1 注意点
一般上来说如果java调用java的话,我们可以使用springcloud来做,而面对这种跨语言的情况下,gRPC就展现出了他的优势。
代码放在这了,请结合前面的go服务器端一起使用
https://gitee.com/guo-zonghao/java-client-grpc
// 这些是在java端生成时候的配置option java_multiple_files = true;//生成文件所属的包option java_package = "com.iq50.client.routeguide";option java_outer_classname = "RouteGuideProto";
在运行插件的时候我们需要运行以下两个命令
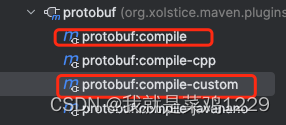
之后我们会获得:
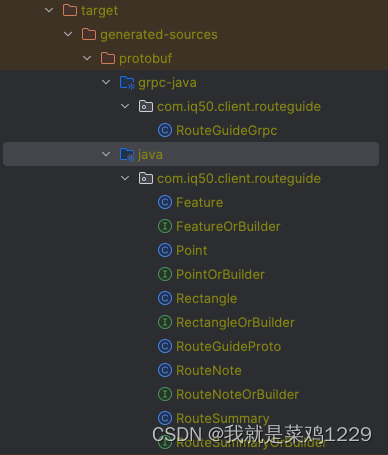
2 如何编写客户端代码
package com.iq50.client.routeguide;import io.grpc.ManagedChannel;
import io.grpc.ManagedChannelBuilder;
import io.grpc.netty.NegotiationType;
import io.grpc.netty.NettyChannelBuilder;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Service
public class RouteGuideClient {//socket通道管理private final ManagedChannel channel;//负责普通调用和服务端到客户端的流调用private final RouteGuideGrpc.RouteGuideBlockingStub blockingStub;//负责双向流调用和客户端到服务端的流调用private final RouteGuideGrpc.RouteGuideStub asyncStub;public RouteGuideClient(){this(ManagedChannelBuilder.forAddress("127.0.0.1", 50051).usePlaintext());}private RouteGuideClient(ManagedChannelBuilder<?> channelBuilder) {this.channel = channelBuilder.build();this.blockingStub = RouteGuideGrpc.newBlockingStub(channel);this.asyncStub = RouteGuideGrpc.newStub(channel);}public RouteGuideGrpc.RouteGuideBlockingStub getRPCMethods(){return this.blockingStub;}public RouteGuideGrpc.RouteGuideStub getRPCAsyncMethods(){return this.asyncStub;}
}
3 如何调用具体的方法
3.1 普通调用和服务端流式调用
so easy!
通过获取stub之后直接调用即可。
package com.iq50.client.service.impl;import com.iq50.client.routeguide.Feature;
import com.iq50.client.routeguide.Point;
import com.iq50.client.routeguide.Rectangle;
import com.iq50.client.routeguide.RouteGuideClient;
import com.iq50.client.service.RouteGuideService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;import java.util.Iterator;@Service
public class RouteGuideServiceImpl implements RouteGuideService {@AutowiredRouteGuideClient routeGuideClient;@Overridepublic Feature GetFeature(Point point) {return routeGuideClient.getRPCMethods().getFeature(point);}@Overridepublic Iterator<Feature> ListFeatures(Rectangle rectangle) {return routeGuideClient.getRPCMethods().listFeatures(rectangle);}
}3.2 客户端流式调用
在这个代码中我们需要使用SettableFuture来进行异步操作的通知,以及重写一个观察者的方法来方便进行异步的回调操作。
在这个方法体中,我们返回了一个匿名 StreamObserver 实例,其中我们:
- 覆写了 onNext() 方法,每次客户端写入一个 Point 到消息流时,拿到特性和其它信息。 覆写了 onCompleted()
- 方法(在 客户端 结束写入消息时调用),用来填充和构建我们的 RouteSummary。然后我们用 RouteSummary调用方法自己的的响应观察者的 onNext(),
- 之后调用它的 onCompleted() 方法,结束服务器端的调用。
List<Feature> features = new ArrayList<Feature>();features.add(Feature.newBuilder().setLocation(Point.newBuilder().setLatitude(1200000).setLongitude(12000).build()).setName("asd").build());features.add(Feature.newBuilder().setLocation(Point.newBuilder().setLatitude(2200000).setLongitude(12000).build()).setName("asdf").build());features.add(Feature.newBuilder().setLocation(Point.newBuilder().setLatitude(3200000).setLongitude(12000).build()).setName("ewfew").build());features.add(Feature.newBuilder().setLocation(Point.newBuilder().setLatitude(4200000).setLongitude(12000).build()).setName("rtgr").build());features.add(Feature.newBuilder().setLocation(Point.newBuilder().setLatitude(5200000).setLongitude(12000).build()).setName("wer").build());int numPoints = features.size();//=========================//用来控制异步操作final SettableFuture<Void> finishFuture = SettableFuture.create();StreamObserver<RouteSummary> responseObserver = new StreamObserver<RouteSummary>() {@Overridepublic void onNext(RouteSummary summary) {try {System.out.printf("Finished trip with %d points. Passed %d features. Travelled %d meters. It took %d seconds.\n",summary.getPointCount(), summary.getFeatureCount(), summary.getDistance(), summary.getElapsedTime());} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}@Overridepublic void onError(Throwable t) {//表示操作已经出错,进行通知finishFuture.setException(t);}@Overridepublic void onCompleted() {//表示操作已经完成finishFuture.set(null);}};//获得一个请求的观察者对象StreamObserver<Point> requestObserver = routeGuideClient.getRPCAsyncMethods().recordRoute(responseObserver);try {// 随机挑选节点发送给服务器StringBuilder numMsg = new StringBuilder();Random rand = new Random();for (int i = 0; i < numPoints; ++i) {int index = rand.nextInt(features.size());Point point = features.get(index).getLocation();System.out.printf("Visiting point %d, %d\n", point.getLatitude(),point.getLongitude());//将点发送给服务器requestObserver.onNext(point);// Sleep for a bit before sending the next one.Thread.sleep(rand.nextInt(1000) + 500);if (finishFuture.isDone()) {break;}}System.out.println(numMsg.toString());//告诉服务器端客户端以及发送完全部信息requestObserver.onCompleted();//等待服务器端完成处理finishFuture.get();System.out.println("Finished RecordRoute\n");} catch (Exception e) {requestObserver.onError(e);System.out.printf("RecordRoute Failed\n", e);}return "调用成功";
3.3 双向流式调用
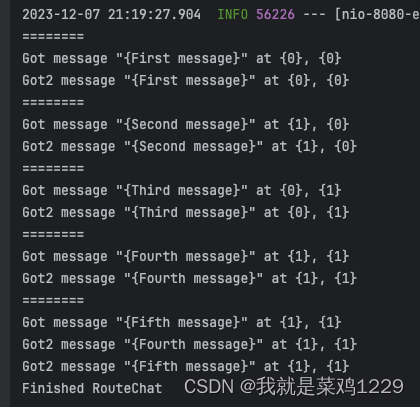
@GetMapping("/routeChat")public String routeChat() {final SettableFuture<Void> finishFuture = SettableFuture.create();StreamObserver<RouteNote> requestObserver = routeGuideClient.getRPCAsyncMethods().routeChat(new StreamObserver<RouteNote>() {@Overridepublic void onNext(RouteNote note) {System.out.println("========");System.out.printf("Got2 message \"{%s}\" at {%d}, {%d}\n", note.getMessage(), note.getLocation().getLatitude(), note.getLocation().getLongitude());}@Overridepublic void onError(Throwable t) {finishFuture.setException(t);}@Overridepublic void onCompleted() {finishFuture.set(null);}});try {RouteNote[] requests ={RouteNote.newBuilder().setMessage("First message").setLocation(Point.newBuilder().setLongitude(0).setLatitude(0).build()).build(),RouteNote.newBuilder().setMessage("Second message").setLocation(Point.newBuilder().setLongitude(0).setLatitude(1).build()).build(),RouteNote.newBuilder().setMessage("Third message").setLocation(Point.newBuilder().setLongitude(1).setLatitude(0).build()).build(),RouteNote.newBuilder().setMessage("Fourth message").setLocation(Point.newBuilder().setLongitude(1).setLatitude(1).build()).build(),RouteNote.newBuilder().setMessage("Fifth message").setLocation(Point.newBuilder().setLongitude(1).setLatitude(1).build()).build(),};for (RouteNote request : requests) {System.out.println("========");System.out.printf("Got message \"{%s}\" at {%d}, {%d}\n", request.getMessage(), request.getLocation().getLatitude(), request.getLocation().getLongitude());//发送请求requestObserver.onNext(request);//线程休眠0.5。这样从结果中才能体现出双向流的调用Thread.sleep(500);}//发送完成requestObserver.onCompleted();//等待服务器完成finishFuture.get();System.out.println("Finished RouteChat");} catch (Exception t) {requestObserver.onError(t);System.out.println("RouteChat Failed");}return "";}
结果如下:确实体现出了双向流




![[论文阅读]BEVFusion](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/7da3ac93c5bc416f98f79c93e0158589.png)