- 同步刷盘: 在消息真正持久化至磁盘后RocketMQ的Broker端才会真正返回给Producer端一个成功的ACK响应。
- 异常刷盘: 能够充分利用OS的PageCache的优势, 只要消息写入PageCache即可将成功的ACK返回给Producer端。消息刷盘采用后台异步线程提交的方式进行, 降低了读写延迟和提高了MQ性能和吞吐量。
-
CommitLog#asyncPutMessage方法中会进行消息的存储, appendMessage仅仅是将消息追加到内存中, 没有在磁盘上。
-
CommitLog#asyncPutMessage方法的最后才会调用submitFlushRequest方法提交刷盘请求, broker将会根据刷盘策略进行刷盘。该方法就是RocketMQ的broker刷盘的入口方法。
文章目录
- 1.初始化存储服务
- 2.submitFlushRequest提交刷盘请求
- 3.GroupCommitService同步刷盘
- 3.1 run同步刷盘
- 3.1.1 waitForRunning等待运行
- 3.1.2. doCommit执行刷盘
- 3.2 putRequest存入请求
- 3.2.1 wakeup唤醒刷盘线程
- 3.3 双队列读写分离设计
- 4.FlushRealTimeService异步刷盘
- 4.1 run异步刷盘
- 5.CommitRealTimeService异步堆外缓存刷盘
- 5.1 run异步堆外缓存刷盘
- 6.MappedFile的刷盘
- 6.1 MappedFileQueue#flush刷盘
- 6.1.1 findMappedFileByOffset根据偏移量获取MappedFile
- 6.1.2 MappedFile#flush执行刷盘
- 6.2 MappedFileQueue#commit提交
- 6.2.1 MappedFile#commit提交
- 6.2.2 commit0
- 7.总结
1.初始化存储服务
CommitLog初始化的时候, 会初始化存储服务。
- GroupCommitService: 同步刷盘服务。
- FlushRealTimeService: 异步刷盘服务。
- CommitRealTimeService: 异常转存服务。
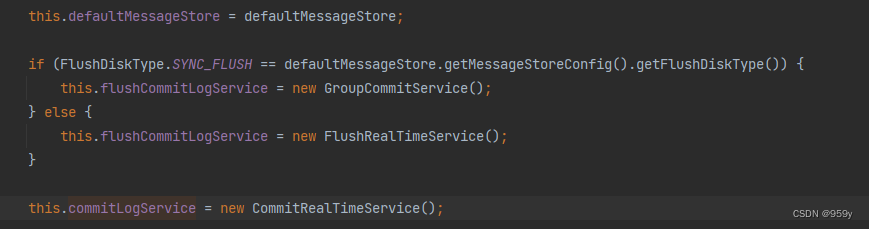
//CommitLog的构造器if (FlushDiskType.SYNC_FLUSH == defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushDiskType()) {//如果是同步刷盘,则初始化GroupCommitService服务this.flushCommitLogService = new GroupCommitService();
} else {//如果是异步刷盘,则初始化GroupCommitService服务this.flushCommitLogService = new FlushRealTimeService();
}
//异步转存数据服务:将堆外内存的数据提交到fileChannel
this.commitLogService = new CommitRealTimeService();
CommitLog#start()启动这些线程服务。
2.submitFlushRequest提交刷盘请求
CommitLog#asyncPutMessage()
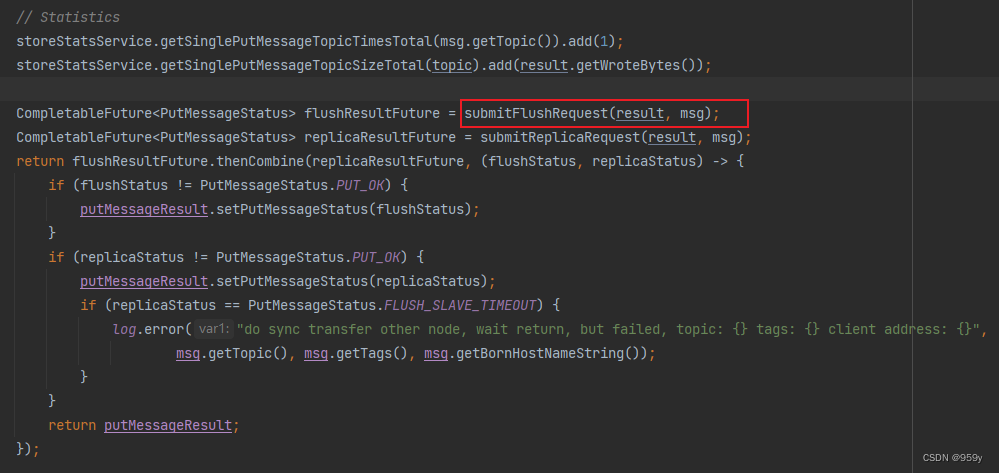
根据broker的配置选择不同的刷盘策略:
- 同步刷盘, 为GroupCommitService服务。
- 同步等待: 如果消息的配置需要等待存储完成后才返回, 那么构建同步刷盘请求, 将请求存入内部的requestsWrite, 并唤醒同步刷盘线程, 返回future, 没有填充刷盘的结果, 在外部的thenCombine方法阻塞。
- 同步不等待: 消息的配置不需要等待存储完成后才返回, 唤醒同步刷盘线程, 返回PUT_OK。
- 异步刷盘:
- 启动了堆外缓存读写分离, transientStorePoolEnable为true和不是slave, 那么唤醒CommitRealTimeService服务。
- 没有启动, 唤醒FlushRealTimeService服务。
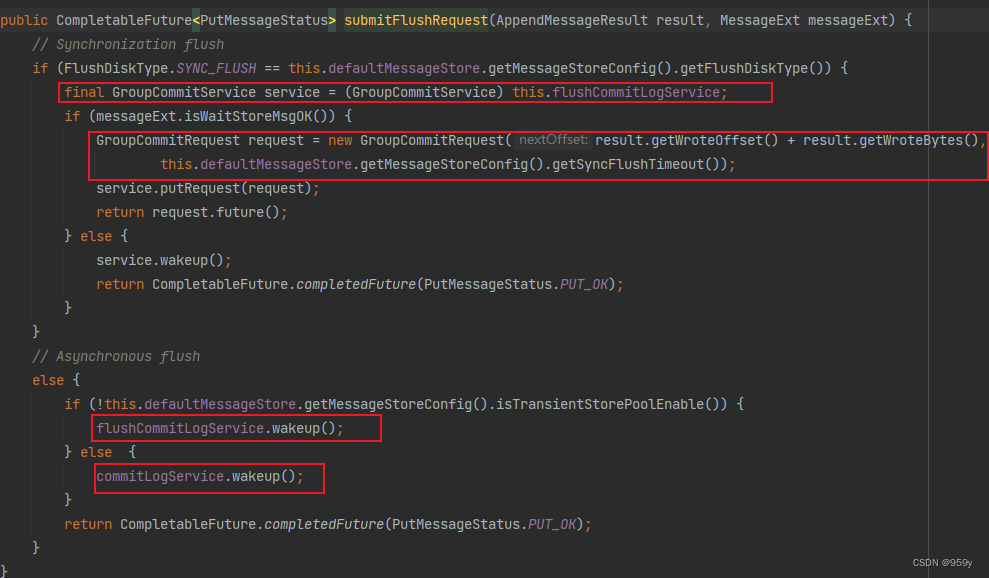
/*** CommitLog的方法* <p>* 提交刷盘请求*/
public CompletableFuture<PutMessageStatus> submitFlushRequest(AppendMessageResult result, MessageExt messageExt) {// Synchronization flush/** 同步刷盘策略*/if (FlushDiskType.SYNC_FLUSH == this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushDiskType()) {//获取同步刷盘服务GroupCommitServicefinal GroupCommitService service = (GroupCommitService) this.flushCommitLogService;//判断消息的配置是否需要等待存储完成后才返回if (messageExt.isWaitStoreMsgOK()) {//同步刷盘并且需要等待刷刷盘结果//构建同步刷盘请求 刷盘偏移量nextOffset = 当前写入偏移量 + 当前消息写入大小GroupCommitRequest request = new GroupCommitRequest(result.getWroteOffset() + result.getWroteBytes(),this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getSyncFlushTimeout());//将请求加入到刷盘监视器内部的commitRequests中flushDiskWatcher.add(request);//将请求存入内部的requestsWrite,并且唤醒同步刷盘线程service.putRequest(request);//仅仅返回future,没有填充结果return request.future();} else {//同步刷盘但是不需要等待刷盘结果,那么唤醒同步刷盘线程,随后直接返回PUT_OKservice.wakeup();return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(PutMessageStatus.PUT_OK);}}// Asynchronous flush/** 异步刷盘策略*/else {//是否启动了堆外缓存if (!this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isTransientStorePoolEnable()) {//如果没有启动了堆外缓存,那么唤醒异步刷盘服务FlushRealTimeServiceflushCommitLogService.wakeup();} else {//如果启动了堆外缓存,那么唤醒异步转存服务CommitRealTimeServicecommitLogService.wakeup();}return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(PutMessageStatus.PUT_OK);}
}
3.GroupCommitService同步刷盘
- 创建GroupCommitService对象时, 会初始化两个内部集合, 为requestsWrite和requestsRead, requestsWrite用于存放putRequest方法写入的刷盘请求, requestsRead用于存放doCommit方法读取的刷盘请求。两个队列实现读写分离, 可以避免putRequest提交刷盘请求与doCommit消费刷盘请求之间的锁竞争。还会初始化一个独占锁, 用于保证存放请求和交换请求操作的线程安全。
//存放putRequest方法写入的刷盘请求
private volatile LinkedList<GroupCommitRequest> requestsWrite = new LinkedList<GroupCommitRequest>();
//存放doCommit方法读取的刷盘请求
private volatile LinkedList<GroupCommitRequest> requestsRead = new LinkedList<GroupCommitRequest>();
//同步服务锁
private final PutMessageSpinLock lock = new PutMessageSpinLock();
3.1 run同步刷盘
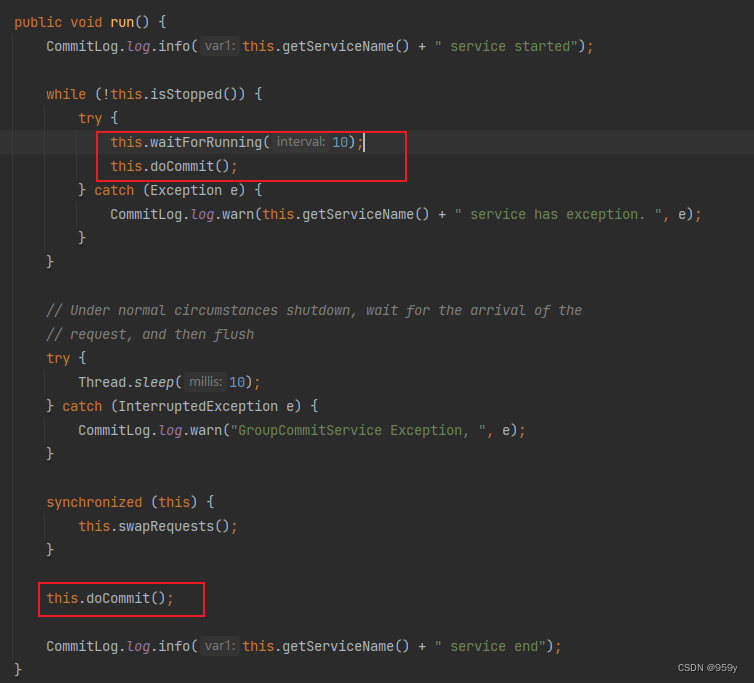
- 在死循环中不断的执行刷盘的操作
- waitForRunning, 等待执行刷盘操作并且交换请求, 同步刷盘服务最多等待10ms。
- doCommit, 尝试执行批量刷盘。
/*** GroupCommitService的方法*/
public void run() {CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started");/** 运行时逻辑* 如果服务没有停止,则在死循环中执行刷盘的操作*/while (!this.isStopped()) {try {//等待执行刷盘,固定最多每10ms执行一次this.waitForRunning(10);//尝试执行批量刷盘this.doCommit();} catch (Exception e) {CommitLog.log.warn(this.getServiceName() + " service has exception. ", e);}}// Under normal circumstances shutdown, wait for the arrival of the// request, and then flush/** 停止时逻辑* 在正常情况下服务关闭时,将会线程等待10ms等待请求到达,然后一次性将剩余的request进行刷盘。*/try {Thread.sleep(10);} catch (InterruptedException e) {CommitLog.log.warn(this.getServiceName() + " Exception, ", e);}synchronized (this) {this.swapRequests();}this.doCommit();CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end");
}
3.1.1 waitForRunning等待运行
刷盘线程等待执行刷盘操作并且交换请求, 该方法是父类ServiceThread的方法, 同步和异步刷盘服务都会调用该方法, 同步刷盘服务最多等待10s。
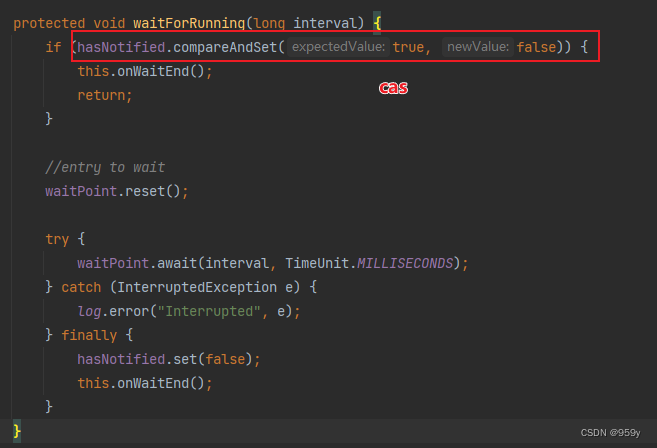
- 首先尝试尝试CAS的将已通知标志位从true改为false, 表示正在或已执行刷盘操作, 如果成功则表示服务线程曾被尝试唤醒过, 或者说wakeup()方法曾被调用过, 即此前曾有过消息存储的请求, 那么此时直接调用onWaitEnd方法交换读写队列, 为后续消息持久化做准备。
- 如果CAS失败, 即已通知标志位已经是false了, 表示服务线程曾没有被尝试唤醒过, 或者说wakeup()方法曾没有被调用过, 即此前这段时间没有提交过消息存储的请求。
- 由于此前没有刷盘请求被提交过, 那么刷盘服务线程等待一定的时间, 减少资源消耗, 等待的时间有参数传递, 同步刷盘服务最多等待10ms。
- 等待时间到了或者因为刷盘请求而被唤醒, 此时将已通知标志位直接改为false, 表示正在或已执行刷盘操作。调用onWaitEnd方法交换读写队列, 为后续消息持久化做准备, 一定会刷盘一次。
-
CAS成功则表示此前有过提交请求, 则交换读写队列并结束, 失败则等待, 直到超时或者被提交请求唤醒。
-
同步刷盘服务在没有提交请求的时候同样会等待, 最多为10s。
/*** ServiceThread的方法* <p>* 等待执行刷盘,同步和异步刷盘服务都会调用该方法** @param interval 时间*/
protected void waitForRunning(long interval) {//尝试CAS的将已通知标志位从true改为false,表示正在或已执行刷盘操作if (hasNotified.compareAndSet(true, false)) {//如果成功则表示服务线程曾被尝试唤醒过,或者说wakeup()方法曾被调用过,即此前曾有过消息存储的请求//那么此时直接调用onWaitEnd方法交换读写队列,为后续消息持久化做准备this.onWaitEnd();return;}/** 进入这里表示CAS失败,即已通知标志位已经是false了* 表示服务线程曾没有被尝试唤醒过,或者说wakeup()方法曾没有被调用过,即此前这段时间没有提交过消息存储的请求*///entry to wait//重置倒计数waitPoint.reset();try {//由于此前没有刷盘请求被提交过,那么刷盘服务线程等待一定的时间,减少资源消耗//同步刷盘服务最多等待10mswaitPoint.await(interval, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);} catch (InterruptedException e) {log.error("Interrupted", e);} finally {//等待时间到了或者因为刷盘请求而被唤醒,此时将已通知标志位直接改为false,表示正在或已执行刷盘操作hasNotified.set(false);//调用onWaitEnd方法交换读写队列,为后续消息持久化做准备,一定会尝试执行一次刷盘操作this.onWaitEnd();}
}
onWaitEnd等待结束交换请求: GroupCommitService服务重写, 用于交换读写队列。
/*** GroupCommitService交换读写队列*/
@Override
protected void onWaitEnd() {//交换请求: 交换读写队列引用, 交换的时候需要加锁this.swapRequests();
} /*** GroupCommitService的方法* 交换请求*/
private void swapRequests() {//加锁lock.lock();try {//交换读写队列LinkedList<GroupCommitRequest> tmp = this.requestsWrite;//requestsRead是一个空队列this.requestsWrite = this.requestsRead;this.requestsRead = tmp;} finally {lock.unlock();}
}
3.1.2. doCommit执行刷盘
requestsRead实际上引用到了requestsWrite队列, doCommit方法将会执行刷盘操作。
-
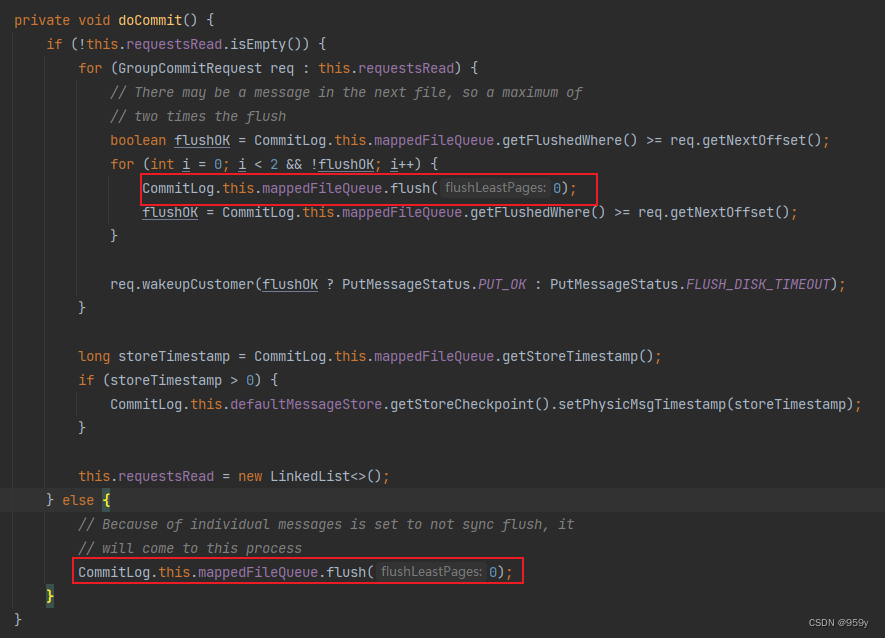
判断requestsRead队列是否存在元素, 如果不存在, 刷盘操作。因为某些消息的设置是同步刷盘但是不等待, 因此这里直接调用mappedFileQueue.flush(0)方法进行一次同步刷盘即可, 无需唤醒线程。
-
如果队列存在元素, 表示有提交同步等待刷盘请求, 遍历队列, 依次刷盘操作。
- 每个刷盘请求最多刷盘两次。
- 判断如果flushedWhere
- 每个刷盘请求最多刷盘两次。
-
刷盘结束后, 将会修改StoreCheckpoint中的physicMsgTimestamp, 最新commitlog文件的刷盘时间戳, 用于重启数据恢复。
-
最后为requestsRead重新创建一个空的队列。当下一次交换队列的时候, requestsWrite又会成为一个空队列
/*** GroupCommitService的方法* 执行同步刷盘操作*/
private void doCommit() {//如果requestsRead读队列不为空,表示有提交请求,那么全部刷盘if (!this.requestsRead.isEmpty()) {//遍历所有的刷盘请求for (GroupCommitRequest req : this.requestsRead) {// There may be a message in the next file, so a maximum of// two times the flush//一个同步刷盘请求最多进行两次刷盘操作,因为文件是固定大小的,第一次刷盘时可能出现上一个文件剩余大小不足的情况//消息只能再一次刷到下一个文件中,因此最多会出现两次刷盘的情况//如果flushedWhere大于下一个刷盘点位,则表示该位置的数据已经刷刷盘成功了,不再需要刷盘//flushedWhere的CommitLog的整体已刷盘物理偏移量boolean flushOK = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.getFlushedWhere() >= req.getNextOffset();//最多循环刷盘两次for (int i = 0; i < 2 && !flushOK; i++) {/** 执行强制刷盘操作,最少刷0页,即所有消息都会刷盘*/CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.flush(0);//判断是否刷盘成功,如果上一个文件剩余大小不足,则flushedWhere会小于nextOffset,那么海选哦再刷一次flushOK = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.getFlushedWhere() >= req.getNextOffset();}//内部调用flushOKFuture.complete方法存入结果,将唤醒因为提交同步刷盘请求而被阻塞的线程req.wakeupCustomer(flushOK ? PutMessageStatus.PUT_OK : PutMessageStatus.FLUSH_DISK_TIMEOUT);}//获取存储时间戳long storeTimestamp = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.getStoreTimestamp();//修改StoreCheckpoint中的physicMsgTimestamp:最新commitlog文件的刷盘时间戳,单位毫秒//这里用于重启数据恢复if (storeTimestamp > 0) {CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getStoreCheckpoint().setPhysicMsgTimestamp(storeTimestamp);}//requestsRead重新创建一个空的队列,当下一次交换队列的时候,requestsWrite又会成为一个空队列this.requestsRead = new LinkedList<>();} else {// Because of individual messages is set to not sync flush, it// will come to this process//某些消息的设置是同步刷盘但是不等待,因此这里直接进行刷盘即可,无需唤醒线程等操作CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.flush(0);}
}
3.2 putRequest存入请求
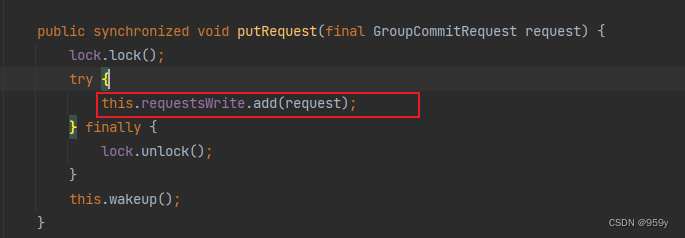
调用该方法将加锁并将刷盘请求存入requestsWrite集合, 调用wakeup方法唤醒同步刷盘线程。
/*** GroupCommitService的方法** 加锁存入requestsWrite* @param request*/
public synchronized void putRequest(final GroupCommitRequest request) {//获取锁lock.lock();try {//存入this.requestsWrite.add(request);} finally {lock.unlock();}//唤醒同步刷盘线程this.wakeup();
}
3.2.1 wakeup唤醒刷盘线程
wakeup方法尝试唤醒同步刷盘线程, 表示有新的同步等待刷盘请求被提交。
/*** ServiceThread的方法* 尝试唤醒等待的线程*/
public void wakeup() {//尝试CAS的将已通知标志位从false改为trueif (hasNotified.compareAndSet(false, true)) {//如果成功则通知刷盘服务线程,如果失败则表示此前已经通知过了waitPoint.countDown(); // notify}
}
3.3 双队列读写分离设计
-
同步刷盘中, 两个队列requestsWrite和requestsRead, requestsWrite用于存放putRequest方法写入的刷盘请求, requestsRead用于存放doCommit方法读取的刷盘请求。
-
同步刷盘请求会首先调用putRequest方法存入requestsWrite队列中, 同步刷盘服务会最多每隔10ms就会调用swapRequests方法进行读写队列引用的交换, requestsWrite和requestsRead指针改变。并且putRequest方法和swapRequests方法会竞争同一把锁。
-
在swapRequests方法之后的doCommit刷盘方法中, 只会获取requestsRead中的刷盘请求进行刷盘, 在刷盘的最后会将requestsRead队列重新构建一个空队列, 而此过程中的刷盘请求都被提交到requestsWrite。
-
调用一次doCommit刷盘方法, 可以进行多个请求的批量刷盘。这里使用两个队列实现读写分离, 以及重置队列操作, 可以使得putRequest方法提交刷盘请求与doCommit方法消费刷盘请求同时进行, 避免了他们的锁竞争。
4.FlushRealTimeService异步刷盘
异步刷盘服务为FlushRealTimeService, 是一个线程任务。
4.1 run异步刷盘
死循环中不断的执行刷盘的操作。
- 获取一系列参数。
- 是否是定时刷盘, 默认是false, 不开启, 通过flushCommitLogTimed配置。
- 获取刷盘间隔时间, 默认是500ms, 通过flushIntervalCommitLog配置。
- 获取刷盘最少页数, 默认为4, 通过flushCommitLogLeastPages配置。
- 最长刷盘延迟间隔时间, 默认10s, 通过flushCommitLogThoroughInterval配置。
- 如果当前时间距离上次刷盘时间大于等于10s, 刷盘, 因此设置刷盘的最少页数为0, 更新刷盘时间戳为当前时间。
- 判断是否是定时刷盘, 如果是, 那么当前线程sleep睡眠指定的间隔时间, 否则那么调用waitForRunning方法, 但可以被中途的wakeup方法唤醒进而直接尝试进行刷盘。
- 线程醒来后调用mappedFileQueue.flush方法刷盘, 指定最少页数, 随后更新最新commitlog文件的刷盘时间戳, 用于启动恢复。
- 当刷盘服务被关闭时, 默认执行10次刷盘操作, 让消息少丢失。
/*** FlushRealTimeService的方法*/
public void run() {CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started");/** 运行时逻辑* 如果服务没有停止,则在死循环中执行刷盘的操作*/while (!this.isStopped()) {//是否是定时刷盘,默认是false,即不开启boolean flushCommitLogTimed = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isFlushCommitLogTimed();//获取刷盘间隔时间,默认500ms,可通过flushIntervalCommitLog配置int interval = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushIntervalCommitLog();//获取刷盘的最少页数,默认4,即16k,可通过flushCommitLogLeastPages配置int flushPhysicQueueLeastPages = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushCommitLogLeastPages();//最长刷盘延迟间隔时间,默认10s,可通过flushCommitLogThoroughInterval配置,即距离上一次刷盘超过10S时,不管页数是否超过4,都会刷盘int flushPhysicQueueThoroughInterval =CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushCommitLogThoroughInterval();boolean printFlushProgress = false;// Print flush progresslong currentTimeMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();//如果当前时间距离上次刷盘时间大于等于10s,那么必定刷盘if (currentTimeMillis >= (this.lastFlushTimestamp + flushPhysicQueueThoroughInterval)) {//更新刷盘时间戳为当前时间this.lastFlushTimestamp = currentTimeMillis;//最少刷盘页数为0,即不管页数是否超过4,都会刷盘flushPhysicQueueLeastPages = 0;printFlushProgress = (printTimes++ % 10) == 0;}try {//判断是否是定时刷盘if (flushCommitLogTimed) {//如果定时刷盘,那么当前线程睡眠指定的间隔时间Thread.sleep(interval);} else {//如果不是定时刷盘,那么调用waitForRunning方法,线程最多睡眠500ms//可以被中途的wakeup方法唤醒进而直接尝试进行刷盘this.waitForRunning(interval);}if (printFlushProgress) {this.printFlushProgress();}/** 开始刷盘*/long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();/** 刷盘指定的页数*/CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.flush(flushPhysicQueueLeastPages);//获取存储时间戳long storeTimestamp = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.getStoreTimestamp();//修改StoreCheckpoint中的physicMsgTimestamp:最新commitlog文件的刷盘时间戳,单位毫秒//这里用于重启数据恢复if (storeTimestamp > 0) {CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getStoreCheckpoint().setPhysicMsgTimestamp(storeTimestamp);}//刷盘消耗时间long past = System.currentTimeMillis() - begin;if (past > 500) {log.info("Flush data to disk costs {} ms", past);}} catch (Throwable e) {CommitLog.log.warn(this.getServiceName() + " service has exception. ", e);this.printFlushProgress();}}// Normal shutdown, to ensure that all the flush before exit/** 停止时逻辑* 在正常情况下服务关闭时,一次性执行10次刷盘操作*/boolean result = false;for (int i = 0; i < RETRY_TIMES_OVER && !result; i++) {result = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.flush(0);CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service shutdown, retry " + (i + 1) + " times " + (result ? "OK" : "Not OK"));}this.printFlushProgress();CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end");
}
- 异步刷盘下, 默认最少需要4页的脏数据才会刷盘, 另外还可以配置定时刷盘策略, 默认500ms, 且最长刷盘延迟间隔时间, 默认为10s。这些配置可以使得RocketMQ高可用, 但是消息丢失可能变大。
5.CommitRealTimeService异步堆外缓存刷盘
异步堆外缓存刷盘服务为CommitRealTimeService。
5.1 run异步堆外缓存刷盘
死循环中不断的执行刷盘的操作。
- 获取一系列的配置参数。
- 获取刷盘间隔时间, 默认为200ms, 通过commitIntervalCommitLog配置。
- 获取刷盘的最少页数, 默认为4, 通过commitCommitLogLeastPages配置。
- 获取刷盘延迟间隔时间, 默认为200ms, 通过commitCommitLogThoroughInterval配置。
- 如果当前时间距离上次刷盘时间大于等于200ms, 必然刷盘, 因此设置刷盘的最少页数为0, 更新刷盘时间戳为当前时间。
- 调用mappedFileQueue.commit方法提交数据到fileChannel, 而不是直接flush, 如果已经提交了一些脏数据到fileChannel, 那么更新最后提交的时间戳, 并且唤醒FlushCommitLogService异步刷盘服务进行真正的刷盘操作。
- 调用waitForRunning方法, 线程最多阻塞指定的间隔时间, 但可以被中途的wakeup方法唤醒进而进行下一轮循环。
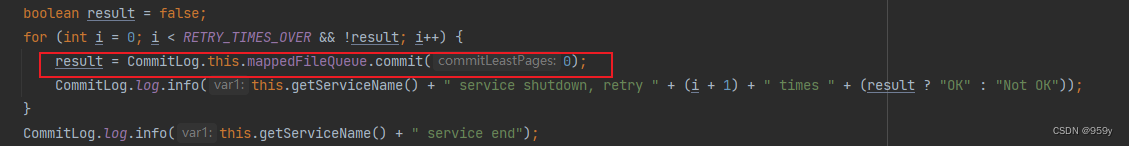
- 当刷盘服务被关闭时, 默认执行10次刷盘操作, 让消息少丢失。
/*** CommitRealTimeService* <p>* 执行异步堆外缓存刷盘服务*/
@Override
public void run() {CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started");/** 运行时逻辑* 如果服务没有停止,则在死循环中执行刷盘的操作*/while (!this.isStopped()) {//获取刷盘间隔时间,默认200ms,可通过commitIntervalCommitLog配置int interval = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getCommitIntervalCommitLog();//获取刷盘的最少页数,默认4,即16k,可通过commitCommitLogLeastPages配置int commitDataLeastPages = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getCommitCommitLogLeastPages();//最长刷盘延迟间隔时间,默认200ms,可通过commitCommitLogThoroughInterval配置,即距离上一次刷盘超过200ms时,不管页数是否超过4,都会刷盘int commitDataThoroughInterval =CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getCommitCommitLogThoroughInterval();long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();//如果当前时间距离上次刷盘时间大于等于200ms,那么必定刷盘if (begin >= (this.lastCommitTimestamp + commitDataThoroughInterval)) {this.lastCommitTimestamp = begin;commitDataLeastPages = 0;}try {/** 调用commit方法提交数据,而不是直接flush*/boolean result = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.commit(commitDataLeastPages);long end = System.currentTimeMillis();//如果已经提交了一些脏数据到fileChannelif (!result) {//更新最后提交的时间戳this.lastCommitTimestamp = end; // result = false means some data committed.//now wake up flush thread.//唤醒flushCommitLogService异步刷盘服务进行刷盘操作flushCommitLogService.wakeup();}if (end - begin > 500) {log.info("Commit data to file costs {} ms", end - begin);}//等待执行this.waitForRunning(interval);} catch (Throwable e) {CommitLog.log.error(this.getServiceName() + " service has exception. ", e);}}/** 停止时逻辑* 在正常情况下服务关闭时,一次性执行10次刷盘操作*/boolean result = false;for (int i = 0; i < RETRY_TIMES_OVER && !result; i++) {result = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.commit(0);CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service shutdown, retry " + (i + 1) + " times " + (result ? "OK" : "Not OK"));}CommitLog.log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end");
}
6.MappedFile的刷盘
同步刷盘:
异步刷盘:
6.1 MappedFileQueue#flush刷盘
同步和异步刷盘服务, 最后调用的是MappedFileQueue#flush方法执行刷盘。
- 首先根据最新刷盘物理位置flushedWhere, 找到MappedFile。
- 如果flushedWhere为0, 表示还没有写消息。
- 那么获取第一个MappedFile, 调用mappedFile#flush方法执行真正的刷盘操作。
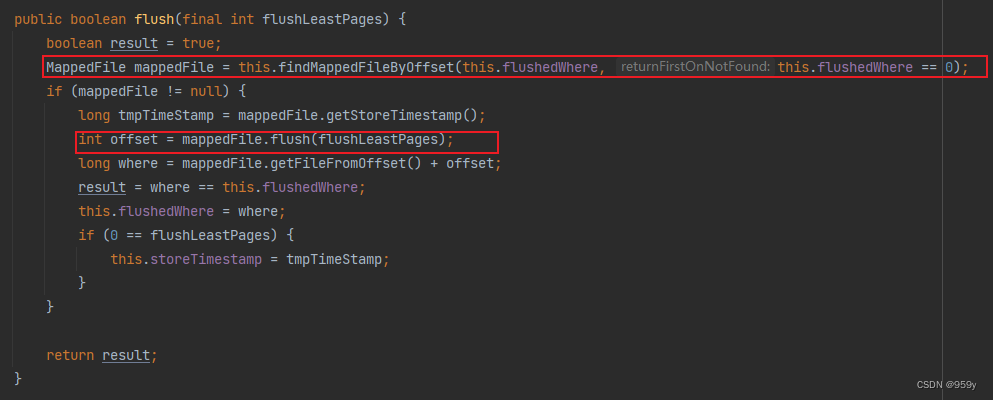
/*** MappedFileQueue的方法* <p>* 执行刷盘** @param flushLeastPages 最少刷盘的页数*/
public boolean flush(final int flushLeastPages) {boolean result = true;//根据最新刷盘物理位置flushedWhere,去找到对应的MappedFile。如果flushedWhere为0,表示还没有开始写消息,则获取第一个MappedFileMappedFile mappedFile = this.findMappedFileByOffset(this.flushedWhere, this.flushedWhere == 0);if (mappedFile != null) {//获取存储时间戳,storeTimestamp在appendMessagesInner方法中被更新long tmpTimeStamp = mappedFile.getStoreTimestamp();/** 执行刷盘操作*/int offset = mappedFile.flush(flushLeastPages);//获取最新刷盘物理偏移量long where = mappedFile.getFileFromOffset() + offset;//刷盘结果result = where == this.flushedWhere;//更新刷盘物理位置this.flushedWhere = where;//如果最少刷盘页数为0,则更新存储时间戳if (0 == flushLeastPages) {this.storeTimestamp = tmpTimeStamp;}}return result;
}
6.1.1 findMappedFileByOffset根据偏移量获取MappedFile
根据偏移量获取对应的MappedFile。
- 获取mappedFiles集合中的第一个MappedFile和最后一个MappedFile。
- 获取当前offset属于的MappedFile在mappedFiles集合中的索引位置。因为MappedFile的名字则是该MappedFile的起始offset, 而每个MappedFile的大小一般是固定的。
- 根据索引位置从mappedFiles中获取对应的MappedFile文件targetFile, 如果指定offset在targetFile的offset范围内, 返回targetFile。
- 否则, 遍历mappedFiles, 依次对每个MappedFile的offset范围进行判断, 找到对应的tmpMappedFile。
- 如果还未找到, 如果returnFirstOnNotFound为true, 返回第一个文件。
- 最后还未找到返回null。
/*** MappedFileQueue的方法* <p>* 根据偏移量获取MappedFile** @param offset 偏移量.* @param returnFirstOnNotFound 如果未找到映射文件,则返回第一个文件。* @return MappedFile 或者 null (当未找到且returnFirstOnNotFound为false时).*/
public MappedFile findMappedFileByOffset(final long offset, final boolean returnFirstOnNotFound) {try {//获取第一个MappedFileMappedFile firstMappedFile = this.getFirstMappedFile();//获取最后一个MappedFileMappedFile lastMappedFile = this.getLastMappedFile();if (firstMappedFile != null && lastMappedFile != null) {//如果偏移量不再正确的范围内,则打印异常日志if (offset < firstMappedFile.getFileFromOffset() || offset >= lastMappedFile.getFileFromOffset() + this.mappedFileSize) {LOG_ERROR.warn("Offset not matched. Request offset: {}, firstOffset: {}, lastOffset: {}, mappedFileSize: {}, mappedFiles count: {}",offset,firstMappedFile.getFileFromOffset(),lastMappedFile.getFileFromOffset() + this.mappedFileSize,this.mappedFileSize,this.mappedFiles.size());} else {//获取当前offset属于的MappedFile在mappedFiles集合中的索引位置int index = (int) ((offset / this.mappedFileSize) - (firstMappedFile.getFileFromOffset() / this.mappedFileSize));MappedFile targetFile = null;try {//根据索引位置获取对应的MappedFile文件targetFile = this.mappedFiles.get(index);} catch (Exception ignored) {}//如果指定offset在targetFile的offset范围内,那么返回if (targetFile != null && offset >= targetFile.getFileFromOffset()&& offset < targetFile.getFileFromOffset() + this.mappedFileSize) {return targetFile;}//否则,遍历mappedFiles,依次对每个MappedFile的offset范围进行判断,找到对应的tmpMappedFile并返回for (MappedFile tmpMappedFile : this.mappedFiles) {if (offset >= tmpMappedFile.getFileFromOffset()&& offset < tmpMappedFile.getFileFromOffset() + this.mappedFileSize) {return tmpMappedFile;}}}//到这里表示没找到任何MappedFile,如果returnFirstOnNotFound为true,则返回第一个文件if (returnFirstOnNotFound) {return firstMappedFile;}}} catch (Exception e) {log.error("findMappedFileByOffset Exception", e);}return null;
}
6.1.2 MappedFile#flush执行刷盘
执行刷盘的MappedFile实例调用的方法, 用于完成刷盘操作。无论是同步还是异步刷盘, 都是调用此方法。
- 判断是否可以刷盘, 如果文件满了, 或者如果flushLeastPages大于0, 且脏页数量大于等于flushLeastPages, 或者如果flushLeastPages等于0并且存在脏数据, 都会刷盘操作。
- 如果可以刷盘了, 增加引用次数, 进行刷盘操作, 如果使用了堆外内存, 通过fileChannel#force强制刷盘, 走异步堆外内存走的逻辑。如果没有使用堆外内存, 通过mappedByteBuffer#force强制刷盘, 这是同步或者异步刷盘走的逻辑。
- 最后更新刷盘位置为写入位置。
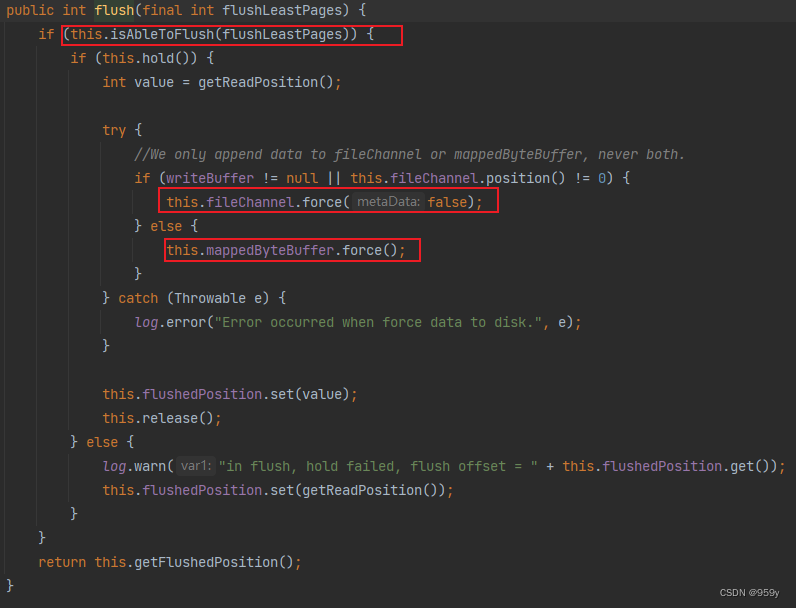
/*** MappedFile的方法* <p>* 刷盘** @param flushLeastPages 最少刷盘的页数* @return 当前刷盘的位置*/
public int flush(final int flushLeastPages) {//判断是否可以刷盘//如果文件已经满了,或者如果flushLeastPages大于0,且脏页数量大于等于flushLeastPages//或者如果flushLeastPages等于0并且存在脏数据,这几种情况都会刷盘if (this.isAbleToFlush(flushLeastPages)) {//增加对该MappedFile的引用次数if (this.hold()) {//获取写入位置int value = getReadPosition();try {/** 只将数据追加到fileChannel或mappedByteBuffer中,不会同时追加到这两个里面。*///We only append data to fileChannel or mappedByteBuffer, never both.//如果使用了堆外内存,那么通过fileChannel强制刷盘,这是异步堆外内存走的逻辑if (writeBuffer != null || this.fileChannel.position() != 0) {this.fileChannel.force(false);} else {//如果没有使用堆外内存,那么通过mappedByteBuffer强制刷盘,这是同步或者异步刷盘走的逻辑this.mappedByteBuffer.force();}} catch (Throwable e) {log.error("Error occurred when force data to disk.", e);}//设置刷盘位置为写入位置this.flushedPosition.set(value);//减少对该MappedFile的引用次数this.release();} else {log.warn("in flush, hold failed, flush offset = " + this.flushedPosition.get());this.flushedPosition.set(getReadPosition());}}//获取最新刷盘位置return this.getFlushedPosition();
}/*** MappedFile的方法* 是否支持刷盘** @param flushLeastPages 至少刷盘的页数*/
private boolean isAbleToFlush(final int flushLeastPages) {//获取刷盘位置int flush = this.flushedPosition.get();//获取写入位置int write = getReadPosition();//如果文件已经满了,那么返回trueif (this.isFull()) {return true;}//如果至少刷盘的页数大于0,则需要比较写入位置与刷盘位置的差值//当差值大于等于指定的页数才能刷盘,防止频繁的刷盘if (flushLeastPages > 0) {return ((write / OS_PAGE_SIZE) - (flush / OS_PAGE_SIZE)) >= flushLeastPages;}//否则,表示flushLeastPages为0,那么只要写入位置大于刷盘位置,即存在脏数据,那么就会刷盘return write > flush;
}6.2 MappedFileQueue#commit提交
MappedFileQueue#commit方法用于提交刷盘。
- 首先根据最新刷盘物理位置flushedWhere, 找到MappedFile。
- 如果flushedWhere为0, 表示还没有写消息。
- 那么获取第一个MappedFile, 调用mappedFile#flush方法执行真正的刷盘操作。
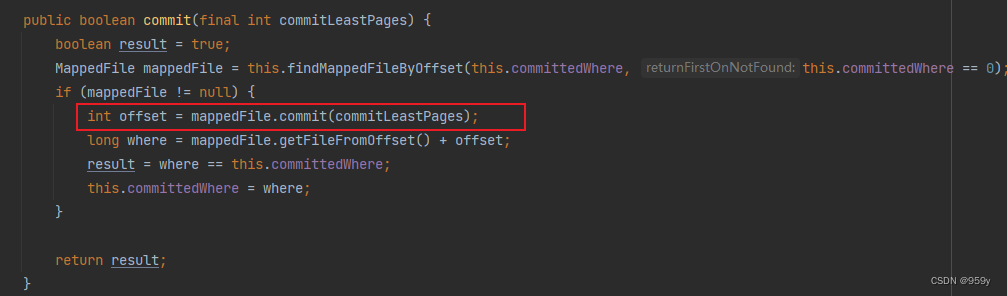
/*** MappedFileQueue的方法* <p>* 提交刷盘** @param commitLeastPages 最少提交的页数* @return false表示提交了部分数据*/
public boolean commit(final int commitLeastPages) {boolean result = true;//根据最新提交物理位置committedWhere,去找到对应的MappedFile。如果committedWhere为0,表示还没有开始提交消息,则获取第一个MappedFileMappedFile mappedFile = this.findMappedFileByOffset(this.committedWhere, this.committedWhere == 0);if (mappedFile != null) {/** 执行提交操作*/int offset = mappedFile.commit(commitLeastPages);//获取最新提交物理偏移量long where = mappedFile.getFileFromOffset() + offset;//如果不相等,表示提交了部分数据result = where == this.committedWhere;//更新提交物理位置this.committedWhere = where;}return result;
}
6.2.1 MappedFile#commit提交
-
该方法是需要执行提交的MappedFile实例调用的方法, 用于完成提交操作。
-
通过isAbleToCommit方法判断是否支持提交, 调用commit0方法将堆外内存中的全部脏数据提交到filechannel。
-
如果所有的脏数据被提交到了FileChannel, 那么归还堆外缓存, 将堆外缓存重置, 并存入内存池availableBuffers的头部, 然后writeBuffer为null, 下次重新获取writeBuffer。
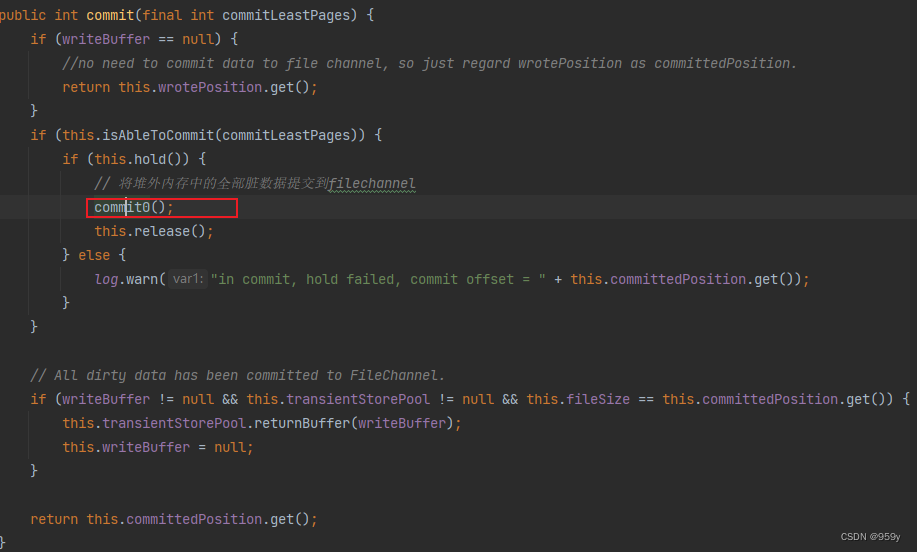
/*** MappedFile的方法* <p>* 提交刷盘** @param commitLeastPages 最少提交页数* @return 提交的offset*/
public int commit(final int commitLeastPages) {//如果堆外缓存为null,那么不需要提交数据到filechannel,所以只需将wrotePosition视为committedPosition返回即可。if (writeBuffer == null) {//no need to commit data to file channel, so just regard wrotePosition as committedPosition.return this.wrotePosition.get();}//是否支持提交,其判断逻辑和isAbleToFlush方法一致if (this.isAbleToCommit(commitLeastPages)) {//增加对该MappedFile的引用次数if (this.hold()) {//将堆外内存中的全部脏数据提交到filechannelcommit0();this.release();} else {log.warn("in commit, hold failed, commit offset = " + this.committedPosition.get());}}// All dirty data has been committed to FileChannel.//所有的脏数据被提交到了FileChannel,那么归还堆外缓存if (writeBuffer != null && this.transientStorePool != null && this.fileSize == this.committedPosition.get()) {//将堆外缓存重置,并存入内存池availableBuffers的头部this.transientStorePool.returnBuffer(writeBuffer);//writeBuffer职位null,下次再重新获取this.writeBuffer = null;}//返回提交位置return this.committedPosition.get();
}
6.2.2 commit0
- 获取到堆外内存的指针, 写入到fileChannel中。
protected void commit0() {int writePos = this.wrotePosition.get();int lastCommittedPosition = this.committedPosition.get();if (writePos - lastCommittedPosition > 0) {try {ByteBuffer byteBuffer = writeBuffer.slice();byteBuffer.position(lastCommittedPosition);byteBuffer.limit(writePos);this.fileChannel.position(lastCommittedPosition);this.fileChannel.write(byteBuffer);this.committedPosition.set(writePos);} catch (Throwable e) {log.error("Error occurred when commit data to FileChannel.", e);}}}
7.总结
-
同步刷盘, 为GroupCommitService服务。
- 同步等待: 如果消息的配置需要等待存储完成后才返回, 那么构建同步刷盘请求, 将请求存入内部的requestsWrite, 并唤醒同步刷盘线程, 返回future, 没有填充刷盘的结果, 在外部的thenCombine方法阻塞。
- 同步不等待: 消息的配置不需要等待存储完成后才返回, 唤醒同步刷盘线程, 返回PUT_OK。
-
异步刷盘:
- 启动了堆外缓存读写分离, transientStorePoolEnable为true和不是slave, 那么唤醒CommitRealTimeService服务。
- 没有启动, 唤醒FlushRealTimeService服务。
-
同步和异步刷盘服务, 最后调用的是MappedFileQueue#flush方法执行刷盘, 该方法内部最终又是通过mappedFile#flush方法刷盘的。
-
同步刷盘双队列读写分离优化: 可以使得putRequest方法提交刷盘请求与doCommit方法消费刷盘请求同时进行, 避免他们竞争。
-
异步堆外缓存刷盘优化: 异步堆外缓存刷盘服务并不会真正的执行flush刷盘, 而是调用commit方法提交数据到fileChannel。