查询重写
- 查询重写
- 系统规则
- 视图和规则系统
- ASLO型规则的查询重写
- 规则系统与触发器的区别
- 查询重写的处理操作
- 定义重写规则
- 删除重写规则
- 对查询树进行重写
声明:本文的部分内容参考了他人的文章。在编写过程中,我们尊重他人的知识产权和学术成果,力求遵循合理使用原则,并在适用的情况下注明引用来源。
本文主要参考了《PostgresSQL数据库内核分析》一书
查询重写
在前一章中,我们重点介绍了查询分析的过程,再来回顾一下函数的调用关系。
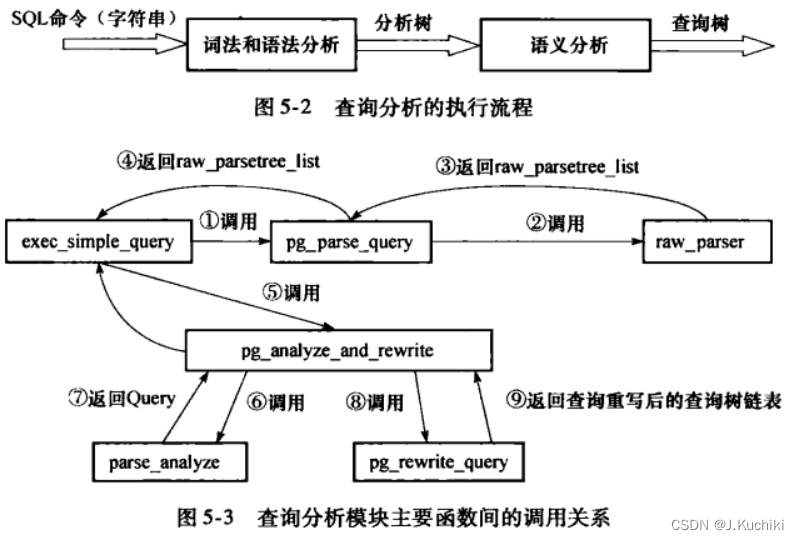
查询分析从exec_simple_query函数开始到调用parse_analyze函数返回Query结构体结束,而pg_rewrite_query则是执行查询重写的入口函数,函数路径为:src/backend/tcop/postgres.c。查询重写模块使用规则系统判断来进行查询树的重写,如果查询树中某个目标被定义了转换规则,则该转换规则会被用来重写查询树。
系统规则
查询重写的核心就是规则系统,而规则系统则由一系列的规则组成。系统表pg_rewrite存储重写规则,具体内容如表5-10所示。pg_rewrite中的每一个元组代表一条规则。
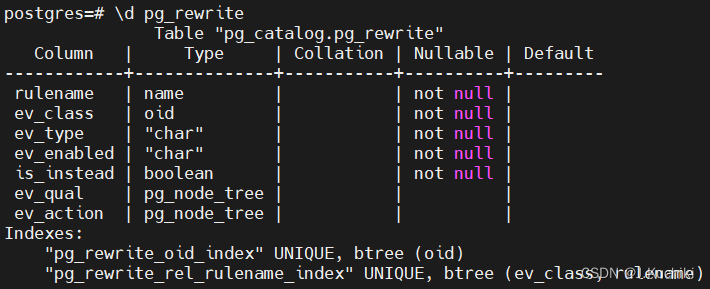
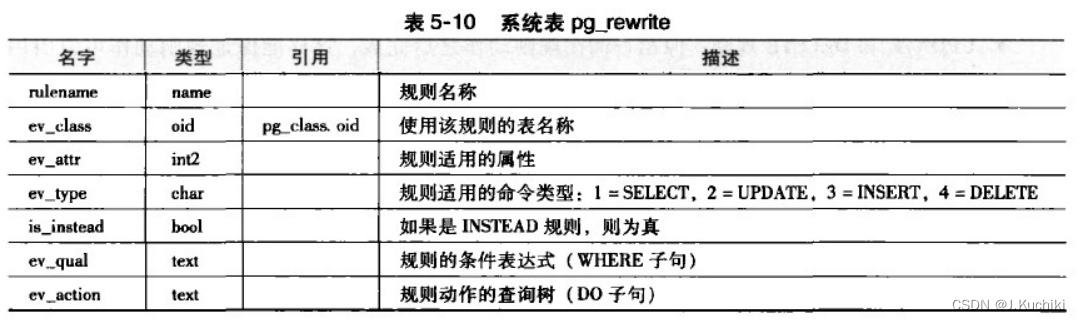
在 PostgreSQL 中,表 pg_rewrite 是系统目录表之一,用于存储查询重写规则(Query Rewrite Rule)。查询重写规则是一种机制,允许用户定义在查询执行前自动将查询转换成其他形式的规则。这个机制可以帮助用户实现查询优化、视图扁平化、安全性控制等功能。
pg_rewrite 表存储了数据库中所有的查询重写规则,它的结构如下:
CREATE TABLE pg_rewrite (rulename name, -- 规则名称ev_class oid, -- 规则所属的表的 OIDev_type "char", -- 规则类型(INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE/SELECT)ev_enabled "char", -- 规则是否启用(A表示启用,D表示禁用)is_instead boolean, -- 是否是 INSTEAD 规则ev_qual pg_node_tree, -- 规则的 WHERE 条件ev_action pg_node_tree, -- 规则的替代动作ev_actiontype "char" -- 替代动作的类型(S表示SQL语句,r表示规则)
);
查询重写规则的添加、修改和删除都可以通过 pg_rewrite 表来实现。通常,规则是由数据库管理员或开发人员根据应用程序的需求来定义和维护的。通过使用查询重写规则,可以实现许多复杂的查询优化和数据访问控制策略,从而更好地满足数据库应用的需求。
是不是只看文字描述很抽象?没关系,我们以一个案例进行说明:
假设我们有一个简单的学生信息管理系统,其中包含两个表:students(学生信息表)和scores(学生成绩表)。管理员希望在查询学生信息时,只显示当前登录用户所管理的学生信息,而不是所有学生的信息。
- 首先,我们创建两个表并插入一些示例数据:
CREATE TABLE students (id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,name TEXT,age INTEGER
);CREATE TABLE scores (id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,student_id INTEGER,subject TEXT,score INTEGER
);INSERT INTO students (name, age) VALUES('Alice', 20),('Bob', 22),('Charlie', 21);INSERT INTO scores (student_id, subject, score) VALUES(1, 'Math', 90),(1, 'Science', 85),(2, 'Math', 95),(2, 'Science', 88),(3, 'Math', 87),(3, 'Science', 92);
- 现在,我们创建一个查询重写规则,以限制用户只能访问他们所管理的学生信息。我们假设用户信息存储在一个名为 users 的表中,包含字段 id(用户ID)和 managed_students(他们所管理的学生ID列表)。
CREATE TABLE users (id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,name TEXT,managed_students INTEGER[]
);INSERT INTO users (name, managed_students) VALUES('Admin', '{1, 2}'),('Manager', '{2, 3}');
- 接下来,我们使用查询重写规则来实现限制访问策略:
-- 创建查询重写规则
CREATE RULE restrict_students ASON SELECT TO studentsWHERE EXISTS (SELECT 1 FROM usersWHERE id = current_userAND student_id = students.id);-- 将查询重写规则标记为启用
UPDATE pg_rewrite
SET ev_enabled = 'A'
WHERE rulename = 'restrict_students';
- 现在,当管理员或经理查询学生信息时,只会返回他们所管理的学生信息,而不会返回其他学生的信息。例如,当管理员(id=1)查询学生信息时:
SET ROLE admin;SELECT * FROM students;-- 输出:
-- id | name | age
-- ----+---------+-----
-- 1 | Alice | 20
-- 2 | Bob | 22
- 同样,当经理(id=2)查询学生信息时:
SET ROLE manager;SELECT * FROM students;-- 输出:
-- id | name | age
-- ----+---------+-----
-- 2 | Bob | 22
-- 3 | Charlie | 21
怎么样?是不是通过一个案例就能更加直观的理解了。
视图和规则系统
视图和规则系统是 PostgreSQL 数据库中的两个重要特性,用于提供数据查询和重写查询的功能。我们来回顾一些视图的基本概念吧。
视图(Views):
视图是一种虚拟表,它是基于一个或多个基本表的查询结果的命名查询。通过创建视图,你可以将复杂的查询封装成一个简单的名称,并像操作表一样使用它。视图不存储数据,它只是一个查询的定义。每当你查询视图时,实际上是执行视图定义中的查询。视图使得查询更加灵活和方便,同时还可以隐藏底层数据结构的细节。
创建视图的语法为:
CREATE VIEW view_name AS
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table_name
WHERE condition;
例如,假设我们有一个名为 “students” 的表,其中包含学生的信息,我们可以创建一个视图来显示只包含特定学院的学生信息:
CREATE VIEW computer_science_students AS
SELECT id, name, age
FROM students
WHERE department = 'Computer Science';
然后我们可以查询这个视图:
SELECT * FROM computer_science_students;
了解了视图,我们再来看看什么是“规则”?
规则系统(Rules):
规则系统允许你在查询执行过程中自动重写查询。它允许你定义一组规则,当一个特定的查询被执行时,这些规则会被应用于查询,然后将查询重写为其他形式。规则通常用于实现数据安全性、限制用户访问和实现数据转换等需求。
规则是由两部分组成:一个触发器函数和一个规则本身。触发器函数是一个函数,它在特定事件发生时被调用,并根据规则的定义执行重写操作。规则则定义了要匹配的查询条件和要应用的重写操作。
创建规则的语法为:
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION trigger_function()
RETURNS TRIGGER AS $$
BEGIN-- 触发器函数的逻辑-- 可以根据需要返回 NEW、OLD 或 NULL
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;CREATE RULE rule_name AS ON event TO table_name
DO INSTEAD (-- 重写查询的逻辑-- 可以调用触发器函数来执行重写操作
);
例如,我们可以创建一个规则来限制用户只能查询与其关联的学生信息:
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION restrict_students_trigger()
RETURNS TRIGGER AS $$
BEGINIF EXISTS (SELECT 1 FROM users WHERE id = current_user AND student_id = NEW.id) THENRETURN NEW;ELSERETURN NULL;END IF;
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;CREATE RULE restrict_students AS ON INSERT OR UPDATE OR DELETE TO students
DO INSTEAD (-- 在这里调用触发器函数来限制用户访问RETURN restrict_students_trigger();
);
以上便是视图和规则系统在 PostgreSQL 中的基本概念和用法。视图用于简化查询,而规则系统用于在查询执行过程中实现查询的自动重写。
ASLO型规则的查询重写
"ALSO"型规则是 PostgreSQL 中一种特殊类型的规则,用于在查询重写时添加额外的查询操作。ALSO型规则可以在原始查询执行之前或之后执行其他查询,并将它们的结果合并到最终查询结果中。这可以在不修改原始查询的情况下,对查询结果进行进一步的处理或增加附加的查询操作。
ALSO型规则的语法如下:
CREATE RULE rule_name ASON event_name TO table_nameDO ALSO (-- 添加额外的查询操作);
其中,rule_name 是规则的名称,event_name 是触发规则的事件类型,可以是 SELECT、INSERT、UPDATE 或 DELETE。table_name 是规则所应用的表名。DO ALSO 后跟着要执行的额外查询操作。
只看定义可能还是不好理解,那我们依旧以一个案例来更加详细的说一说。下面是一个示例,演示如何使用ALSO型规则实现在查询结果中同时返回学生的成绩信息。
- 假设有两个表:students 存储学生信息,scores 存储学生的成绩信息。students 表的主键是 id,scores 表有一个外键 student_id 关联到 students 表的 id。
首先,我们创建这两个表并插入一些示例数据:
-- 创建 students 表
CREATE TABLE students (id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,name VARCHAR(50),age INTEGER,department VARCHAR(50)
);-- 创建 scores 表
CREATE TABLE scores (id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,student_id INTEGER REFERENCES students(id),subject TEXT,score INTEGER
);-- 插入示例数据
INSERT INTO students (name, age, department) VALUES('Alice', 20, 'Computer Science'),('Bob', 22, 'Mathematics');INSERT INTO scores (student_id, subject, score) VALUES(1, 'Math', 90),(1, 'Science', 85),(2, 'Math', 88),(2, 'Science', 92);
- 接下来,我们创建一个ALSO型规则 add_scores,当用户查询学生信息时,同时返回学生的成绩信息。
CREATE RULE add_scores ASON SELECT TO studentsDO ALSO (SELECT scores.student_id, scores.subject, scores.scoreFROM scoresWHERE scores.student_id = students.id);
- 现在,让我们来测试这个规则。查询学生信息时,将同时返回学生的成绩信息:
SELECT * FROM students;-- 查询结果:
-- id | name | age | department | student_id | subject | score
-- ----+-------+-----+--------------------+------------+----------+-------
-- 1 | Alice | 20 | Computer Science | 1 | Math | 90
-- 1 | Alice | 20 | Computer Science | 1 | Science | 85
-- 2 | Bob | 22 | Mathematics | 2 | Math | 88
-- 2 | Bob | 22 | Mathematics | 2 | Science | 92
可以看到,使用ALSO型规则,我们成功地在查询结果中同时返回了学生的成绩信息,而不需要修改原始查询语句。这样可以方便地将多个查询操作合并到一起,增强数据库的查询灵活性。
规则系统与触发器的区别
规则系统(Rule System)和触发器(Trigger)是 PostgreSQL 中两种不同的机制,用于在数据库操作时实现额外的逻辑处理。虽然它们都可以用于在数据库中定义和执行额外的操作,但它们之间有一些重要的区别。
触发器(Trigger):
- 触发器是与表相关联的数据库对象,它在特定的数据库操作(如INSERT、UPDATE、DELETE)发生时触发执行。
- 触发器的执行是自动的,无需手动调用,它们与特定的数据库操作紧密绑定。
- 触发器可以在操作执行之前(BEFORE)或之后(AFTER)触发,也可以定义为每个行(FOR EACH ROW)或每个语句(FOR EACH STATEMENT)触发。
- 触发器的执行可以修改正在进行的操作,也可以对其他表执行额外的操作,但触发器不能返回结果集。
- 触发器通常用于实现数据完整性约束、日志记录、审计跟踪等业务逻辑。
规则系统(Rule System):
- 规则系统是一个高级查询重写机制,它可以在查询解析之后,在查询执行之前对查询进行修改和扩展。
- 规则系统通过使用 CREATE RULE 命令创建规则,允许在指定的事件上应用规则,并对查询进行重写。规则可以在 SELECT、INSERT、UPDATE 和 DELETE 等操作上应用。
- 规则的执行是在查询执行之前,对查询进行预处理,根据规则定义的规则条件进行查询重写。
- 规则系统允许在原始查询的基础上添加附加的查询操作,这些操作可以是 SELECT、INSERT、UPDATE 和 DELETE 等。可以使用 DO ALSO 子句在规则中执行其他查询,并将其结果合并到最终查询结果中。
- 规则系统的主要用途是实现查询优化、添加额外的查询操作、隐藏敏感数据等。
触发器和规则系统都提供了在数据库操作时执行额外逻辑的机制,但它们的应用场景和实现方式不同。触发器用于特定的数据库操作,在操作前或操作后触发执行,而规则系统是对查询进行重写的高级机制,允许在查询执行之前对查询进行修改和扩展。触发器通常用于数据完整性约束和日志记录等场景,而规则系统主要用于查询优化和添加额外的查询操作。
查询重写的处理操作
查询重写部分的处理操作主要包括定义规则、删除规则以及利用规则进行查询重写。下面分别对这些操作进行介绍。
定义重写规则
在 PostgreSQL 中,定义重写规则是指创建规则以指定在查询重写过程中应用的转换规则。这些规则可以根据需要对查询进行修改、优化或添加额外的逻辑。
以下是定义重写规则的一般步骤:
- 创建规则:
使用 CREATE RULE 语句创建新的重写规则。语法如下:
CREATE RULE rule_name AS ON event [ WHERE condition ]DO [ INSTEAD ] { query | command }
- rule_name 是规则的名称,可以根据需要命名。
- event 指定了触发规则的事件类型,如 SELECT、UPDATE、INSERT、DELETE 等。
- condition 是一个可选的条件,用于指定规则应用的条件。
- query 或 command 是规则应用的替换部分,可以是查询语句或其他命令。
- 定义规则的替换部分:
在 DO 关键字后,指定规则应用时的替换部分。替换部分可以是查询语句、修改语句或其他合法的 SQL 命令。 - 添加规则的条件:
可以使用 WHERE 子句来定义规则应用的条件。条件可以是一个布尔表达式,当条件满足时才会应用规则。 - 选择合适的事件类型:
根据需求选择合适的事件类型来触发规则。例如,对于查询重写,可以选择 SELECT 事件类型来匹配查询语句。 - 理解规则的匹配顺序:
PostgreSQL 中的规则系统会按照特定的顺序匹配规则并应用它们。规则的匹配顺序是按照规则创建的顺序进行的。因此,在定义多个规则时,确保规则的顺序正确,以便按照预期应用规则。
由上述可知,在使用规则系统之前首先需要定义规则,规则的定义通过CREATE RULE命令来完成。而定义重写规则的操作主要由函数DefineRule实现,“CREATE RUILE”命令被词法和语法分析模块处理之后,相关信息被存储在一个RuleStmt 结构中,最后查询执行模块会把该结构交给DefineRule来完成规则的创建。
DefineRule的源码如下:(路径:src/backend/rewrite/rewriteDefine.c)
/** DefineRule* Execute a CREATE RULE command.*/
ObjectAddress
DefineRule(RuleStmt *stmt, const char *queryString)
{List *actions;Node *whereClause;Oid relId;/* Parse analysis. *//* 首先调用transformRuleStmt对RuleStmt结构体进行处理 */transformRuleStmt(stmt, queryString, &actions, &whereClause);/** Find and lock the relation. Lock level should match* DefineQueryRewrite.* RangeVarGetRelid函数通过调用RangeVarGetRelidExtended函数选择正确的命名空间并找到表的OID*/relId = RangeVarGetRelid(stmt->relation, AccessExclusiveLock, false);/* ... and execute * 调用DefineQueryRewrite函数,* 将已经处理好的规则,作为一个元组,插入到系统表pg_rewrite中,* DefineQueryRewrite会把处理好的where子句的表达式树以及规则的动作作为其参数之一*/return DefineQueryRewrite(stmt->rulename,relId,whereClause,stmt->event,stmt->instead,stmt->replace,actions);
}
RuleStmt结构如下:(路径:src/include/nodes/parsenodes.h)
/* ----------------------* Create Rule Statement* ----------------------*/
typedef struct RuleStmt
{NodeTag type;RangeVar *relation; /* relation the rule is for */char *rulename; /* name of the rule */Node *whereClause; /* qualifications */CmdType event; /* SELECT, INSERT, etc */bool instead; /* is a 'do instead'? */List *actions; /* the action statements */bool replace; /* OR REPLACE */
} RuleStmt;

DefineRule的流程如下:
- 首先调用transformRuleStmt对RuleStmt进行处理:
在 PostgreSQL 中,transformRuleStmt 函数是用于将 RuleStmt 结构转换为 RuleData 结构的主要函数。它的作用是将用户定义的规则语句进行语义分析和转换,生成相应的规则对象,用于后续的查询重写和触发器处理。
以下是 transformRuleStmt 函数的主要处理步骤:
- 语义分析:首先,transformRuleStmt 函数会对 RuleStmt 结构进行语义分析,检查规则的合法性和正确性。它会验证规则名是否已经存在、表是否存在、规则的定义语句是否有效等。
- 解析规则定义:接着,函数会解析 RuleStmt 结构,提取其中的信息,例如规则名、表名、触发事件类型、规则的定义语句等。
- 获取触发函数信息:对于 RuleStmt 中的 actions,即规则的定义语句,函数会解析其中的触发函数信息,并进行一系列验证,例如函数是否存在、函数的参数是否匹配等。
- 创建规则对象:经过语义分析和解析后,transformRuleStmt 函数会创建一个新的 RuleData 结构,用于表示要添加的规则。这个结构中包含了规则的详细信息,如规则名、表名、触发事件类型、触发函数等。
- 完成处理:最后,transformRuleStmt 函数会返回创建的 RuleData 结构,将它作为规则定义的结果。这个 RuleData 结构可以用于后续的处理,例如添加到全局规则列表 RuleRelation 中,或写入系统表 pg_rewrite,从而将规则持久化到数据库中。
DefineRule调用的transformRuleStmt函数的源码如下:
/** transformRuleStmt -* transform a CREATE RULE Statement. The action is a list of parse* trees which is transformed into a list of query trees, and we also* transform the WHERE clause if any.** actions and whereClause are output parameters that receive the* transformed results.** Note that we must not scribble on the passed-in RuleStmt, so we do* copyObject() on the actions and WHERE clause.*/
void
transformRuleStmt(RuleStmt *stmt, const char *queryString,List **actions, Node **whereClause)
{Relation rel;ParseState *pstate;RangeTblEntry *oldrte;RangeTblEntry *newrte;/** To avoid deadlock, make sure the first thing we do is grab* AccessExclusiveLock on the target relation. This will be needed by* DefineQueryRewrite(), and we don't want to grab a lesser lock* beforehand.*/rel = heap_openrv(stmt->relation, AccessExclusiveLock);if (rel->rd_rel->relkind == RELKIND_MATVIEW)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_FEATURE_NOT_SUPPORTED),errmsg("rules on materialized views are not supported")));/* Set up pstate */pstate = make_parsestate(NULL);pstate->p_sourcetext = queryString;/** NOTE: 'OLD' must always have a varno equal to 1 and 'NEW' equal to 2.* Set up their RTEs in the main pstate for use in parsing the rule* qualification.*/oldrte = addRangeTableEntryForRelation(pstate, rel,makeAlias("old", NIL),false, false);newrte = addRangeTableEntryForRelation(pstate, rel,makeAlias("new", NIL),false, false);/* Must override addRangeTableEntry's default access-check flags */oldrte->requiredPerms = 0;newrte->requiredPerms = 0;/** They must be in the namespace too for lookup purposes, but only add the* one(s) that are relevant for the current kind of rule. In an UPDATE* rule, quals must refer to OLD.field or NEW.field to be unambiguous, but* there's no need to be so picky for INSERT & DELETE. We do not add them* to the joinlist.*/switch (stmt->event){case CMD_SELECT:addRTEtoQuery(pstate, oldrte, false, true, true);break;case CMD_UPDATE:addRTEtoQuery(pstate, oldrte, false, true, true);addRTEtoQuery(pstate, newrte, false, true, true);break;case CMD_INSERT:addRTEtoQuery(pstate, newrte, false, true, true);break;case CMD_DELETE:addRTEtoQuery(pstate, oldrte, false, true, true);break;default:elog(ERROR, "unrecognized event type: %d",(int) stmt->event);break;}/* take care of the where clause */*whereClause = transformWhereClause(pstate,(Node *) copyObject(stmt->whereClause),EXPR_KIND_WHERE,"WHERE");/* we have to fix its collations too */assign_expr_collations(pstate, *whereClause);/* this is probably dead code without add_missing_from: */if (list_length(pstate->p_rtable) != 2) /* naughty, naughty... */ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_INVALID_OBJECT_DEFINITION),errmsg("rule WHERE condition cannot contain references to other relations")));/** 'instead nothing' rules with a qualification need a query rangetable so* the rewrite handler can add the negated rule qualification to the* original query. We create a query with the new command type CMD_NOTHING* here that is treated specially by the rewrite system.*/if (stmt->actions == NIL){Query *nothing_qry = makeNode(Query);nothing_qry->commandType = CMD_NOTHING;nothing_qry->rtable = pstate->p_rtable;nothing_qry->jointree = makeFromExpr(NIL, NULL); /* no join wanted */*actions = list_make1(nothing_qry);}else{ListCell *l;List *newactions = NIL;/** transform each statement, like parse_sub_analyze()*/foreach(l, stmt->actions){Node *action = (Node *) lfirst(l);ParseState *sub_pstate = make_parsestate(NULL);Query *sub_qry,*top_subqry;bool has_old,has_new;/** Since outer ParseState isn't parent of inner, have to pass down* the query text by hand.*/sub_pstate->p_sourcetext = queryString;/** Set up OLD/NEW in the rtable for this statement. The entries* are added only to relnamespace, not varnamespace, because we* don't want them to be referred to by unqualified field names* nor "*" in the rule actions. We decide later whether to put* them in the joinlist.*/oldrte = addRangeTableEntryForRelation(sub_pstate, rel,makeAlias("old", NIL),false, false);newrte = addRangeTableEntryForRelation(sub_pstate, rel,makeAlias("new", NIL),false, false);oldrte->requiredPerms = 0;newrte->requiredPerms = 0;addRTEtoQuery(sub_pstate, oldrte, false, true, false);addRTEtoQuery(sub_pstate, newrte, false, true, false);/* Transform the rule action statement */top_subqry = transformStmt(sub_pstate,(Node *) copyObject(action));/** We cannot support utility-statement actions (eg NOTIFY) with* nonempty rule WHERE conditions, because there's no way to make* the utility action execute conditionally.*/if (top_subqry->commandType == CMD_UTILITY &&*whereClause != NULL)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_INVALID_OBJECT_DEFINITION),errmsg("rules with WHERE conditions can only have SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE actions")));/** If the action is INSERT...SELECT, OLD/NEW have been pushed down* into the SELECT, and that's what we need to look at. (Ugly* kluge ... try to fix this when we redesign querytrees.)*/sub_qry = getInsertSelectQuery(top_subqry, NULL);/** If the sub_qry is a setop, we cannot attach any qualifications* to it, because the planner won't notice them. This could* perhaps be relaxed someday, but for now, we may as well reject* such a rule immediately.*/if (sub_qry->setOperations != NULL && *whereClause != NULL)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_FEATURE_NOT_SUPPORTED),errmsg("conditional UNION/INTERSECT/EXCEPT statements are not implemented")));/** Validate action's use of OLD/NEW, qual too*/has_old =rangeTableEntry_used((Node *) sub_qry, PRS2_OLD_VARNO, 0) ||rangeTableEntry_used(*whereClause, PRS2_OLD_VARNO, 0);has_new =rangeTableEntry_used((Node *) sub_qry, PRS2_NEW_VARNO, 0) ||rangeTableEntry_used(*whereClause, PRS2_NEW_VARNO, 0);switch (stmt->event){case CMD_SELECT:if (has_old)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_INVALID_OBJECT_DEFINITION),errmsg("ON SELECT rule cannot use OLD")));if (has_new)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_INVALID_OBJECT_DEFINITION),errmsg("ON SELECT rule cannot use NEW")));break;case CMD_UPDATE:/* both are OK */break;case CMD_INSERT:if (has_old)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_INVALID_OBJECT_DEFINITION),errmsg("ON INSERT rule cannot use OLD")));break;case CMD_DELETE:if (has_new)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_INVALID_OBJECT_DEFINITION),errmsg("ON DELETE rule cannot use NEW")));break;default:elog(ERROR, "unrecognized event type: %d",(int) stmt->event);break;}/** OLD/NEW are not allowed in WITH queries, because they would* amount to outer references for the WITH, which we disallow.* However, they were already in the outer rangetable when we* analyzed the query, so we have to check.** Note that in the INSERT...SELECT case, we need to examine the* CTE lists of both top_subqry and sub_qry.** Note that we aren't digging into the body of the query looking* for WITHs in nested sub-SELECTs. A WITH down there can* legitimately refer to OLD/NEW, because it'd be an* indirect-correlated outer reference.*/if (rangeTableEntry_used((Node *) top_subqry->cteList,PRS2_OLD_VARNO, 0) ||rangeTableEntry_used((Node *) sub_qry->cteList,PRS2_OLD_VARNO, 0))ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_FEATURE_NOT_SUPPORTED),errmsg("cannot refer to OLD within WITH query")));if (rangeTableEntry_used((Node *) top_subqry->cteList,PRS2_NEW_VARNO, 0) ||rangeTableEntry_used((Node *) sub_qry->cteList,PRS2_NEW_VARNO, 0))ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_FEATURE_NOT_SUPPORTED),errmsg("cannot refer to NEW within WITH query")));/** For efficiency's sake, add OLD to the rule action's jointree* only if it was actually referenced in the statement or qual.** For INSERT, NEW is not really a relation (only a reference to* the to-be-inserted tuple) and should never be added to the* jointree.** For UPDATE, we treat NEW as being another kind of reference to* OLD, because it represents references to *transformed* tuples* of the existing relation. It would be wrong to enter NEW* separately in the jointree, since that would cause a double* join of the updated relation. It's also wrong to fail to make* a jointree entry if only NEW and not OLD is mentioned.*/if (has_old || (has_new && stmt->event == CMD_UPDATE)){/** If sub_qry is a setop, manipulating its jointree will do no* good at all, because the jointree is dummy. (This should be* a can't-happen case because of prior tests.)*/if (sub_qry->setOperations != NULL)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_FEATURE_NOT_SUPPORTED),errmsg("conditional UNION/INTERSECT/EXCEPT statements are not implemented")));/* hack so we can use addRTEtoQuery() */sub_pstate->p_rtable = sub_qry->rtable;sub_pstate->p_joinlist = sub_qry->jointree->fromlist;addRTEtoQuery(sub_pstate, oldrte, true, false, false);sub_qry->jointree->fromlist = sub_pstate->p_joinlist;}newactions = lappend(newactions, top_subqry);free_parsestate(sub_pstate);}*actions = newactions;}free_parsestate(pstate);/* Close relation, but keep the exclusive lock */heap_close(rel, NoLock);
}- 获取要定义规则的表的OID。
- 调用函数DefineQueryRewrite将己处理好的规则作为一个元组插人到系统表pg_rewrite中,DefineQueryRewrite 会把处理好的WHERE子句的表达式树以及规则的动作作为其参数之一。
DefineQueryRewrite函数调用的InsertRule函数源码如下:路径(src/backend/rewrite/rewriteDefine.c)
/** DefineQueryRewrite* Create a rule** This is essentially the same as DefineRule() except that the rule's* action and qual have already been passed through parse analysis.*/
ObjectAddress
DefineQueryRewrite(char *rulename,Oid event_relid,Node *event_qual,CmdType event_type,bool is_instead,bool replace,List *action)
{Relation event_relation;ListCell *l;Query *query;bool RelisBecomingView = false;Oid ruleId = InvalidOid;ObjectAddress address;/** If we are installing an ON SELECT rule, we had better grab* AccessExclusiveLock to ensure no SELECTs are currently running on the* event relation. For other types of rules, it would be sufficient to* grab ShareRowExclusiveLock to lock out insert/update/delete actions and* to ensure that we lock out current CREATE RULE statements; but because* of race conditions in access to catalog entries, we can't do that yet.** Note that this lock level should match the one used in DefineRule.*/event_relation = heap_open(event_relid, AccessExclusiveLock);/** Verify relation is of a type that rules can sensibly be applied to.* Internal callers can target materialized views, but transformRuleStmt()* blocks them for users. Don't mention them in the error message.*/if (event_relation->rd_rel->relkind != RELKIND_RELATION &&event_relation->rd_rel->relkind != RELKIND_MATVIEW &&event_relation->rd_rel->relkind != RELKIND_VIEW &&event_relation->rd_rel->relkind != RELKIND_PARTITIONED_TABLE)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_WRONG_OBJECT_TYPE),errmsg("\"%s\" is not a table or view",RelationGetRelationName(event_relation))));if (!allowSystemTableMods && IsSystemRelation(event_relation))ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_INSUFFICIENT_PRIVILEGE),errmsg("permission denied: \"%s\" is a system catalog",RelationGetRelationName(event_relation))));/** Check user has permission to apply rules to this relation.*/if (!pg_class_ownercheck(event_relid, GetUserId()))aclcheck_error(ACLCHECK_NOT_OWNER, ACL_KIND_CLASS,RelationGetRelationName(event_relation));/** No rule actions that modify OLD or NEW*/foreach(l, action){query = lfirst_node(Query, l);if (query->resultRelation == 0)continue;/* Don't be fooled by INSERT/SELECT */if (query != getInsertSelectQuery(query, NULL))continue;if (query->resultRelation == PRS2_OLD_VARNO)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_FEATURE_NOT_SUPPORTED),errmsg("rule actions on OLD are not implemented"),errhint("Use views or triggers instead.")));if (query->resultRelation == PRS2_NEW_VARNO)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_FEATURE_NOT_SUPPORTED),errmsg("rule actions on NEW are not implemented"),errhint("Use triggers instead.")));}if (event_type == CMD_SELECT){/** Rules ON SELECT are restricted to view definitions** So there cannot be INSTEAD NOTHING, ...*/if (list_length(action) == 0)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_FEATURE_NOT_SUPPORTED),errmsg("INSTEAD NOTHING rules on SELECT are not implemented"),errhint("Use views instead.")));/** ... there cannot be multiple actions, ...*/if (list_length(action) > 1)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_FEATURE_NOT_SUPPORTED),errmsg("multiple actions for rules on SELECT are not implemented")));/** ... the one action must be a SELECT, ...*/query = linitial_node(Query, action);if (!is_instead ||query->commandType != CMD_SELECT)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_FEATURE_NOT_SUPPORTED),errmsg("rules on SELECT must have action INSTEAD SELECT")));/** ... it cannot contain data-modifying WITH ...*/if (query->hasModifyingCTE)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_FEATURE_NOT_SUPPORTED),errmsg("rules on SELECT must not contain data-modifying statements in WITH")));/** ... there can be no rule qual, ...*/if (event_qual != NULL)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_FEATURE_NOT_SUPPORTED),errmsg("event qualifications are not implemented for rules on SELECT")));/** ... the targetlist of the SELECT action must exactly match the* event relation, ...*/checkRuleResultList(query->targetList,RelationGetDescr(event_relation),true,event_relation->rd_rel->relkind !=RELKIND_MATVIEW);/** ... there must not be another ON SELECT rule already ...*/if (!replace && event_relation->rd_rules != NULL){int i;for (i = 0; i < event_relation->rd_rules->numLocks; i++){RewriteRule *rule;rule = event_relation->rd_rules->rules[i];if (rule->event == CMD_SELECT)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_OBJECT_NOT_IN_PREREQUISITE_STATE),errmsg("\"%s\" is already a view",RelationGetRelationName(event_relation))));}}/** ... and finally the rule must be named _RETURN.*/if (strcmp(rulename, ViewSelectRuleName) != 0){/** In versions before 7.3, the expected name was _RETviewname. For* backwards compatibility with old pg_dump output, accept that* and silently change it to _RETURN. Since this is just a quick* backwards-compatibility hack, limit the number of characters* checked to a few less than NAMEDATALEN; this saves having to* worry about where a multibyte character might have gotten* truncated.*/if (strncmp(rulename, "_RET", 4) != 0 ||strncmp(rulename + 4, RelationGetRelationName(event_relation),NAMEDATALEN - 4 - 4) != 0)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_INVALID_OBJECT_DEFINITION),errmsg("view rule for \"%s\" must be named \"%s\"",RelationGetRelationName(event_relation),ViewSelectRuleName)));rulename = pstrdup(ViewSelectRuleName);}/** Are we converting a relation to a view?** If so, check that the relation is empty because the storage for the* relation is going to be deleted. Also insist that the rel not have* any triggers, indexes, child tables, policies, or RLS enabled.* (Note: these tests are too strict, because they will reject* relations that once had such but don't anymore. But we don't* really care, because this whole business of converting relations to* views is just a kluge to allow dump/reload of views that* participate in circular dependencies.)*/if (event_relation->rd_rel->relkind != RELKIND_VIEW &&event_relation->rd_rel->relkind != RELKIND_MATVIEW){HeapScanDesc scanDesc;Snapshot snapshot;if (event_relation->rd_rel->relkind == RELKIND_PARTITIONED_TABLE)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_WRONG_OBJECT_TYPE),errmsg("cannot convert partitioned table \"%s\" to a view",RelationGetRelationName(event_relation))));if (event_relation->rd_rel->relispartition)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_WRONG_OBJECT_TYPE),errmsg("cannot convert partition \"%s\" to a view",RelationGetRelationName(event_relation))));snapshot = RegisterSnapshot(GetLatestSnapshot());scanDesc = heap_beginscan(event_relation, snapshot, 0, NULL);if (heap_getnext(scanDesc, ForwardScanDirection) != NULL)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_OBJECT_NOT_IN_PREREQUISITE_STATE),errmsg("could not convert table \"%s\" to a view because it is not empty",RelationGetRelationName(event_relation))));heap_endscan(scanDesc);UnregisterSnapshot(snapshot);if (event_relation->rd_rel->relhastriggers)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_OBJECT_NOT_IN_PREREQUISITE_STATE),errmsg("could not convert table \"%s\" to a view because it has triggers",RelationGetRelationName(event_relation)),errhint("In particular, the table cannot be involved in any foreign key relationships.")));if (event_relation->rd_rel->relhasindex)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_OBJECT_NOT_IN_PREREQUISITE_STATE),errmsg("could not convert table \"%s\" to a view because it has indexes",RelationGetRelationName(event_relation))));if (event_relation->rd_rel->relhassubclass)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_OBJECT_NOT_IN_PREREQUISITE_STATE),errmsg("could not convert table \"%s\" to a view because it has child tables",RelationGetRelationName(event_relation))));if (event_relation->rd_rel->relrowsecurity)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_OBJECT_NOT_IN_PREREQUISITE_STATE),errmsg("could not convert table \"%s\" to a view because it has row security enabled",RelationGetRelationName(event_relation))));if (relation_has_policies(event_relation))ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_OBJECT_NOT_IN_PREREQUISITE_STATE),errmsg("could not convert table \"%s\" to a view because it has row security policies",RelationGetRelationName(event_relation))));RelisBecomingView = true;}}else{/** For non-SELECT rules, a RETURNING list can appear in at most one of* the actions ... and there can't be any RETURNING list at all in a* conditional or non-INSTEAD rule. (Actually, there can be at most* one RETURNING list across all rules on the same event, but it seems* best to enforce that at rule expansion time.) If there is a* RETURNING list, it must match the event relation.*/bool haveReturning = false;foreach(l, action){query = lfirst_node(Query, l);if (!query->returningList)continue;if (haveReturning)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_FEATURE_NOT_SUPPORTED),errmsg("cannot have multiple RETURNING lists in a rule")));haveReturning = true;if (event_qual != NULL)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_FEATURE_NOT_SUPPORTED),errmsg("RETURNING lists are not supported in conditional rules")));if (!is_instead)ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_FEATURE_NOT_SUPPORTED),errmsg("RETURNING lists are not supported in non-INSTEAD rules")));checkRuleResultList(query->returningList,RelationGetDescr(event_relation),false, false);}}/** This rule is allowed - prepare to install it.*//* discard rule if it's null action and not INSTEAD; it's a no-op */if (action != NIL || is_instead){ruleId = InsertRule(rulename,event_type,event_relid,is_instead,event_qual,action,replace);/** Set pg_class 'relhasrules' field TRUE for event relation.** Important side effect: an SI notice is broadcast to force all* backends (including me!) to update relcache entries with the new* rule.*/SetRelationRuleStatus(event_relid, true);}/* ---------------------------------------------------------------------* If the relation is becoming a view:* - delete the associated storage files* - get rid of any system attributes in pg_attribute; a view shouldn't* have any of those* - remove the toast table; there is no need for it anymore, and its* presence would make vacuum slightly more complicated* - set relkind to RELKIND_VIEW, and adjust other pg_class fields* to be appropriate for a view** NB: we had better have AccessExclusiveLock to do this ...* ---------------------------------------------------------------------*/if (RelisBecomingView){Relation relationRelation;Oid toastrelid;HeapTuple classTup;Form_pg_class classForm;relationRelation = heap_open(RelationRelationId, RowExclusiveLock);toastrelid = event_relation->rd_rel->reltoastrelid;/* drop storage while table still looks like a table */RelationDropStorage(event_relation);DeleteSystemAttributeTuples(event_relid);/** Drop the toast table if any. (This won't take care of updating the* toast fields in the relation's own pg_class entry; we handle that* below.)*/if (OidIsValid(toastrelid)){ObjectAddress toastobject;/** Delete the dependency of the toast relation on the main* relation so we can drop the former without dropping the latter.*/deleteDependencyRecordsFor(RelationRelationId, toastrelid,false);/* Make deletion of dependency record visible */CommandCounterIncrement();/* Now drop toast table, including its index */toastobject.classId = RelationRelationId;toastobject.objectId = toastrelid;toastobject.objectSubId = 0;performDeletion(&toastobject, DROP_RESTRICT,PERFORM_DELETION_INTERNAL);}/** SetRelationRuleStatus may have updated the pg_class row, so we must* advance the command counter before trying to update it again.*/CommandCounterIncrement();/** Fix pg_class entry to look like a normal view's, including setting* the correct relkind and removal of reltoastrelid of the toast table* we potentially removed above.*/classTup = SearchSysCacheCopy1(RELOID, ObjectIdGetDatum(event_relid));if (!HeapTupleIsValid(classTup))elog(ERROR, "cache lookup failed for relation %u", event_relid);classForm = (Form_pg_class) GETSTRUCT(classTup);classForm->reltablespace = InvalidOid;classForm->relpages = 0;classForm->reltuples = 0;classForm->relallvisible = 0;classForm->reltoastrelid = InvalidOid;classForm->relhasindex = false;classForm->relkind = RELKIND_VIEW;classForm->relhasoids = false;classForm->relhaspkey = false;classForm->relfrozenxid = InvalidTransactionId;classForm->relminmxid = InvalidMultiXactId;classForm->relreplident = REPLICA_IDENTITY_NOTHING;CatalogTupleUpdate(relationRelation, &classTup->t_self, classTup);heap_freetuple(classTup);heap_close(relationRelation, RowExclusiveLock);}ObjectAddressSet(address, RewriteRelationId, ruleId);/* Close rel, but keep lock till commit... */heap_close(event_relation, NoLock);return address;
}
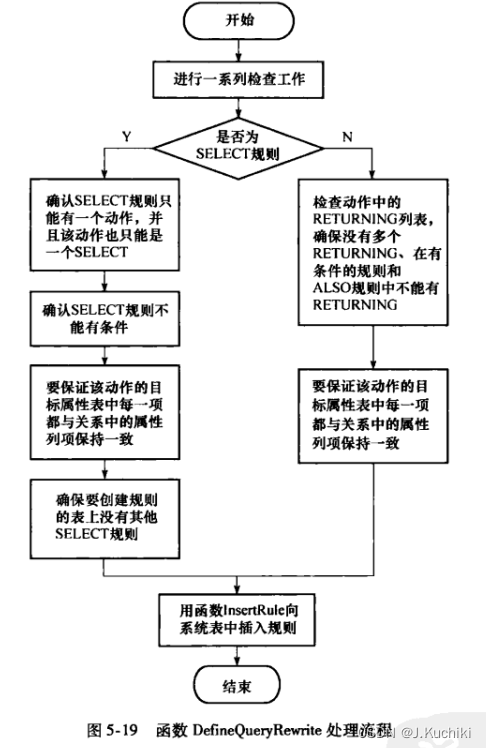
函数 DefineQueryRewrite 的流程如图5-19 所示:
删除重写规则
删除重写规则是指从数据库中删除一个已经存在的规则。重写规则是一种特殊类型的规则,它允许在执行查询或修改数据库时,自动将查询重写为另一个查询。
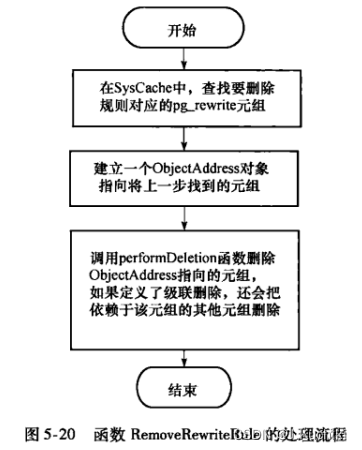
在PostgresSQL中实现了两种删除规则的方式:第一种是根据规则名删除规则,由函数RemoveRewriteRule实现;第二种是根据规则的OID删除规则,由函数RemoveRewriteRuleById实现。当我们输入“DROP RULE”命令删除规则时,实际的删除工作将由RemoveRewriteRule完成;而RemoveRewriteRuleByld的作用是在删除其他对象(比如视图)时,用于级联删除与这个对象相关的规则。
RemoveRewriteRule函数的主要流程如图5-20所示。
对查询树进行重写
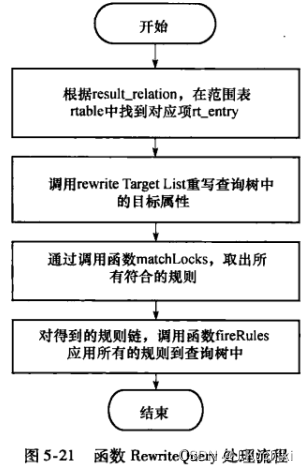
Pg_rewrite_query中会调用函数QueryRewrite来完成查询树的重写。重写规则定义了在查询执行过程中,将一个查询树转换成另一个查询树的规则。这些规则存储在系统表 pg_rewrite 中。
QueryRewrite 函数的流程如下:
- 获取要执行的规则列表:
首先,QueryRewrite 函数会根据查询树中的关联表和查询类型(SELECT、INSERT、UPDATE、DELETE等)来获取与该表相关的重写规则。它会查询系统表 pg_rewrite 来找到适用于当前查询的规则列表。- 根据规则排序:
获取到的规则列表会按照 ev_priority 字段进行排序,优先级越高的规则排在前面。如果有多个规则适用于当前查询,按照优先级从高到低的顺序依次应用规则。- 检查规则条件:
对于每个规则,QueryRewrite 函数会检查规则的 ev_qual 字段,即规则的条件表达式。如果规则定义了条件,并且条件不满足(即返回值为 false),则该规则不会被应用于当前查询,继续尝试下一个规则。- 应用规则:
如果规则的条件满足,QueryRewrite 函数将应用规则中定义的查询树转换操作。这通常涉及替换查询树的部分或全部节点,以便得到一个新的查询树。应用规则后,函数将继续检查下一个规则。- 合并规则结果:
重写过程中可能会应用多个规则,每个规则可能会生成一个新的查询树。QueryRewrite 函数会合并所有应用过的规则的结果,以确保最终得到一个最终的查询树。- 完成重写:
一旦所有适用的规则都应用完毕,QueryRewrite 函数将返回重写后的最终查询树。