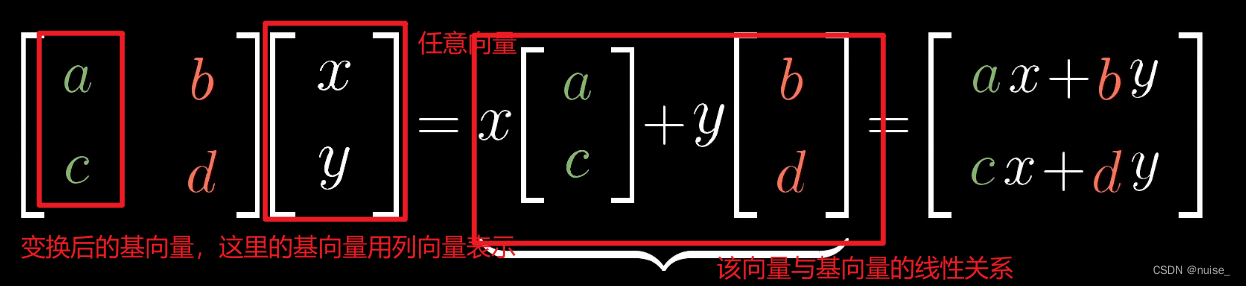
力扣官网
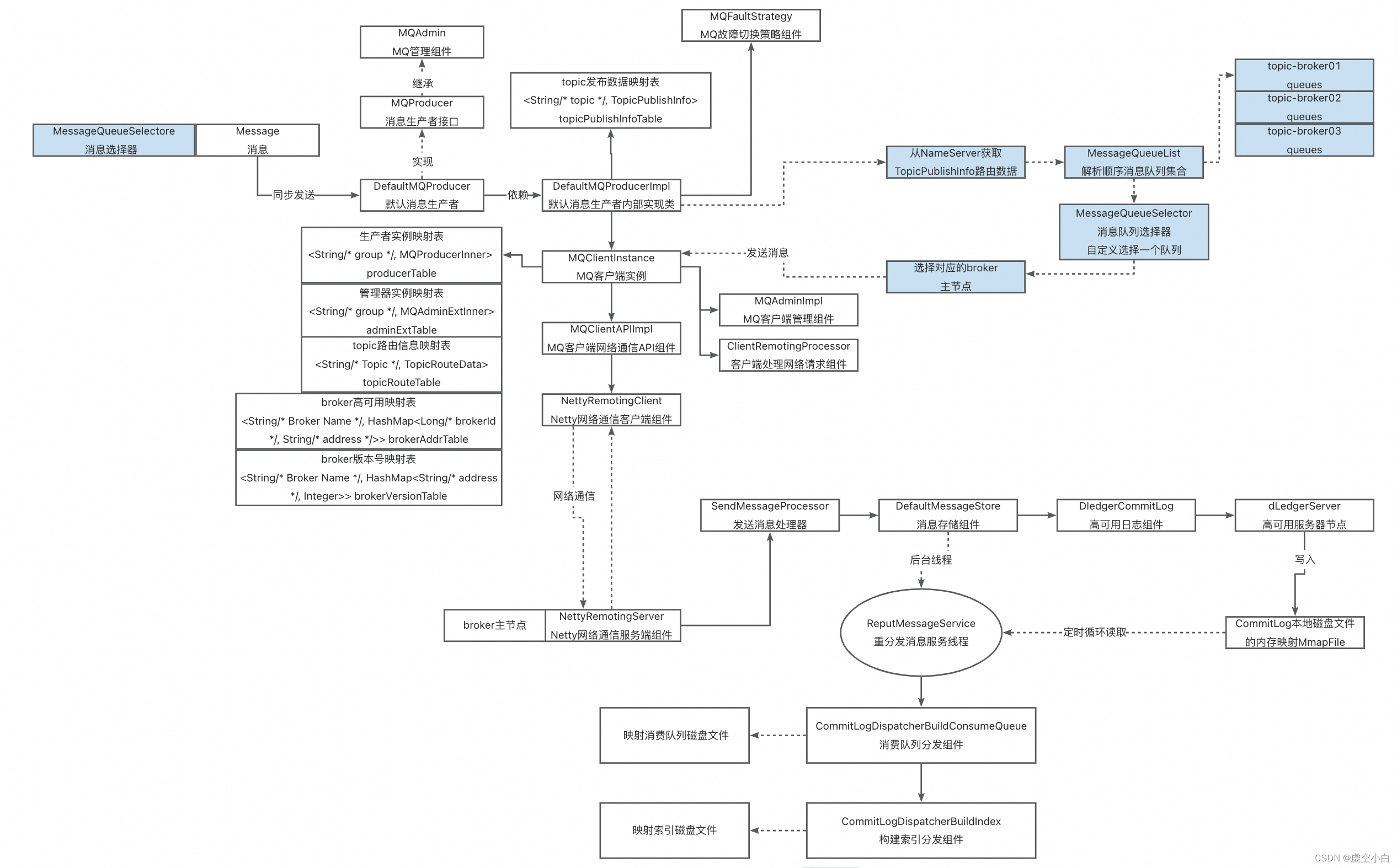
1.1移动零
给定一个数组 n u m s nums nums,编写一个函数将所有 0 移动到数组的末尾,同时保持非零元素的相对顺序,在不复制数组的情况下原地对数组进行操作。
输入: nums = [0,1,0,3,12]
输出: [1,3,12,0,0]
代码
def moveZeroea(self,nums):if not nums:return 0j=0# 将所有非零的元素依次提前,最后将剩下的全修改为0for i in range(len(nums)):if nums[i]!=0:nums[j]=nums[i]j+=1for i in range(j,len(nums)):nums[i]=0return nums
1.2盛最多水的容器
给定一个长度为 n n n的整数数组 h e i g h t height height 。有 n n n 条垂线,第 i i i 条线的两个端点是 ( i , 0 ) (i, 0) (i,0) 和 ( i , h e i g h t [ i ] ) (i, height[i]) (i,height[i]) 。找出其中的两条线,使得它们与 x x x 轴共同构成的容器可以容纳最多的水。返回容器可以储存的最大水量。说明:你不能倾斜容器。

输入:[1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]
输出:49
设两指针 i , j ( j > i ) i,j(j>i) i,j(j>i)指向的水槽板高度分别为 h [ i ] , h [ j ] h[i],h[j] h[i],h[j] ,此状态下水槽面积为 S(i,j) 。由于可容纳水面积如下 :
S ( i , j ) = m i n ( h [ i ] , h [ j ] ) × ( j − i ) S(i,j)=min(h[i],h[j])×(j−i) S(i,j)=min(h[i],h[j])×(j−i)
在每个状态下,无论长板或短板向中间收窄一格,都会导致水槽 底边宽度−1:
1.若向内 移动短板 ,水槽的短板 m i n ( h [ i ] , h [ j ] ) min(h[i],h[j]) min(h[i],h[j]) 可能变大,因此下个水槽的面积 可能增大 。
2.若向内 移动长板 ,水槽的短板 m i n ( h [ i ] , h [ j ] ) min(h[i],h[j]) min(h[i],h[j]) 不变或变小,因此下个水槽的面积 一定变小 。
因此,初始化双指针分列水槽左右两端,循环每轮将短板向内移动一格,并更新面积最大值,直到两指针相遇时跳出;即可获得最大面积。
代码
def maxArea(self,height):i,j,ares=0,len(height)-1,0while i<j:if height[i]<height[j]:ares=max(ares,height[i]*(j-i))i+=1else:ares=max(ares,height[i]*(j-i))j-=1return ares
1.3三数之和
给你一个整数数组 n u m s nums nums ,你返回所有和为 0且不重复的三元组 [ n u m s [ i ] , n u m s [ j ] , n u m s [ k ] ] [nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]] [nums[i],nums[j],nums[k]] 满足 i ! = j 、 i ! = k 且 j ! = k i != j、i != k 且 j != k i!=j、i!=k且j!=k ,同时还满足 n u m s [ i ] + n u m s [ j ] + n u m s [ k ] = = 0 nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] == 0 nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[k]==0 。
输入:nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4]
输出:[[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]]
解释:
nums[0] + nums[1] + nums[2] = (-1) + 0 + 1 = 0 。
nums[1] + nums[2] + nums[4] = 0 + 1 + (-1) = 0 。(和1重复了)
nums[0] + nums[3] + nums[4] = (-1) + 2 + (-1) = 0 。
不同的三元组是 [-1,0,1] 和 [-1,-1,2] 。

def treeSum(self,nums):res=[]n=len(nums)if (not nums or n<3): #数组为空或者长度小于3return []nums.sort() #=升序排序 ,nums.sort(reverse=True)=降序排序for i in range(n):if nums[i]>0:#如果第一个元素超过零了,后面找不出两个和他相加等于零的数了return resif i>0 and nums[i]==nums[i-1]:continuel=i+1r=n-1while l<r:if nums[i]+nums[l]+nums[r]==0:res.append([nums[i],nums[l],nums[r]])while l<r and nums[l]==nums[l+1]:l=l+1while l<r and nums[r]==nums[r-1]:r=r-1l=l+1r=r-1elif nums[i]+nums[l]+nums[r]>0:r=r-1else:l=l+1return res
1.4接雨水
给定 n n n 个非负整数表示每个宽度为 1 1 1 的柱子的高度图,计算按此排列的柱子,下雨之后能接多少雨水。

栈
类似于括号匹配,仔细观察蓝色的部分,每次匹配出一对括号(找到对应的一堵墙),就计算这两堵墙中的水。
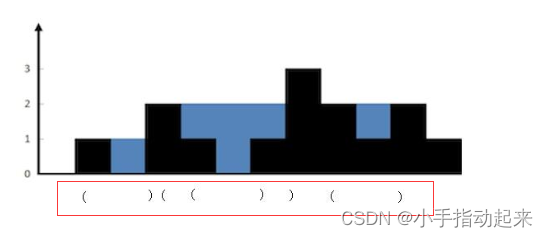
用栈保存每堵墙。当遍历墙的高度的时候,如果当前高度小于栈顶的墙高度,说明这里会有积水,我们将墙的高度的下标入栈。如果当前高度大于栈顶的墙的高度,说明之前的积水到这里停下,我们可以计算下有多少积水了。计算完,就把当前的墙继续入栈,作为新的积水的墙。
步骤为:
1.当前高度小于等于栈顶高度,入栈,指针后移。
2.当前高度大于栈顶高度,出栈,计算出当前墙和栈顶的墙之间水的多少,然后计算当前的高度和新栈的高度的关系,重复第 2 步,直到当前墙的高度不大于栈顶高度或者栈空,然后把当前墙入栈,指针后移。
代码:
class stack:def __init__(self,size):self.max=size #栈的容量self.elem=[None]*self.maxself.top=0 #栈顶self.base=0 #栈尾def push(self,num):if self.top-self.base==self.max:print("the stack is full")self.elem[self.top]=numself.top+=1def pop(self):if self.top==self.base:print("the stack is empty")self.top-=1e=self.elem[self.top]return edef get_pop(self):return self.elem[self.top-1]def isEmpty(self):if self.top==self.base:return Trueelse:return Falseclass question:def trap(self,height):sum=0hstack=stack(len(height))i=0while i<len(height):#如果栈不为空,并且指向高度大于栈顶的高度就一直循环while not hstack.isEmpty() and height[i]>height[hstack.get_pop()]:h=height[hstack.get_pop()] #栈顶元素hstack.pop()if hstack.isEmpty():breakdistance=i-hstack.get_pop()-1 #两墙之间的距离dmin=min(height[hstack.get_pop()],height[i])sum=sum+distance*(dmin-h) #距离乘以当前元素和栈顶元素的差值hstack.push(i) #当前指针入栈i+=1 #指针后移return sum