析
运行ifconfig eth0 up命令
// 文件系统输入ifconfig eth0 up
// 状态机切换phy_Up并启动自动配置
case PHY_UP: // 开启(ifconfig eth0 up) needs_aneg = true;phydev->link_timeout = PHY_AN_TIMEOUT;break;if (needs_aneg) // 需要自动配置(例如ifconfig eth0 up就会调用) err = phy_start_aneg(phydev); // 开始自动配置
// 1、调用驱动的配置函数(没有特殊的phy芯片配置,就调用通用的配置)
// 2、调整phy当前的状态
/*** _phy_start_aneg - start auto-negotiation for this PHY device* @phydev: the phy_device struct** Description: Sanitizes the settings (if we're not autonegotiating* them), and then calls the driver's config_aneg function.* If the PHYCONTROL Layer is operating, we change the state to* reflect the beginning of Auto-negotiation or forcing.*/
static int _phy_start_aneg(struct phy_device *phydev)
{int err;lockdep_assert_held(&phydev->lock);if (!phydev->drv)return -EIO;if (AUTONEG_DISABLE == phydev->autoneg)phy_sanitize_settings(phydev);err = phy_config_aneg(phydev); // 调用驱动的config_aneg方法,默认是genphy_config_aneg if (err < 0)return err;if (phy_is_started(phydev))err = phy_check_link_status(phydev);return err;
}/*** phy_start_aneg - start auto-negotiation for this PHY device* @phydev: the phy_device struct** Description: Sanitizes the settings (if we're not autonegotiating* them), and then calls the driver's config_aneg function.* If the PHYCONTROL Layer is operating, we change the state to* reflect the beginning of Auto-negotiation or forcing.*/
int phy_start_aneg(struct phy_device *phydev)
{int err;mutex_lock(&phydev->lock);err = _phy_start_aneg(phydev);mutex_unlock(&phydev->lock);return err;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(phy_start_aneg);
// drivers/net/phy/phy_device.c
/*** __genphy_config_aneg - restart auto-negotiation or write BMCR* @phydev: target phy_device struct* @changed: whether autoneg is requested** Description: If auto-negotiation is enabled, we configure the* advertising, and then restart auto-negotiation. If it is not* enabled, then we write the BMCR.*/
int __genphy_config_aneg(struct phy_device *phydev, bool changed)
{int err;err = genphy_c45_an_config_eee_aneg(phydev);if (err < 0)return err;else if (err)changed = true;err = genphy_setup_master_slave(phydev);if (err < 0)return err;else if (err)changed = true;if (AUTONEG_ENABLE != phydev->autoneg)return genphy_setup_forced(phydev);err = genphy_config_advert(phydev);if (err < 0) /* error */return err;else if (err)changed = true;return genphy_check_and_restart_aneg(phydev, changed); // 重新开启自动协商机制
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(__genphy_config_aneg);
// drivers/net/phy/phy_device.c
// drivers/net/phy/phy_device.c
/*** genphy_restart_aneg - Enable and Restart Autonegotiation* @phydev: target phy_device struct*/
int genphy_restart_aneg(struct phy_device *phydev)
{/* Don't isolate the PHY if we're negotiating */return phy_modify(phydev, MII_BMCR, BMCR_ISOLATE,BMCR_ANENABLE | BMCR_ANRESTART);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(genphy_restart_aneg);
8、设备驱动与控制驱动之间的框图
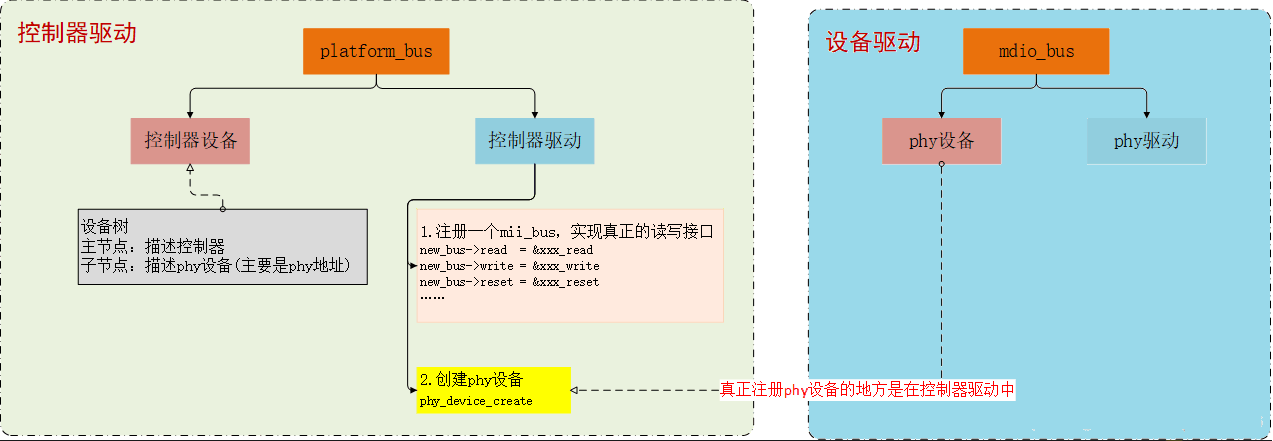
本期的内容到这就结束了,如果觉得文章不错,可以点赞、收藏和关注哦,谢谢大家收看,下期再见!
关于更多嵌入式C语言、FreeRTOS、RT-Thread、Linux应用编程、linux驱动等相关知识,关注公众号【嵌入式Linux知识共享】,后续精彩内容及时收看了解。