题目描述:罗马数字由七种字符组成,分别为 I、V、X、L、C、D 和 M,对应的数值分别为 1、5、10、50、100、500 和 1000。在一般情况下,小的数字位于大的数字右边,但有特殊情况,如 IV 表示 4,IX 表示 9,XL 表示 40,XC 表示 90,CD 表示 400,CM 表示 900。给定一个罗马数字,需要将其转换成整数。
例如:罗马数字
2写做II,即为两个并列的 1 。12写做XII,即为X+II。27写做XXVII, 即为XX+V+II。
方法1 模拟
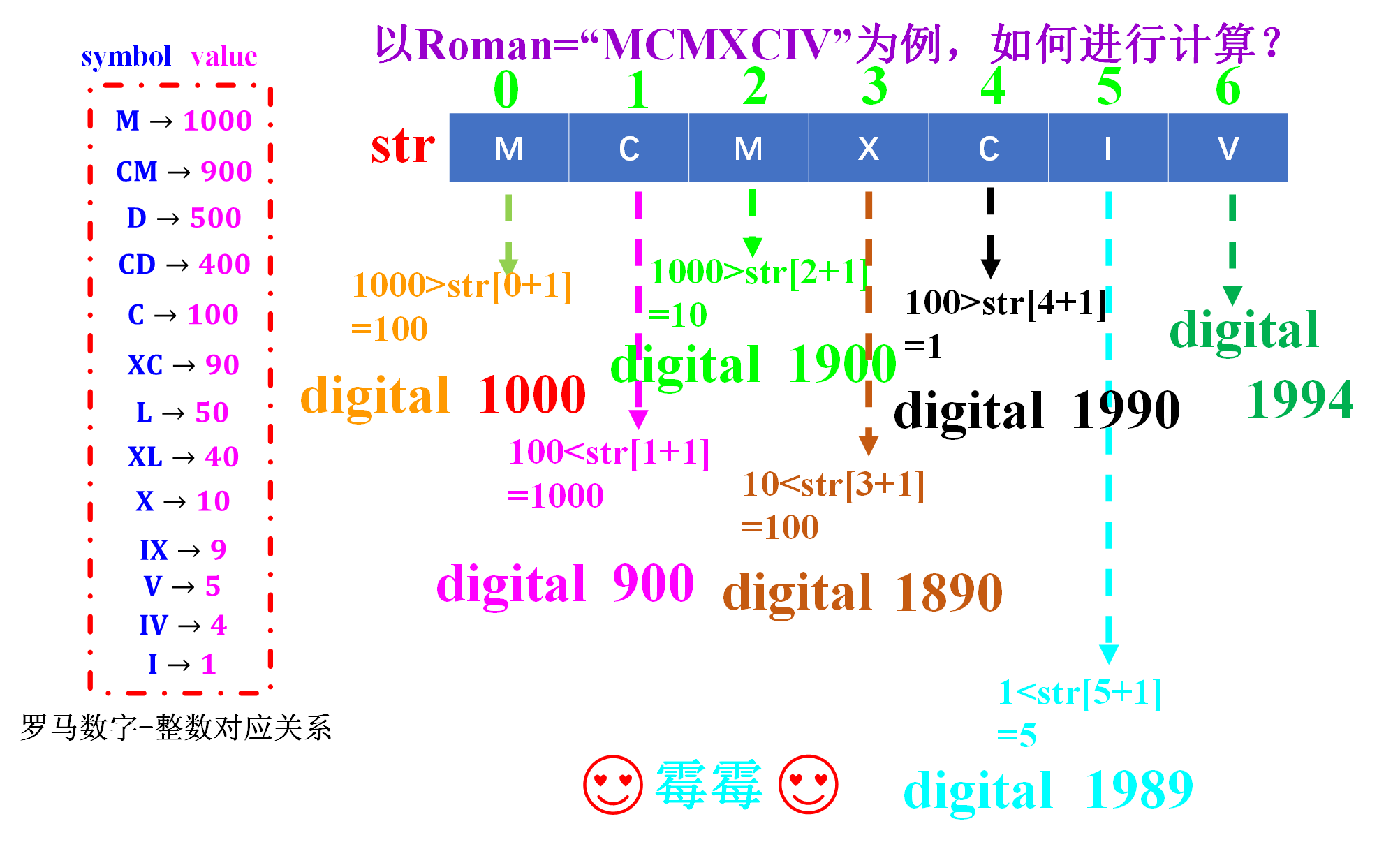
该方法的思想类似于“对号入座”,找到什么罗马符号对应的什么值就写进去,但是最关键的是要搞清楚前后的加减关系,以Roman=“MCMXCIV”为例,第二个位置上的C所对应的值要比第三个位置上的M所对应的值要小,关于前后是进行加法运算还是减法运算,可以看下图的图解,通过图解就可以清楚的知道该如何进行运算。
python完整代码:
class Solution:symbol_values = {"I": 1,"V": 5,"X": 10,"L": 50,"C": 100,"D": 500,"M": 1000}def romanToInt(self, str):digital = 0 # 定义当前数字n = len(str) # 罗马字数字长度for i, ch in enumerate(str):value = Solution.symbol_values[ch]if i < n - 1 and value < Solution.symbol_values[str[i + 1]]:digital -= value # 左边比右边小--->减else:digital += value # 左边比右边大--->加return digital# 设置罗马数字
Roman = "MCMXCIV"
solution = Solution()
result = solution.romanToInt(Roman)
print("罗马数字转整数的结果为: ", result)c++完整代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;class Solution{
private:unordered_map<char, int> symbol_values ={{'I', 1},{'V', 5},{'X', 10},{'L', 50},{'C', 100},{'D', 500},{'M', 1000}};
public:int romanToInt(string str){int digital = 0;int n = str.length();for(int i = 0;i < n;++i){int value = symbol_values[str[i]];if(i < n - 1 && value < symbol_values[str[i + 1]]){digital -= value;} else{digital += value;}}return digital;}
};int main(){string Roman = {"MCMXCIV"};Solution solution;int result = solution.romanToInt(Roman);cout << Roman << " into roman digital " << result << endl;// 输出转换结果return 0;
}java完整代码:
import java.util.HashMap;public class RomanToInt {HashMap<Character, Integer> symbolValues = new HashMap<Character, Integer>() {{put('I', 1);put('V', 5);put('X', 10);put('L', 50);put('C', 100);put('D', 500);put('M', 1000);}};public int romanToInt(String str) {int digital = 0;int n = str.length();for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {int value = this.symbolValues.get(str.charAt(i));if (i < n - 1 && value < this.symbolValues.get(str.charAt(i + 1))) {digital -= value;} else {digital += value;}}return digital;}public static void main(String[] args) {// 创建 RomanToInt 类的实例RomanToInt converter = new RomanToInt();// 设置当前罗马数字String Roman = "MCMXCIV";// 调用方法将罗马数字转换为整数int result = converter.romanToInt(Roman);// 输出转换结果System.out.println("罗马数字转整数为: " + result);}
}方法2 贪心哈希表
该方法其实和上面的方法差不多,也是逐一逐二的遍历哈希表中存储的罗马字符,在根据所对应的值生成我们想要的整数,其中关键的还是怎样分清楚什么时候加,什么时候进行减。
python完整代码:
class Solution:def romanToInt(self, str): # 添加 self 参数roman_dict = {'I': 1, 'V': 5, 'X': 10, 'L': 50, 'C': 100, 'D': 500, 'M': 1000} # 哈希表digital = 0 # 整数结果for i in range(len(str)): # 遍历每个字符# 如果当前字符比下一个字符小,则减去当前字符的值if i < len(str) - 1 and roman_dict[str[i]] < roman_dict[str[i + 1]]:digital -= roman_dict[str[i]] # 当前字符比下一个字符小--->减else:digital += roman_dict[str[i]] # 当前字符比下一个字符大--->加return digital# 示例
Roman = "MCMXCIV"
solution = Solution()
integer_value = solution.romanToInt(Roman)
print(f"罗马数字 {Roman} 转换为整数为: {integer_value}")c++完整代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;class Solution {
public:int romanToInt(string str) {unordered_map<char, int> roman_dict = {{'I', 1}, {'V', 5}, {'X', 10}, {'L', 50}, {'C', 100}, {'D', 500}, {'M', 1000}};int digital = 0;for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); ++i) {// 如果当前字符比下一个字符小,则减去当前字符的值if (i < str.length() - 1 && roman_dict[str[i]] < roman_dict[str[i + 1]]) {digital -= roman_dict[str[i]]; //当前字符比下一个字符小--->减} else {digital += roman_dict[str[i]]; //当前字符比下一个字符大--->加}}return digital;}
};int main() {Solution solution;string Roman = "MCMXCIV";int integer_value = solution.romanToInt(Roman);cout << "Roman digital " << Roman << " into int: " << integer_value << endl;return 0;
}java完整代码:
import java.util.HashMap;
public class RomanToInt1 {public int romanToInt(String str) {HashMap<Character, Integer> romanDict = new HashMap<>();romanDict.put('I', 1);romanDict.put('V', 5);romanDict.put('X', 10);romanDict.put('L', 50);romanDict.put('C', 100);romanDict.put('D', 500);romanDict.put('M', 1000);int digital = 0;for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); ++i) {// 如果当前字符比下一个字符小,则减去当前字符的值// 在Java中,charAt 是一个用于获取字符串中指定位置字符的方法。它是String类的一个成员方法// 语法为char charAt(int index) // 其中,index 是字符串中字符的索引,从0开始计数。返回值是指定索引位置的字符if (i < str.length() - 1 && romanDict.get(str.charAt(i)) < romanDict.get(str.charAt(i + 1))) {digital -= romanDict.get(str.charAt(i));} else {digital += romanDict.get(str.charAt(i));}}return digital;}public static void main(String[] args) {RomanToInt1 solution = new RomanToInt1();String roman = "MCMXCIV";int integerValue = solution.romanToInt(roman);System.out.println("罗马数字 " + roman + " 转换为整数为: " + integerValue);}
}
方法3 if-else方法
if-else方法的思路很简答,主要思想就是从罗马数字的最右边往左遍历,假如输入的都是图(a)中的罗马数字,那么我们根本不用费什么劲,直接划拉一遍,直接M对应1000,I对应1等等等等,然后把得到的对应的整数加一块就皆大欢喜了,但是最重要的问题是输入的罗马数字会出现图(b)所示的情况,那么怎么解决这种情况呢?方法很简单,我们图(a)中所对应的罗马数字的情况中再加上图(b)这种情况,也就是在当前位置再往前一位进行比较,如果出现图(b)的情况时,再补充上,最后全部遍历完后,把所有数字加一块就功成身退了。、
 c++完整代码:
c++完整代码:
// -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
// @Time : 2024/1/4 10:28
// @Author : 长沙有肥鱼
// @FileName: 罗马数字转整数_if.cpp
// @Software: CLion
// @Blog : https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_53660567?spm=1010.2135.3001.5343#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Solution {
public:int romanToInt(std::string str) {int len = str.length();int digital = 0;for (int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) { //从右往左边遍历if (str[i] == 'V') {if (i - 1 >= 0 && str[i - 1] == 'I') {//当V左边的罗马数字为I时 digital--->+4//当V左边的罗马数字不为I时 digital--->+5 因为除I以外的罗马数字都比它大digital += 4;i--;continue;} else {digital += 5;continue;}}if (str[i] == 'X') {//当X左边的罗马数字为X时 digital--->+9//当X左边的罗马数字不为I时 digital--->+10if (i - 1 >= 0 && str[i - 1] == 'I') {digital += 9;i--;continue;} else {digital += 10;continue;}}if (str[i] == 'L') {if (i - 1 >= 0 && str[i - 1] == 'X') {//当L左边的罗马数字为X时 digital--->+40//当L左边的罗马数字不为X时 digital--->+50digital += 40;i--;continue;} else {digital += 50;continue;}}if (str[i] == 'C') {if (i - 1 >= 0 && str[i - 1] == 'X') {//当C左边的罗马数字为X时 digital--->+90//当C左边的罗马数字不为X时 digital--->+100digital += 90;i--;continue;} else {digital += 100;continue;}}if (str[i] == 'D') {if (i - 1 >= 0 && str[i - 1] == 'C') {//当D左边的罗马数字为C时 digital--->+400//当D左边的罗马数字不为C时 digital--->+500digital += 400;i--;continue;} else {digital += 500;continue;}}if (str[i] == 'M') {if (i - 1 >= 0 && str[i - 1] == 'C') {//当M左边的罗马数字为C时 digital--->+900//当M左边的罗马数字不为C时 digital--->+1000digital += 900;i--;continue;} else {digital += 1000;continue;}}if (str[i] == 'I') {//当L左边的罗马数字为I时 digital--->+1digital++;}}return digital;}
};int main() {Solution solution;std::string roman = "MCMXCIV";int integerValue = solution.romanToInt(roman);std::cout << "Roman digital " << roman << " into int: " << integerValue << std::endl;return 0;
}python完整代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2024/1/4 10:22
# @Author : 长沙有肥鱼
# @FileName: 罗马数字转整数_if_else.py
# @Software: PyCharm
# @Blog : https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_53660567?spm=1010.2135.3001.5343
class Solution:def romanToInt(self, str):length = len(str)digital = 0i = length - 1while i >= 0:if str[i] == 'V':if i - 1 >= 0 and str[i - 1] == 'I':digital += 4i -= 1else:digital += 5i -= 1elif str[i] == 'X':if i - 1 >= 0 and str[i - 1] == 'I':digital += 9i -= 1else:digital += 10i -= 1elif str[i] == 'L':if i - 1 >= 0 and str[i - 1] == 'X':digital += 40i -= 1else:digital += 50i -= 1elif str[i] == 'C':if i - 1 >= 0 and str[i - 1] == 'X':digital += 90i -= 1else:digital += 100i -= 1elif str[i] == 'D':if i - 1 >= 0 and str[i - 1] == 'C':digital += 400i -= 1else:digital += 500i -= 1elif str[i] == 'M':if i - 1 >= 0 and str[i - 1] == 'C':digital += 900i -= 1else:digital += 1000i -= 1elif str[i] == 'I':digital += 1return digital# 示例
solution = Solution()
roman_numeral = "MCMXCIV"
integer_value = solution.romanToInt(roman_numeral)
print(f"罗马数字 {roman_numeral} 转换为整数为: {integer_value}")Java完整代码:
public class RomanToInt2 {public int romanToInt(String str) {int len = str.length();int digital = 0;// 如果当前字符比下一个字符小,则减去当前字符的值// 在Java中,charAt 是一个用于获取字符串中指定位置字符的方法。它是String类的一个成员方法// 语法为char charAt(int index)// 其中,index 是字符串中字符的索引,从0开始计数。返回值是指定索引位置的字符for(int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {if(str.charAt(i) == 'V') {if((i - 1 >= 0) && (str.charAt(i - 1) == 'I')){digital += 4;i--;continue;}else {digital+=5;continue;}}if(str.charAt(i) == 'X') {if((i - 1 >= 0) && (str.charAt(i - 1) == 'I')){digital += 9;i--;continue;}else {digital += 10;continue;}}if(str.charAt(i) == 'L') {if((i - 1 >= 0) && (str.charAt(i - 1) == 'X')){digital += 40;i--;continue;}else {digital += 50;continue;}}if(str.charAt(i) == 'C') {if((i - 1 >= 0) && (str.charAt(i - 1) == 'X')){digital += 90;i--;continue;}else {digital += 100;continue;}}if(str.charAt(i) == 'D') {if((i - 1 >= 0) && (str.charAt(i - 1) == 'C')){digital += 400;i--;continue;}else {digital += 500;continue;}}if(str.charAt(i) == 'M') {if((i - 1 >= 0) && (str.charAt(i - 1) == 'C')){digital += 900;i--;continue;}else {digital += 1000;continue;}}if(str.charAt(i) == 'I') {digital++;}}return digital;}public static void main(String[] args) {RomanToInt2 solution = new RomanToInt2();String roman = "MCMXCIV";int integerValue = solution.romanToInt(roman);System.out.println("罗马数字 " + roman + " 转换为整数为: " + integerValue);}
}