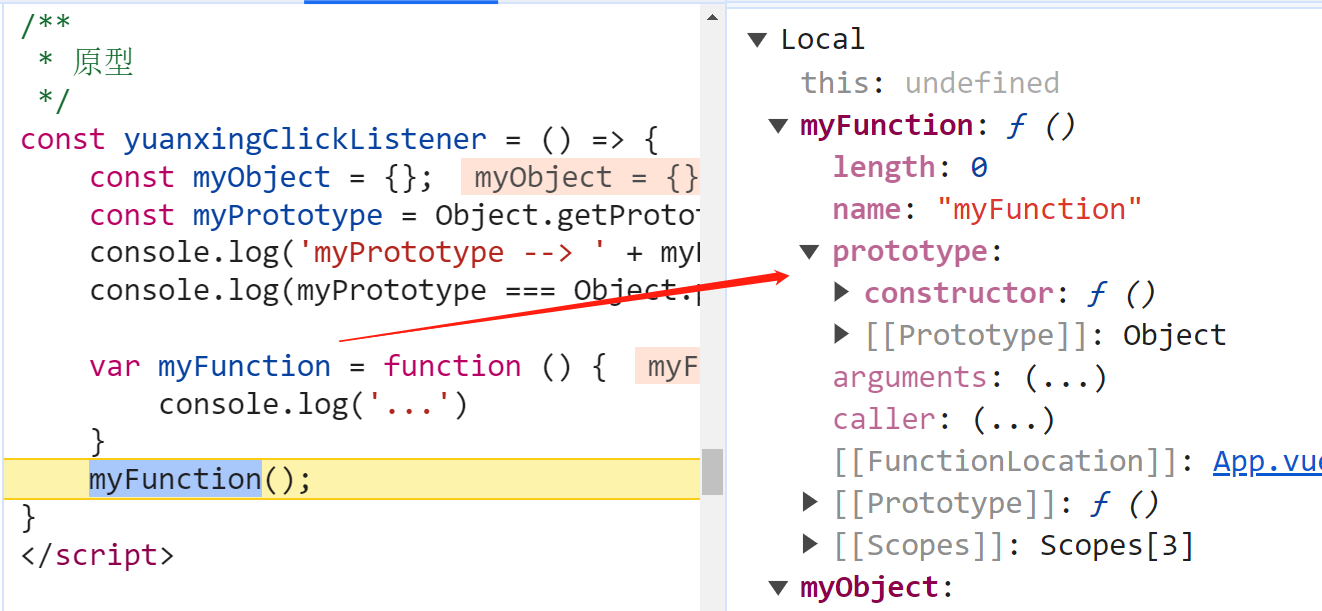
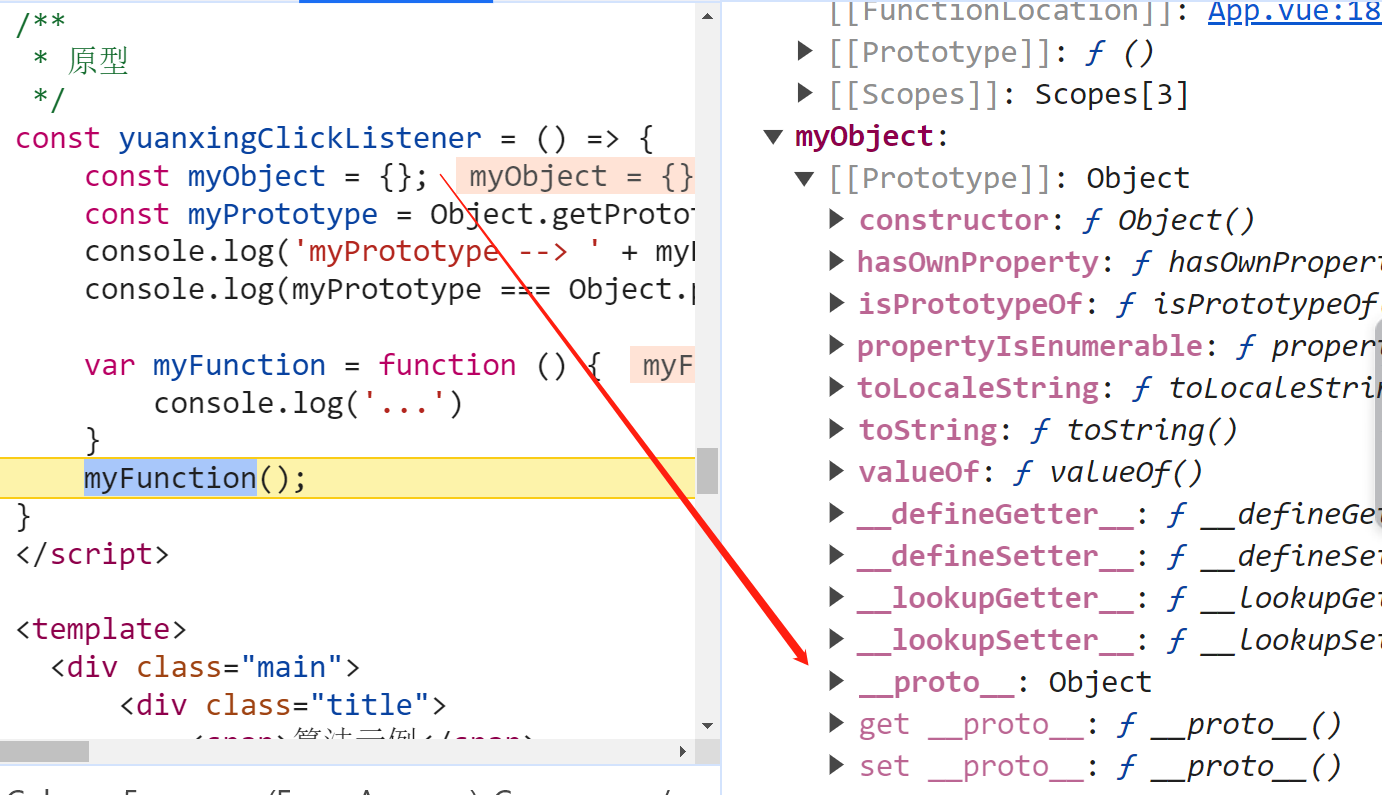
在 JavaScript 中,每个对象都有一个关联的原型(prototype)。原型是一个对象,其他对象可以通过原型实现属性和方法的继承。原型链是一种由对象组成的链式结构,它通过原型的引用连接了一系列对象,形成了一种继承关系。
在学习原型和原型链之前,我们需要首先掌握以下三个属性:
prototype: 每一个函数都有一个特殊的属性,叫做原型(prototype)constructor: 相比于普通对象的属性,prototype属性本身会有一个属性constructor,该属性的值为prototype所在的函数__proto__: 每一个对象都有一个__proto__属性,该属性指向对象(实例)所属构造函数(类)的原型prototype
原型(Prototype):
每个 JavaScript 对象都有一个原型对象,它用于查找对象的属性和方法。对象可以通过 __proto__ 属性访问它的原型。在 ES6 中,可以使用 Object.getPrototypeOf() 方法获取对象的原型。
const myObject = {};
const myPrototype = Object.getPrototypeOf(myObject);console.log(myPrototype === Object.prototype); // 输出: true
原型链(Prototype Chain):
原型链是一种对象之间通过原型引用连接起来的链式结构。当我们访问一个对象的属性或方法时,JavaScript 引擎首先在该对象本身查找,如果找不到,则会沿着原型链向上查找,直到找到对应的属性或方法,或者查找到达原型链的顶端(Object.prototype)。
function Animal(name) {this.name = name;
}Animal.prototype.sayHello = function() {console.log(`Hello, I'm ${this.name}`);
};const cat = new Animal('Whiskers');
cat.sayHello(); // 输出: Hello, I'm Whiskers
在上述例子中,cat 对象的原型是 Animal.prototype,Animal.prototype 的原型是 Object.prototype。因此,当调用 sayHello 方法时,JavaScript 引擎首先在 cat 对象中查找,找不到的话就沿着原型链向上查找,最终在 Animal.prototype 中找到了 sayHello 方法。
原型链的终点:
原型链的终点是 Object.prototype,它是所有对象的根原型。Object.prototype 没有自己的原型,形成了原型链的终点。
构造函数与原型链:
通过构造函数创建的对象共享同一个原型。当我们创建一个新对象时,它的原型会指向构造函数的原型对象。
function Car(make, model) {this.make = make;this.model = model;
}Car.prototype.drive = function() {console.log('Vroom!');
};const myCar = new Car('Toyota', 'Camry');
myCar.drive(); // 输出: Vroom!
在上述例子中,myCar 对象的原型是 Car.prototype,而 Car.prototype 的原型是 Object.prototype,形成了原型链。
继承与原型链:
通过原型链,可以实现对象之间的继承。一个对象可以继承另一个对象的属性和方法,从而减少代码冗余。
function Bird(name) {this.name = name;
}Bird.prototype.fly = function() {console.log(`${this.name} is flying.`);
};function Penguin(name) {Bird.call(this, name);
}Penguin.prototype = Object.create(Bird.prototype);
Penguin.prototype.constructor = Penguin;Penguin.prototype.swim = function() {console.log(`${this.name} is swimming.`);
};const penguin = new Penguin('Happy Feet');
penguin.fly(); // 输出: Happy Feet is flying.
penguin.swim(); // 输出: Happy Feet is swimming.
在上述例子中,Penguin 构造函数通过 Bird.call(this, name) 继承了 Bird 构造函数的属性。然后,通过 Object.create(Bird.prototype) 创建了一个新对象,将其设置为 Penguin.prototype,从而继承了 Bird.prototype 中的方法。最后,将 Penguin.prototype.constructor 设置为 Penguin,确保正确指向构造函数。这样,Penguin 对象就能够继承 Bird 对象的方法。
Vue进阶:
在 Vue.js 2 中,原型链主要用于两个方面:全局方法和实例属性的访问。
1. 全局方法的访问:
Vue.js 在其原型链上定义了一些全局方法,可以通过实例对象或者全局引用来调用。例如,$emit、$on 等方法。
// 在组件中使用
export default {methods: {handleClick() {this.$emit('custom-event', 'Hello from child!');}}
};// 在全局使用
Vue.prototype.$myGlobalMethod = function() {console.log('This is a global method!');
};// 然后在任何组件中
this.$myGlobalMethod();
2. 实例属性的访问:
在 Vue.js 2 中,实例对象上有一些特定的属性,可以通过原型链访问。
// 创建 Vue 实例
const vm = new Vue({data: {message: 'Hello, Vue!'}
});// 访问实例的属性
console.log(vm.$data.message); // 输出: Hello, Vue!
上述代码中,vm.$data.message 中的 $data 就是通过原型链访问到实例对象的属性。同样,还有其他一些实例属性,如 $props、$el、$options 等,它们可以提供对实例的不同方面的访问。
总的来说,原型链在 Vue.js 2 中主要用于提供全局方法和实例属性的访问。这样的设计使得在组件中可以方便地使用一些全局方法,同时也让开发者能够通过实例对象访问一些特定的实例属性。
3、Vue是一个函数