哈夫曼树
完整可编译运行代码见:Github::Data-Structures-Algorithms-and-Applications/_29huffmanTree
定长编码与可变长编码
定长编码
每个字符都用固定长度的编码来表示。
例如假设一个文本是由字符 a、u、x 和 z 组成的字符串,每个字符用2位二进制来编码(00=a,01=x,10=u,11=z)。利用此编码方法,字符串aaxuaxz的编码为00000110000111。解码时,从左到右,每次从编码中提取2位数字通过编码表翻译,便可获得原字符串。
可变长编码
字符存在不同长度的编码。 哈夫曼编码是一种可变长编码。
在字符串 aaxuaxz 中,a 出现 3 次。一个符号出现的次数称为频率(frequency)。符号 a、x、u、z在这个字符串中出现的频率分别是3、2、1、1。当不同字符出现的频率有很大差别时,我们可以通过可变长编码来缩短编码串的长度。
例如,如果使用编码(0=a,10=x,110=u,111=z),则aaxuaxz的编码为0010110010111,编码串长度是13位,比原来的14位要稍短一些。当不同字符的出现频率相差更大时,编码串的长度差别就会更明显。如果4个字符的频率分别为(996,2,1,1),则每个字符用2位编码所得到编码串长度为2000位,而用可变长编码所得到编码串长度仅为1006位。
为了保证正确解码,要求编码时没有任何一个代码是另一个代码的前缀。
可以使用二叉树来实现可变长编码,从根到外部节点的路径可用来编码,用0表示向左子树移动一步,用1表示向右子树移动一步。由于路径是从根节点到叶子节点,因此没有一个路径编码是另一个路径编码的前缀。
编码位串长度
可以对字符a,b,…,f编码。令S是由这些字符组成的字符串,F(x)是字符 x 的出现频率,其中 x 属于集合{a,s,c,d,e,f}。若利用这些代码对 S 进行编码,则编码位串的长度:
2 ∗ F ( a ) + 3 ∗ F ( b ) + 3 ∗ F ( c ) + 3 ∗ F ( d ) + 3 ∗ F ( e ) + 2 ∗ F ( f ) 2*F(a)+3*F(b)+3*F(c)+3*F(d)+3*F(e)+2*F(f) 2∗F(a)+3∗F(b)+3∗F(c)+3∗F(d)+3∗F(e)+2∗F(f)
对于一颗有n个外部节点的二叉树,且外部节点标记为1,…, n,则对应的位串长度为:
W E P = ∑ i = 1 n L ( i ) ∗ F ( i ) WEP = \sum_{i=1}^nL(i) * F(i) WEP=i=1∑nL(i)∗F(i)
其中L(i)从根到外部节点i的路径长度(即路径的边数);WEP是二叉树的加权外部路径长度(weighted external path length)。为了缩短编码串的长度,必须使用二叉树代码,二叉树的外部节点与要编码的字符串的字符对应,且WEP最小。一棵二叉树,如果对一组给定的频率,其 WEP 最小,那么这棵二叉树称为霍夫曼树(Huffman tree)。
哈夫曼编码
哈夫曼编码的流程:
1)确定字符串的符号和它们出现的频率。
2)建立霍夫曼树,其中外部节点用字符串中的符号表示,外部节点的权用相应符号的频率表示。
3)沿着从根到外部节点的路径遍历,取得每个符号的代码。
4)用代码替代字符串中的符号。
为了便于解码,需要保存从符号到代码的映射表或每个符号的频率表。
构造霍夫曼树的过程是,首先建立一组二叉树集合,每棵二叉树仅含一个外部节点,每个外部节点代表字符串的一个符号,其权等于该符号的频率。然后,不断从集合中选择两棵权最小的二叉树,把它们合并成一棵新的二叉树,合并方法是增加一个根节点,把这两棵二叉树分别作为左右子树。新二叉树的权是两棵子树的权之和。这个过程一直持续到仅剩下一棵树为止。
举例如图所示:
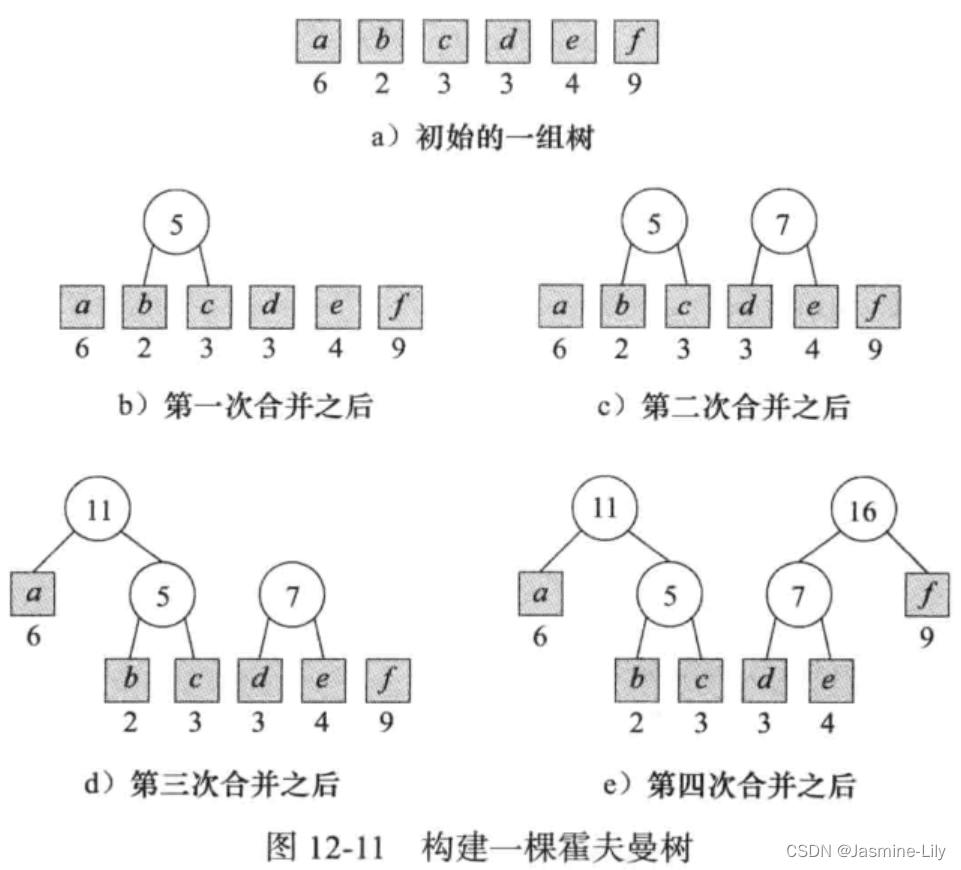
构建哈夫曼树
main.cpp
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2023年12月15日21点59分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 哈夫曼树的构建函数与main函数
*/
#include "_28binaryTreeChains.h"
#include "huffmanNode.h"template <class T>
binaryTreeChains<int>* huffmanTree(T weight[], int n)
{// 建立一个二叉树集合,每个节点的weight为weight[i],tree为element为i,左右子树为空的树vector<huffmanNode<T>> hNode(n);binaryTreeChains<int> emptyTree;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){hNode[i-1].weight = weight[i-1];hNode[i-1].tree = new binaryTreeChains<int>;hNode[i-1].tree->makeTree(i, emptyTree, emptyTree);}// 将节点存储为一个小根堆std::priority_queue<huffmanNode<T>, std::vector<huffmanNode<T>>, std::greater<>> heap(hNode.begin(),hNode.end());// 从小根堆里面不断合并树// 直到小根堆里只有一颗树huffmanNode<T> w, x, y;binaryTreeChains<int> *z;for (int i = 1; i < n; i++){// 从小根堆取出两个元素x = heap.top(); heap.pop();y = heap.top(); heap.pop();// 将两棵树合并为一颗树z = new binaryTreeChains<int>;z->makeTree(0, *x.tree, *y.tree);w.weight = x.weight + y.weight;w.tree = z;heap.push(w);delete x.tree;delete y.tree;}// 返回小根堆里的最后一颗树return heap.top().tree;
}int main()
{int a[5];int n = 5;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)a[i-1] = 2 * i;binaryTreeChains<int> *x = huffmanTree(a, n);x->postOrderOutput();x->preOrderOutput();x->inOrderOutput();return 0;
}
huffmanNode.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2023年12月15日21点59分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 哈夫曼树的结点结构体
*/
#ifndef _29HUFFMANTREE_HUFFMANNODE_H
#define _29HUFFMANTREE_HUFFMANNODE_H
#include "_28binaryTreeChains.h"
template<class T>
struct huffmanNode
{binaryTreeChains<int> *tree{};// 对于外部节点,element域的值是它所表示的符号,对于内部节点,element域的值是0。T weight;// 表示符号出现的频率huffmanNode(){weight = 0;}explicit huffmanNode(T pweight){weight = pweight;}operator T () const {return weight;}bool operator>(const huffmanNode &a) const { return weight > a.weight; }
};#endif //_29HUFFMANTREE_HUFFMANNODE_H
_28binaryTreeChains.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月27日09点44分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 用链表表示的二叉树.h
笔记:1.静态函数指针初始化格式:void (*binaryTreeChains<E>::visit)(binaryTreeNode<E>*) = 0;2.不能单独专门化成员模板函数,只能针对整个类专门化。3.在模板函数中可以使用typeid()区别对待特定数据类型。
本程序注意事项:1.所有关于前缀、后缀、中缀表达式的全部使用了char类型代表元素,char类型数组存储整个表达式
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _BINARYTREECHAINS_H_
#define _BINARYTREECHAINS_H_
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include "_1myExceptions.h"
#include "_28binaryTreeNode.h"
#include "_28binaryTree.h"
using namespace std;template<class E>
class binaryTreeChains : public binaryTree<binaryTreeNode<E>>
{
public:/*二叉树的基础成员函数*//*构造函数函数*/binaryTreeChains() {root = nullptr; treeSize = 0;}/*练习44:编写类linkedBinaryTree的一个复制构造函数。测试代码。*//* 计算时间复杂性。复制构造函数*/binaryTreeChains(binaryTreeChains<E>& m) {root = treeCreateTree(m.root);}/*练习题33和练习题35*//*构造函数---先序和中序遍历或后序和中序创建二叉树*//*flag == false时,是先序和中序遍历构建二叉树;flag == true时,是后序和中序构建二叉树*/binaryTreeChains(E preOrPostOrder[], E inOrder[],int length,bool flag){if(flag == false)root = preInCreateTree(preOrPostOrder, inOrder, length);elseroot = postInCreateTree(preOrPostOrder, inOrder, length);}/*构造函数---前缀或后缀或中缀表达式创建二叉树*//*练习37:当flag = 1时,前缀表达式创建二叉树当flag = 2时,中缀表达式创建二叉树练习36:当flag = 3时,后缀表达式创建二叉树*/binaryTreeChains(E expression[], int length,int flag){switch (flag){case 1:root = preExprCreateTree(expression, length);break;case 2:root = inExprCreateTree(expression, length);break;case 3:root = postExprCreateTree(expression, length);break;}}/*析构函数*/~binaryTreeChains() { erase(); }/*当树为空时,返回true;否则,返回false*/bool empty() const { return treeSize == 0; }/*返回元素个数*/int size() const { return treeSize; }/*前序遍历二叉树,使用函数指针的目的是是的本函数可以实现多种目的*/void preOrder(void(*theVisit)(binaryTreeNode<E>*)){visit = theVisit;/*是因为递归,所以才要这样的*/preOrder(root);/*这里调用的是成员函数,preOrder()*/}/*前序遍历---输出endl*/void preOrderOutput() { preOrder(output); cout << endl; }/*前序遍历---不使用递归而使用迭代函数*/vector<E> iterativePreOrder();/*中序遍历二叉树,使用函数指针的目的是是的本函数可以实现多种目的*/void inOrder(void(*theVisit)(binaryTreeNode<E>*)){visit = theVisit;/*是因为递归,所以才要这样的*/inOrder(root);/*这里调用的是静态成员函数inOrder()*/}/*中序遍历---输出endl*/void inOrderOutput() { inOrder(output); cout << endl; }/*中序遍历---不使用递归而使用迭代函数*/vector<E> iterativeInOrder();/*后续遍历二叉树,使用函数指针的目的是是的本函数可以实现多种目的*/void postOrder(void(*theVisit)(binaryTreeNode<E>*)){visit = theVisit;/*是因为递归,所以才要这样的*/postOrder(root);/*这里调用的是静态成员函数inOrder()*/}/*后序遍历---输出endl*/void postOrderOutput() { postOrder(output); cout << endl; }/*后序遍历---不使用递归而使用迭代函数*/vector<E> iterativePostOrder();/*层次遍历二叉树*/void levelOrder(void (*theVisit)(binaryTreeNode<E>*));/*层次遍历---输出endl*/void levelOrderOutput() { levelOrder(output); cout << endl; }/*清空二叉树 这里必须使用后序遍历 不然会出错*/void erase(){postOrder(dispose);root = nullptr;treeSize = 0;}/*输入时为了将root根节点传递给createBiTree()函数*/void input(void){createBiTree(root);}/*是一个手动创建二叉树的函数,使用本函数得手动设置各节点之间的关系,见信号放大器应用的使用*//*将左数和右数合并为一个树(也就是this树)*/void makeTree(const E& element, binaryTreeChains<E>&, binaryTreeChains<E>&);/*练习45:比较二叉树*this和二叉树m*/bool compare(binaryTreeChains<E>& m){return compareTree(root, m.root);}/*练习46:交换每一个结点的左右子树*/void swapTrees(){swapTrees(root);}/*练习27:计算二叉树高度*/int height() const { return height(root); }/*练习47:计算二叉树的最大高度差*/int maxHeightDifference(){return maxHeightDifference(root);}/*练习29:计算二叉树在那一层具有最多的结点---返回值为结点最多的层*/int layerMaxNumOfNode();/*计算二叉树在在哪一层具有最多的结点--返回值为结点最多的层的结点数量*/int maxNumOfNodeInLayer();/*二叉树表达式的成员函数*//*计算树的表达式的值*/int compulateTree(){return compulateTree(root);}
private:/*二叉树基础私有成员*/binaryTreeNode<E>* root;//指向根的指针int treeSize;//树的结点个数static void (*visit)(binaryTreeNode<E>*);//是一个函数指针,返回值为void 函数参数为binaryTreeNode<E>*static void preOrder(binaryTreeNode<E>* t);static void inOrder(binaryTreeNode<E>* t);static void postOrder(binaryTreeNode<E>* t);static void dispose(binaryTreeNode<E>* t) { delete t; }static void output(binaryTreeNode<E>* t) { cout << t->element << " "; }/*创建二叉树---递归---作为私有成员只能被成员函数调用*/void createBiTree(binaryTreeNode<E>*& tree);/*复制构造函数调用的函数*/binaryTreeNode<E>* treeCreateTree(binaryTreeNode<E>*& node);/*私有成员函数---用于比较二叉树compare()*/bool compareTree(binaryTreeNode<E>* thisNode, binaryTreeNode<E>* xNode);/*私有成员函数---交换树的每个结点的左右子树---递归*/void swapTrees(binaryTreeNode<E>*& node);/*私有成员函数---计算二叉树高度---返回根为node的树的高度*/int height(binaryTreeNode<E>* node) const;/*私有成员函数---计算结点node的左右子树高度的差值*/int heightDifference(binaryTreeNode<E>* node) const;/*私有成员函数---计算二叉树的最大高度差---返回值为二叉树的最大高度差*/int maxHeightDifference(binaryTreeNode<E>* node) const;binaryTreeNode<E>* preInCreateTree(E preOrder[], E inOrder[], int size);binaryTreeNode<E>* postInCreateTree(E postOrder[], E inOrder[], int size);/*二叉树表达式的私有成员*//*计算树的表达式的值*//*本程序所有关于前缀、中缀、后缀表达式的处理全部是char类型,并且只能进行个位数的计算*/int compulateTree(binaryTreeNode<E>* node) const;binaryTreeNode<E>* preExprCreateTree(E expression[], int length);binaryTreeNode<E>* inExprCreateTree(E expression[], int length);binaryTreeNode<E>* postExprCreateTree(E expression[], int length);
};/*私有静态成员初始化*/
/*这里是静态函数指针成员的初始化,不初始化会引发LINK错误*/
template<class E>
void (*binaryTreeChains<E>::visit)(binaryTreeNode<E>*) = 0; // visit function/*二叉树的普通成员函数*/
/*前序遍历 递归*/
template<class E>
void binaryTreeChains<E>::preOrder(binaryTreeNode<E>* t)
{if (t != nullptr){visit(t);/*访问树根*/preOrder(t->leftChild);/*前序遍历左子树*/preOrder(t->rightChild);/*前序遍历右子树*/}
}
/*前序遍历---不使用递归而使用迭代函数*/
template<class E>
vector<E> binaryTreeChains<E>::iterativePreOrder()
{binaryTreeNode<E>* currentNode = root;stack<binaryTreeNode<E>*> st;vector<E> result;/*写法1---前序中序后序遍历非递归统一版*//*首先将父节点入栈*/if (currentNode != nullptr)st.push(currentNode);while (!st.empty()){currentNode = st.top();st.pop();/*如果遇到nullptr,则输出当前栈顶元素*/if (currentNode == nullptr){result.push_back(st.top()->element);st.pop();}/*如果没有遇到nullptr,则按照右左中的顺序入栈结点,最后入栈nullptr*/else{if (currentNode->rightChild != nullptr)st.push(currentNode->rightChild);if (currentNode->leftChild != nullptr)st.push(currentNode->leftChild);st.push(currentNode);/*每次都在已遍历的根节点后入栈nullptr*/st.push(nullptr);}}///*写法2*////*当结点为nullptr并且栈为空时结束循环*///while (currentNode != nullptr || !st.empty())//{// /*先将左边的左边的元素入栈*/// while (currentNode != nullptr)// {// st.push(currentNode);// result.push_back(currentNode->element);// currentNode = currentNode->leftChild;// }// /*然后一个一个遍历左边的元素,并将该元素存储到vector中*/// currentNode = st.top();// st.pop();// currentNode = currentNode->rightChild;//}return result;
}/*中序遍历 递归*/
template<class E>
void binaryTreeChains<E>::inOrder(binaryTreeNode<E>* t)
{if (t != nullptr){inOrder(t->leftChild);/*中序遍历左子树*/visit(t);/*访问树根*/inOrder(t->rightChild);/*中序遍历右子树*/}
}
/*中序遍历---不使用递归而使用迭代函数*/
template<class E>
vector<E> binaryTreeChains<E>::iterativeInOrder()
{binaryTreeNode<E>* currentNode = root;stack<binaryTreeNode<E>*> st;vector<E> result;/*写法1---前序中序后序遍历非递归统一版*//*首先将父节点入栈*/if (currentNode != nullptr)st.push(currentNode);while (!st.empty()){currentNode = st.top();st.pop();/*如果遇到nullptr,则输出当前栈顶元素*/if (currentNode == nullptr){result.push_back(st.top()->element);st.pop();}/*如果没有遇到nullptr,则按照右左中的顺序入栈结点,最后入栈nullptr*/else{if (currentNode->rightChild != nullptr)st.push(currentNode->rightChild);st.push(currentNode);/*每次都在已遍历的根节点后入栈nullptr*/st.push(nullptr);if (currentNode->leftChild != nullptr)st.push(currentNode->leftChild);}}/*写法2*////*当结点为nullptr并且栈为空时结束循环*///while (currentNode != nullptr || !st.empty())//{// /*先将左边的左边的元素入栈*/// while (currentNode != nullptr)// {// st.push(currentNode);// currentNode = currentNode->leftChild;// }// /*然后一个一个遍历左边的元素,并将该元素存储到vector中*/// currentNode = st.top();// st.pop();// result.push_back(currentNode->element);// currentNode = currentNode->rightChild;//}return result;
}/*后序遍历 递归*/
template<class E>
void binaryTreeChains<E>::postOrder(binaryTreeNode<E>* t)
{if (t != nullptr){postOrder(t->leftChild);/*后序遍历左子树*/postOrder(t->rightChild);/*后序遍历右子树*/visit(t);/*访问树根*/}
}
/*后序遍历---不使用递归而使用迭代函数*/
template<class E>
vector<E> binaryTreeChains<E>::iterativePostOrder()
{binaryTreeNode<E>* currentNode = root;stack<binaryTreeNode<E>*> st;vector<E> result;/*前序中序后序遍历非递归统一版*//*首先将父节点入栈*/if (currentNode != nullptr)st.push(currentNode);while (!st.empty()){currentNode = st.top();st.pop();/*如果遇到nullptr,则输出当前栈顶元素*/if (currentNode == nullptr){result.push_back(st.top()->element);st.pop();}/*如果没有遇到nullptr,则按照右左中的顺序入栈结点,最后入栈nullptr*/else{st.push(currentNode);/*每次都在已遍历的根节点后入栈nullptr*/st.push(nullptr);if (currentNode->rightChild != nullptr)st.push(currentNode->rightChild);if (currentNode->leftChild != nullptr)st.push(currentNode->leftChild);}}return result;
}/*层次遍历二叉树 非递归*/
template<class E>
void binaryTreeChains<E>::levelOrder(void (*theVisit)(binaryTreeNode<E>*))
{visit = theVisit;binaryTreeNode<E>* temp;queue<binaryTreeNode<E>*> que;que.push(root);while (!que.empty()){temp = que.front();que.pop();visit(temp);if (temp->leftChild != nullptr)que.push(temp->leftChild);if (temp->rightChild != nullptr)que.push(temp->rightChild);}
}
/*创建二叉树---递归---模板的实现*/
template<class E>
void binaryTreeChains<E>::createBiTree(binaryTreeNode<E>*& tree)
{E data;cout << "Please enter the tree element:";while (!(cin >> data)){cin.clear();//清空标志位while (cin.get() != '\n')//删除无效的输入continue;cout << "Please enter the tree element:";}cin.get();/*针对char类型的特例*/if (typeid(data) == typeid(char)) {if (data == '#')tree = nullptr;else {treeSize++;tree = new binaryTreeNode<E>(data);createBiTree(tree->leftChild);createBiTree(tree->rightChild);}/*关于二叉树对于设置信号放大器的应用我新定义了成员函数maketree()生成二叉树这里会报错:C2228“.degradeFromParent”的左边必须有类/结构/联合我实在是不知道怎么改*///else if (typeid(data) == typeid(booster))// if (data.degradeFromParent == 999)// tree = nullptr;// else// {// treeSize++;// tree = new binaryTreeNode<E>(data);// createBiTree(tree->leftChild);// createBiTree(tree->rightChild);// }}else/*针对其他类型*/{if (data == 999)tree = nullptr;//当遇到999时,令树的根节点为nullptr,从而结束该分支的递归else{treeSize++;tree = new binaryTreeNode<E>(data);createBiTree(tree->leftChild);createBiTree(tree->rightChild);}}
}
/*是一个手动创建二叉树的函数,使用本函数得手动设置各节点之间的关系,见信号放大器应用的使用*/
/*将左树和右树合并为一个树*/
template<class E>
void binaryTreeChains<E>::makeTree(const E& element, binaryTreeChains<E>& left, binaryTreeChains<E>& right)
{// Combine left, right, and element to make new tree.// left, right, and this must be different trees.// create combined treeroot = new binaryTreeNode<E>(element, left.root, right.root);treeSize = left.treeSize + right.treeSize + 1;// deny access from trees left and rightleft.root = right.root = NULL;left.treeSize = right.treeSize = 0;
}/*练习24:根据二叉树创建二叉树---用于复制构造函数*/
template<class E>
binaryTreeNode<E>* binaryTreeChains<E>::treeCreateTree(binaryTreeNode<E>*& node)
{binaryTreeNode<E>* head = nullptr;if (node != nullptr){treeSize++;
// cout << "node->element = " << node->element << endl;head = new binaryTreeNode<E>(node->element);head->leftChild = treeCreateTree(node->leftChild);head->rightChild = treeCreateTree(node->rightChild);}return head;
}/*练习45:私有成员函数---用于比较二叉树compare()*/
template<class E>
bool binaryTreeChains<E>::compareTree(binaryTreeNode<E>* thisNode, binaryTreeNode<E>* xNode)
{/*两个结点都为空时,二叉树相等*/if (thisNode == nullptr && xNode == nullptr)return true;/*一个结点为空,一个结点非空,则二叉树不相等*/if ((thisNode == nullptr && xNode != nullptr) || (thisNode != nullptr && xNode == nullptr))return false;/*两个结点的元素不等,则二叉树不相等*/if (thisNode->element != xNode->element)return false;else/*两个结点相等,则比较彼此的左子树和右子树*/return compareTree(thisNode->leftChild, xNode->leftChild) && compareTree(thisNode->rightChild, xNode->rightChild);
}/*练习46:私有成员函数---交换树的每个结点的左右子树---递归*/
template<class E>
void binaryTreeChains<E>::swapTrees(binaryTreeNode<E>*& node)
{if (node != nullptr){swapTrees(node->leftChild);swapTrees(node->rightChild);binaryTreeNode<E>* temp = node->leftChild;node->leftChild = node->rightChild;node->rightChild = temp;}
}/*练习27:私有成员函数---计算二叉树高度---返回根为node的树的高度*/
template<class E>
int binaryTreeChains<E>::height(binaryTreeNode<E>* node) const
{if (node == nullptr)return 0;int hl = height(node->leftChild);int hr = height(node ->rightChild);if (hl > hr)return ++hl;elsereturn ++hr;
}/*私有成员函数---计算结点node的左右子树高度的差值*/
template<class E>
int binaryTreeChains<E>::heightDifference(binaryTreeNode<E>* node) const
{if (node == nullptr)return 0;int lh = height(node->leftChild);int rh = height(node->rightChild);
// cout << node->element << ":" << lh << endl;
// cout << node->element << ":" << rh << endl;if (lh > rh)return lh - rh;elsereturn rh - lh;
}/*练习47:私有成员函数---计算二叉树的最大高度差---返回值为二叉树的最大高度差*/
template<class E>
int binaryTreeChains<E>::maxHeightDifference(binaryTreeNode<E>* node) const
{if (node == nullptr)return 0;int height = heightDifference(node);//当前结点的左右子树的高度差int hl = maxHeightDifference(node->leftChild);//当前结点的左子树的左右子树的高度差int hr = maxHeightDifference(node->rightChild);//当前结点的右子树的左右子树的高度差if (height >= hl && height >= hr)return height;else if (hl >= height && hl >= hr)return hl;else if (hr >= height && hr >= hl)return hr;
}/*练习29:计算二叉树在那一层具有最多的结点---返回值为结点最多的层*/
/*当二叉树为空时,返回0*/
template<class E>
int binaryTreeChains<E>::layerMaxNumOfNode()
{if (root == nullptr)return 0;int num = 0;//累加每层的结点数int layer = 0;//记录当前的层数int maxNum = 0;//存储结点最多的层的结点个数int maxLayer = 0;//存储结点最多的层的层数binaryTreeNode<E>* lastNode = root;//存储上一层最后一个结点的元素位置binaryTreeNode<E>* nextNode = nullptr;//存储当前层最后一个结点的元素位置binaryTreeNode<E>* currentNode;queue<binaryTreeNode<E>*> que;que.push(root);while (!que.empty()){currentNode = que.front();que.pop();num++;if (currentNode->leftChild != nullptr){que.push(currentNode->leftChild);nextNode = currentNode->leftChild;}if (currentNode->rightChild != nullptr){que.push(currentNode->rightChild);nextNode = currentNode->rightChild;}if (currentNode == lastNode){layer++;//刚刚处理完第几层lastNode = nextNode;nextNode = nullptr;if (num > maxNum){maxNum = num;maxLayer = layer;}num = 0;}}return maxLayer;
}/*计算二叉树在在哪一层具有最多的结点--返回值为结点最多的层的结点数量*/
/*当二叉树为空时,返回0*/
template<class E>
int binaryTreeChains<E>::maxNumOfNodeInLayer()
{if (root == nullptr)return 0;int num = 0;//累加每层的结点数int layer = 0;//记录当前的层数int maxNum = 0;//存储结点最多的层的结点个数int maxLayer = 0;//存储结点最多的层的层数binaryTreeNode<E>* lastNode = root;//存储上一层最后一个结点的元素位置binaryTreeNode<E>* nextNode = nullptr;//存储当前层最后一个结点的元素位置binaryTreeNode<E>* currentNode = nullptr;queue<binaryTreeNode<E>*> que;que.push(root);while (!que.empty()){currentNode = que.front();que.pop();num++;if (currentNode->leftChild != nullptr){que.push(currentNode->leftChild);nextNode = currentNode->leftChild;}if (currentNode->rightChild != nullptr){que.push(currentNode->rightChild);nextNode = currentNode->rightChild;}if (currentNode == lastNode){layer++;//刚刚处理完第几层lastNode = nextNode;nextNode = nullptr;if (num > maxNum){maxNum = num;maxLayer = layer;}num = 0;}}return maxNum;
}/*使用前序和中序遍历构建二叉树*/
/*关键点在于找到根节点在中序中的位置,该位置之前为该根的左子树,该位置之后为该根的右子树*/
template<class E>
binaryTreeNode<E>* binaryTreeChains<E>::preInCreateTree(E preOrder[], E inOrder[], int size)
{/*如果没有左右子树,则返回nullptr*/if (size == 0)return nullptr;binaryTreeNode<E>* rootData = new binaryTreeNode<E>(preOrder[0]);/*找到根节点的位置,中序中该位置左侧就是该根节点的左子树,该位置右侧就是该根节点的右子树*/int rootLoc = findRootLoc<E>(inOrder, preOrder[0] ,size);/*创建左子树和右子树*/rootData->leftChild = preInCreateTree(preOrder + 1, inOrder, rootLoc);rootData->rightChild = preInCreateTree(preOrder + 1 + rootLoc, inOrder + rootLoc + 1, size - 1 - rootLoc);return rootData;
}
/*使用后序和中序遍历构建二叉树*/
/*关键点在于找到根节点在中序中的位置,该位置之前为该根的左子树,该位置之后为该根的右子树*/
template<class E>
binaryTreeNode<E>* binaryTreeChains<E>::postInCreateTree(E postOrder[], E inOrder[], int size)
{/*如果没有左右子树,则返回nullptr*/if (size == 0)return nullptr;binaryTreeNode<E>* rootData = new binaryTreeNode<E>(postOrder[size-1]);/*找到根节点的位置,中序中该位置左侧就是该根节点的左子树,该位置右侧就是该根节点的右子树*/int rootLoc = findRootLoc<E>(inOrder, postOrder[size-1], size);/*创建左子树和右子树*/rootData->leftChild = postInCreateTree(postOrder, inOrder, rootLoc);rootData->rightChild = postInCreateTree(postOrder + rootLoc, inOrder + rootLoc + 1, size - 1 - rootLoc);return rootData;
}/*二叉树表达式的成员函数*/
/*计算树的表达式的值*/
/*用字符串记录表达式*/
/*这个函数需要使用char类型的树,其他类型的二叉树不满足要求*/
template<class E>
int binaryTreeChains<E>::compulateTree(binaryTreeNode<E>* node) const
{if (node == nullptr)return 0;if (node->leftChild == nullptr && node->rightChild == nullptr) //左右子树都是nullptr时,说明它是叶子节点,而叶子结点就是数而非符号return node->element - '0';//就返回叶子结点int a = compulateTree(node->leftChild);//先计算左子树int b = compulateTree(node->rightChild);//再计算右子树switch (node->element)//当前结点不是叶子节点时,说明他是符号结点{case '+':return a + b;case '-':return a - b;case '*':return a * b;case '/':if (b != 0)return a / b;elsethrow illegalParameterValue("除数不能为0!");}
}/*使用全部是二元操作符的前缀表达式创建二叉树*/
/*从尾元素开始遍历表达式的元素*/
/*如果是数据,则生成binaryTreeNode并入栈*/
/*如果不是数据,则生成binaryTreeNode,从栈中弹出两个数据形成其子树,第一个弹出的是其左子树,第二个弹出的是其右子树;然后再将当前结点入栈*/
template<class E>
binaryTreeNode<E>* binaryTreeChains<E>::preExprCreateTree(E expression[],int length)
{stack<binaryTreeNode<E>*> st;//用于存储已经处理的数据生成的binaryTreeNodebinaryTreeNode<E>* temp = nullptr;for (int i = length-1; i >= 0; i--){/*如果是数据,则生成二叉树结点入栈*/if (expression[i] >= '0' && expression[i] <= '9'){temp = new binaryTreeNode<E>(expression[i]);st.push(temp);}else{temp = new binaryTreeNode<E>(expression[i]);temp->leftChild = st.top();st.pop();temp->rightChild = st.top();st.pop();st.push(temp);}}return temp;
}/*使用全部是二元操作符的中缀表达式(包含括号以表明优先级)创建二叉树*/
/*如果是数据,则生成binaryTreeNode并入数据栈*/
/*
操作符处理规则:如果当前操作符优先级大于操作符栈的顶部元素,直接入操作符栈如果当前操作符优先级小于或等于操作符栈的顶部元素,先将顶部元素出操作符栈再将当前操作符入操作符栈当前操作符为左括号时直接入栈当前操作符为右括号时,让栈顶到左括号为止的操作符出操作符栈,括号不出现在后缀表达式中
出操作符栈时:生成当前符号的binaryTreeNode,其右子树为数据栈的栈顶元素,数据栈顶元素出栈,其左子树为数据栈当前的栈顶元素,数据栈顶元素出栈;当前符号binaryTreeNode入数据栈。
*/
/*获取操作符优先级的getPriority()函数是一个非成员函数*/
template<class E>
binaryTreeNode<E>* binaryTreeChains<E>::inExprCreateTree(E expression[], int length)
{stack<binaryTreeNode<E>*> st;//用于存储已经处理的数据生成的binaryTreeNodestack<E> opStack;binaryTreeNode<E>* temp = nullptr;E data;for (int i = 0; i < length; i++){data = expression[i];/*如果是数据,则生成二叉树结点入栈*/if (data >= '0' && data <= '9'){temp = new binaryTreeNode<E>(data);st.push(temp);}else{if (opStack.empty())opStack.push(data);elseswitch (data){case '(':opStack.push(data); break;//当遇到左括号时,直接将其入栈case ')'://当遇到右括号时,让栈顶到左括号的操作符出栈while (opStack.top() != '('){temp = new binaryTreeNode<E>(opStack.top());opStack.pop();temp->rightChild = st.top();st.pop();temp->leftChild = st.top();st.pop();st.push(temp);}opStack.pop();//让(出栈break;/*当遇到+ - * /时,当其优先级大于栈顶元素时,入栈;否则,先将栈顶元素出栈,再将当前元素入栈*/case '+':case '-':case '*':case '/':if (getPriority(data) > getPriority(opStack.top()))opStack.push(data);else{temp = new binaryTreeNode<E>(opStack.top());opStack.pop();temp->rightChild = st.top();st.pop();temp->leftChild = st.top();st.pop();st.push(temp);}break;default:break;}/*当检查到中缀表达式的最后一个元素且栈非空时,将栈中的元素全部输出到后缀表达式*/if (!opStack.empty() && i == length - 1)while (!opStack.empty()){temp = new binaryTreeNode<E>(opStack.top());opStack.pop();temp->rightChild = st.top();st.pop();temp->leftChild = st.top();st.pop();st.push(temp);}}}return temp;
}/*使用全部是二元操作符的后缀表达式创建二叉树*/
/*从首元素开始遍历表达式的元素*/
/*如果是数据,则生成binaryTreeNode并入栈*/
/*如果不是数据,则生成binaryTreeNode,从栈中弹出两个数据形成其子树,第一个弹出的是其右子树,第二个弹出的是其左子树;然后再将当前结点入栈*/
template<class E>
binaryTreeNode<E>* binaryTreeChains<E>::postExprCreateTree(E expression[], int length)
{stack<binaryTreeNode<E>*> st;//用于存储已经处理的数据生成的binaryTreeNodebinaryTreeNode<E>* temp = nullptr;for (int i = 0; i < length; i++){/*如果是数据,则生成二叉树结点入栈*/if (expression[i] >= '0' && expression[i] <= '9'){temp = new binaryTreeNode<E>(expression[i]);st.push(temp);}else{temp = new binaryTreeNode<E>(expression[i]);temp->rightChild = st.top();st.pop();temp->leftChild = st.top();st.pop();st.push(temp);}}return temp;
}#endif
_28binaryTree.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月27日09点43分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 二叉树的抽象类
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _BINARYTREE_H_
#define _BINARYTREE_H_
template<class T>
class binaryTree
{
public:virtual ~binaryTree() {}virtual bool empty() const = 0;virtual int size() const = 0;virtual void preOrder(void (*)(T*)) = 0;virtual void inOrder(void (*)(T*)) = 0;virtual void postOrder(void (*)(T*)) = 0;virtual void levelOrder(void (*)(T*)) = 0;
};
#endif
_28binaryTreeNode.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月27日09点44分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 二叉树的结点结构体
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _BINARYTREENODE_H_
#define _BINARYTREENODE_H_
template<class T>
struct binaryTreeNode
{T element;binaryTreeNode<T>* leftChild,//左子树*rightChild;//右子树/*默认构造函数*/binaryTreeNode() { leftChild = rightChild = nullptr; }/*只初始化element*/binaryTreeNode(T melement){element = melement;leftChild = rightChild = nullptr;}/*三个元素都初始化*/binaryTreeNode(T melement, binaryTreeNode<T>* mleftChild, binaryTreeNode<T>* mrightChild){element = melement;leftChild = mleftChild;rightChild = mrightChild;}
};#endif
_1myExceptions.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月13日17点38分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 综合各种异常
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _MYEXCEPTIONS_H_
#define _MYEXCEPTIONS_H_
#include <string>
#include<iostream>using namespace std;// illegal parameter value
class illegalParameterValue
{
public:illegalParameterValue(string theMessage = "Illegal parameter value"){message = theMessage;}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:string message;
};// illegal input data
class illegalInputData
{
public:illegalInputData(string theMessage = "Illegal data input"){message = theMessage;}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:string message;
};// illegal index
class illegalIndex
{
public:illegalIndex(string theMessage = "Illegal index"){message = theMessage;}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:string message;
};// matrix index out of bounds
class matrixIndexOutOfBounds
{
public:matrixIndexOutOfBounds(string theMessage = "Matrix index out of bounds"){message = theMessage;}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:string message;
};// matrix size mismatch
class matrixSizeMismatch
{
public:matrixSizeMismatch(string theMessage ="The size of the two matrics doesn't match"){message = theMessage;}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:string message;
};// stack is empty
class stackEmpty
{
public:stackEmpty(string theMessage ="Invalid operation on empty stack"){message = theMessage;}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:string message;
};// queue is empty
class queueEmpty
{
public:queueEmpty(string theMessage ="Invalid operation on empty queue"){message = theMessage;}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:string message;
};// hash table is full
class hashTableFull
{
public:hashTableFull(string theMessage ="The hash table is full"){message = theMessage;}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:string message;
};// edge weight undefined
class undefinedEdgeWeight
{
public:undefinedEdgeWeight(string theMessage ="No edge weights defined"){message = theMessage;}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:string message;
};// method undefined
class undefinedMethod
{
public:undefinedMethod(string theMessage ="This method is undefined"){message = theMessage;}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:string message;
};
#endif
运行结果
"C:\Users\15495\Documents\Jasmine\prj\_Algorithm\Data Structures, Algorithms and Applications in C++\_29huffmanTree\cmake-build-debug\_29huffmanTree.exe"
3 1 2 0 0 4 5 0 0
0 0 3 0 1 2 0 4 5
3 0 1 0 2 0 4 0 5Process finished with exit code 0