前言
在不同的场景下,执行不同的业务逻辑,在日常工作中是很寻常的事情。比如,订阅系统。在收到阿里云的回调事件、与收到AWS的回调事件,无论是收到的参数,还是执行的逻辑都可能是不同的。为了避免,每次新增一种场景,就要改变原有的代码结构,比如,改变原有逻辑,添加 if-else结构,一种可行的方案是,使用策略模式。
策略模式
贴个链接
简单来说,就是根据请求方的类型,执行特定的业务逻辑。
问题点
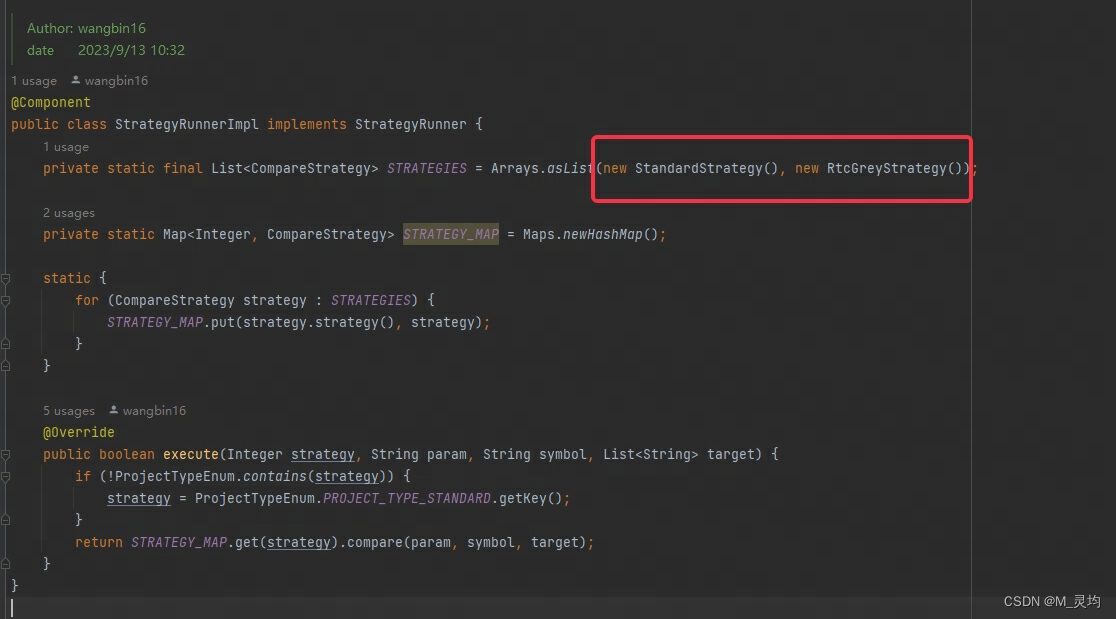
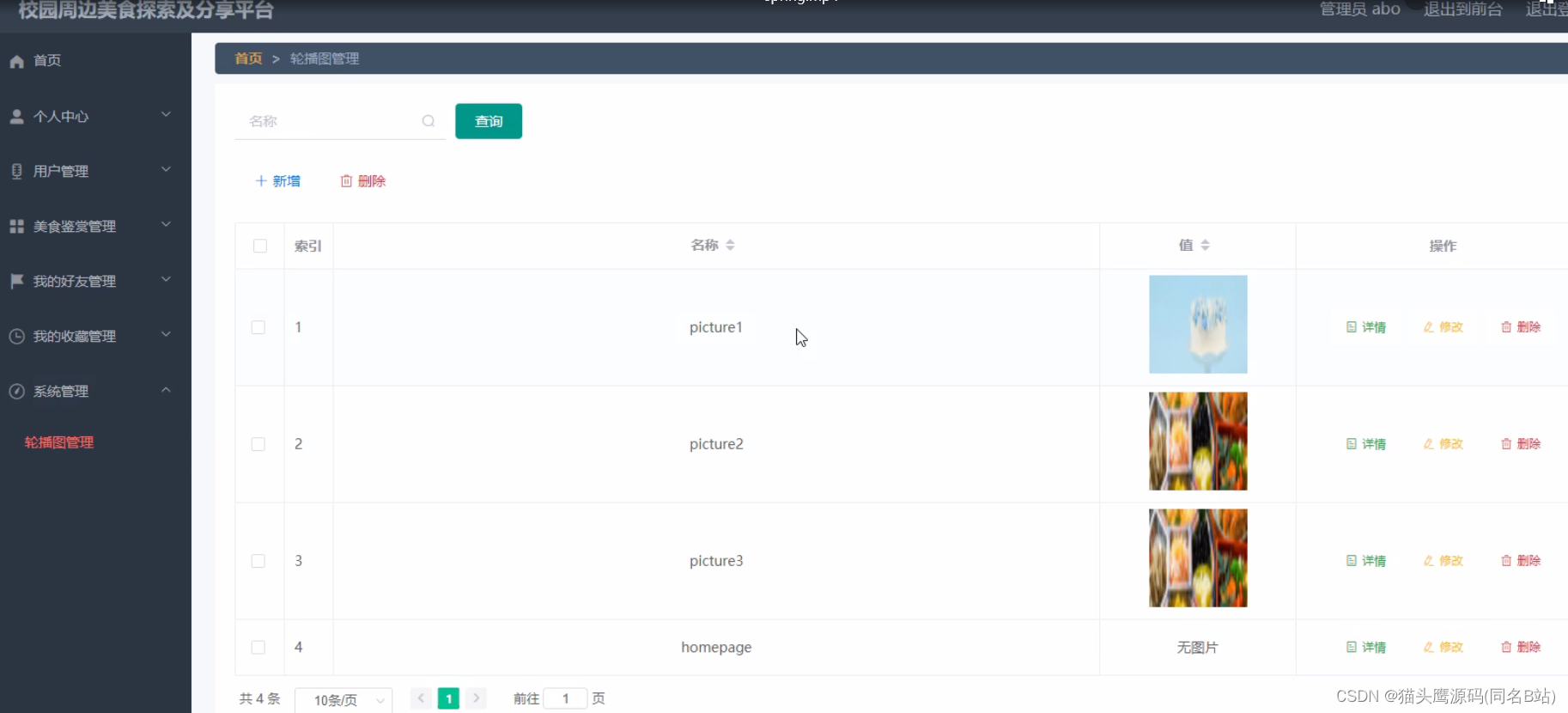
网络上大部分实现策略模式的代码,很多在将具体的策略注入到Map中时,是以硬编码的方式实现的,比如掘金上的这篇文章:如何优雅的将设计模式运用到实际项目中去?
在工作中借鉴,使用截图:
这种方案,虽然可以实现策略模式,但是每次新增策略都要修改这个集合。期望的方案是,新增的策略,自动注入到map中,而不必手动添加。
为了解决新增策略时,要修改map的情况,调研之后,发现有两种方案:
- 美团文章推介的 基于单例的方式,每次启动时,自动将策略注入到map中。
- 掘金上另一种方案:基于注解+反射的方式,动态将策略加载到map中。
相比,美团的方案更加优秀,代码改动少,且性能高。不过,本次以方案2为例说明。
代码实现
业务场景
需要提供给外部云厂商回调API,当云服务发生告警时,调用此API,将告警事情同步到服务使用方。
考虑点:
- 因为每家厂商的回调参数各有不同,此时,需要定义一个回调对象基类,每个云厂商对应的回调对象继承这个基类,并实现添加其特定的属性。
- 因为API是放开到公网上的,因此,为了避免被攻击,除了从集团域名出去外,还对IP进行了频控,比如,调用次数100次/秒。
代码结构

具体代码
定义实体类
基类
import lombok.Data;/*** @author wangbin16* @date 2024/1/18 15:33*/
@Data
public class CloudAlertBase {/*** name = "alertType", value = "告警类型"*/private Integer alertType;/*** 业务*/private Integer business;
}阿里云
import lombok.Data;/*** 阿里云监控告警* @author wangbin16* @date 2024/1/18 15:35*/
@Data
public class AliyunCloudAlertAo extends CloudAlertBase {private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;/*** name = "alertName", value = "报警名称"*/private String alertName;/*** name = "alertState", value = "报警状态"*/private String alertState;/*** name = "curValue", value = "报警发生或恢复时监控项的当前值"*/private String curValue;/*** name = "dimensions", value = "发生报警的对象"*/private String dimensions;/*** name = "expression", value = "报警规则的表达式"*/private String expression;
策略模式
策略基类
/*** @author wangbin16* @date 2024/1/18 15:41*/
public interface CloudAlertStrategy {/*** 处理云监控告警* @param param*/void handleCloudAlert(CloudAlertBase param);
}阿里云策略
@Slf4j
@Service
@CloudAlertAnnotation(alertType = CloudAlertTypeEnum.ALIYUN)
public class AliyunCloudAlertStrategy implements CloudAlertStrategy {@Overridepublic void handleCloudAlert(CloudAlertBase param) {// TODO 处理阿里云监控告警// 暂时先发送给我 @wangbin16SendMsgUtils sendMsgUtils = new SendMsgUtils();sendMsgUtils.sendP2pPopoMsg(JSON.toJSONString(param), "wangbin16@xxx", "【阿里云监控告警】");}
}策略注册
import org.reflections.Reflections;import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;/*** @author wangbin16* @date 2024/1/18 15:50*/
public class AnnotationCloudAlertStrategyFactory {/*** 存储策略*/static Map<Integer, CloudAlertStrategy> strategyMap = new HashMap<>();static {registerStrategy();}/*** 自动注册策略*/private static void registerStrategy() {// 通过反射获取所有的策略类Reflections reflections = new Reflections(CloudAlertStrategy.class.getPackage().getName());Set<Class<? extends CloudAlertStrategy>> cloudStrategyClassSet = reflections.getSubTypesOf(CloudAlertStrategy.class);if (cloudStrategyClassSet != null) {for (Class<?> clazz : cloudStrategyClassSet) {// 找到类型注解,自动完成策略注册if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(CloudAlertAnnotation.class)) {CloudAlertAnnotation alertTypeAnnotation = clazz.getAnnotation(CloudAlertAnnotation.class);CloudAlertTypeEnum chargeType = alertTypeAnnotation.alertType();try {strategyMap.put(chargeType.getCode(), (CloudAlertStrategy) clazz.newInstance());} catch (InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException e) {e.getStackTrace();}}}}}/*** 提供注册策略接口,外部只需要调用此接口接口新增策略* 策略定义时,即注入,这是口子*/public static void registerChargeStrategy(CloudAlertTypeEnum alertType, CloudAlertStrategy strategy) {strategyMap.put(alertType.getCode(), strategy);}
}
策略选择器
@Service
@Slf4j
public class CloudAlertStrategySelector {public CloudAlertStrategy selector(Integer alertType) {if (alertType == null) {return null;}return AnnotationCloudAlertStrategyFactory.strategyMap.get(alertType);}
}
服务调用
@Slf4j
@Service("cloudMonitorService")
public class CloudMonitorService {@Autowiredprivate CloudAlertStrategySelector cloudAlertStrategySelector;public void handleCloudMonitor(CloudAlertBase param) {logger.info("handleCloudMonitor param:{}", JSON.toJSONString(param));CloudAlertStrategy selector = cloudAlertStrategySelector.selector(param.getAlertType());if (selector != null) {selector.handleCloudAlert(param);} else {logger.error("外部云告警异常调用, param:{}", JSON.toJSONString(param));}}
}
测试
调用指定的接口,执行指定的逻辑