《代码随想录》--二叉树 第一部分
- 1、二叉树的递归遍历
- 2、二叉树的迭代遍历
- 3、统一风格的迭代遍历代码
- 4、二叉树的层序遍历
- 226.翻转二叉树
1、二叉树的递归遍历
前序遍历
中序遍历
后序遍历
代码
- 前序遍历
class Solution {public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();preOrder(root,list);return list;}public void preOrder(TreeNode root,List<Integer> list){if(root == null) return;list.add(root.val);preOrder(root.left,list);preOrder(root.right,list);}
}
- 中序遍历
class Solution {public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();inOrder(root,list);return list;}public void inOrder(TreeNode root,List<Integer> list){if(root == null) return;inOrder(root.left,list);list.add(root.val);inOrder(root.right,list);}
}
- 后序遍历
class Solution {public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();postOrder(root,list);return list;}public void postOrder(TreeNode root,List<Integer> list){if(root == null) return;postOrder(root.left,list);postOrder(root.right,list);list.add(root.val);}
}
2、二叉树的迭代遍历
前序遍历
中序遍历
后序遍历
代码
- 前序遍历
class Solution {public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();if(root == null) return result;Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();stack.push(root);while(!stack.isEmpty()){TreeNode node = stack.pop();result.add(node.val);if(node.right != null) stack.push(node.right);if(node.left != null) stack.push(node.left);}return result;}
}
- 中序遍历
class Solution {public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();TreeNode cur = root;while(cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()){if(cur != null){stack.push(cur);cur = cur.left;}else{TreeNode node = stack.pop();list.add(node.val);cur = node.right;}}return list;}
}
- 后序遍历
class Solution {public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();if(root == null) return list;Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();stack.push(root);while(!stack.isEmpty()){TreeNode node = stack.pop();list.add(node.val);if(node.left != null) stack.push(node.left);if(node.right != null) stack.push(node.right);}Collections.reverse(list);return list;}
}
分析
- 非递归的遍历都需要借助栈来编写代码
- 前序遍历:
- 前序遍历是中左右的顺序
- 先把中间节点放入栈中
- 再放入右孩子(为什么?因为栈先入后出)
- 再放入左孩子
- 中序遍历:
- 中序遍历的顺序是左中右,但是我们的处理顺序和访问顺序不一致,所以借助指针
- 定义一个
cur指针帮助我们遍历,栈用来处理节点上的元素
- 后序遍历:
- 后序遍历的顺序是左右中,可以根据前序遍历改变得到
- 将遍历顺序改为中左右,最后得到的结果是中右左
- 反转数组得到正确结果
3、统一风格的迭代遍历代码
- 前面的迭代遍历代码风格不统一,不像递归代码一样修改代码的位置就能写出三种遍历方式
- 这里借助空节点标记法
代码
- 前序
class Solution {public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();if(root != null) stack.push(root);while(!stack.isEmpty()){TreeNode node = stack.peek();if(node != null){node = stack.pop();if(node.right != null) stack.push(node.right);if(node.left != null) stack.push(node.left);stack.push(node);stack.push(null);}else{stack.pop();node = stack.pop();list.add(node.val);}}return list;}
}
- 中序
class Solution {public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();if(root != null) stack.push(root);while(!stack.isEmpty()){TreeNode node = stack.peek();if(node != null){node = stack.pop(); //将该节点弹出if(node.right != null) stack.push(node.right); //添加左节点stack.push(node); //添加中节点stack.push(null); //中间节点访问过,但是还没有处理,加入空节点标记if(node.left != null) stack.push(node.left); //添加右节点}else{stack.pop(); //弹出空节点node = stack.pop(); //取出栈中元素list.add(node.val);}}return list;}
}
- 后序
class Solution {public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();if(root != null) stack.push(root);while(!stack.isEmpty()){TreeNode node = stack.peek();if(node != null){node = stack.pop();stack.push(node);stack.push(null);if(node.right != null) stack.push(node.right);if(node.left != null) stack.push(node.left);}else{stack.pop();node = stack.pop();list.add(node.val);}}return list;}
}
分析
- 可以看到使用空节点标记法,只需要修改两行代码就能写出不同的遍历代码
4、二叉树的层序遍历
学会二叉树的层序遍历,可以一口气打完以下十题:
- 102.二叉树的层序遍历
- 107.二叉树的层次遍历II
- 199.二叉树的右视图
- 637.二叉树的层平均值
- 429.N叉树的层序遍历
- 515.在每个树行中找最大值
- 116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
- 117.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II
- 104.二叉树的最大深度
- 111.二叉树的最小深度
代码 102题
- 迭代
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();if(root == null) return list;Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);while(!queue.isEmpty()){List<Integer> tempList = new ArrayList<>();int len = queue.size();while(len > 0){TreeNode node = queue.poll();tempList.add(node.val);if(node.left != null) queue.offer(node.left);if(node.right != null) queue.offer(node.right);len--;}list.add(tempList);}return list;}
}
- 递归
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();level(root,list,0);return list;}public void level(TreeNode node,List<List<Integer>> list,int depth){if(node == null) return;depth++;if(list.size() < depth){List<Integer> tempList = new ArrayList<>();list.add(tempList);}list.get(depth-1).add(node.val);level(node.left,list,depth);level(node.right,list,depth);}
}
分析
- 迭代法借助了数据结构队列,先入先出。
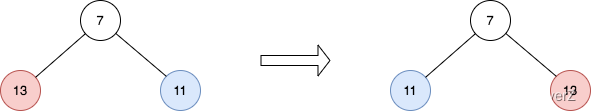
226.翻转二叉树
leetcode链接

代码
- 前序遍历
class Solution {public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {preOrderReverse(root);return root;}public void preOrderReverse(TreeNode node){if(node == null) return;TreeNode temp = node.left;node.left = node.right;node.right = temp;preOrderReverse(node.left);preOrderReverse(node.right);}
}
- 后序遍历
class Solution {public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {preOrderReverse(root);return root;}public void preOrderReverse(TreeNode node){if(node == null) return;preOrderReverse(node.left);preOrderReverse(node.right);TreeNode temp = node.left;node.left = node.right;node.right = temp;}
}
- BFS
class Solution {public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {if(root == null) return root;Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);while(queue.size()>0){int size = queue.size();for(int i = 0;i < size;i++){TreeNode node = queue.poll();TreeNode temp = node.left;node.left = node.right;node.right = temp;if(node.left != null) queue.offer(node.left);if(node.right != null) queue.offer(node.right);}}return root;}
}
- 统一法
class Solution {public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {if(root == null) return root;Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();stack.push(root);while(!stack.isEmpty()){TreeNode node = stack.peek();if(node != null){stack.pop();if(node.right != null) stack.push(node.right);if(node.left != null) stack.push(node.left);stack.push(node);stack.push(null);}else{stack.pop();node = stack.pop();TreeNode temp = node.left;node.left = node.right;node.right = temp;}}return root;}
}
分析
- 第一种递归的方式,只能写前序和后序,中序代码会导致有些节点反转了两次
- 第二种BFS,也就是层序遍历
- 第三种,统一的写法满足前中后序三种遍历方式