目录
1. 快速回顾
2. 为可执行文件分配 capabilities
3. 构建半特权环境
4. 容器与 capabilities
Linux Capabilities 基础概念与基本使用
上一篇学习了LinuxCapabilities的基础知识和基本使用,因为后面需要学习Docker的逃逸,理解Linux Capabilities是很必要的,本篇和大家一起学习一下进阶实战,这里的进阶实战、与前面的基础概念与基本应用都是龙哥总结好的,这篇内容我也是学习+总结这些实战例子
本文将会继续研究 Linux capabilities 更高级的应用案例,并结合 Docker 和 Kubernetes 来加深理解。
1. 快速回顾
如果你看过上一篇,那你应该大致了解下面的计算公式:
P’(ambient) = (file is privileged) ? 0 : P(ambient)
P’(permitted) = (P(inheritable) & F(inheritable)) | (F(permitted) & P(bounding))) | P’(ambient)
P’(effective) = F(effective) ? P’(permitted) : P’(ambient)
P’(inheritable) = P(inheritable) [i.e., unchanged]
P’(bounding) = P(bounding) [i.e., unchanged]
这里需要复习以下了解如何通过基本的工具来设置 capabilities。
在 centos上,以普通用户的身份运行 capsh 将会得到如下结果:
$ capsh --print
Current: =
Bounding set =cap_chown,cap_dac_override,cap_dac_read_search,cap_fowner,cap_fsetid,cap_kill,cap_setgid,cap_setuid,cap_setpcap,cap_linux_immutable,cap_net_bind_service,cap_net_broadcast,cap_net_admin,cap_net_raw,cap_ipc_lock,cap_ipc_owner,cap_sys_module,cap_sys_rawio,cap_sys_chroot,cap_sys_ptrace,cap_sys_pacct,cap_sys_admin,cap_sys_boot,cap_sys_nice,cap_sys_resource,cap_sys_time,cap_sys_tty_config,cap_mknod,cap_lease,cap_audit_write,cap_audit_control,cap_setfcap,cap_mac_override,cap_mac_admin,cap_syslog,cap_wake_alarm,cap_block_suspend,cap_audit_read
Securebits: 00/0x0/1'b0secure-noroot: no (unlocked)secure-no-suid-fixup: no (unlocked)secure-keep-caps: no (unlocked)
uid=1000(fox)
gid=1000(fox)
groups=4(adm),24(cdrom),27(sudo),30(dip),46(plugdev),108(lxd),114(docker),1000(fox)可以看到普通用户当前所在的 shell 进程没有任何 capabilities(即 Effective 集合为空),Bounding 集合包含了所有 capabilities。
这个命令输出的信息比较有限,完整的信息可以查看 /proc 文件系统,比如当前 shell 进程就可以查看 /proc/$$/status。
$ grep Cap /proc/$$/status
CapInh: 0000000000000000
CapPrm: 0000000000000000
CapEff: 0000000000000000
CapBnd: 0000003fffffffff
CapAmb: 0000000000000000输出中的 16 进制掩码表示对应集合中的 capabilities,可以使用 capsh 对其进行解码:
$ capsh --decode=0000003fffffffff
0x0000003fffffffff=cap_chown,cap_dac_override,cap_dac_read_search,cap_fowner,cap_fsetid,cap_kill,cap_setgid,cap_setuid,cap_setpcap,cap_linux_immutable,cap_net_bind_service,cap_net_broadcast,cap_net_admin,cap_net_raw,cap_ipc_lock,cap_ipc_owner,cap_sys_module,cap_sys_rawio,cap_sys_chroot,cap_sys_ptrace,cap_sys_pacct,cap_sys_admin,cap_sys_boot,cap_sys_nice,cap_sys_resource,cap_sys_time,cap_sys_tty_config,cap_mknod,cap_lease,cap_audit_write,cap_audit_control,cap_setfcap,cap_mac_override,cap_mac_admin,cap_syslog,cap_wake_alarm,cap_block_suspend,cap_audit_read和 capsh --print 命令输出的结果一样。
如果是 root 用户,得到的结果和普通用户是不一样的:
$ grep Cap /proc/$$/status
CapInh: 0000000000000000
CapPrm: 0000003fffffffff
CapEff: 0000003fffffffff
CapBnd: 0000003fffffffff
CapAmb: 0000000000000000所有的 capabilities 都包含在了 Permitted、Effective 和 Bounding 集合中,所以 root 用户可以执行任何内核调用。
2. 为可执行文件分配 capabilities
我在上一篇文章中提到过,通过适当的配置,进程可以获取可执行文件的 Bounding 集合中的 capabilities。
下面通过一个例子来加深理解。
以 ping 这个命令为例,它的二进制文件被设置了 SUID,所以可以以 root 身份运行:
[root@centos111 dockerfile]# which ping
/usr/bin/ping
[root@centos111 dockerfile]# ls -al /usr/bin/ping
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 66176 8月 4 2017 /usr/bin/ping
也可以使用getcap查看一下它的capability权限
getcap /usr/bin/ping
/usr/bin/ping = cap_net_admin,cap_net_raw+p更安全的机制是使用 capabilities,不过 centos上面的 ping 没有这么做,没关系,我们可以通过 ping 的源码来自己编译,首先克隆源代码:
$ git clone https://github.com/iputils/iputils注:如果网络不太行,可以去github上下载源码包
安装编译所需的依赖:
$ sudo apt install -y ninja-build meson libcap-dev gettext开始编译:
$ cd iputils
$ ./configure
$ make新编译的 ping 文件并没有设置 SUID:
ls -l builddir/ping/ping
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 173632 1月 7 19:41 builddir/ping/ping
也没有任何的 capabilities:
$ getcap builddir/ping/ping所以无法正常工作:
$ builddir/ping/ping www.baidu.com
builddir/ping/ping: socket: Operation not permitted
我们可以手动设置 capabilities:
$ setcap 'cap_net_raw+p' builddir/ping/ping
unable to set CAP_SETFCAP effective capability: Operation not permitted$ sudo setcap 'cap_net_raw+p' builddir/ping/ping$ getcap builddir/ping/ping
builddir/ping/ping = cap_net_raw+p$ builddir/ping/ping www.baidu.com -c 1
PING www.a.shifen.com (180.101.49.12) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 180.101.49.12 (180.101.49.12): icmp_seq=1 ttl=53 time=10.0 ms--- www.a.shifen.com ping statistics ---
1 packets transmitted, 1 received, 0% packet loss, time 0ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 10.028/10.028/10.028/0.000 ms 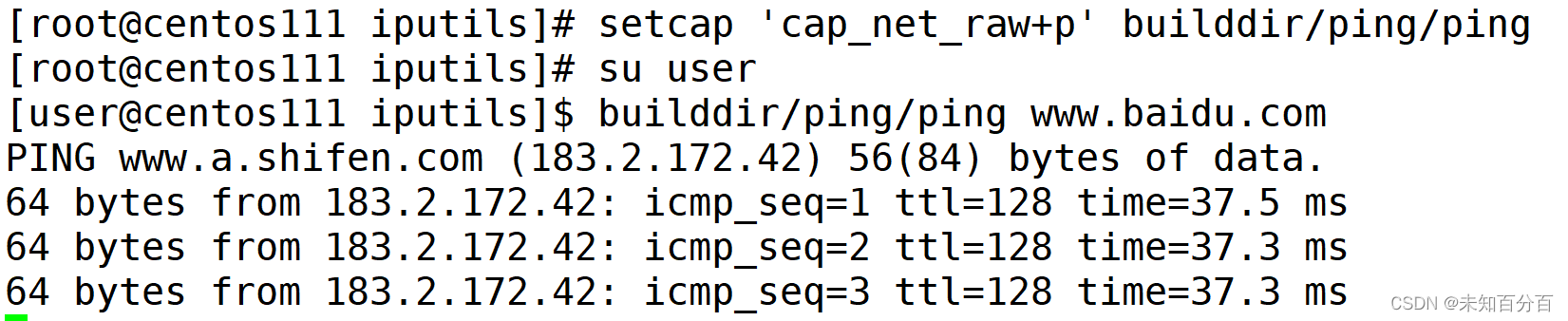
这里再活学活用一下,为什么普通用户无法执行 setcap 呢?因为执行 setcap 的用户需要在 Permitted 集合中包含 CAP_SETFCAP capabilities,而普通用户不具备这个 capabilities,所以必须使用 root 用户。
查看 ping 进程的 capabilities:
$ builddir/ping/ping wwww.baidu.com > /dev/null&
[1] 9823$ grep Cap /proc/9823/status
CapInh: 0000000000000000
CapPrm: 0000000000002000
CapEff: 0000000000000000
CapBnd: 0000003fffffffff
CapAmb: 0000000000000000$ $ capsh --decode=0000000000002000
0x0000000000002000=cap_net_raw只有 Permitted 集合中包含了 CAP_NET_RAW capabilities,Effective 集合中并不包含,按常理 ping 是无法正常工作的。
这是为啥呢?
其实 ping 在执行过程中会将 Permitted 集合中的 CAP_NET_RAW capabilities 加入 Effective 集合中,打开 Socket 之后再将该 capabilities 从 Effective 集合中移除,所以 grep 是看不到的。
其中这就是我在 第一篇文章提到的 ping 文件具有 capabilities 感知能力。
可以通过 stace 跟踪系统调用来验证:
$ sudo strace builddir/ping/ping -c 1 wwwww.baidu.com
...
capget({version=_LINUX_CAPABILITY_VERSION_3, pid=0}, NULL) = 0
capget({version=_LINUX_CAPABILITY_VERSION_3, pid=0}, {effective=0, permitted=1<<CAP_NET_ADMIN|1<<CAP_NET_RAW, inheritable=0}) = 0
capset({version=_LINUX_CAPABILITY_VERSION_3, pid=0}, {effective=1<<CAP_NET_RAW, permitted=1<<CAP_NET_ADMIN|1<<CAP_NET_RAW, inheritable=0}) = 0
socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, IPPROTO_ICMP) = -1 EACCES (Permission denied)
socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_ICMP) = 3
socket(AF_INET6, SOCK_DGRAM, IPPROTO_ICMPV6) = -1 EACCES (Permission denied)
socket(AF_INET6, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_ICMPV6) = 4
capget({version=_LINUX_CAPABILITY_VERSION_3, pid=0}, NULL) = 0
capget({version=_LINUX_CAPABILITY_VERSION_3, pid=0}, {effective=1<<CAP_NET_RAW, permitted=1<<CAP_NET_ADMIN|1<<CAP_NET_RAW, inheritable=0}) = 0
capset({version=_LINUX_CAPABILITY_VERSION_3, pid=0}, {effective=0, permitted=1<<CAP_NET_ADMIN|1<<CAP_NET_RAW, inheritable=0}) = 0
...第三行表示 CAP_NET_RAW capabilities 被添加到了 Effective 集合中,下一行试图创建一个 IPV4 ping socket,但创建失败,这是由 ping_group_range 内核配置参数导致的。然后再次尝试创建 IPV4 ping socket,这次创建成功了。IPv6 重复上面的步骤。
最后将 CAP_NET_RAW capabilities 从 Effective 集合中移除。
如果 ping 二进制文件不具备 capabilities 感知能力,即没有调用 capset 和 capget 的权限,我们就必须要开启 Effective 标志位(F(Effective)),这样就会将该 capabilities 自动添加到进程的 Effective 集合中:
$ setcap 'cap_net_raw+ep' builddir/ping/ping不明白为什么的,再好好理解下这个公式:P'(effective) = F(effective) ? P'(permitted) : P'(ambient)。
3. 构建半特权环境
前文中只用到了 Permitted 和 Effective 集合,下面再来聊聊 Ambient 和 Inheritable 集合。
这两个集合的意义就在于可以帮助我们在进程树或 namespace 的范围内创建一个允许任意进程使用某些 capabilities 的环境。
例如,我们可以在 Ambient 集合中加入 CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE capabilities 来创建一个可以绑定到 80 端口的 “webserver” 环境,不需要额外的 capabilities,也不需要以 root 用户身份运行。
webserver 可以通过解释器或辅助脚本启动,并且不需要给可执行文件设置 capabilities。
如果不明白为什么,再看十分钟这两个公式:
P’(ambient) = (file is privileged) ? 0 : P(ambient) P’(effective) = F(effective) ? P’(permitted) : P’(ambient)
如果理解了,再往下动手实践。
这里有一个简单的程序 set_ambient,核心功能是使用 cap-ng library 将 CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE capabilities 添加到新进程的 Ambient 集合中。
编译完成后,需要给二进制文件添加该 capabilities,如果它自己没有这个 capabilities,是无法将其添加到新进程中的:
程序代码:
[root@centos111 dockerfile]# cat set_ambient.c
/** * Simple program to start the given process with CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE in the* * ambient capabilities. * ** * Based on test program by Christoph Lameter.* ** * (C) 2015 Christoph Lameter <cl@linux.com>* * (C) 2019 Adrian Mouat <adrian.mouat@container-solutions.com>* ** * Released under: GPL v3 or later.* ** ** * Compile using:* ** * gcc ./set_ambient.c -o set_ambient -lcap-ng* ** * (requires cap-ng headers, which is in libcap-ng-dev in debian)* ** * This program must have the CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE capability in the permitted * * set to run properly.* ** * This can be set on the file with:* ** * sudo setcap cap_net_bind_service+p set_ambient* ** * To get a shell with CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE that can be inherited by other * * processes:* ** * ./set_ambient /bin/bash* ** * Verifying that it works:* ** * From the bash spawed by set_ambient run* ** * cat /proc/$$/status* ** * and have a look at the capabilities (use capsh --decode to interpret the* * hex).* */#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <cap-ng.h>
#include <sys/prctl.h>
#include <linux/capability.h>/** * Definitions from the kernel header files. These are going to be removed* * when the /usr/include files have these defined.* ** * AM: This should be updated, I was just being lazy.* */
#define PR_CAP_AMBIENT 47
#define PR_CAP_AMBIENT_IS_SET 1
#define PR_CAP_AMBIENT_RAISE 2
#define PR_CAP_AMBIENT_LOWER 3
#define PR_CAP_AMBIENT_CLEAR_ALL 4static void set_ambient_cap(int cap)
{int rc;capng_get_caps_process();rc = capng_update(CAPNG_ADD, CAPNG_INHERITABLE, cap);if (rc) {printf("Cannot add inheritable cap\n");exit(2);}capng_apply(CAPNG_SELECT_CAPS);/* Note the two 0s at the end. Kernel checks for these */if (prctl(PR_CAP_AMBIENT, PR_CAP_AMBIENT_RAISE, cap, 0, 0)) {perror("Cannot set cap");exit(1);}
}int main(int argc, char **argv)
{int rc;set_ambient_cap(CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE);printf("Starting process with CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE in ambient\n");if (execv(argv[1], argv + 1))perror("Cannot exec");return 0;
}
下载依赖库:
yum install libcap-ng-devel编译:
gcc ./set_ambient.c -o set_ambient -lcap-ng程序授权:
$ sudo setcap cap_net_bind_service+p set_ambient
$ getcap ./set_ambient
./set_ambient = cap_net_bind_service+p通过 set_ambient 来启动一个 bash 环境:
$ ./set_ambient /bin/bash
Starting process with CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE in ambient
$ grep Cap /proc/$BASHPID/status
CapInh: 0000000000000400
CapPrm: 0000000000000400
CapEff: 0000000000000400
CapBnd: 0000003fffffffff
CapAmb: 0000000000000400
$ capsh --decode=0000000000000400
0x0000000000000400=cap_net_bind_service
$ exit可以看到 CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE capabilities 被添加到 bash 环境的 Ambient 集合中,同时也会添加到 Permitted 和 Inheritable 集合中,不明白为什么的继续看文章开头的公式
接着运行一个 Go Web 服务,并绑定到 80 端口,既不给它相应的 capabilities,也不以 root 身份运行:
go语言的安装见:centos下安装go环境 - 简书 (jianshu.com)
安装完成后我们编辑一个go文件:
cat server.go
package main// Simple webserver that responds to http request on port 80.// Based on web server code in https://golang.org/doc/articles/wiki/import ("fmt""log""net/http"
)func handler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {fmt.Fprintf(w, "Successfully serving on port 80\n")
}func main() {http.HandleFunc("/", handler)log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(":80", nil))
}
然后编译和运行服务:
[user1@centos111 dockerfile]$ go build server.go
[user1@centos111 dockerfile]$ ./server
2024/01/07 21:00:31 listen tcp :80: bind: permission denied
运行失败,因为它没有绑定到小于 1024 的端口的权限。
下面利用 set_ambient 创建一个 “webserver” 环境再运行试试:
[user1@centos111 dockerfile]$ ./set_ambient /bin/bash
Starting process with CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE in ambient
然后我们来运行:
[user1@centos111 dockerfile]$ ./server &
[1] 8974
可以看到这样就运行成功了
然后我们访问一下:
[user1@centos111 dockerfile]$ curl localhost:80
Successfully serving on port 80
这次运行成功了!你也可以直接执行 ./set_ambient ./server,但使用 shell 的好处是:具有 Ambient 集合中 capabilities 的 bash 环境变成了一个半特权环境,在这个环境中不仅可以运行 Web 服务,也可以运行相关脚本和程序,而这些脚本和程序又可以正常启动 webserver。
这个方法对 Python 很有效,如果不希望给 Python 可执行文件赋予更多的 capabilities,可以使用上面的方法来实现这个目的:
[user1@centos111 dockerfile]$ python3 -m http.server 80
Traceback (most recent call last):
....
PermissionError: [Errno 13] Permission denied$ ./set_ambient /usr/bin/python3 -m http.server 80
Starting process with CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE in ambient
Serving HTTP on 0.0.0.0 port 80 (http://0.0.0.0:80/) ...
或者分开执行
[batman@blackstone ~]$ ./set_ambient /bin/bash
Starting process with CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE in ambient
[batman@blackstone ~]$ python3 -m http.server 80
Serving HTTP on 0.0.0.0 port 80 (http://0.0.0.0:80/) ...
最后讲一下 Inheritable 与 Ambient 集合的区别,如果想使用 Inheritable 达到上述目的,需要将 CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE capabilities 添加到 Go web 服务可执行文件的 Inheritable 集合中,同时还需要开启 Effective 标志位。
看起来很有道理,但有一个问题:如果可执行文件的有效用户是普通用户,且没有 Inheritable 集合,即 F(inheritable) = 0,那么 P(inheritable) 将会被忽略(P(inheritable) & F(inheritable))。
由于绝大多数可执行文件都是这种情况,因此 Inheritable 集合的可用性受到了限制。
4. 容器与 capabilities
如果你理解了上一节的内容,应该可以猜到 capabilities 和容器是相辅相成的,至少在一定程度上是这样。
本节内容将在容器中实践 capabilities。
我已经创建了一个测试镜像,并安装了 capsh 和上文所述的程序,代码在 GitHub 仓库中。
如果不加任何参数直接运行容器,结果如下:
docker run -it amouat/caps
Unable to find image 'amouat/caps:latest' locally
latest: Pulling from amouat/caps
4a56a430b2ba: Pull complete
a66cc40807b2: Pull complete
1793030292fb: Pull complete
49e8b8e391f8: Pull complete
8f3f8896bb62: Pull complete
fd4a6c8d6f4f: Pull complete
4e732d5ddd3d: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:e62ada848fd067e16cad1e7c8ea1fd8d80a180cbe010c669dd60cb8091c106ee
Status: Downloaded newer image for amouat/caps:latestroot@84bb57aa7b5e:/# capsh --print
Current: = cap_chown,cap_dac_override,cap_fowner,cap_fsetid,cap_kill,cap_setgid,cap_setuid,cap_setpcap,cap_net_bind_service,cap_net_raw,cap_sys_chroot,cap_mknod,cap_audit_write,cap_setfcap+ep
Bounding set =cap_chown,cap_dac_override,cap_fowner,cap_fsetid,cap_kill,cap_setgid,cap_setuid,cap_setpcap,cap_net_bind_service,cap_net_raw,cap_sys_chroot,cap_mknod,cap_audit_write,cap_setfcap
Securebits: 00/0x0/1'b0secure-noroot: no (unlocked)secure-no-suid-fixup: no (unlocked)secure-keep-caps: no (unlocked)
uid=0(root)
gid=0(root)
groups=0(root)
root@84bb57aa7b5e:/# grep Cap /proc/$BASHPID/status
CapInh: 0000000000000000
CapPrm: 00000000a80425fb
CapEff: 00000000a80425fb
CapBnd: 00000000a80425fb
CapAmb: 0000000000000000
和宿主机还是有些区别的,容器中的 root 用户并没有包含所有的 capabilities,比如 SYS_TIME。如果你可以在容器中修改系统时间,那么宿主机和其他容器中的系统时间都会被改变。
另外需要注意的是,容器中的 Ambient 集合是空的,目前在 Docker 和 Kubernetes 中还无法配置 Ambient 集合,过在底层的 runc 运行时中是可以配置的。
具体参考 Kubernetes 项目的 issue。
如果使用指定的用户运行容器,会得到全新的结果:
[root@centos111 capabilities-blog-master]# docker run -it --user=nobody amouat/caps
nobody@7022d21f9cc9:/$
nobody@7022d21f9cc9:/$ grep Cap /proc/$BASHPID/status
CapInh: 0000000000000000
CapPrm: 0000000000000000
CapEff: 0000000000000000
CapBnd: 00000000a80425fb
CapAmb: 0000000000000000
Permitted 和 Effective 集合被清空了,这跟上文提到的特殊规则有关,从 root 用户切换到普通用户, Permitted 和 Effective 集合中的 capabilities 都会被清空。可以通过将 capabilities 添加到可执行文件的 Inheritable 集合中,同时开启 Effective 标志位来使其正常工作。amouat/caps 已经包含了一个具备此条件的可执行文件,可以用来测试一下:
下面我们就使用普通用户的docker下来运行程序:
[root@centos111 capabilities-blog-master]# docker run --user nobody amouat/caps getcap /inh_server
/inh_server = cap_net_bind_service+ei
[root@centos111 capabilities-blog-master]# docker run -d -p 8000:80 --user nobody amouat/caps /inh_server
f401106fe1bdb894cd3c603927d7f6cc5974be6e330000211d48e98d9bb810b8
[root@centos111 capabilities-blog-master]# curl localhost:80
Successfully serving on port 80
要想在容器中利用 capabilities 实现一个可以正常工作的非 root 环境,需要使用上文所述的 set_ambient 程序。
下面就演示一下容器中半特权环境的构建:
[root@centos111 capabilities-blog-master]# docker run -p 8000:80 --user nobody amouat/caps /server
2024/01/07 13:56:43 listen tcp :80: bind: permission denied
[root@centos111 capabilities-blog-master]# docker run -d -p 8000:80 --user nobody amouat/caps /set_ambient /server
e3b32121b0c11d2ed71a0ea3a8edf0c346012fd230c293f91cf275b5e6fac014
[root@centos111 capabilities-blog-master]# curl localhost:80
Successfully serving on port 80
在容器中限制 capabilities 最简单最常见的方法是 --cap-drop 和 --cap-add 参数,这些参数只会影响所有用户的 Bounding 集合,包括 root 用户。
安全的做法是移除所有的 capabilities,只添加需要的 capabilities,例如:
[root@centos111 capabilities-blog-master]# docker run --cap-drop all --cap-add NET_BIND_SERVICE -it amouat/caps capsh --print
Current: = cap_net_bind_service+ep
Bounding set =cap_net_bind_service
Securebits: 00/0x0/1'b0secure-noroot: no (unlocked)secure-no-suid-fixup: no (unlocked)secure-keep-caps: no (unlocked)
uid=0(root)
gid=0(root)
groups=0(root)
然后就可以以 root 身份或普通用户身份运行容器,例如:
[root@centos111 capabilities-blog-master]$ run --cap-drop all --cap-add NET_BIND_SERVICE \
-d -p 8000:80 --user nobody amouat/caps /set_ambient /server[root@centos111 capabilities-blog-master]$ curl localhost:80
Successfully serving on port 80
[root@centos111 capabilities-blog-master]#$ docker top 9c17
UID ... CMD
nobody ... /server现在容器中的进程只有单一的 NET_BIND_SERVICE capabilities,并且是以非 root 用户身份运行的。即使容器的进程被黑客攻击,攻击者只会拥有有限的文件系统权限,无法施展拳脚。
Docker 中还有一个选项可以防止容器中的用户获得新的 capabilities,它可以有效阻止攻击者提升权限来避免受到攻击,同时也阻止了再容器中执行 set_ambient 程序。例如:
docker run -p 8000:80 --security-opt=no-new-privileges:true \
--user nobody amouat/caps /set_ambient /server对于容器玩家,我的最终建议是:移除所有非必要的 capabilities,并以非 root 身份运行。
使用 Ambient 集合与可执行文件的 capabilities 进行逻辑运算可以得到一个相对安全的容器环境,大部分情况下应该不需要使用 set_ambient 这样的辅助程序。
Linux capabilities 与容器领域有着紧密的联系,我很期待看到 Ambient capabilities 被广泛应用到容器领域,以支持以非 root 身份运行的半特权容器。