一. ioc
1.1 bd的收集
1.1.1 基于xml

-
入口 AbstracApplicationtContext.refresh -> AbstracApplicationtContext.obtainFreshBeanFactory() -> 调用到子类 AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext.loadBeanDefinitions() -> AbstractXmlApplicationContext.loadBeanDefinitions()
对于spring来说,第一步要收集到容器中bd,但是收集的方式很多,那基于xml的收集最终就跑到子类xmlApplicationContext通过xml的方式来收集bd
-
AbstractXmlApplicationContext.loadBeanDefinitions() 使用委托模式,创建了XmlBeanDefinitionReader来完成xml到bd的转换
-
XmlBeanDefinitionReader在解析bd的时候,先把xml通过sax解析出来,然后通过委托模式,创建了DocumentBeanDefinitionReader,完成Document到bd的转换
-
遍历每个element,然后又通过委托模式,创建了BeanDefinitionParseDelegate来完成每个elemement转换成bd
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
以上是通过bean标签收集bd,往下是通过component-scan来搜集bd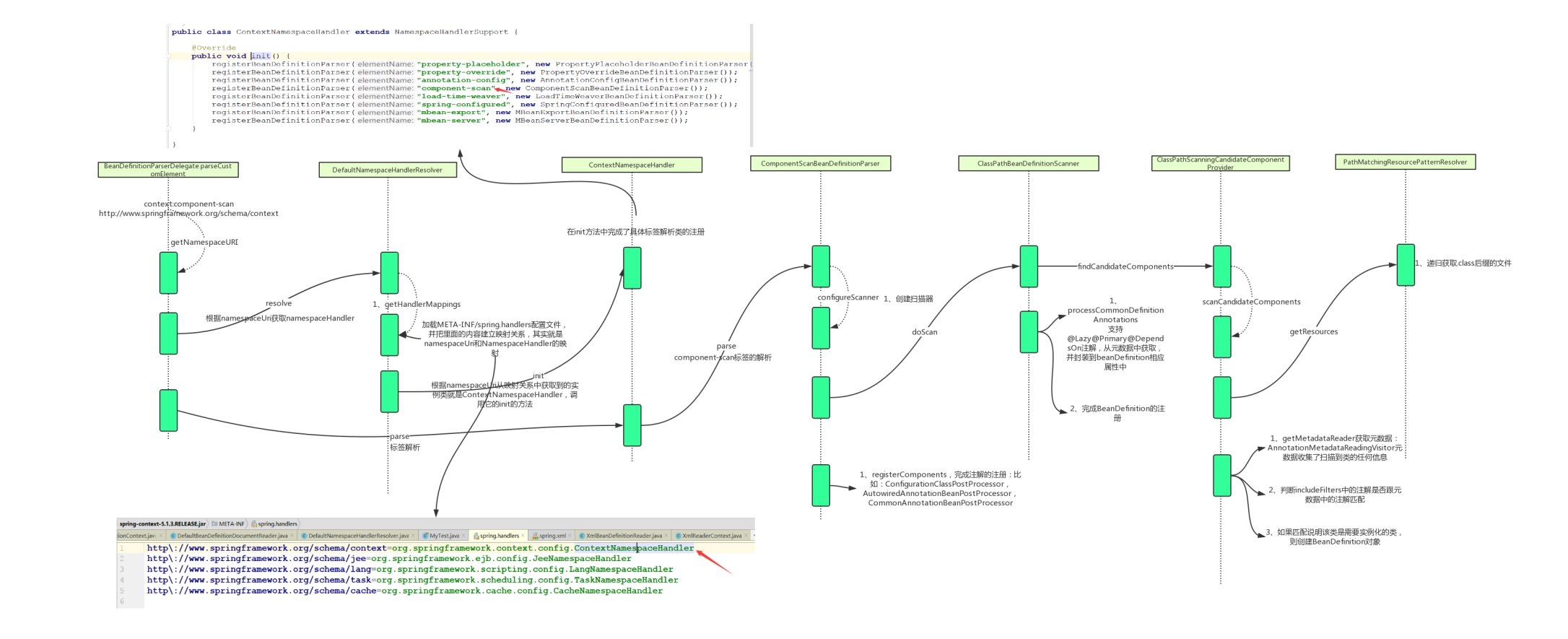
- 分为2种element解析,一种是默认便签解析,比如 那就直接把它解析成bd,然后注册到容器中,另外一种自定义标签解析,比如<context: component-scan />,第一步,通过context命名空间找到对应NamespaceHandler类,然后从NamespaceHandler类中获取component-scan的解析类ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser,调用ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser.parse来解析
- parse解析过程:创建了ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner扫描类,扫描.class文件,然后判断上面是否有component注解,如果有的话,创建bd,并且把bd注册到容器中
- 这里有一步非常重要的操作,将AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,ConfigurationClassPostProcessor,
CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 注册到容器中
1.1.2 基于注解 @ComponentScan& @Component
1.2 实例化
1.2.1 在实例化之前的2个操作
- invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory):完成对BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor调用、对BeanFactoryPostProcessor调用,增加了运行期干预的手段
- registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory):将实现了BeanPostProcessor的db实例化,比如AutoWiredProcessor、CommonPostProcessor、ConfigurationPostProcessor
1.2.2 实例化
- 入口是AbstracApplicationtContext.finishBeanFactoryInitialization
-> DefaultListableBeanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons 遍历beanNames 这个list,然后
-> 调到父类AbstractBeanFactory的getBean
->AbstractBeanFactory的doGetBean
- 从缓存中获取实例,先从一级缓存拿实例,如果拿不到从二级缓存拿,如果还拿不到,从三级缓存拿,如果拿到,将对象从三级升级到二级缓存,并且从三级中删除
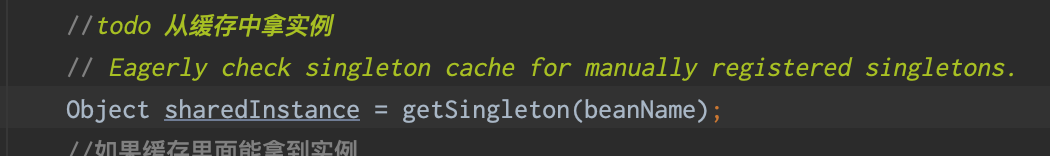
- 如果从三级缓存还拿不到,那确实要新建了。将beanName放到一个set中,标识我正在创建它。然后开始真正的创建对象。AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.create开始真正创建对象。
- 通过beanName来获取bd的class,然后反射调用获取class对象
- 通过determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors方法来获取当前class对象上面有@autowire的有参构造函数,如果有的话,那就使用构造函数实例化,同时会触发有参构造函数的getBean,最终返回实例化对象
- 如果存在有参构造函数的话,上面已经返回了,接下来就是无参构造函数实例化,最终返回一个属性为空的实例化对象
--------------这时候大部分会生成一个光秃秃的实例化对象,通过无参函数返回,等待依赖注入------
在依赖注入之前,CommonPostProcessor收集了@PostContruct、@preDestry、@Resource
AutowiredPostProcessor收集了@Autowired、@value
- 如果支持提前暴露的话,会把这个光秃秃的对象先放到三级缓存中
- AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory. populateBean,开始di。通过循环调用beanPostProcessor.postProcessProperties最终调用 AutowirePostProcessor触发属性的getBean操作
- ioc和di全部做完之后,会调用AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory. initializeBean。分别完成 @PostContruct方法调用、afterPropertiesSet等方法调用
- 最后判断当前类有没有切面,如果有的话,要生存动态代理

2. aop
2.1 动态代理
简单复习一下jdk动态代理的知识
public class ServiceFactory {public static Object getService(Object service){//这里返回的是代理类对象return new TransactionInvocationHandler(service).getProxy(); }
}import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;public class TransactionInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler{private Object target;public TransactionInvocationHandler(Object target){this.target = target;}public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {SqlSession session = null;Object obj = null;try{session = SqlSessionUtil.getSqlSession();obj = method.invoke(target, args);session.commit();}catch(Exception e){session.rollback();e.printStackTrace();//处理的是什么异常,继续往上抛什么异常throw e.getCause();}finally{SqlSessionUtil.myClose(session);}return obj;}public Object getProxy(){return Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.getClass().getClassLoader(), target.getClass().getInterfaces(),this);}
}- 一个被代理类,一个InvocationHandler实现类,来完成对被代理类的增强操作
- 通过一个工厂来获取代理类,传一个被代理类进去,得到动态代理类。
2.2 aop流程
@Aspect
public class AspectAnnotation {@Pointcut("execution(public * com.xiangxue.service.*.*(..))")public void pc1() {}@Around("pc1()")public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();System.out.println("==============AspectAnnotation around前置通知=========");Object result = joinPoint.proceed();System.out.println("==============AspectAnnotation around后置通知=========");return result;}
}

2.2.1 判断这个对象需不需要被代理
- 寻找切面:寻找类上有@Aspect的类,然后遍历方法上不是@PointCut注解的方法(也就是说遍历@before、@after这些),然后创建AspectJAnnotation对象来获取@Before、@After这些注解的属性值,接下来根据AspectJAnnotation对象创建出AspectJExpressionPointcut对象,里面封装了从AspectJAnnotation获取的pointcut表达式。根据遍历的@before、@after这些methd + **AspectJExpressionPointcut ** 就可以生成切面
- 判断当前的bean是否要代理:拿到切面和类,然后做一层匹配,看当前的bean对象要不要被代理。
- 如果要,就进入下面的创建动态代理对象步骤
2.2.2 创建动态代理对象
- 创建一个ProxyFactory代理工厂,把切面、被代理方式(cglib、jdk)、被代理类传进去
- 第一步通过ProxyFactory代理工厂来生成实现了InvocationHandler类的JdkDynamicAopProxy代理类,同时会把ProxyFactory传进去,也就是动态代理会持有 ProxyFactory => 持有了增强
- 第二步通过代理类来获取动态代理对象,具体调用就是**Proxy.newProxyInstance()**方法
2.2.4 动态代理对象被调用
链式调用
会调用到JdkDynamicAopProxy.invoke方法,会把所以增强Advice拿出来,然后进行链式调用
3. 事务
3.1 加入事务切面
- @EnableTransactionManager注解注入了两个bean:
1、AutoProxyRegistrar 2、ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration
AutoProxyRegistrar : 注册了一个InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator的bean, 这个类继承了 AbstractAdvsorAutoProxyCreator,这个类的作用就是开始事务的动态代理。
因为是否要给bean创建代理,就是这里是入口,会走到AbstractAdvsorAutoProxyCreator.postProcessAfterInitialization(这是个beanPostProcessor),然后就是看具体的子类是否要给这个类创建代理对象,比如想要使用@Aspectj,就需要引入AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator,来支持,不然没有AbstractAdvsorAutoProxyCreator的实现类,就走不进去。所以说,有@Transaction,也需要引入AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator的实现类-InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator。
ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration:可以定义了三个bean
- BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor: 一个PointAdvisor
- AnnotitionTransactionAttributeSource: 就是PointCut
- TransactionInterceptor: 就是代理逻辑Advice
小结:就是ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration会向spring容器中添加一个 事物Advisor,然后在匹配的时候,就判断当前bean有没有@Transaction或者某个方法有没有@transaction,如果匹配就需要生成代理对象
3.2 事务处理流程
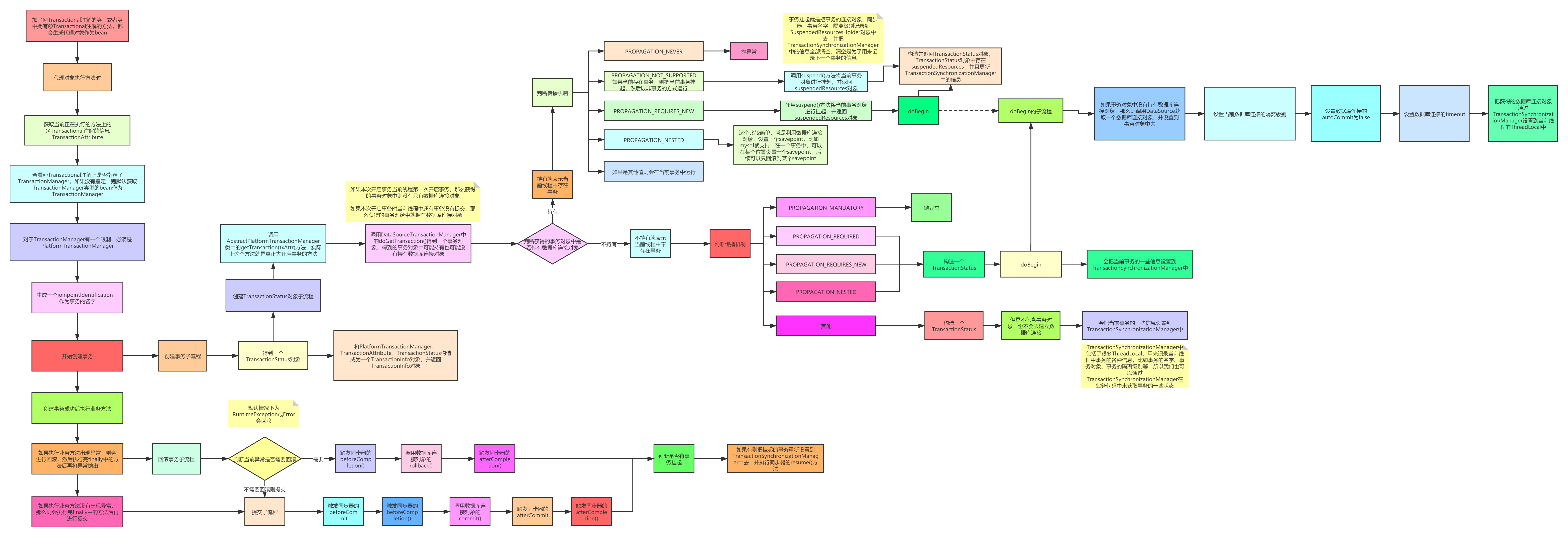
3.2.1 创建事务流程
- TransactionAttribute对象:拿到@Transaction 上面的注解信息,生成TransactionAttribute对象
- TransactionManager对象:看@Transaction有没有指定TransactionManager,如果没有指定,默认生成TransactionManager类型bean 作为TransactionManager
- TransactionStatus对象:调用AbstractPlatformTransactionManager.getTransaction()方法来生成
- 看当前线程的事物对象有没有数据库连接对象,如果有,就根据传播级别,没有就新建
- 如果已经存在事务对象,看传播级别,是抛异常、新建一个事务、将原来事务挂起再新建一个,假设是新建一个,设置隔离级别、autoCommit=false、数据库连接的timeout
- 把数据库连接对象 放到ThreadLocal中
- TransactionInfo对象:最后把这些组装成 TransacitonInfo返回
3.2.2 执行业务方法
- 如果业务方法执行有异常,则会进行回滚,最后在finally里面把异常抛出
- 也就说如果存在嵌套事务,里面那个抛出异常,它会先回滚,然后抛出异常。同时看有没有事务被挂起,如果有就resume。
4. mvc
4.1 Servlet
4.2 mvc 初始化
<web-app><listener><listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class></listener><context-param><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><param-value>/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml</param-value></context-param><servlet><servlet-name>app</servlet-name><servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class><init-param><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value></init-param><load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup></servlet><servlet-mapping><servlet-name>app</servlet-name><url-pattern>/*</url-pattern></servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
Servelt容器在启动的时候留了一些钩子来触发自定义的东西, mvc的初始化也利用了这些钩子:Listener。ContextLoadListener:
ContextLoadListener:通过实现了ServletContextListener接口,将spring容器融入到web容器中。
web容器:web容器通过ServeltConfig来保持xml配置,通过ServletContext来维护一个web应用
spring容器:接受web容器启动的通知,开始自身配置的解析,然后创建bean实例,并且通过WebApplicaitonContext来存放spring项目主容器的相关bean。ContextLoadListener将Spring容器(webApplicaitonContext)作为ServletContext的attribute,key为Root_Web_Application_Context_Attribte, 保存到ServeltContext中,Spring容器和Web容器可以通过ServletContext来交互。
- 父容器初始化:
ContextLoaderListener.contextInitlized() => initWebApplicationContext()
- Web容器初始化触发监听:web容器初始化调用到ContextLoadListener.contextInitlized
- Spring父容器初始化:看WebApplicationContext有没有创建过,如果创建了就报错,如果没有就创建一个Web ApplicationContext,调用configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) 从ServletContext拿出配置application.xml,最终调用wac.refresh容器初始化
- 将Spring父容器设置到Web容器中:servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE
//监听servlet容器的启动
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());//在父类ContextLoader中实现
}
//创建和初始化spring主容器对应的WebApplicationContext对象实例并调用refresh方法完成从contextConfigLocation指定的配置中,加载BeanDefinitions和创建bean实例
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {//判断是否已经有Root WebApplicationContext,已经有则抛出异常if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");}servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");}long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();try {if (this.context == null) {//创建上下文对象 XmlWebApplicationContext(静态方法中从ContextLoader.properties文件中读取) 并赋值给全局变量contextthis.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);}if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;if (!cwac.isActive()) {if (cwac.getParent() == null) {// 设置父容器(如果有)ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);cwac.setParent(parent);}//核心方法,完成配置加载,BeanDefinition定义和bean对象创建configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);}}//ioc容器上下文设置到servlet上下文servletContextservletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {currentContext = this.context;}else if (ccl != null) {//将当前类加载器和上下文绑定currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);}if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext initialized in " + elapsedTime + " ms");}return this.context;}catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);throw ex;}
}protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) {if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {String idParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_ID_PARAM);if (idParam != null) {wac.setId(idParam);}else {wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getContextPath()));}}wac.setServletContext(sc);//获取web.xml中的配置contextConfigLocationString configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM);if (configLocationParam != null) {wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam);}ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(sc, null);}// 使用ApplicationContextInitializer对ApplicationContext进行初始化customizeContext(sc, wac);//ApplicationContext的核心方法wac.refresh();
}
- 子容器初始化:DispatcherServlet
<servlet><servlet-name>app</servlet-name><servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class><init-param><param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name><param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value></init-param><load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet><servlet-mapping><servlet-name>app</servlet-name><url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
继承关系:
public abstract class HttpServletBean extends HttpServlet implements EnvironmentCapable, EnvironmentAware {
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
HttpServletBean: 继承了HttpServlet,实现了EnvironmentAware(注入Environment对象)和EnvironmentCapable(访问Environment对象)接口,其中Environment主要从类路径的属性文件,运行参数,@PropertySource注解等获取应用的相关属性值,以提供给spring容器相关组件访问,或者写入属性到Environment来给其他组件访问。HttpServletBean的主要作用就是将于该servlet相关的init-param,封装成bean属性,然后保存到Environment当中,从而可以在spring容器中被其他bean访问。
FrameworkServlet:因为DispatcherServlet通常包含一个独立的WebApplication,所以FrameworkServlet就是完成DispatcherServlet所绑定的WebApplicationContext的创建和管理工作。???从contextConfigLocation获取xml或者WebApplicationInitizlizer配置信息,根据contextClass创建WebApplicaitonContext,获取Application ContextInitizlizer来对WebApplicaitonContext来初始化 这里需要再研究一下
DispatcherServlet:从FrameworkServlet中获取WebApplicaitonContext,然后从WebApplicationContext中获取DispatcherServlet相关功能子组件bean。
DispatcherServlet其实就是一个Servlet,生命周期(init、service、destory),DisPatcherServlet 初始化过程
- HttpServletBean的init():
- 获取web.xml配置DispatcherServlet的初始化参数,存放到一个参数容器ServletConfigPropertyValues
- 根据传进来this创建BeanWrapper,本质上它就是DispatchServlet
- 通过bw.setPropertyValue,将参数设置进去
- 掉到子类FrameworkServlet的initServletBean
//DispatcherServlet第一次加载时调用init方法
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {...try {//加载web.xml文件中的servlet标签中的init-param,其中含有springMVC的配置文件的名字和路径若没有,则默认为(servlet-name)-servlet.xml,默认路径为WEF—INF下,设置到DispatcherServlet中PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);//创建BeanWrapper实例,为DispatcherServlet设置属性BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));initBeanWrapper(bw);//把init-param中的参数设置到DispatcherServlet里面去bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);}catch (BeansException ex) {logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);throw ex;}//调用子类(FrameworkServlet)进行初始化// 模版方法,此方法在HttpServletBean本身是空的,但是因为调用方法的对象是DispatcherServlet,所以优先在DispatcherServlet找,找不到再去父类找,最后在FrameworkServlet找到initServletBean();if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Servlet '" + getServletName() + "' configured successfully");}
}
- FrameworkSevlet的initServletBean()->initWebApplicationContext():
- 创建Spring mvc的容器,比父容器关联
- 把创建出来的mvc容器放到ServletContext
- 模版方法调用子类 DispatcherServlet的onRefersh方法
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {...try {//创建springmvc的ioc容器实例,初始化WebApplicationContext并调用子类(DispatcherServlet)的onRefresh(wac)方法this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();initFrameworkServlet();}...
}protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {//通过ServletContext获得spring容器,获取root WebApplicationContext,即web.xml中配置的listener(ContextLoaderListener)WebApplicationContext rootContext =WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());//定义springMVC容器wacWebApplicationContext wac = null;//判断容器是否由编程式传入(即是否已经存在了容器实例),存在的话直接赋值给wac,给springMVC容器设置父容器//最后调用刷新函数configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac),作用是把springMVC的配置信息加载到容器中去(之前已经将配置信息的路径设置到了bw中)if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {// context上下文在构造时注入wac = this.webApplicationContext;if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;if (!cwac.isActive()) {// context没有被refreshed,设置父context、设置应用context id等服务if (cwac.getParent() == null) {//将spring ioc设置为springMVC ioc的父容器cwac.setParent(rootContext);}configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);}}}if (wac == null) {// 在ServletContext中寻找是否有springMVC容器,初次运行是没有的,springMVC初始化完毕ServletContext就有了springMVC容器wac = findWebApplicationContext();}//当wac既没有没被编程式注册到容器中的,也没在ServletContext找得到,此时就要新建一个springMVC容器if (wac == null) {// 创建springMVC容器wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);//会加载并触发监听 执行onRefresh,refreshEventReceived设置为true}if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {//如果监听器未接收到事件//到这里mvc的容器已经创建完毕,接着才是真正调用DispatcherServlet的初始化方法onRefresh(wac),模板模式synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {onRefresh(wac);}}if (this.publishContext) {//将springMVC容器存放到ServletContext中去,方便下次取出来String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);}return wac;
}protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) {Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass();if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {this.logger.debug("Servlet with name '" + getServletName() +"' will try to create custom WebApplicationContext context of class '" +contextClass.getName() + "'" + ", using parent context [" + parent + "]");}if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {throw new ApplicationContextException("Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() +"': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() +"] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext");}//实例化空白的ioc容器ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);//给容器设置环境wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());//给容器设置父容器(就是spring容器),两个ioc容器关联在一起了wac.setParent(parent);//给容器加载springMVC的配置信息,之前已经通过bw将配置文件路径写入到了DispatcherServlet中wac.setConfigLocation(getContextConfigLocation());//上面提到过这方法,刷新容器,根据springMVC配置文件完成初始化操作,此时springMVC容器创建完成configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);return wac;
}protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {if (this.contextId != null) {wac.setId(this.contextId);}else {wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(getServletContext().getContextPath()) + '/' + getServletName());}}wac.setServletContext(getServletContext());wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig());wac.setNamespace(getNamespace());wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(getServletContext(), getServletConfig());}postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac);applyInitializers(wac);wac.refresh();//registerListeners会注册ContextRefreshListener,finishRefresh中发布事件(publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this)))并触发监听逻辑,调用DispatcherServlet的onRefresh
}
- DispatcherServlet的onRresh()->initStrategies():
- 获取ApplicationContext
- 初始化九大组件
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {initStrategies(context);
}//初始化九大核心组件
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {initMultipartResolver(context);//文件上传解析initLocaleResolver(context);//本地解析initThemeResolver(context);//主题解析initHandlerMappings(context);//url请求映射initHandlerAdapters(context);//初始化真正调用controloler方法的类initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);//异常解析initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);initViewResolvers(context);//视图解析initFlashMapManager(context);
}
4.3 mvc处理请求
HttpServlet.service / doGet /doPost -> FrameworkServlet.service / doGet /doPost ->Framwork
servlet.processRequest -> DispatcherServlet.doService
- HttpServlet接入请求,转发到FrameworkServlet处理:
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)throws ServletException, IOException {String method = req.getMethod();if (method.equals(METHOD_GET)) {long lastModified = getLastModified(req);if (lastModified == -1) {// servlet doesn't support if-modified-since, no reason// to go through further expensive logicdoGet(req, resp); ...doPost...doHead}}
}
- FrameServlet将请求做了一些处理,最终全部转发到Dispatcher.doServie:
protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)throws ServletException, IOException {processRequest(request, response);
} protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)throws ServletException, IOException {long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();Throwable failureCause = null;//previousLocaleContext获取和当前线程相关的LocaleContext,根据已有请求构造一个新的和当前线程相关的LocaleContextLocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request);//previousAttributes获取和当前线程绑定的RequestAttributesRequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();//为已有请求构造新的ServletRequestAttributes,加入预绑定属性ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);//异步请求处理asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor());//initContextHolders让新构造的RequestAttributes和ServletRequestAttributes和当前线程绑定,加入到ThreadLocal,完成绑定initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);try {//抽象方法doService由FrameworkServlet子类DispatcherServlet重写doService(request, response);}catch (ServletException | IOException ex) {failureCause = ex;throw ex;}catch (Throwable ex) {failureCause = ex;throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);}finally {//解除RequestAttributes,ServletRequestAttributes和当前线程的绑定resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);if (requestAttributes != null) {requestAttributes.requestCompleted();}logResult(request, response, failureCause, asyncManager);//注册监听事件ServletRequestHandledEvent,在调用上下文的时候产生EventpublishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);}
}
- DispatcherServlet.doService(重点): doService -> doDispatcher -> processDispatchResult
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {logRequest(request);// Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<>();//保存request域中的数据,存一份快照Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));}}}//设置web应用上下文request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());//国际化本地request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);//样式request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);//设置样式资源request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());//请求刷新时保存属性if (this.flashMapManager != null) {FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);if (inputFlashMap != null) {request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));}//Flash attributes 在对请求的重定向生效之前被临时存储(通常是在session)中,并且在重定向之后被立即移除request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());//FlashMap 被用来管理 flash attributes 而 FlashMapManager 则被用来存储,获取和管理 FlashMap 实体request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);}try {doDispatch(request, response);//核心方法}finally {if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.if (attributesSnapshot != null) {restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);//将快照覆盖回去}}}
}protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;//异步管理WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);try {ModelAndView mv = null;Exception dispatchException = null;try {//文件上传processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);//todo 这个方法很重要,重点看// Determine handler for the current request.mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);if (mappedHandler == null) {noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);return;}//获取跟HandlerMethod匹配的HandlerAdapter对象// Determine handler adapter for the current request.HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.String method = request.getMethod();boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {return;}}//前置过滤器,如果为false则直接返回if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {return;}//调用到Controller具体方法,核心方法调用,重点看看// Actually invoke the handler.mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {return;}applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);//中置过滤器mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);}catch (Exception ex) {dispatchException = ex;}catch (Throwable err) {// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);}//视图渲染processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);}catch (Exception ex) {triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);}catch (Throwable err) {triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));}finally {if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletionif (mappedHandler != null) {mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);}}else {// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.if (multipartRequestParsed) {cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);}}}
}
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,@Nullable HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, @Nullable ModelAndView mv,@Nullable Exception exception) throws Exception {boolean errorView = false;//异常处理if (exception != null) {//ModelAndViewDefiningException类型,会携带对应的ModelAndViewif (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) {logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception);mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView();}else {//由对应的处理器handler进行异常处理,返回ModelAndView。其中使用了HandlerExceptionResolver。Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception);errorView = (mv != null);}}....
protected ModelAndView processHandlerException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,@Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {// Success and error responses may use different content typesrequest.removeAttribute(HandlerMapping.PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE);// Check registered HandlerExceptionResolvers...ModelAndView exMv = null;if (this.handlerExceptionResolvers != null) {for (HandlerExceptionResolver resolver : this.handlerExceptionResolvers) {exMv = resolver.resolveException(request, response, handler, ex);if (exMv != null) {break;}}}......4.4 DispatcherServlet处理请求流程图:

- 请求发送到DispatchServlet
- DispatchServlet将request传给HandlerMapping(可以理解为map<request,handler >),HandlerMapping返回 HandlerExectionChain(Handler+HandlerInterceptoer拦截器),比如RequestMappingHandlerMapping在初始化的时候,就通过@RequestMapping和@controller把方法和对应处理的路径Url放到map中,所以request请求来的时候,就知道用哪个方法+有没有interceptor, BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping在初始化的时候,把 Bean名称和 bean映射起来
public class WelcomeController implements Controller {@Overridepublic ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView("welcome");mav.addObject("now", LocalDateTime.now().toString());String name = request.getParameter("name");mav.addObject("name", name == null ? "你是?" : name);return mav;}
}@Configuration
public class ControllerBeanConfig {/*** 这里定义一个 web controller bean, 注意 :* 1. 该 bean 实现了接口 Controller,* 2. 该 bean 没有使用注解 @Controller,* (如果使用了注解@Controller,就会被RequestMappingHandlerMapping接管,而不是由BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping处理)* 3. 映射到匹配 welcome* 的url* @return*/@Bean(name = "/welcome*")public WelcomeController beanWelcomeController() {return new WelcomeController();}
}
接下来访问http://localhost:8080/welcome,或者http://localhost:8080/welcome.html之类任何匹配/welcome*的地址,都会跳出 “你是?”
- 在这里我可能拿到的是不同的Handler对象,可能是RequestMappingHandler这种、或者是BeanNameUrlHandler这种,那我是不是要写 if else, spring 设计就通过适配器模式,去包装了Handler,统一对外提供 hande方法
public class AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter {// 只处理HandlerMethod 类型的处理器。抽象方法supportsInternal默认返回true// 是留出的钩子可以给你自己扩展的@Overridepublic final boolean supports(Object handler) {return (handler instanceof HandlerMethod && supportsInternal((HandlerMethod) handler));}@Overridepublic final ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)throws Exception {// 抽象方法交给子类handleInternal去实现return handleInternal(request, response, (HandlerMethod) handler);}
}
- 所以我主逻辑只要通过handler拿到适配器,然后统一调用 Adapter.handle方法就行
- 适配器再通过Handler调用,拿到ModelAndView
- 最终通过视图解析器 解析ModelAndView拿到真正的视图
4.5 HandlerMapping
SpringMVC中HandlerMapping和HandlerAdapter详解(适配器模式)_止步前行的博客-CSDN博客_handlermapping和handleradapter
帮助理解 HandlerMapping与HandlerAdapters
//多种Controller实现
public interface Controller {}// 注意这里每个实现,都用了不同的方法名, 如果都用一样的话,就可以放到接口中了
class HttpController implements Controller {public void doHttpHandler() {System.out.println("http...");}
}class SimpleController implements Controller {public void doSimplerHandler() {System.out.println("simple...");}
}class AnnotationController implements Controller {public void doAnnotationHandler() {System.out.println("annotation...");}
}// 定义一个Adapter接口
public interface HandlerAdapter {public boolean supports(Object handler);public void handle(Object handler);
}// 多种适配器类
class SimpleHandlerAdapter implements HandlerAdapter {public void handle(Object handler) {((SimpleController) handler).doSimplerHandler();}public boolean supports(Object handler) {return (handler instanceof SimpleController);}
}class HttpHandlerAdapter implements HandlerAdapter {public void handle(Object handler) {((HttpController) handler).doHttpHandler();}public boolean supports(Object handler) {return (handler instanceof HttpController);}
}class AnnotationHandlerAdapter implements HandlerAdapter {public void handle(Object handler) {((AnnotationController) handler).doAnnotationHandler();}public boolean supports(Object handler) {return (handler instanceof AnnotationController);}
}public class DispatchServlet {public static List<HandlerAdapter> handlerAdapters = new ArrayList<HandlerAdapter>();public DispatchServlet() {handlerAdapters.add(new AnnotationHandlerAdapter());handlerAdapters.add(new HttpHandlerAdapter());handlerAdapters.add(new SimpleHandlerAdapter());}public void doDispatch() {// 此处模拟SpringMVC从request取handler的对象,// 适配器可以获取到希望的ControllerHttpController controller = new HttpController();// AnnotationController controller = new AnnotationController();//SimpleController controller = new SimpleController();// 得到对应适配器HandlerAdapter adapter = getHandler(controller);// 通过适配器执行对应的controller对应方法adapter.handle(controller);}public HandlerAdapter getHandler(Controller controller) {//遍历:根据得到的controller(handler), 返回对应适配器for (HandlerAdapter adapter : this.handlerAdapters) {if (adapter.supports(controller)) {return adapter;}}return null;}public static void main(String[] args) {new DispatchServlet().doDispatch(); // http...}
}