案例一:买飞机票
题目
用户购买机票时,机票原价会按照淡季、旺季,头等舱还是经济舱的情况进行相应的优惠,优惠方案如下:5-10月为旺季,头等舱9折,经济舱8.5折。11月到来年4月为淡季,头等舱7折,经济舱6.5折请开发程序计算出用户当前机票的优惠价。
分析
本节重点是对方法的练习,因此需要确定
1、方法是否需要接收数据?
2、方法是否需要返回数据
3、方法逻辑结构如何写呢?
第一个问题:我们需要接收机票原价、当前月份和仓位类型。
第二个问题:需要返回计算出的机票优惠价。
第三个问题:用if和switch组合即可
代码
public class Example_03 {public static void main(String[] args) {int month = 5;double money = 547;String type = "头等舱";money = calPrice(money, month, type);System.out.println("飞机票的优惠价为:" + money);}private static double calPrice(double money, int month, String type) {// 旺季if (month <= 10 && month >= 5) {switch (type) {case "头等舱":money = money * 0.9;break;case "经济舱":money = money * 0.85;break;}} else {// 淡季switch (type) {case "头等舱":money = money * 0.7;break;case "经济舱":money = money * 0.65;break;}}return money;}
}案例二:生成验证码
题目
在登陆时候一般需要填写验证码,验证码正确后才能进行登录,验证码一般包含数字和大小写字母。

分析
输入:生成验证码个数
输出:字符串类型的验证码
代码
import java.util.Random;public class Example_03 {public static void main(String[] args) {int len = 4;String code = getCode(len);System.out.println("生成的验证码为:" + code);}private static String getCode(int len) {Random r = new Random();String code = "";for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {int type = r.nextInt(3);switch (type){case 0:code += r.nextInt(10);break;case 1:// A - Z : 65 + 25code += (char) (r.nextInt(25) + 65);break;case 2:// a - z : 97 + 25code += (char) (r.nextInt(25) + 97);break;}}return code;}
}
案例三:评委打分
题目
某歌唱比赛,需要开发一个系统:可以录入 � 个评委的打分,录入完毕,去掉最大值和最小值后计算平均分作为选手得分。
分析
1、评委的分数是后期录入的,一开始不知道具体分数,因此需要定义一个动态数组。 2、由于分数是手动录入的,因此需要使用Scanner读取评分。
代码
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
import java.util.Scanner;public class Example_03 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("输入评委的人数:");int n = sc.nextInt();double[] scores = new double[n];for (int i = 0; i < scores.length; i++) {System.out.println("请输入第" + (i + 1) + "个评委的评分:");scores[i] = sc.nextDouble();}getScore(scores);}private static void getScore(double[] scores) {double max = scores[0];int indexMax = 0;for (int i = 1; i < scores.length; i++) {if (scores[i] > max ){max = scores[i];indexMax = i;}}double min = scores[0];int indexMin = 0;for (int i = 1; i < scores.length; i++) {if (scores[i] < min ){min = scores[i];indexMin = i;}}int sum = 0;for (int i = 0; i < scores.length; i++) {if (i == indexMax || i == indexMin) {continue;}sum += scores[i];}DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("#.00");System.out.println(df.format(sum/(scores.length-2)));
// return df.format(sum/(scores.length-2));}}案例四:发红包
案例
过年微信群里面发起了抢红包活动,分别有:9、666、188、520、99999五个红包。请模拟其他人来抽奖,按照先来先得,随机抽取,抽完即止,注意:一个红包只能被抽一次,先抽或后抽哪一个红包是随机的,示例如下(不一定是下面的顺序)
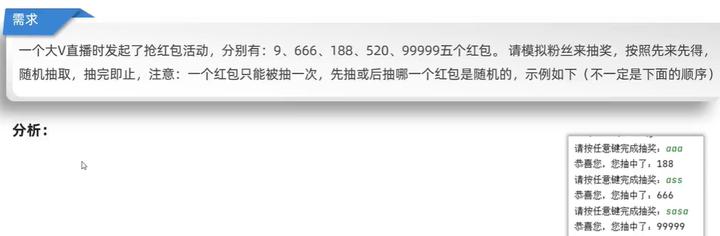
分析
1、如何确保每个红包只能抽一次;
2、如何保证随机抽取;
3、如何确保抽完后结束活动。
其实很简单,只需要将数组随机打乱就行了,然后一次输出即可。
代码
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Scanner;public class Example_03 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("输入抽取红包的个数:");int n = sc.nextInt();ArrayList<Integer> redBug = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {System.out.println("请输入第" + (i+1) + "个红包的金额");redBug.add(sc.nextInt());}// 打乱数组顺序Collections.shuffle(redBug);int num = 0;while (++num <= n){System.out.print("请输按任意键获取红包:");sc.next();System.out.println("你获得的红包金额为:" + redBug.get(num-1));}System.out.println("红包领取完毕!");}
}
希望多点赞收藏关注,评论或私信交流!~




![[python]gym安装报错ERROR: Failed building wheel for box2d-py](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/7f45274d283e4d3d849f9b67567d58a4.png)