1、友元
1.1 概念
类实现了数据的隐藏和封装,类的数据一般定义为私有成员,仅能通过类的成员函数才能读写。如果数据成员定义为公有的,则破坏了类的封装性。但是某些情况下,需要频繁的读写类的成员函数,特别是在对成员函数多次调用时,由于参数的传递,类型检查和安全性检查等都需要时间开销,从而影响到程序的运行效率。
友元是一种定义在类外部的“普通函数”,但他还需要再类内进行声明,为了和该类的成员函数加以却别,再声明前面加一个关键字friend。友元函数不是成员函数,但是可以访问到类中的私有成员。
在于提高程序的运行效率,但是他破坏了类的封装性和隐藏性。使得非成员函数能够访问到类中私有成员。导致程序的维护性和安全性变差,因此使用友元要谨慎。
友元有三种实现方式:
- 友元函数你p
- 友元类
- 友元成员函数
1.2 友元函数
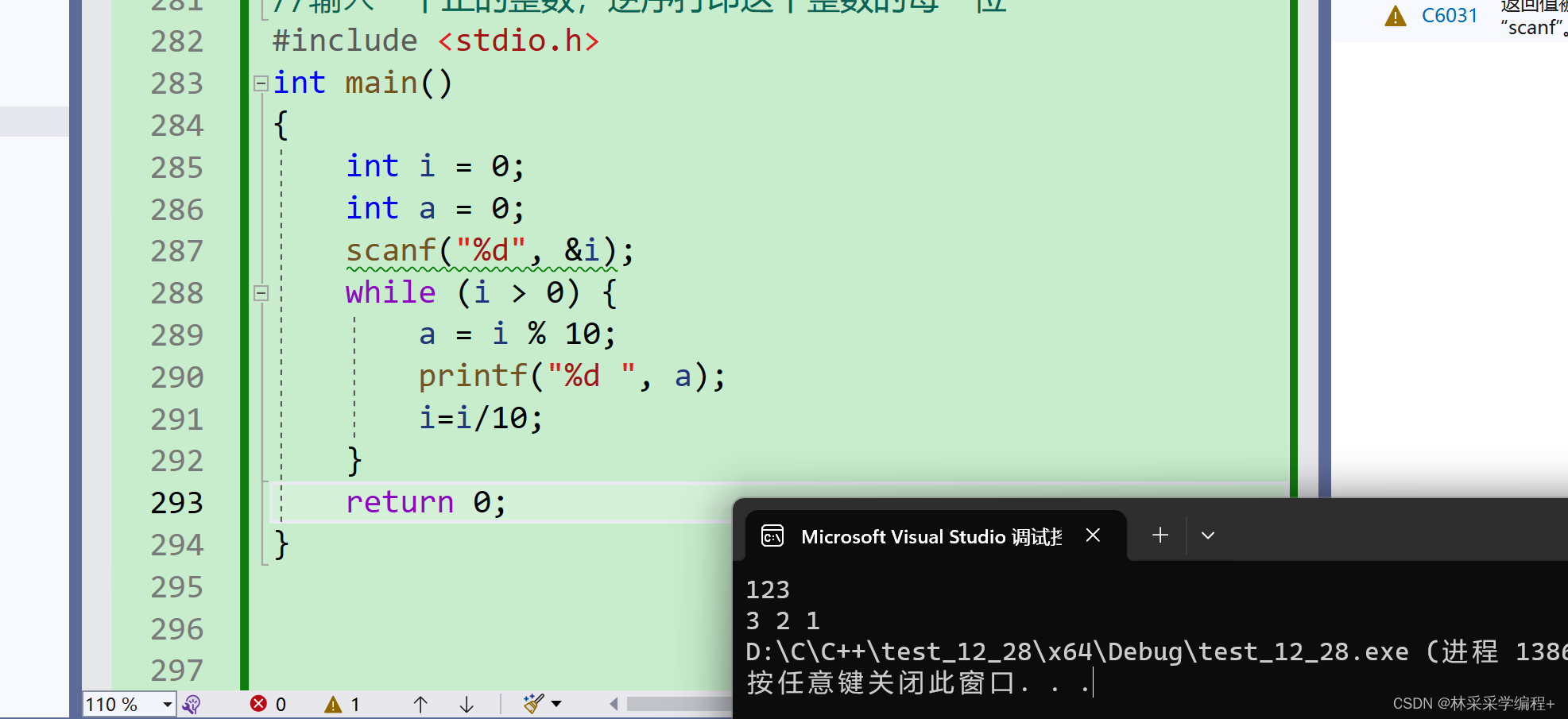
友元函数不属于任何一个类,是一个类外的函数,但是在类内进行“声明”。虽然友元函数不是类中的函数,但是却可以访问类中的所有成员(包括私有成员)。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
private:int a;//私有成员变量
public:Test(int a):a(a){}void show(){
cout<<a<<" "<<&a<<endl;}friend void and_test(Test &t);//友元函数声明
};
void and_test(Test &t)//友元函数本体
{
cout<<t.a<<" "<<&t.a<<endl;
}
int main()
{
Test t1(1);and_test(t1);
t1.show();//调用类内成员函数return 0;
}
友元函数的使用需要注意以下几点:
- 友元函数没有this指针
- 友元函数的“声明”可以放置到类中任意的位置,不受权限修饰符的影响。
- 一个友元函数理论上可以访问多个类,只需要在各个类中进行“声明”。
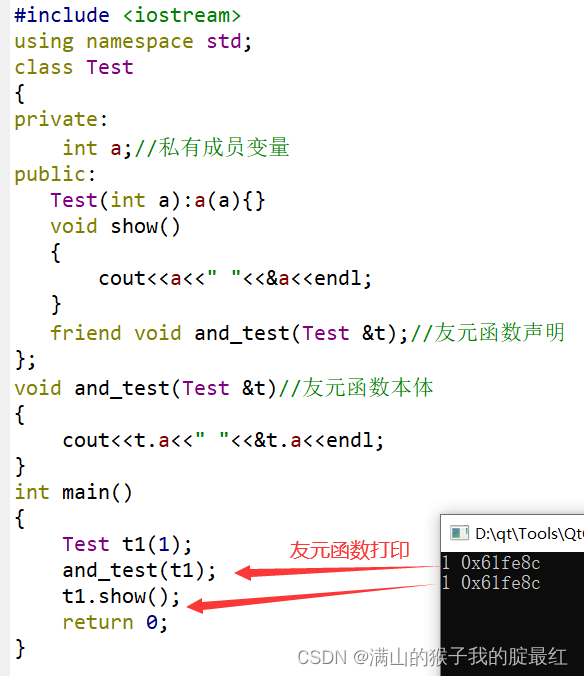
1.3 友元类
当一个类B成为了另一个Test的友元时,类Test的所有成员都可以被类B访问,此时类B就是类Test的友元类。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Test
{// 友元函数,类内声明friend void and_test(Test &t);int a;
public:Test(int a):a(a){}void show(){
cout << a << " " << &a << endl;}// 友元类,类内声明friend class B;
};
class B
{
public:void and_test(Test &t){
cout << t.a << " " << &t.a << endl;}
};
int main()
{
Test t1(1);
t1.show(); B b;
b.and_test(t1);return 0;
}友元类的使用也需要注意以下几点:
- 友元关系不能被继承。
- 友元关系不具有交换性(比如:类B声明称类Test的友元,类B可以访问类Test中的成员,但是类Test不能访问类B中的私有成员,如果需要访问,需要将类Test声明称类B的友元)
互为友元代码。需要类内声明,类外实现
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class B;
class Test
{
private:int a;
public:Test(int i):a(i){}void show(){
cout << a << " " << &a << endl;}void test(B &b);// 友元类 类内声明friend class B;};
class B
{
private:int b = 20;public:void show(Test &t);friend class Test;
};
void Test::test(B &b)
{
cout << b.b << endl;
}
void B::show(Test &t)
{
cout << ++t.a << " " << &t.a << endl;
}
int main()
{
Test t1(2);
B b;
b.show(t1); // 3 0x61fe8c
t1.show(); // 3 0x61fe8c
t1.test(b);return 0;
}
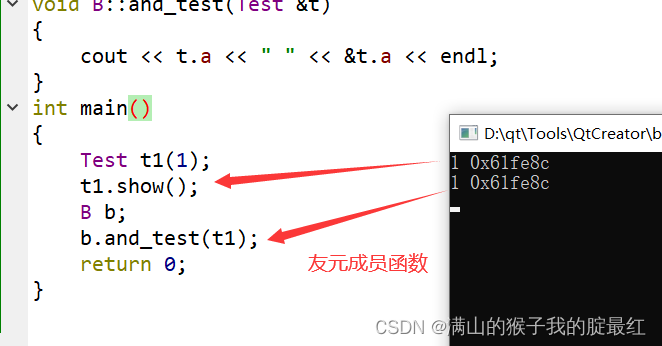
1.4 友元成员函数
使类B中的成员函数成为类Test的友元成员函数,这样类B的该成员函数就可以访问类Test的所有成员。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 第四步:声明被访问的类
class Test;
class B
{
public:// 第二步:声明友元成员函数(类内声明,类外实现)void and_test(Test &t);
};
class Test
{int a;
public:Test(int a):a(a){}void show(){
cout << a << " " << &a << endl;}// 友元成员函数,第一步:确定友元函数的格式并声明friend void B::and_test(Test &t);
};
// 第三步:类外定义友元成员函数
void B::and_test(Test &t)
{
cout << t.a << " " << &t.a << endl;
}
int main()
{
Test t1(1);
t1.show();
B b;
b.and_test(t1);return 0;
}
2、std::string 字符串类(掌握)
字符串对象是一种特殊类型的容器,专门设计用于操作字符串。
常用语法
1、string s; // 创建一个字符串2、cout << s.empty() << endl; // 判断是否为空3、string s1 = "hello";// 隐式调用构造函数4、string s2("world"); // 显示调用构造函数5、// == != < > 判断的编码
cout << (s1 == s2) << endl; // 0 不相等
cout << (s1 != s2) << endl; // 1
cout << (s1 < s2) << endl; // 1
cout << (s1 > s2) << endl; // 06、string s3(s2);// 拷贝构造7、// 参数1:char* 原字符串// 参数2:保留的字符数string s4("ABCDEFG",3);//ABC 字符截取:保留的字符数8、// 参数1:std::string 原字符串// 参数2:不保留的字符数,从头开始string s5(s2,3); // ld 字符截取:不保留的字符数,剩下的字符数9、// 参数1:字符数量// 参数2:字符内容 charstring s6(5,'a');// aaaaa 打印字符内容
10、swap(s5,s6); // ld aaaaa->aaaaa ld 交换两个字符串内容
11、string s7 = s5 + s6;//aaaaald 字符串拼接
12、s7.append("jiajia");// aaaaaldjiajia 向后追加字符串
13、s7.push_back('s');// aaaaaldjiajias 向后追加单字符
14、// 参数1:插入的位置// 参数2:插入的内容
s7.insert(1,"234");//a234aaaaldjiajias 插入
15、// 参数1:起始位置// 参数2:删除字符串的数量
s7.erase(2,5);// a2aldjiajias 删除字符串
16、// 参数1:起始位置// 参数2:被替换的字符数// 参数3:替换的新内容
s7.replace(0,3,"*****"); // *****ldjiajias 指定替换
17、s7.clear();//0 清空string s8 = "hahaha";// 直接赋值初始化(隐式调用构造函数)
18、// 参数1:拷贝的目标// 参数2:拷贝的字符串数量// 参数3:拷贝的起始位置
s8 = "ABCDEFGH";
char arr[20] = {0};
s8.copy(arr,6,1);//从某个位置开始拷贝几个字符,需要初始化 否则有乱码
cout << arr <<endl; // BCDEFG
19、// C++ string 到 c string 用到了c语言的strcpy// c_str C++的字符串转成C语言的字符数组// c_str 返回一个 const char *
char c[20] = {0};strcpy(c,s8.c_str());
cout << c << endl; // ABCDEFGH
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s; // 创建一个字符串// 判断是否为空
cout << s.empty() << endl;// 隐式调用构造函数
string s1 = "hello";
cout << s1 << endl;// 显示调用构造函数
string s2("world");
cout << s2 << endl;// == != < > 判断的编码
cout << (s1 == s2) << endl; // 0 不相等
cout << (s1 != s2) << endl; // 1
cout << (s1 < s2) << endl; // 1
cout << (s1 > s2) << endl; // 0// 拷贝构造
string s3(s2);
cout << s3 << endl;// 参数1:char* 原字符串// 参数2:保留的字符数
string s4("ABCDEFG",3);//字符截取:保留的字符数
cout << s4 << endl; // ABC// 参数1:std::string 原字符串// 参数2:不保留的字符数,从头开始
string s5(s2,3); //字符截取:不保留的字符数,剩下的字符数
cout << s5 << endl;// ld // 参数1:字符数量// 参数2:字符内容 char
string s6(5,'a');//打印字符内容
cout << s6 << endl;//aaaaa // 交换
cout << "原字符串s5 = " << s5 <<" "<< "原s6=" << s6 << endl;swap(s5,s6); // aaaaa ld 交换两个字符串内容
cout << "后s5= " << s5 <<" "<< "后s6=" << s6 << endl;// 字符串连接
string s7 = s5 + s6;//字符串拼接
cout << s7 << endl; // aaaaald// 向后追加字符串
s7.append("jiajia");
cout << s7 << endl; // aaaaaldjiajia// 向后追加单字符
s7.push_back('s');
cout << s7 << endl; // aaaaaldjiajias// 插入// 参数1:插入的位置// 参数2:插入的内容
s7.insert(1,"234");
cout << s7 << endl; // a234aaaaldjiajias// 删除字符串// 参数1:起始位置// 参数2:删除字符串的数量
s7.erase(2,5);
cout << s7 << endl; // a2aldjiajias// 替换// 参数1:起始位置// 参数2:被替换的字符数// 参数3:替换的新内容
s7.replace(0,3,"*****"); // *****ldjiajias
cout << s7 << endl;// 清空
s7.clear();
cout << s7.size() << endl; // 0// 直接赋值初始化(隐式调用构造函数)
string s8 = "hahaha";
cout << s8 << endl;
s8 = "ABCDEFGH";
cout << s8 << endl;// 参数1:拷贝的目标// 参数2:拷贝的字符串数量// 参数3:拷贝的起始位置char arr[20] = {0};
s8.copy(arr,6,1);
cout << arr <<endl; // BCDEFG// C++ string 到 c string 用到了c语言的strcpy// c_str C++的字符串转成C语言的字符数组// c_str 返回一个 const char *char c[20] = {0};strcpy(c,s8.c_str());
cout << c << endl; // ABCDEFGHreturn 0;
}