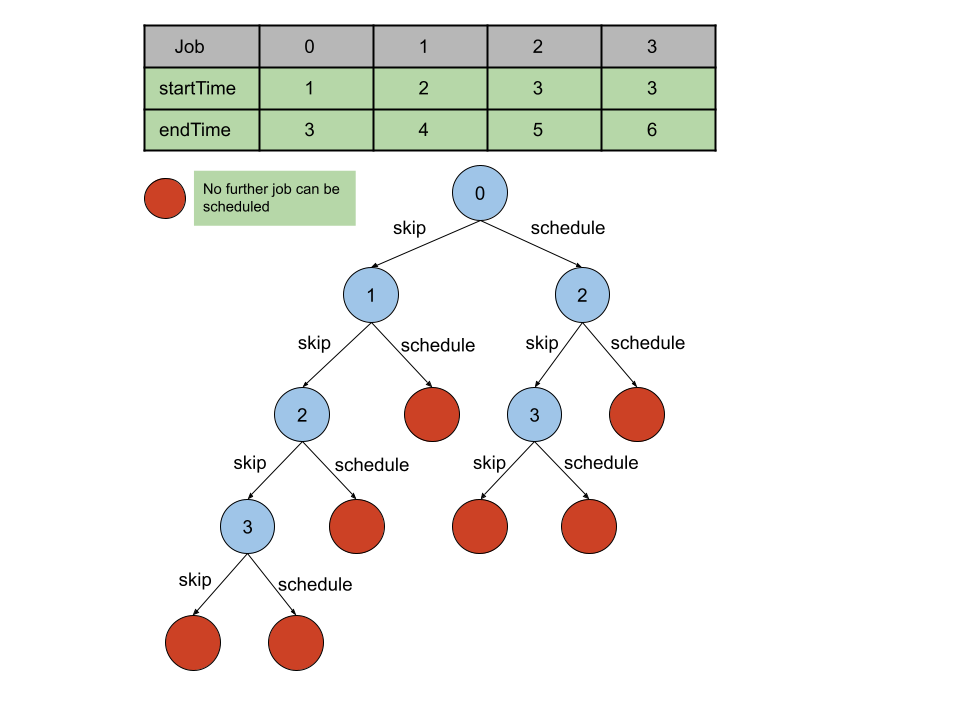
1 isShutdown()方法
public boolean isShutdown()方法的作用是判断线程池是否已经关闭
public class Run1 {public static void main(String[] args) {Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {System.out.println("开始: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());Thread.sleep(1000);System.out.println("结束: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());}catch (InterruptedException e){e.printStackTrace();}}};ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,2,Integer.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new LinkedBlockingDeque<>());pool.execute(runnable);System.out.println("A = " + pool.isShutdown());pool.shutdown();System.out.println("B = " + pool.isShutdown());}
}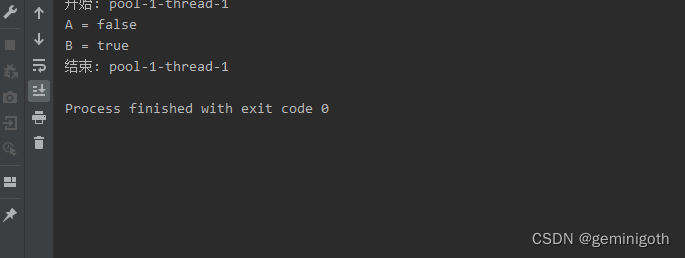
由运行结果可知,只要调用了shutdown()方法,isShutdown()方法的返回值就是true。
2 isTerminating()和isTerminated()方法
public boolean isTerminating()方法:如果此执行程序处于在shutdown或shutdownNow之后且正在终止但尚未完全终止的过程中,也就是还有任务在执行,则返回true。此方法可以比喻成门是否正在关闭。
public boolean isTerminated()方法:如果关闭后所有任务都已完成,则返回true。此方法可以比喻成门是否已经关闭。
shutdown或shutdownNow方法的功能是发出一个关闭线程池的命令,isShutdown方法用于判断关闭线程池的命令发出或未发出。 isTerminating方法用于判断线程池是否正在关闭中,isTerminated方法判断线程池是否已经关闭了。
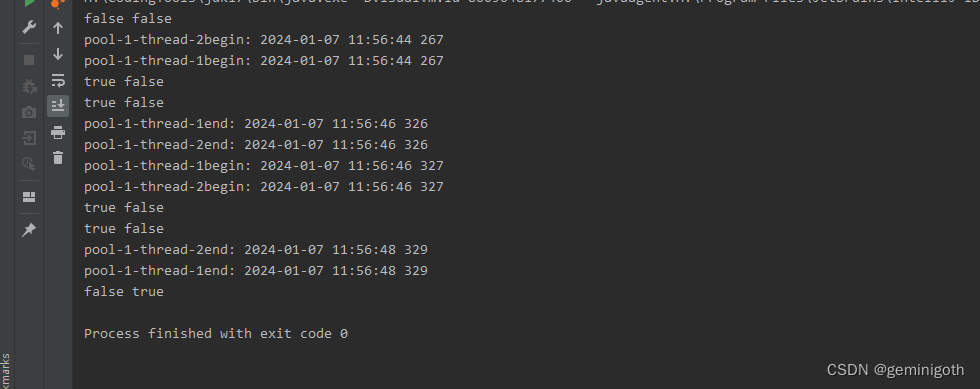
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run() {try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"begin: "+ Utils.data(System.currentTimeMillis()));Thread.sleep(2000);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"end: "+ Utils.data(System.currentTimeMillis()));}catch (InterruptedException e){e.printStackTrace();}}
}public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {MyRunnable runnable = new MyRunnable();ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,99999,99999, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new LinkedBlockingDeque<>());pool.execute(runnable);pool.execute(runnable);pool.execute(runnable);pool.execute(runnable);System.out.println(pool.isTerminating() + " " + pool.isTerminated());pool.shutdown();Thread.sleep(1000);System.out.println(pool.isTerminating() + " " + pool.isTerminated());Thread.sleep(1000);System.out.println(pool.isTerminating() + " " + pool.isTerminated());Thread.sleep(1000);System.out.println(pool.isTerminating() + " " + pool.isTerminated());Thread.sleep(1000);System.out.println(pool.isTerminating() + " " + pool.isTerminated());Thread.sleep(1000);System.out.println(pool.isTerminating() + " " + pool.isTerminated());}
}
3 awaitTermination(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
public boolean awaitTermination(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)方法:查看在指定的时间内,线程池是否已经终止工作,也就是“最多”等待多少时间后去判断线程池是否已经终止工作。如果在指定的时间之内,线程池销毁会导致该方法不再阻塞,而超过timeout时间也会导致该方法不再阻塞。此方法的使用需要shutdown()方法的配合。
public class MyRunnable1 implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run() {try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + Utils.data(System.currentTimeMillis()));Thread.sleep(4000);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + Utils.data(System.currentTimeMillis()));}catch (InterruptedException e){e.printStackTrace();}}
}public class Test1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {MyRunnable1 runnable1 = new MyRunnable1();ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,99999,9999L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new LinkedBlockingQueue<>());pool.execute(runnable1);System.out.println("main开始:" + Utils.data(System.currentTimeMillis()));System.out.println(pool.awaitTermination(10,TimeUnit.SECONDS));System.out.println("main结束:" + Utils.data(System.currentTimeMillis()));}
}
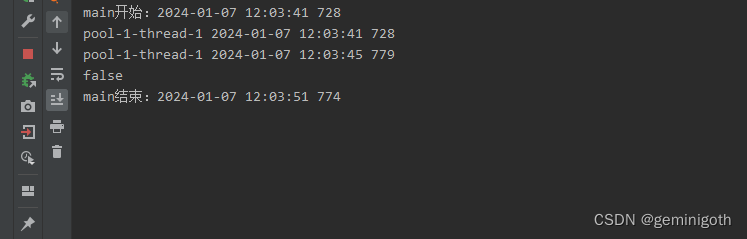
从控制台可以看出,main开始到main结束需要10秒,因为main线程并未销毁,所以 awaitTermination方法需要阻塞10秒。打印false的原因是未对线程池执行shutdown方法。如果对线程池执行shutdown方法,在运行时间上会有什么效果呢?
public class Test2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {MyRunnable1 runnable1 = new MyRunnable1();ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,99999,9999L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new LinkedBlockingQueue<>());pool.execute(runnable1);pool.shutdown();System.out.println("main开始:" + Utils.data(System.currentTimeMillis()));System.out.println(pool.awaitTermination(10,TimeUnit.SECONDS));System.out.println("main结束:" + Utils.data(System.currentTimeMillis()));}
}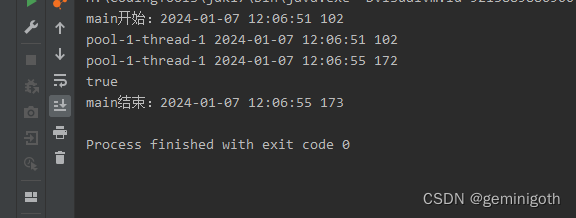
可以看出,main开始和mian结束之间耗时4秒,因为4秒后线程池销毁了,导致 awaitTermination方法取消阻塞。
4 set/getRejectedExceptionHandler()方法
public void setRejectedExecutionHandler(RejectedExecutionHandler handler)和
public RejectedExecutionHandler getRejectedExecutionHandler()方法的作用是可以处理任务被拒绝执行时的行为。
public class MyRunnable1 implements Runnable{private String username;public MyRunnable1(String username) {this.username = username;}public String getUsername() {return username;}public void setUsername(String username) {this.username = username;}@Overridepublic void run() {try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ "开始时间 = " + Utils.data(System.currentTimeMillis()));Thread.sleep(4000);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ "结束时间 = " + Utils.data(System.currentTimeMillis()));}catch (InterruptedException e){e.printStackTrace();}}
}public class Run1 {public static void main(String[] args) {MyRunnable1 myRunnable1 = new MyRunnable1("a1");MyRunnable1 myRunnable2 = new MyRunnable1("a2");MyRunnable1 myRunnable3 = new MyRunnable1("a3");MyRunnable1 myRunnable4 = new MyRunnable1("a4");ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,3,999L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new SynchronousQueue<>());pool.execute(myRunnable1);pool.execute(myRunnable2);pool.execute(myRunnable3);pool.execute(myRunnable4);}
}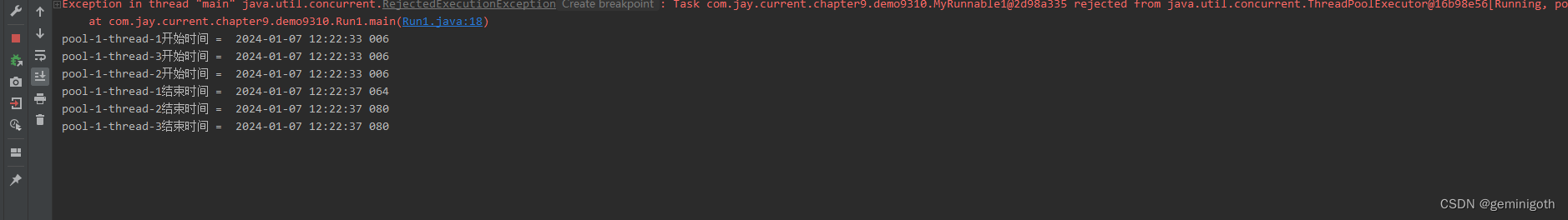
控制台打印的信息说明 MyRunnable1 myRunnable4 = new MyRunnable1("a4");任务被拒绝执行,在出现这样的异常时可以自定义拒绝执行任务的行为。创建MyRejectedExecutionHandler.java类。
public class MyRejectedExecutionHandler implements RejectedExecutionHandler {@Overridepublic void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {System.out.println(((MyRunnable1) r).getUsername() + "被拒绝执行");}
}
public class Run2 {public static void main(String[] args) {MyRunnable1 myRunnable1 = new MyRunnable1("a1");MyRunnable1 myRunnable2 = new MyRunnable1("a2");MyRunnable1 myRunnable3 = new MyRunnable1("a3");MyRunnable1 myRunnable4 = new MyRunnable1("a4");ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,3,999L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new SynchronousQueue<>());pool.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new MyRejectedExecutionHandler());pool.execute(myRunnable1);pool.execute(myRunnable2);pool.execute(myRunnable3);pool.execute(myRunnable4);pool.shutdown();}
}
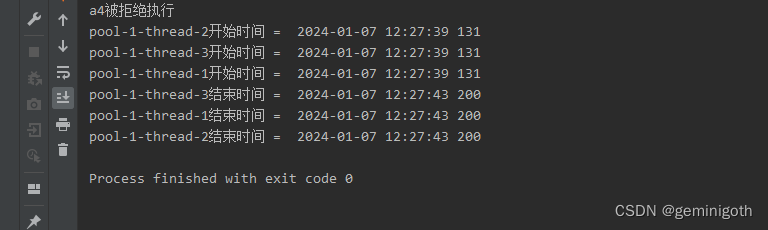
5 allowsCoreThreadTimeOut()和allowCoreThreadTimeOut(bool)方法
allowsCoreThreadTimeOut(true)可使核心池中的空闲线程具有超时销毁的特性。其中,public boolean allowsCoreThreadTimeOut() 方法的作用是判断是否具有这个特性。
public void allowCoreThreadTimeOut(boolean value)方法的作用是设置是否有这个特性。
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "开始:" + Utils.data(System.currentTimeMillis()));System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "结束:" + Utils.data(System.currentTimeMillis()));}
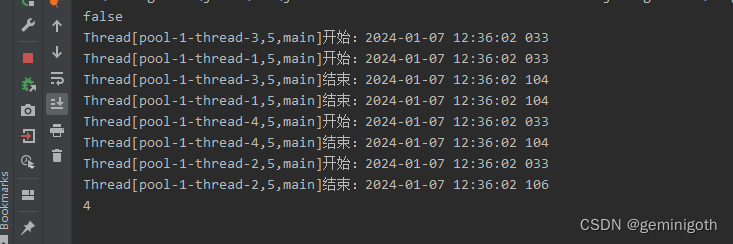
}public class Run1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(4,5,5, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new SynchronousQueue<>());System.out.println(pool.allowsCoreThreadTimeOut());for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {MyRunnable myRunnable = new MyRunnable();pool.execute(myRunnable);}Thread.sleep(8000);System.out.println(pool.getPoolSize());}
}
创建Run2.java类
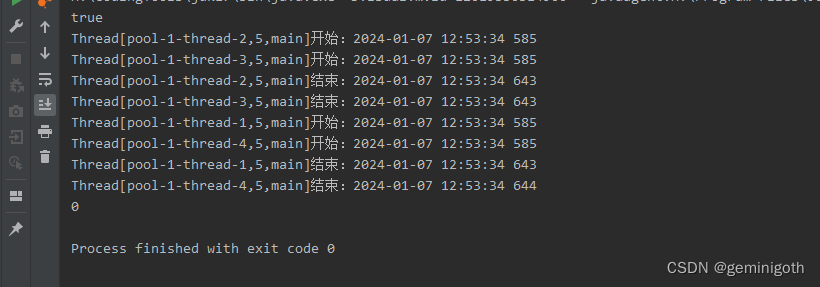
public class Run2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(4,5,5, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new SynchronousQueue<>());pool.allowCoreThreadTimeOut(true);System.out.println(pool.allowsCoreThreadTimeOut());for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {MyRunnable myRunnable = new MyRunnable();pool.execute(myRunnable);}Thread.sleep(8000);System.out.println(pool.getPoolSize());}
} 
6 prestartCoreThread()和prestartAllCoreThreads()方法
在实例化ThreadPoolExecutor类后,线程池并没有核心线程,除非执行execute()方法,但是在不执行execute()方法时也可以通过执行prestartCoreThread()和prestartAllCoreThreads()方法来创建核心线程。
public boolean prestartCoreThread()方法的作用是每调用一次就创建一个核心线程并使它变成启动状态,返回值类型为boolean,代表是否创建成功。
public int prestartAllCoreThreads()方法的作用是同时启动全部核心线程,返回值是启动核心线程的数量。
public class Run1 {public static void main(String[] args) {ThreadPoolExecutor pools = new ThreadPoolExecutor(4,8,5, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new LinkedBlockingQueue<>());System.out.println("线程池中的线程数a= " + pools.getPoolSize());System.out.println("Z1 = " + pools.prestartCoreThread());System.out.println("线程池中的线程数a= " + pools.getPoolSize());System.out.println("Z2 = " + pools.prestartCoreThread());System.out.println("线程池中的线程数a= " + pools.getPoolSize());System.out.println("Z3 = " + pools.prestartCoreThread());System.out.println("线程池中的线程数a= " + pools.getPoolSize());System.out.println("Z4 = " + pools.prestartCoreThread());System.out.println("线程池中的线程数a= " + pools.getPoolSize());System.out.println("Z5 = " + pools.prestartCoreThread());System.out.println("线程池中的线程数a= " + pools.getPoolSize());System.out.println("Z6 = " + pools.prestartCoreThread());}
} 
最后连续打印了2个false代表核心池中的线程数量已经到了最大值,是4。不能再创建新的核心池中的线程了。
创建Run2.java类。
public class Run2 {public static void main(String[] args) {ThreadPoolExecutor pools = new ThreadPoolExecutor(4,8,5, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new LinkedBlockingQueue<>());System.out.println("线程池中的线程数a= " + pools.getPoolSize());System.out.println("Z1 = " + pools.prestartAllCoreThreads());System.out.println("线程池中的线程数a= " + pools.getPoolSize());System.out.println();System.out.println("Z2 = " + pools.prestartAllCoreThreads());System.out.println("线程池中的线程数a= " + pools.getPoolSize());}
}
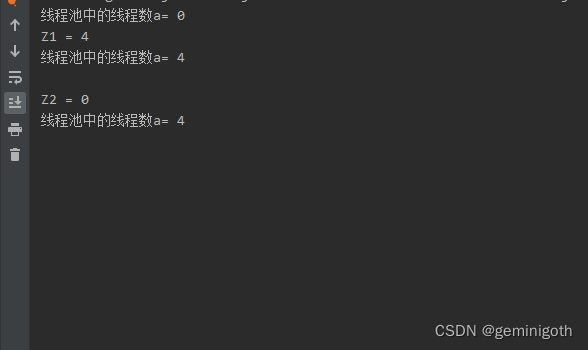
打印信息Z2 = 0,说明核心池中的线程已满,不需要创建新的核心池中的线程。


![[Linux] 一文理解HTTPS协议:什么是HTTPS协议、HTTPS协议如何加密数据、什么是CA证书(数字证书)...](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/543dfa000d3648162ab5c79d1f022a07.webp?x-oss-process=image/format,png)