文章目录
- 一、简介
- 二、设计
- 2.1 队列结构设计
- 2.2 队列接口设计
- 三、实现
- 3.1 队列锁的实现
- 3.2 创建队列
- 3.3 写入队列
- 3.4 读出数据
- 3.5 判断队列是否为空
- 3.6 判断队列是否为满
- 3.7 清空队列
- 3.8 删除队列
- 四、测试
- 参考
一、简介
- 收到消息时先把接收到的消息放到队列中。
- 在任务中从队列获取数据。
- 如果解析过程中再来一帧数据,这帧数据会先存放在消息队列中。
- 当队列中的上一帧数据解析完成后,任务会从队列中的下一条数据开始解析处理,以此循环,直到队列中的消息解析处理完毕。
二、设计
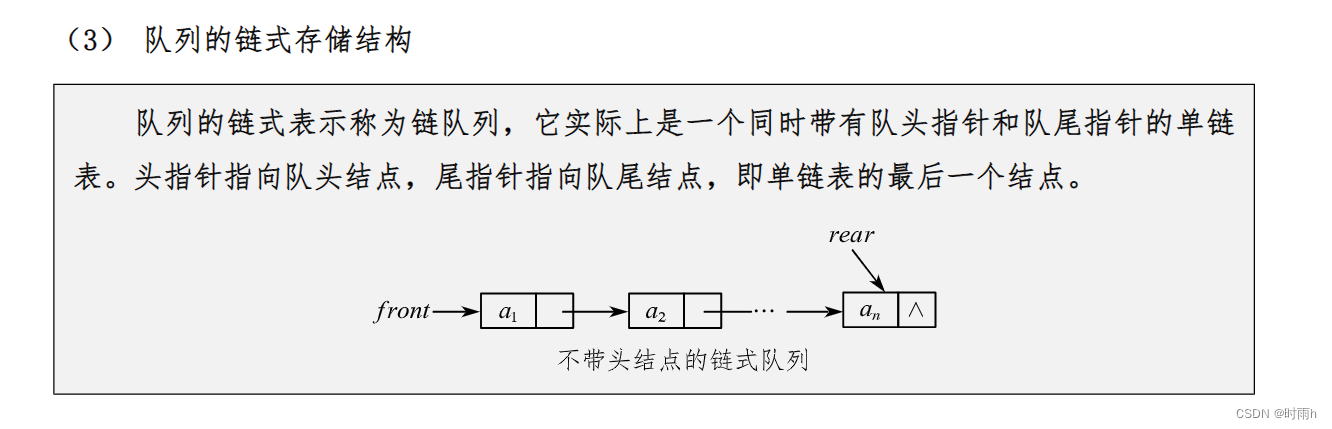
2.1 队列结构设计
有头尾指针分别指向写入的位置和读出的位置
需要配置队列中最多能存储几帧数据即几个列表项,每一项有多大的空间去保存接收到的数据

LiteQueue相当于是头部,后面紧跟着的是数据,而且每一个数据的存储大小都是确定的。
考虑到多线程不能同时读或者写,要互斥访问,因此还需要加一个读写锁
/*
LiteQueue : Structure describing queue parameters.
item_num_x: Number of items.
item_size : The size of each list item set when creating the queue,unit: bytes, used to store data received in the queue.
item_size : The counter of items
*/
typedef struct { volatile uint8_t queue_write_lock;volatile uint8_t queue_read_lock;uint8_t *head; uint8_t *tail;size_t item_num; size_t item_size;size_t item_count;
}LiteQueue, *pLiteQueue;
2.2 队列接口设计
使用队列前必定先要创建队列,并确定创建队列的大小,其次是读写队列的接口,以及判断队列是否为空/满、清空队列、删除队列
LiteQueue *LiteQueue_Create(size_t item_num, size_t item_size);
LiteQueue_Status Write_To_LiteQueue(LiteQueue *queue, uint8_t *buff);
LiteQueue_Status Read_From_LiteQueue(LiteQueue *queue, uint8_t *buff);
LiteQueue_Status isLiteQueue_Empty(LiteQueue *queue);
LiteQueue_Status LiteQueue_Clear(LiteQueue *queue);
LiteQueue_Status LiteQueue_Delete(LiteQueue *queue);
LiteQueue_Status isLiteQueue_Full(LiteQueue *queue);
LiteQueue_Status isLiteQueue_Empty(LiteQueue *queue);
队列的状态用一个枚举类型实现
typedef enum{ LITE_QUEUE_IDLE = 0, LITE_QUEUE_BUSY, LITE_QUEUE_ERR, LITE_QUEUE_OK,LITE_QUEUE_EMPTY, LITE_QUEUE_NONEMPTY,LITE_QUEUE_FULL,LITE_QUEUE_NONFULL
}LiteQueue_Status;
三、实现
3.1 队列锁的实现
队列锁使用宏定义的方式实现
typedef enum{ LITE_QUEUE_UNLOCK = 0, LITE_QUEUE_LOCK,
}LiteQueueLock;#define LITE_QUEUE_WRITE_LOCK(__QUEUE__) do{ \if((__QUEUE__)->queue_write_lock == LITE_QUEUE_LOCK){\return LITE_QUEUE_BUSY; \} else { \(__QUEUE__)->queue_write_lock = LITE_QUEUE_LOCK; \} \
}while(0) #define LITE_QUEUE_WRITE_UNLOCK(__QUEUE__) do{ \(__QUEUE__)->queue_write_lock = LITE_QUEUE_UNLOCK; \
}while(0) #define LITE_QUEUE_READ_LOCK(__QUEUE__) do{ \if((__QUEUE__)->queue_read_lock == LITE_QUEUE_LOCK){ \return LITE_QUEUE_BUSY; \} else { \(__QUEUE__)->queue_read_lock = LITE_QUEUE_LOCK; \} \
}while(0) #define LITE_QUEUE_READ_UNLOCK(__QUEUE__) do{ \(__QUEUE__)->queue_read_lock = LITE_QUEUE_UNLOCK; \
}while(0)
3.2 创建队列
/**
* @ brief : Create message queue.
* @ param : {size_t } item_num : The number of list items in the queue.{size_t } item_size: The size of each list item, unit: bytes.
* @ return: {LiteQueue *} queue : Message queue handle pointer.
* @ note : Create a queue and initialize the queue items to 0, with the head and tail pointers pointing to the starting position of the list items.
*/
LiteQueue *LiteQueue_Create(size_t item_num, size_t item_size){if((item_num < 1) || (item_size < 1)){return NULL;}LiteQueue *queue = (LiteQueue *)malloc(sizeof(LiteQueue) + item_num * item_size);if( queue == NULL ) {printf("LiteQueue malloc failed.\r\n");return NULL;}memset((uint8_t *)queue, 0, sizeof(LiteQueue) + item_num * item_size);queue->head = (uint8_t *)((uint8_t *)queue + sizeof(LiteQueue));queue->tail = queue->head;queue->item_num = item_num;queue->item_size = item_size;queue->item_count = 0;queue->queue_read_lock = LITE_QUEUE_UNLOCK;queue->queue_write_lock = LITE_QUEUE_UNLOCK;return queue;
}
3.3 写入队列
/**
* @ brief : Write data to the queue.
* @ param : {LiteQueue *} queue: Message queue handle pointer.{uint8_t *} buff : Data to be written to the queue.
* @ return: {LiteQueue_Status} Returns the status of the queue.
* @ note : Writing data when the queue is full will automatically overwrite the first frame of data.
*/
LiteQueue_Status Write_To_LiteQueue(LiteQueue *queue, uint8_t *buff){if((queue == NULL) || (buff == NULL)){return LITE_QUEUE_ERR;}LITE_QUEUE_WRITE_LOCK(queue);if(isLiteQueue_Full(queue) == LITE_QUEUE_FULL){return LITE_QUEUE_FULL;}memcpy(queue->tail, buff, queue->item_size);if(queue->tail == (uint8_t *)queue + sizeof(LiteQueue) + (queue->item_num - 1) * queue->item_size){queue->tail = (uint8_t *)queue + sizeof(LiteQueue);}else{queue->tail += queue->item_size;}queue->item_count += 1;LITE_QUEUE_WRITE_UNLOCK(queue);return LITE_QUEUE_OK;
}
3.4 读出数据
/**
* @ brief : Read data from queue.
* @ param : {LiteQueue *} queue: Message queue handle pointer.{uint8_t *} buff : Data to be read from the queue.
* @ return: {LiteQueue_Status} Returns the status of the queue.
* @ note : Read data starting from the position of the head pointer and save it to the buff.
*/
LiteQueue_Status Read_From_LiteQueue(LiteQueue *queue, uint8_t *buff){if((queue == NULL) || (buff == NULL) || (isLiteQueue_Empty(queue) == LITE_QUEUE_EMPTY)){return LITE_QUEUE_ERR;}LITE_QUEUE_READ_LOCK(queue);if(isLiteQueue_Empty(queue) == LITE_QUEUE_EMPTY){return LITE_QUEUE_EMPTY;}memcpy(buff, queue->head, queue->item_size); if(queue->head == (uint8_t *)queue + sizeof(LiteQueue) + (queue->item_num - 1) * queue->item_size){queue->head = (uint8_t *)queue + sizeof(LiteQueue);}else{queue->head += queue->item_size;}queue->item_count -= 1;LITE_QUEUE_READ_UNLOCK(queue);return LITE_QUEUE_OK;
}
3.5 判断队列是否为空
/**
* @ brief : Determine whether the queue is empty.
* @ param : {LiteQueue *} queue: Message queue handle pointer.
* @ return: {LiteQueue_Status} Returns the status of the queue.
* @ note : Determine whether the head and tail pointers are the same. If they are the same, it means there is no data in the queue, otherwise it means there is still data that has not been read out.
*/
inline LiteQueue_Status isLiteQueue_Empty(LiteQueue *queue){if(queue == NULL){return LITE_QUEUE_ERR;}if( queue->item_count == 0 ) {return LITE_QUEUE_EMPTY;}else{return LITE_QUEUE_NONEMPTY;}
}
3.6 判断队列是否为满
/**
* @ brief : Determine whether the queue is full.
* @ param : {LiteQueue *} queue: Message queue handle pointer.
* @ return: {LiteQueue_Status} Returns the status of the queue.
* @ note : Determine whether the head and tail pointers are the same. If they are the same, it means there is no data in the queue, otherwise it means there is still data that has not been read out.
*/
inline LiteQueue_Status isLiteQueue_Full(LiteQueue *queue){if(queue == NULL){return LITE_QUEUE_ERR;}if( queue->item_count == queue->item_num) {return LITE_QUEUE_FULL;}else{return LITE_QUEUE_NONFULL;}
}
3.7 清空队列
/**
* @ brief : Clear the message queue.
* @ param : {LiteQueue *} queue: Message queue handle pointer.
* @ return: {LiteQueue_Status} Returns the status of the queue.
* @ note : Determine whether the head and tail pointers are the same. If they are the same,it means there is no data in the queue, otherwise it means there is still data that has not been read out.
*/
LiteQueue_Status LiteQueue_Clear(LiteQueue *queue){if(queue == NULL) {return LITE_QUEUE_ERR;}LITE_QUEUE_WRITE_LOCK(queue);queue->head = (uint8_t *)((uint8_t *)queue + sizeof(LiteQueue));queue->tail = queue->head;queue->item_count = 0;memset(queue->head, 0, queue->item_num * queue->item_size);LITE_QUEUE_WRITE_UNLOCK(queue);return LITE_QUEUE_OK;
}
3.8 删除队列
/**
* @ brief : Clear the message queue.
* @ param : {LiteQueue *} queue: Message queue handle pointer.
* @ return: {LiteQueue_Status} Returns the status of the queue.
* @ note : Determine whether the head and tail pointers are the same. If they are the same,it means there is no data in the queue, otherwise it means there is still data that has not been read out.
*/
LiteQueue_Status LiteQueue_Delete(LiteQueue *queue){if(queue == NULL) {return LITE_QUEUE_ERR;}//memset((uint8_t *)queue, 0, sizeof(LiteQueue) + queue->item_num * queue->item_size);free(queue);queue = NULL;return LITE_QUEUE_OK;
}
四、测试
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>typedef unsigned char uint8_t;
typedef unsigned int uint32_t;/*
LiteQueue : Structure describing queue parameters.
item_num_x: Number of items.
item_size : The size of each list item set when creating the queue,unit: bytes, used to store data received in the queue.
*/
typedef struct { volatile uint8_t queue_write_lock;volatile uint8_t queue_read_lock;uint8_t *head; uint8_t *tail;size_t item_num; size_t item_size;size_t item_count;
}LiteQueue, *pLiteQueue;typedef enum{ LITE_QUEUE_IDLE = 0, LITE_QUEUE_BUSY, LITE_QUEUE_ERR, LITE_QUEUE_OK,LITE_QUEUE_EMPTY, LITE_QUEUE_NONEMPTY,LITE_QUEUE_FULL,LITE_QUEUE_NONFULL
}LiteQueue_Status;typedef enum{ LITE_QUEUE_UNLOCK = 0, LITE_QUEUE_LOCK,
}LiteQueueLock;#define LITE_QUEUE_WRITE_LOCK(__QUEUE__) do{ \if((__QUEUE__)->queue_write_lock == LITE_QUEUE_LOCK){\return LITE_QUEUE_BUSY; \} else { \(__QUEUE__)->queue_write_lock = LITE_QUEUE_LOCK; \} \
}while(0) #define LITE_QUEUE_WRITE_UNLOCK(__QUEUE__) do{ \(__QUEUE__)->queue_write_lock = LITE_QUEUE_UNLOCK; \
}while(0) #define LITE_QUEUE_READ_LOCK(__QUEUE__) do{ \if((__QUEUE__)->queue_read_lock == LITE_QUEUE_LOCK){ \return LITE_QUEUE_BUSY; \} else { \(__QUEUE__)->queue_read_lock = LITE_QUEUE_LOCK; \} \
}while(0) #define LITE_QUEUE_READ_UNLOCK(__QUEUE__) do{ \(__QUEUE__)->queue_read_lock = LITE_QUEUE_UNLOCK; \
}while(0) LiteQueue *LiteQueue_Create(size_t item_num, size_t item_size);
LiteQueue_Status Write_To_LiteQueue(LiteQueue *queue, uint8_t *buff);
LiteQueue_Status Read_From_LiteQueue(LiteQueue *queue, uint8_t *buff);
LiteQueue_Status isLiteQueue_Empty(LiteQueue *queue);
LiteQueue_Status LiteQueue_Clear(LiteQueue *queue);
LiteQueue_Status LiteQueue_Delete(LiteQueue *queue);
LiteQueue_Status isLiteQueue_Full(LiteQueue *queue);
LiteQueue_Status isLiteQueue_Empty(LiteQueue *queue); /**
* @ brief : Create message queue.
* @ param : {size_t } item_num : The number of list items in the queue.{size_t } item_size: The size of each list item, unit: bytes.
* @ return: {LiteQueue *} queue : Message queue handle pointer.
* @ note : Create a queue and initialize the queue items to 0, with the head and tail pointers pointing to the starting position of the list items.
*/
LiteQueue *LiteQueue_Create(size_t item_num, size_t item_size){if((item_num < 1) || (item_size < 1)){return NULL;}LiteQueue *queue = (LiteQueue *)malloc(sizeof(LiteQueue) + item_num * item_size);if( queue == NULL ) {printf("LiteQueue malloc failed.\r\n");return NULL;}memset((uint8_t *)queue, 0, sizeof(LiteQueue) + item_num * item_size);queue->head = (uint8_t *)((uint8_t *)queue + sizeof(LiteQueue));queue->tail = queue->head;queue->item_num = item_num;queue->item_size = item_size;queue->item_count = 0;queue->queue_read_lock = LITE_QUEUE_UNLOCK;queue->queue_write_lock = LITE_QUEUE_UNLOCK;return queue;
}/**
* @ brief : Write data to the queue.
* @ param : {LiteQueue *} queue: Message queue handle pointer.{uint8_t *} buff : Data to be written to the queue.
* @ return: {LiteQueue_Status} Returns the status of the queue.
* @ note : Writing data when the queue is full will automatically overwrite the first frame of data.
*/
LiteQueue_Status Write_To_LiteQueue(LiteQueue *queue, uint8_t *buff){if((queue == NULL) || (buff == NULL)){return LITE_QUEUE_ERR;}LITE_QUEUE_WRITE_LOCK(queue);if(isLiteQueue_Full(queue) == LITE_QUEUE_FULL){return LITE_QUEUE_FULL;}memcpy(queue->tail, buff, queue->item_size);if(queue->tail == (uint8_t *)queue + sizeof(LiteQueue) + (queue->item_num - 1) * queue->item_size){queue->tail = (uint8_t *)queue + sizeof(LiteQueue);}else{queue->tail += queue->item_size;}queue->item_count += 1;LITE_QUEUE_WRITE_UNLOCK(queue);return LITE_QUEUE_OK;
}/**
* @ brief : Read data from queue.
* @ param : {LiteQueue *} queue: Message queue handle pointer.{uint8_t *} buff : Data to be read from the queue.
* @ return: {LiteQueue_Status} Returns the status of the queue.
* @ note : Read data starting from the position of the head pointer and save it to the buff.
*/
LiteQueue_Status Read_From_LiteQueue(LiteQueue *queue, uint8_t *buff){if((queue == NULL) || (buff == NULL) || (isLiteQueue_Empty(queue) == LITE_QUEUE_EMPTY)){return LITE_QUEUE_ERR;}LITE_QUEUE_READ_LOCK(queue);if(isLiteQueue_Empty(queue) == LITE_QUEUE_EMPTY){return LITE_QUEUE_EMPTY;}memcpy(buff, queue->head, queue->item_size); if(queue->head == (uint8_t *)queue + sizeof(LiteQueue) + (queue->item_num - 1) * queue->item_size){queue->head = (uint8_t *)queue + sizeof(LiteQueue);}else{queue->head += queue->item_size;}queue->item_count -= 1;LITE_QUEUE_READ_UNLOCK(queue);return LITE_QUEUE_OK;
}/**
* @ brief : Determine whether the queue is empty.
* @ param : {LiteQueue *} queue: Message queue handle pointer.
* @ return: {LiteQueue_Status} Returns the status of the queue.
* @ note : Determine whether the head and tail pointers are the same. If they are the same, it means there is no data in the queue, otherwise it means there is still data that has not been read out.
*/
inline LiteQueue_Status isLiteQueue_Empty(LiteQueue *queue){if(queue == NULL){return LITE_QUEUE_ERR;}if( queue->item_count == 0 ) {return LITE_QUEUE_EMPTY;}else{return LITE_QUEUE_NONEMPTY;}
}/**
* @ brief : Determine whether the queue is full.
* @ param : {LiteQueue *} queue: Message queue handle pointer.
* @ return: {LiteQueue_Status} Returns the status of the queue.
* @ note : Determine whether the head and tail pointers are the same. If they are the same, it means there is no data in the queue, otherwise it means there is still data that has not been read out.
*/
inline LiteQueue_Status isLiteQueue_Full(LiteQueue *queue){if(queue == NULL){return LITE_QUEUE_ERR;}if( queue->item_count == queue->item_num) {return LITE_QUEUE_FULL;}else{return LITE_QUEUE_NONFULL;}
}/**
* @ brief : Clear the message queue.
* @ param : {LiteQueue *} queue: Message queue handle pointer.
* @ return: {LiteQueue_Status} Returns the status of the queue.
* @ note : Determine whether the head and tail pointers are the same. If they are the same,it means there is no data in the queue, otherwise it means there is still data that has not been read out.
*/
LiteQueue_Status LiteQueue_Clear(LiteQueue *queue){if(queue == NULL) {return LITE_QUEUE_ERR;}LITE_QUEUE_WRITE_LOCK(queue);queue->head = (uint8_t *)((uint8_t *)queue + sizeof(LiteQueue));queue->tail = queue->head;queue->item_count = 0;memset(queue->head, 0, queue->item_num * queue->item_size);LITE_QUEUE_WRITE_UNLOCK(queue);return LITE_QUEUE_OK;
}/**
* @ brief : Clear the message queue.
* @ param : {LiteQueue *} queue: Message queue handle pointer.
* @ return: {LiteQueue_Status} Returns the status of the queue.
* @ note : Determine whether the head and tail pointers are the same. If they are the same,it means there is no data in the queue, otherwise it means there is still data that has not been read out.
*/
LiteQueue_Status LiteQueue_Delete(LiteQueue *queue){if(queue == NULL) {return LITE_QUEUE_ERR;}//memset((uint8_t *)queue, 0, sizeof(LiteQueue) + queue->item_num * queue->item_size);free(queue);queue = NULL;return LITE_QUEUE_OK;
}/**
* @ brief : Print the contents of each list item in the queue.
* @ param : {LiteQueue *} queue: Message queue handle pointer.
* @ return: None.
*/
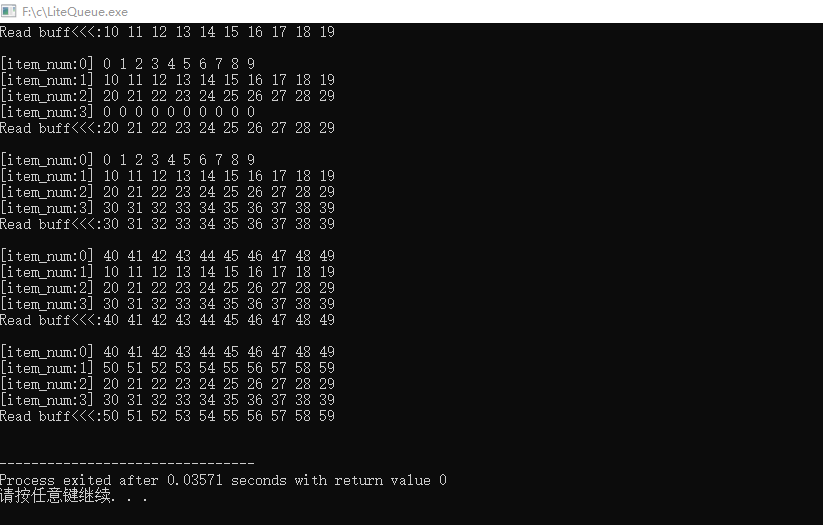
static void PrintLiteQueue(LiteQueue *queue){if(queue == NULL){return ;}for(int i = 0; i < queue->item_num; i++){printf("[item_num:%d] ", i);for(int n = 0; n < queue->item_size; n++){printf("%d ", *((uint8_t *)queue + sizeof(LiteQueue) + i * queue->item_size + n));}printf("\r\n");}
}/**
* @ brief : Print the data in buff.
* @ param : {LiteQueue *} queue: Message queue handle pointer.
* @ return: None.
* @ note : Used to observe buff data changes and test to verify the correctness of written or read data.
*/
static void PrintBuff(uint8_t *buff, size_t len){if((buff == NULL) || (len < 1)){return ;}printf("Read buff<<<:");for(size_t i = 0; i < len; i++){printf("%d ", buff[i]);}printf("\r\n\r\n");
}int main(){uint8_t writebuff[10] = {0};uint8_t readbuff[10] = {0};/* Create message queue, 4 list items, each list item has 10 bytes of memory space */pLiteQueue msgQueue = LiteQueue_Create(4, 10);PrintLiteQueue(msgQueue);printf("\r\n");/* Simulate writing and reading to the queue 6 times, and observe the data in the queue by printing */for(int i=0;i<6;i++ ) {/* Simulate data, change the writebuff data and write it to the queue */for(int n = 0; n < msgQueue->item_size; n++){writebuff[n] = (i * msgQueue->item_size + n) % 256;}/* Data is written to the queue */Write_To_LiteQueue(msgQueue, writebuff);PrintLiteQueue(msgQueue);/* Read data from queue */Read_From_LiteQueue(msgQueue, readbuff);PrintBuff(readbuff, sizeof(readbuff));}return 0;
}
参考
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/vI3g4JmSXMyKrpnIV1vjbg