给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 层序遍历 。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
示例 1:
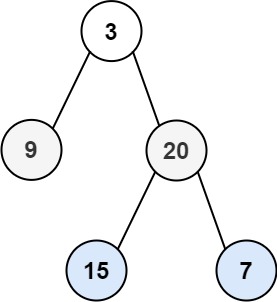
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:[[3],[9,20],[15,7]]
示例 2:
输入:root = [1] 输出:[[1]]
示例 3:
输入:root = [] 输出:[]
层序遍历一个二叉树。就是从左到右一层一层的去遍历二叉树
需要借用一个辅助数据结构即队列来实现,队列先进先出,符合一层一层遍历的逻辑,而是用栈先进后出适合模拟深度优先遍历也就是递归的逻辑。
而这种层序遍历方式就是图论中的广度优先遍历
使用队列实现二叉树广度优先遍历
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<TreeNode>();List<List<Integer>> result= new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();if(root==null) return result;queue.add(root);while(!queue.isEmpty()){int size=queue.size();List<Integer> res=new ArrayList<>();while(size>0){TreeNode cur=queue.poll();res.add(cur.val);if(cur.left!=null){queue.add(cur.left);}if(cur.right!=null){queue.add(cur.right);}size--;}result.add(res);}return result;}
}