链表就是将所有数据都用一个链子串起来,其中链表也有多种形式,包含单向链表、双向链表等;
现在毕竟还是基础阶段,就先学习单链表吧;
链表用头结点head表示一整个链表,每个链表的节点包含当前节点的值val和下一个节点next。
链表的好处就是删除和插入比较容易,不需要移动其他元素。只需要改变下一个节点的指向值即可。
第一题 面试题 02.02. 返回倒数第 k 个节点
https://leetcode.cn/problems/kth-node-from-end-of-list-lcci/description/
返回第k个节点的值,这里使用双指针的思路,定义一个快指针和慢指针,两个指针之间间隔k位,快指针移动到最后一个节点的下一个节点(即节点为空时)时就停止,此时慢指针对应的就是倒数第k个节点值。
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/int kthToLast(struct ListNode* head, int k){struct ListNode * fast = head;struct ListNode * slow = head;for(int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {fast = fast->next;}while(fast) {fast = fast->next;slow = slow->next;}return slow->val;
}
第二题 19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/description/
删除倒数第n个节点,思路和上一题一样,先找到倒数第N个节点,我们要删除这个节点,所以需要找到这个节点的前一个节点N+1;
直接将下一个值指向N的下一个值即可。
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
struct ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(struct ListNode* head, int n) {struct ListNode * fast = head;struct ListNode * slow = head;for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {fast = fast->next;if(fast == NULL) {return head->next;}}fast = fast->next;while(fast) {fast = fast->next;slow = slow->next;}slow->next = slow->next->next;return head;}
第三题 206. 反转链表
https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/description/
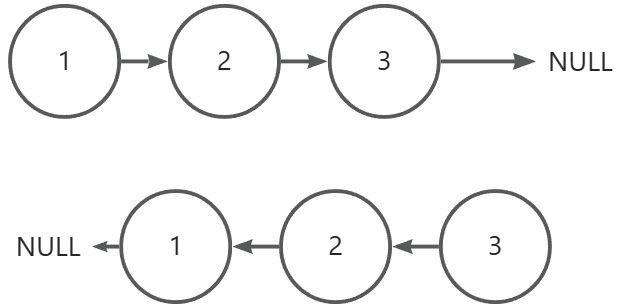
第一种:迭代方法,定义一个当前节点cur和前一个节点pre,遍历链表,将指向换一下方向即可,注意保存cur->next
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {struct ListNode * pre = NULL;struct ListNode * cur = head;while(cur) {struct ListNode * temp = cur->next;cur->next = pre;pre = cur;cur = temp;}return pre;
}
第二种:递归
主要思想就是从最后一个开始,将它的指针指向前一个节点,然后前一个节点指向NULL;
这时又递归到前一个节点,和上面操作一样,一直到第一个头结点,这时头结点会置为NULL;
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/struct ListNode * doReverse(struct ListNode * head, struct ListNode ** outHead) {递归临界点,如果到最后一个节点则开始往回走;if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL) {*outHead = head; outhead是最终翻转后的头结点,所以这里head最后一个节点就是outhead的头结点return head;}
每次递归都向下一层,返回值为反转后的struct ListNode * tail = doReverse(head->next, outHead);tail->next = head;head->next = NULL;return head;
}struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {struct ListNode * outHead;doReverse(head, &outHead);return outHead;
}
第四题 237. 删除链表中的节点
https://leetcode.cn/problems/delete-node-in-a-linked-list/description/
这道题代码不难,主要的是思想,能不能想到这样的方法。
只给了一个需要删除的节点node,让你删除这个节点。
那么我们只需要将node->next的值赋值给node,那么这样就可以删除node->next,这样同样可以达到需要的结果。
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
void deleteNode(struct ListNode* node) {node->val = node->next->val;node->next = node->next->next;
}
第五题 24. 两两交换链表中的节点
https://leetcode.cn/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/description/
本题有两种做法,迭代和递归,递归相对来说难理解。
一、递归
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
struct ListNode* swapPairs(struct ListNode* head) {定义临界点,即递到最后一个节点或者空时开始归。if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL) {return head;}这里就是记录递归的当前节点和下一个节点,用于后续交换struct ListNode* now = head;struct ListNode* next = head->next;这里记录的是后面已经完成交换的头结点nextnext;struct ListNode* nextnext = swapPairs(now->next->next);这里算是核心,now->next = nextnext; 每次将当前节点的下个节点指向已经完成交换的头结点next->next = now; 将当前节点下一个节点又指向当前节点,即完成本轮交换return next;
}
二、迭代
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {ListNode * virhead = new ListNode();virhead->next = head;ListNode * cur = virhead;while (cur->next != nullptr && cur->next->next != nullptr) {ListNode * temp1 = cur->next;ListNode * temp2 = cur->next->next->next;cur->next = cur->next->next;cur->next->next = temp1;cur->next->next->next = temp2;cur = cur->next->next;}return virhead->next;}
};