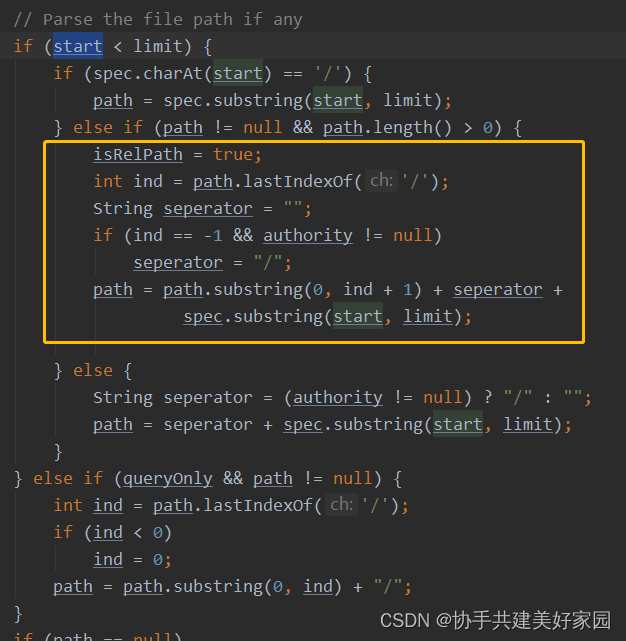
代码结构如下图:

其中topologicalSort(float**, int, int*, bool*, int, int)用来递归求解拓扑排序,topologicalSort(float**, int*&, int, int, int)传参图的邻接矩阵mat与结点个数n,与一个引用变量数组topo,返回一个布尔值表示该图是否存在拓扑排序,同时将引用变量数组topo赋值为该图的拓扑序列。
getEdges(float**, int**&, int)传参图的邻接矩阵mat,引用变量二维数组edge,结点数n。然后将返回该图的边数,同时将float赋值为一个存储图的边的起点与终点的edgeNum * 2维的数组。
aoe(float**, int, int*&, int&, float*&, float*&, float*&, float*&, int*&, int**&, int&)分别传参邻接矩阵mat,结点数n,引用变量criticalPath表示关键路径,引用变量ve,vl,e,l正如名字所示,topo与edges表示拓扑序列与边,edgeNum表示边的数量。
aoe(float**, int, int*&, int&, float*&, float*&, float*&, float*&)与上一个函数差不多,只是少了topo与edges,edgeNum两个参数,并且多了一个布尔类型的返回值,返回的是关键路径是否存在。
aoe(float**, int*&, int&)则更是只有三个参数,他不对ve,vl,e,l进行返回。
aoe
static const float INF = 1.0f/0.0f;// x is what you are, and y is meaning to you are the no.y numbers to sort.
void topologicalSort(float** mat, int n, int* arr, bool* flags, int x=0, int y=0) {arr[y] = x;flags[x] = true;float tmp[n];// first, set all the elements of the no.x row to INF, and store the original value to tmp;// just like delete this vertexfor (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {tmp[i] = mat[x][i];mat[x][i] = INF;}for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {int k = (x + i) % n;// if k have not recorded in arr.if (!flags[k]) {bool flag = true;// this loop is aim to find a vertex whose in_degree is equals to 0.for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {if (j != k && mat[j][k] != INF) {flag = false;break;}}// if you delete x, the in_degree of k is equals to 0. so do a recursive call.if (flag) {topologicalSort(mat, n, arr, flags, k, y+1);}}}// restore the no.x rowfor (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {mat[x][i] = tmp[i];}}bool topologicalSort(float** mat, int* &topo, int n, int x=0, int y=0) {topo = new int[n];bool *flags = new bool[n];for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {flags[i] = false;}topologicalSort(mat, n, topo, flags, x, y);for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {if (!flags[i]) return false;}return true;}int getEdges(float** mat, int** &edges, int n) {// e is for the edges, whose account is unsure// ans is for the number of edgesint ans = 0;int** e = new int*[n * (n - 1)];for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {if (i == j || mat[i][j] == INF) continue;e[ans++] = new int[]{i, j};}}// copy e into edgesedges = new int*[ans];for (int i = 0; i < ans; ++i) {edges[i] = e[i];}delete[] e;return ans;}void aoe(float** mat, int n, int* &criticalPath, int &length, float* &ve, float* &vl, float* &e, float* &l, int* &topo, int** &edges, int &edgeNum) {ve = new float[n];vl = new float[n];e = new float[edgeNum];l = new float[edgeNum];for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {ve[i] = 0;}for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {int max = i;for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j) {if (mat[topo[j]][topo[i]] == 0 || mat[topo[j]][topo[i]] == INF) continue;if (ve[topo[j]] + mat[topo[j]][topo[i]] > ve[topo[max]] + mat[topo[max]][topo[i]]) {max = j;}}ve[topo[i]] = ve[topo[max]] + mat[topo[max]][topo[i]];}for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {vl[i] = ve[topo[n - 1]];}for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; --i) {int min = i;for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {if (mat[topo[i]][topo[j]] == 0 || mat[topo[i]][topo[j]] == INF) continue;if (vl[topo[j]] - mat[topo[i]][topo[j]] < vl[topo[min]] - mat[topo[i]][topo[min]]) {min = j;}}vl[topo[i]] = vl[topo[min]] - mat[topo[i]][topo[min]];}for (int i = 0; i < edgeNum; ++i) {e[i] = ve[edges[i][0]];l[i] = vl[edges[i][1]] - mat[edges[i][0]][edges[i][1]];}int* critical = new int[n];critical[0] = topo[0];length = 1;for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {critical[i] = -1;}for (int i = 0; i < edgeNum; ++i) {float le = l[i] - e[i];if (le < 1e-32) {critical[edges[i][0]] = edges[i][1];length++;}}criticalPath = new int[length];int p = 0;int q = 0;while (p != -1) {criticalPath[q++] = p;p = critical[p];}delete[] critical;}bool aoe(float** mat, int n, int* &criticalPath, int &length, float* &ve, float* &vl, float* &e, float* &l) {int* topo;int flag = topologicalSort(mat, topo, n);if (!flag) return false;int** edges;int edgeNum = getEdges(mat, edges, n);aoe(mat, n, criticalPath, length, ve, vl, e, l, topo, edges, edgeNum);return true;}bool aoe(float** mat, int n, int* &criticalPath, int &length) {float* ve;float* vl;float* e;float* l;return aoe(mat, n, criticalPath, length, ve, vl, e, l);}
在main函数中进行一个测试,传参如下图:
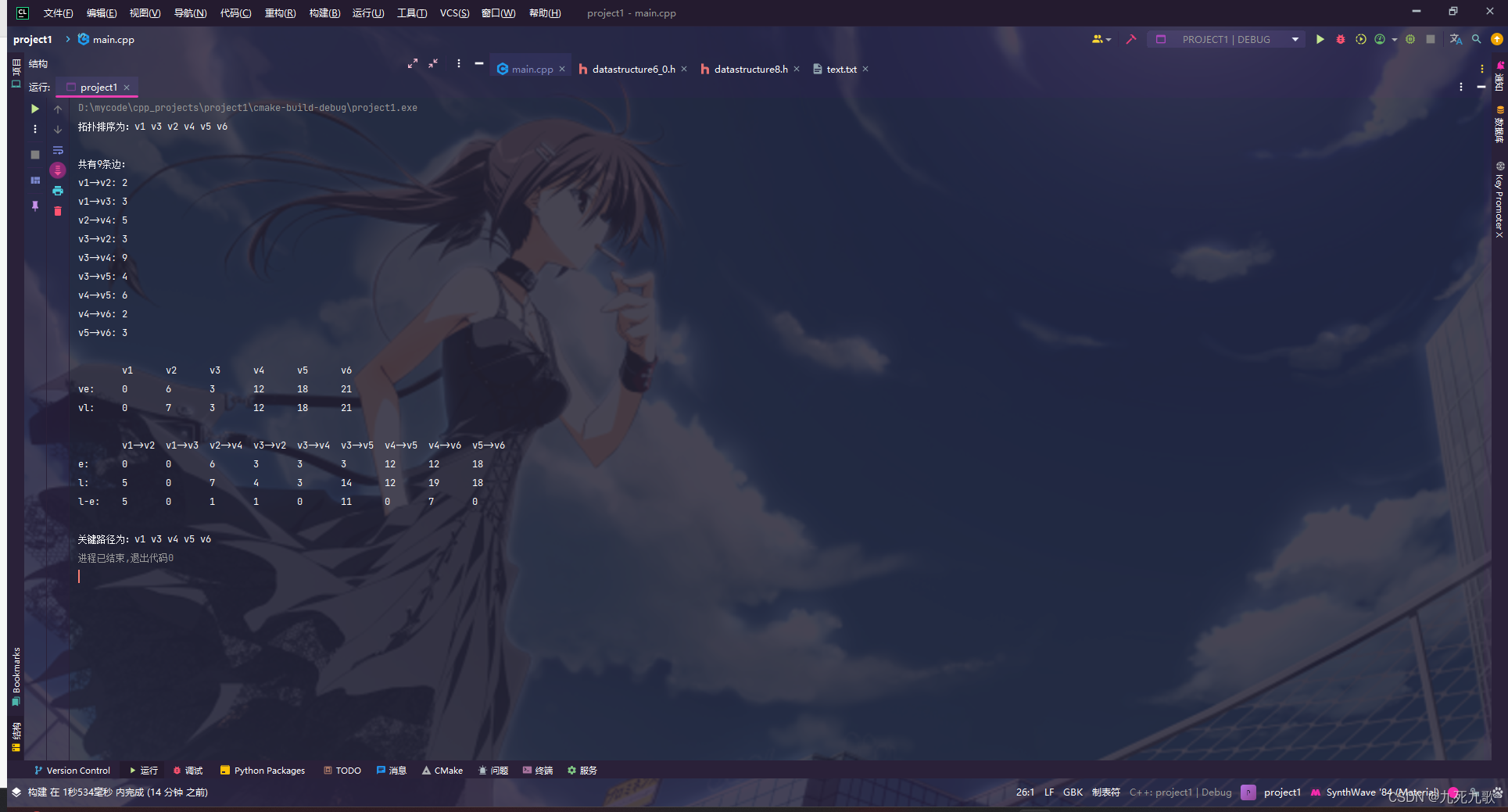
int main() {int n = 6;float** mat = new float*[] {new float[] {0, 2, 3, INF, INF, INF },new float[] {INF, 0, INF, 5, INF, INF },new float[] {INF, 3, 0, 9, 4, INF },new float[] {INF, INF, INF, 0, 6, 2 },new float[] {INF, INF, INF, INF, 0, 3 },new float[] {INF, INF, INF, INF, INF, 0 }};char** value = new char*[n]{"v1", "v2", "v3", "v4", "v5", "v6"};float *ve, *vl, *e, *l;int* criticalPath;int length;int** edges;int* topo;topologicalSort(mat, topo, n);int edgeNum = getEdges(mat, edges, n);aoe(mat, n, criticalPath, length, ve, vl, e, l);cout << "拓扑排序为:";for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {cout << value[topo[i]] << " ";}cout << "\n\n";cout << "共有" << edgeNum << "条边:\n";for (int i = 0; i < edgeNum; ++i) {cout << value[edges[i][0]] << "->" << value[edges[i][1]] << ": " << mat[edges[i][0]][edges[i][1]] << endl;}cout << endl;for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {cout << '\t' << value[i];}cout << endl;cout << "ve:";for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {cout << '\t' << ve[i];}cout << endl;cout << "vl:";for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {cout << '\t' << vl[i];}cout << "\n\n";for (int i = 0; i < edgeNum; ++i) {cout << '\t' << value[edges[i][0]] << "->" << value[edges[i][1]];}cout << endl;cout << "e:";for (int i = 0; i < edgeNum; ++i) {cout << '\t' << e[i];}cout << endl;cout << "l:";for (int i = 0; i < edgeNum; ++i) {cout << '\t' << l[i];}cout << endl;cout << "l-e:";for (int i = 0; i < edgeNum; ++i) {cout << '\t' << l[i] - e[i];}cout << "\n\n";cout << "关键路径为:";for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i) {cout << value[criticalPath[i]] << " ";}return 0;}
运行结果如下:
![[Android]使用Git将项目提交到GitHub](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/275fc29f07c546c3b3a08c17184e32ac.png)