目录
- 机试涉及到的算法
- 一、字符串
- 二、vector
- 二、map
- 三、set
- 四、queue
- 五、并查集
- 五、cmath
- 六、读入数据
- 6.1 示例1
- 6.2 示例2
- 6.3 示例3
- 6.4 示例4
- 6.5 示例5
- 6.6 示例6
- 6.7 示例7
- 6.8 示例8
- 6.9 示例9
- 6.10 示例10
- 6.11 示例11
- 七、输入输出
- 八、排序
- 九、数学相关
- 十、大数的表示
- 十一、IDE
机试涉及到的算法
排序算法,BFS,DFS,回溯法,打表法,双指针算法,贪心算法(背包问题、活动安排问题),动态规划(最大连续子序列和、LIS、LCS等等),压缩路径的并查集问题,dijkstra算法(最短路径),kruskal算法(最小生成树),树的前序中序后序转换及还原,二分图及图的着色问题,快速幂和快速乘算法,大整数/高精度运算,STL的运用(如vector、string、stack、queue的常见操作)
一、字符串
- 判断字符串中是否包含字符串
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string a= "abcdefghigklmn" ;string b= "def" ;string c= "123" ;string::size_type idx;idx=a.find(b); //在a中查找b.if (idx == string::npos) //不存在。cout << "not found\n" ;else //存在。cout << "found\n" ; idx=a.find(c); //在a中查找c。if (idx == string::npos ) //不存在。cout << "not found\n" ;else //存在。cout << "found\n" ; return 0;
}
- int 转 string
int val = 15;
// 使用 std 命名空间内的方法
string str = to_string(val);
- string 转 int
string str = "15";
// 转换为C字符串,然后利用 C 提供的函数 atoi 转换为 int 类型
int val = atoi(str.c_str())
- 在指定位置插入字符
string str = "abc";
int pos = 2;
// 在指定位置插入字符
str.insert(str.begin() + pos, 'd');
cout<<str<<endl; // 输出:abdc
- 在指定位置插入字符串
string str = "abc";
int pos = 2;
// 在指定位置插入字符串
str.insert(2, "de");
cout<<str<<endl; // 输出:abdec
二、vector
- 指定位置插入元素
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{vector<int> digits = {1, 2, 3};for (int i = 0; i < digits.size(); i++){cout << digits[i] << " ";}cout << endl;int pos = 1;digits.insert(digits.cbegin() + pos, 0);// digits = {1, 0, 2, 3}for (int i = 0; i < digits.size(); i++){cout << digits[i] << " ";}return 0;
}
二、map
- 查找元素
// 判断 mp 中是否存在 key
if (mp.find(key) == mp.end()) {return -1;
}
- 插入/修改元素(关于通过下标访问map(或unordered_map)中不存在的元素,对容器的影响,可以参考:https://blog.csdn.net/myf_666/article/details/132192002)
// 更新哈希表
mp[key] = cur;
- 删除元素
mp.erase(key);
- 对于map和unordered_map,当我们采用下标运算符访问不存在的key值时,会先插入一个value(调用默认构造函数),然后返回。这样就会对原有变量造成破坏。如果我们不想拥有这种访问map或unordered_map导致的副作用,我们可以使用find操作,该操作不会对原有变量造成破坏。
三、set
- 添加元素
srcNames.insert(srcName);
srcNames.emplace(srcName); // 效率比insert更高一些
- 查找元素
opNames.find("*") == opNames.end()
- 合并两个集合
#include<algorithm>
set_union(roleSets.begin(), roleSets.end(),tmp.begin(), tmp.end(), inserter(roleSets, roleSets.begin()));
四、queue
- 优先队列,默认是大根堆:
priority_queue<int> girlsLike;priority_queue<int> boysLike;
- 如果想使用小根堆,在模板中添加参数,greater表示后面的元素要大于前面的:
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> girlsLike;priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> boysLike;
在使用小根堆来实例化自定义类型时,需要注意重载运算符>,重载<运算符会报错。示例代码如下:
struct Point
{int val;int x;int y;Point(int val, int x, int y) : val(val), x(x), y(y) {}// 重载>运算符,同时函数末尾注意添加constbool operator>(const Point &point) const{return this->val > point.val;}
};
greater是一个模板,关于这个模板的介绍可以参考:C++中的 greate/less 比较器模板的实现原理及作用:https://blog.csdn.net/myf_666/article/details/135374270
五、并查集
不带有路径压缩的并查集:
class UFSets {
public:vector<int> vec;UFSets(int sz) {vec = vector<int>(sz, -1);}int Find(int x) {while (vec[x] >= 0)x = vec[x];return x;}bool Union(int root1, int root2) {int r1 = Find(root1);int r2 = Find(root2);if (r1 == r2) {return false;}if (vec[r2] < vec[r1]) {vec[r2] = vec[r1] + vec[r2];vec[r1] = r2;}else {vec[r1] = vec[r1] + vec[r2];vec[r2] = r1;}return true;}
};
带有路径压缩的并查集:
// 加权并查集
class UFSets {
public:vector<int> parent;UFSets(int n) {parent = vector<int>(n);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {parent[i] = i;}}int Find(int x) {if (x != parent[x]) {// 递归进行路径压缩parent[x] = Find(parent[x]);}return parent[x];}void Union(int x, int y) {int rootX = Find(x);int rootY = Find(y);if (rootX == rootY) {return;}parent[rootX] = rootY;}
};
五、cmath
#include<cmath>
里面角度的大小均为弧度制,如果是角度,需要进行转换 θ ∗ P I / 180 \theta*PI/180 θ∗PI/180
#define PI acos(-1.0)
函数相关功能如下:
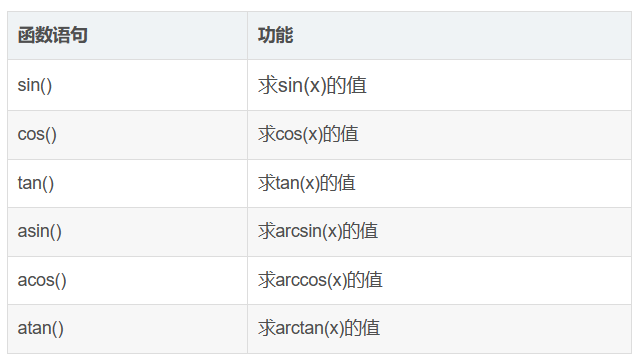
六、读入数据
6.1 示例1
输入描述:
输入包括两个正整数a,b(1 <= a, b <= 1000),输入数据包括多组。
输出描述:
输出a+b的结果
输入例子:
1 5
10 20
输出例子:
6
30
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {int a, b;while (cin >> a >> b) { // 注意 while 处理多个 casecout << a + b << endl;}
}
// 64 位输出请用 printf("%lld")
6.2 示例2
输入描述:
输入第一行包括一个数据组数t(1 <= t <= 100)
接下来每行包括两个正整数a,b(1 <= a, b <= 1000)
输出描述:
输出a+b的结果
输入例子:
2
1 5
10 20
输出例子:
6
30
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {int a, b;int n;cin >> n;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {cin >> a >> b;cout << a + b << endl;}
}
// 64 位输出请用 printf("%lld")
6.3 示例3
输入描述:
输入包括两个正整数 a , b ( 1 < = a , b < = 1 0 9 ) a,b(1 <= a, b <= 10^9) a,b(1<=a,b<=109),输入数据有多组, 如果输入为0 0则结束输入
输入例子:
1 5
10 20
0 0
输出例子:
6
30
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {int a, b;while (true) {cin >> a >> b;if (a == 0 && b == 0) {break;}cout << a + b << endl;}
}
// 64 位输出请用 printf("%lld")
6.4 示例4
输入描述:
输入数据包括多组。
每组数据一行,每行的第一个整数为整数的个数n(1 <= n <= 100), n为0的时候结束输入。
接下来n个正整数,即需要求和的每个正整数。
输出描述:
每组数据输出求和的结果
输入例子:
4 1 2 3 4
5 1 2 3 4 5
0
输出例子:
10
15
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {int a, b;while (true) { // 注意 while 处理多个 caseint n;cin >> n;if (n == 0)break;int sum = 0;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {int tmp;cin >> tmp;sum += tmp;}cout << sum << endl;}
}
// 64 位输出请用 printf("%lld")
6.5 示例5
输入描述:
输入的第一行包括一个正整数t(1 <= t <= 100), 表示数据组数。
接下来t行, 每行一组数据。
每行的第一个整数为整数的个数n(1 <= n <= 100)。
接下来n个正整数, 即需要求和的每个正整数。
输出描述:
每组数据输出求和的结果
输入例子:
2
4 1 2 3 4
5 1 2 3 4 5
输出例子:
10
15
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {int n;cin >> n;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {int numberNum;cin >> numberNum;int sum = 0;for (int j = 0; j < numberNum; j++) {int tmp;cin >> tmp;sum += tmp;}cout << sum << endl;}
}
// 64 位输出请用 printf("%lld")
6.6 示例6
输入描述:
输入数据有多组, 每行表示一组输入数据。
每行的第一个整数为整数的个数n(1 <= n <= 100)。
接下来n个正整数, 即需要求和的每个正整数。
输出描述:
每组数据输出求和的结果
输入例子:
4 1 2 3 4
5 1 2 3 4 5
输出例子:
10
15
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {int n;while (cin >> n) {int sum = 0;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {int tmp;cin >> tmp;sum += tmp;}cout << sum << endl;}
}
// 64 位输出请用 printf("%lld")
6.7 示例7
输入描述:
输入数据有多组, 每行表示一组输入数据。
每行不定有n个整数,空格隔开。(1 <= n <= 100)。
输出描述:
每组数据输出求和的结果
输入例子:
1 2 3
4 5
0 0 0 0 0
输出例子:
6
9
0
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {int tmp;int sum = 0;while (cin >> tmp) {sum += tmp;if (cin.get() == '\n') {cout << sum << endl;sum = 0;}}
}
// 64 位输出请用 printf("%lld")
6.8 示例8
输入描述:
输入有两行,第一行n
第二行是n个字符串,字符串之间用空格隔开
输出描述:
输出一行排序后的字符串,空格隔开,无结尾空格
输入例子:
5
c d a bb e
输出例子:
a bb c d e
#include <iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;int main() {string str;int n;cin >> n;vector<string> vec;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {cin >> str;vec.push_back(str);}sort(vec.begin(), vec.end());for (int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i++) {cout << vec[i] << " ";}
}
// 64 位输出请用 printf("%lld")
6.9 示例9
输入描述:
多个测试用例,每个测试用例一行。
每行通过空格隔开,有n个字符,n<100
输出描述:
对于每组测试用例,输出一行排序过的字符串,每个字符串通过空格隔开
输入例子:
a c bb
f dddd
nowcoder
输出例子:
a bb c
dddd f
nowcoder
#include <iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;int main() {string str;vector<string> vec;while (cin >> str) {vec.push_back(str);if (cin.get() == '\n') {sort(vec.begin(), vec.end());for (int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i++) {cout << vec[i] << " ";}cout << endl;vec.clear();}}}
6.10 示例10
输入描述:
多个测试用例,每个测试用例一行。
每行通过,隔开,有n个字符,n<100
输出描述:
对于每组用例输出一行排序后的字符串,用’,'隔开,无结尾空格
输入例子:
a,c,bb
f,dddd
nowcoder
输出例子:
a,bb,c
dddd,f
nowcoder
#include <iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;int main() {string str;vector<string> vec;while (cin >> str) {string cur;for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++) {while (str[i] != ',' && i < str.size()) {cur += str[i];i++;}vec.push_back(cur);cur = "";}sort(vec.begin(), vec.end());for (int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i++) {if (i == vec.size() - 1) {cout << vec[i] << endl;} else {cout << vec[i] << ",";}}vec.clear();}}
6.11 示例11
数据范围:
0 < a , b < 2 × 1 0 10 0<a,b<2×10^{10} 0<a,b<2×1010
时间限制:C/C++ 1秒,其他语言2秒
空间限制:C/C++ 256M,其他语言512M
输入描述:
输入有多组测试用例,每组空格隔开两个整数
输出描述:
对于每组数据输出一行两个整数的和
输入例子:
1 1
输出例子:
2
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {long a, b; // 不要用 int a, b, 因为测试数据会越界,为了效果,所以这个题目故意不在题面说数据范围while (cin >> a >> b) { // 注意 while 处理多个 casecout << a + b << endl;}
}
// 64 位输出请用 printf("%lld")
七、输入输出
- 控制输出位数:
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;int main(){double result = 3.1415926;std::cout << fixed << setprecision(3) << result << std::endl;
}
- 关掉缓冲区同步,提高输入输出效率
//提高cin,cout的速度 ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
- 将
endl替换为\n可以提高效率。因为在插入换行符的同时,endl还会刷新缓冲区,使得输出字符立即显示到屏幕上,这一操作会造成较为昂贵的开销。在输入数据较小的情况下,区别不大,但如果需要大量输出换行的题目,时间提升很明显。
八、排序
- 排序主要利用sort函数,默认从小到大排
vector<int> A(M, 0);for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) { // 朋友近视眼度数cin >> A[i];}sort(A.begin(), A.end()); // 从小到大
- 排序map,并自定义排序规则
vector<pair<int,int>> HP(N);for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { // 高度cin >> HP[i].first;}for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { // 位置cin >> HP[i].second;}sort(HP.begin(), HP.end(), [&](pair<int, int> a, pair<int, int> b) {return a.second < b.second;});
- 从大到小排
vector<int> A(M, 0);for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) { // 朋友近视眼度数cin >> A[i];}sort(A.begin(), A.end(), greater<int>()); // 从大到小,用greater<int>()
九、数学相关
- PI如何定义
通过下面这种反函数,来定义宏进行实现。
# define PI acos(-1)
十、大数的表示
在设置一些无限大的参数时,我们往往纠结于要设置多大。具体选择这两个数的原因参见博客:https://blog.csdn.net/tigercoder/article/details/70338623 和 https://blog.csdn.net/u010129448/article/details/37941123
int minVal = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int maxVal = -0x3f3f3f3f - 1;
或者,当所有情况的值都大于0,而且我们想要保存某个最大值的时候:
int maxVal = 0;
因为不会出现负数的情况嘛,所以没有必要考虑无穷小。
十一、IDE
VS2012中需要使用下面代码来停住窗口,查看结果。
system("pause");