1、list介绍
2、list用法
list的接口有很多,具体如下

具体用法可以查看 https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/list/list/?kw=list
下面我介绍一些常用的接口的用法
2.1 list的构造
| 构造函数(constructor) | 接口说明 |
| list (size_type n, const value_type& val = value_type()) | 构造的 list 中包含 n 个值为 val 的元素 |
| list() | 构造空的 list |
| list (const list& x) | 拷贝构造函数 |
| list (InputIterator first, InputIterator last) | 用 [first, last) 区间中的元素构造 list |
// list的构造
void TestList1()
{list<int> l1; // 构造空的l1list<int> l2(4, 100); // l2中放4个值为100的元素list<int> l3(l2.begin(), l2.end()); // 用l2的[begin(), end())左闭右开的区间构造l3list<int> l4(l3); // 用l3拷贝构造l4// 以数组为迭代器区间构造l5int array[] = { 16,2,77,29 };list<int> l5(array, array + sizeof(array) / sizeof(int));// 列表格式初始化C++11list<int> l6{ 1,2,3,4,5 };// 用迭代器方式打印l5中的元素list<int>::iterator it = l5.begin();while (it != l5.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;} cout << endl;// C++11范围for的方式遍历for (auto& e : l5)cout << e << " ";cout << endl;
}
2.2list iterator的使用
迭代器底层是使用指针实现的,所以,我们可以把迭代器当成一个指针,指向list的某个结点。所有的容器的迭代器都被重命名为iterator
| 函数声明 | 接口说明 |
| begin + end | 返回第一个元素的迭代器 + 返回最后一个元素下一个位置的迭代器 |
| rbegin + rend | 返回第一个元素的 reverse_iterator, 即 end 位置 , 返回最后一个元素下一个位置的 reverse_iterator, 即 begin 位置 |
//iterator
void PrintList(const list<int>& l)
{for (list<int>::const_iterator it = l.begin(); it != l.end(); ++it){cout << *it << " ";// *it = 10; 这里是const_iterator ,it指向的内容不能被修改,所以编译不通过}cout << endl;
}void TestList2()
{int array[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 };list<int> l(array, array + sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]));// 使用正向迭代器正向list中的元素// list<int>::iterator it = l.begin(); auto it = l.begin(); while (it != l.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;// 使用反向迭代器逆向打印list中的元素// list<int>::reverse_iterator rit = l.rbegin();auto rit = l.rbegin();while (rit != l.rend()){cout << *rit << " ";++rit;}cout << endl;
}
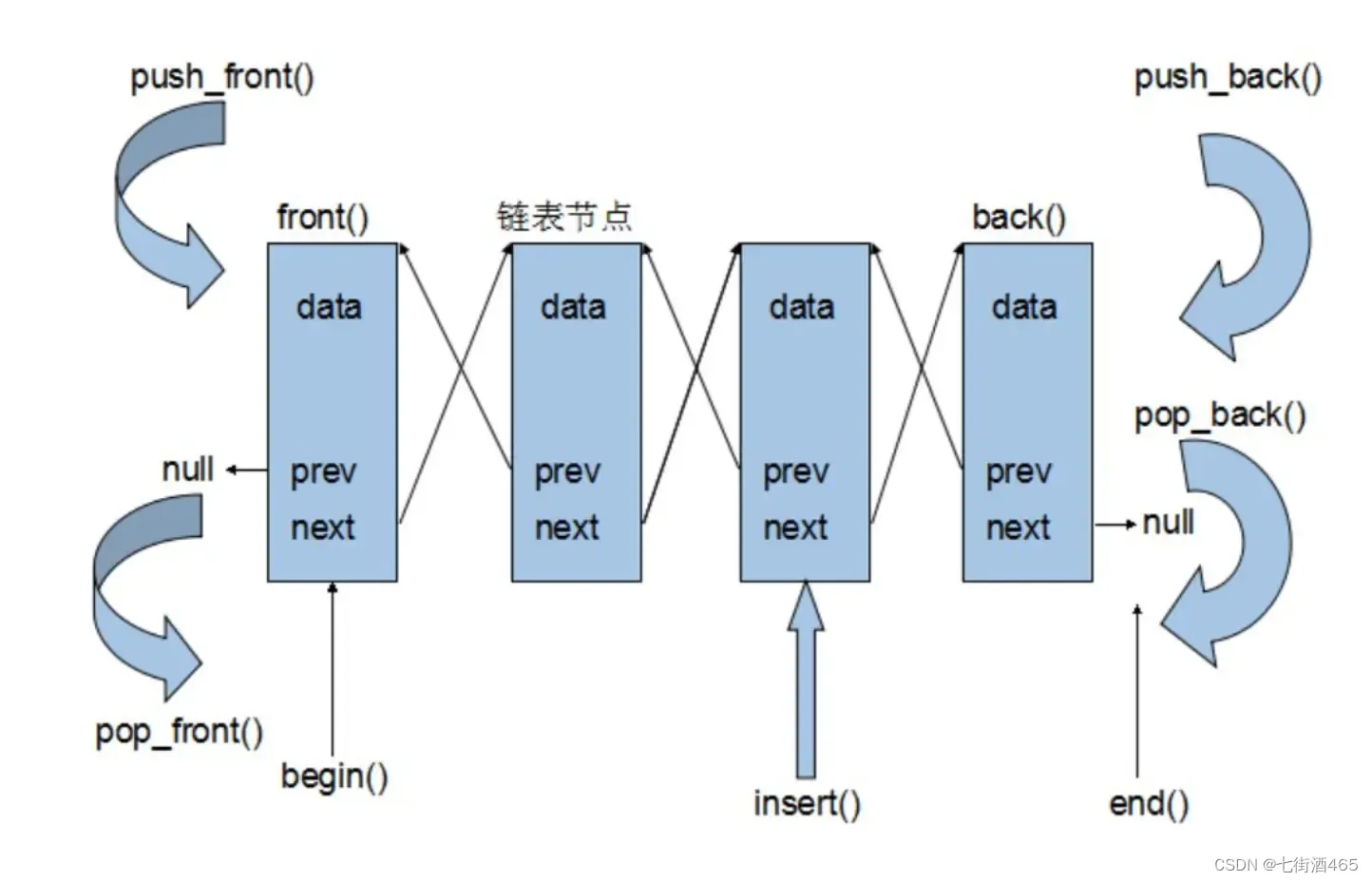
2.3list modifiers
| 函数声明 | 接口说明 |
| push_front | 在 list 首元素前插入值为 val 的元素 |
| pop_front | 删除 list 中第一个元素 |
| push_back | 在 list 尾部插入值为 val 的元素 |
| pop_back | 删除 list 中最后一个元素 |
| insert | 在 list position 位置中插入值为val的元素 |
| erase | 删除 list position 位置的元素 |
| swap | 交换两个 list 中的元素 |
| clear | 清空 list 中的有效元素 |
void TestList1()
{int array[] = { 1, 2, 3 };list<int> L(array, array + sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]));// 在list的尾部插入4,头部插入0L.push_back(4);L.push_front(0);PrintList(L);// 删除list尾部节点和头部节点L.pop_back();L.pop_front();PrintList(L);
}// insert /erase
void TestList2()
{int array1[] = { 1, 2, 3 };list<int> L(array1, array1 + sizeof(array1) / sizeof(array1[0]));// 获取链表中第二个节点auto pos = ++L.begin();cout << *pos << endl;// 在pos前插入值为4的元素L.insert(pos, 4);PrintList(L);// 在pos前插入5个值为5的元素L.insert(pos, 5, 5);PrintList(L);// 在pos前插入[v.begin(), v.end)区间中的元素vector<int> v{ 7, 8, 9 };L.insert(pos, v.begin(), v.end());PrintList(L);// 删除pos位置上的元素L.erase(pos);PrintList(L);// 删除list中[begin, end)区间中的元素,即删除list中的所有元素L.erase(L.begin(), L.end());PrintList(L);
}// resize/swap/clear
void TestList3()
{// 用数组来构造listint array1[] = { 1, 2, 3 };list<int> l1(array1, array1 + sizeof(array1) / sizeof(array1[0]));PrintList(l1);// 交换l1和l2中的元素list<int> l2;l1.swap(l2);PrintList(l1);PrintList(l2);// 将l2中的元素清空l2.clear();cout << l2.size() << endl;
}2.4list的迭代器失效
//这是一个模拟List的clear的实现
//这是错误写法
void clear()
{iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){erase(it);it++;}
}
//这段代码之所以错误,主要是因为,it指向的那个结点已经被删除了,所以it再++是找不到后面节点的位置的。
///
//正确写法
void clear()
{iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){it=erase(it);//删除这个结点,返回这个结点的下一个位置给it。}
}3、list的模拟实现
3、1node类模板
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;
namespace A
{
//用命名区间A把自己实现的list圈起来,防止与库里面的混淆........
}首先先构造出结点的类模板list_node<T>,因为struct默认所有成员都是public,我们需要在类外面使用list_node,所以这里使用struct。定义三个成员变量 _next下一个节点,_pre上一个结点和数据data。
template <class T>
struct list_node
{typedef list_node<T> Node;Node* _next;Node* _pre;T _data;list_node(const T& val=T()):_next(nullptr),_pre(nullptr),_data(val){}
};3、2迭代器类模板
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct __list_iterator
{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef __list_iterator<T,Ref,Ptr> self;__list_iterator(Node* node):_node(node){}Node* _node;self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}self operator++(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}self& operator--(){_node = _node->_pre;return *this;}self operator--(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->pre;return tmp;}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}bool operator != (const self& s){return _node != s._node;}
};3、3list类模板
实现出list的迭代器,我们就可以正式来模拟list接口了。
首先定义一个哨兵位结点,这也是list类模板唯一的成员变量。在此我们复用list_node类模板和迭代器类模板,然后我们实现list的各个接口
template<class T>
class list
{typedef list_node<T> Node;public:typedef __list_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;typedef __list_iterator<T,const T&,const T*> const_iterator;void init(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_pre = _head;}list(){init();}void clear(){iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){it=erase(it);}}~list(){clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}void swap(list<T>& lt){std::swap(_head, lt._head);}list(const list<T>& lt)//构造{_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_pre = _head;for (auto e : lt){push_back(e);}}list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt){swap(lt);return *this;}void push_back(const T& x){Node* tail = _head->_pre;Node* newnode = new Node(x);tail->_next = newnode;newnode->_pre = tail;newnode->_next = _head;_head->_pre = newnode;}void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}iterator insert(iterator pos,const T& x){Node* newnode = new Node(x);Node* cur = pos._node;Node* pre = cur->_pre;pre->_next = newnode;newnode->_pre = pre;newnode->_next = cur;cur->_pre = newnode;return newnode;}iterator erase(iterator pos){assert(pos != end());Node* cur = pos._node;Node* pre = cur->_pre;Node* next = cur->_next;pre->_next=next;next->_pre = pre;delete cur;return next;}void pop_back(){erase(--end());}void pop_front(){erase(begin());}iterator begin(){return _head->_next;}iterator end(){return _head;}const_iterator begin() const{return _head->_next;}const_iterator end() const{return _head;}
private:Node* _head;
};上面就是list的常见接口的模拟实现,有些并不常见的我没有在此写出原来,如果以后见到的时候大家查一下List的文档就可以了,使用方法都很简单。
4、list的优缺点
带头结点的双向循环链表 ,list这个容器常用于适合大量插入删除数据的场景,由于它是一个个结点链接,所以它移动节点会很方便,并不需要挪动数据,头插头删,或者任意位置插入删除都很高效。但是它的缺点也很明显:不支持随机访问,访问某个元素效率O(N),底层节点动态开辟,小节点容易造成内存碎片,空间利用率低,缓存利用率低。大家使用的时候注意能否适合使用List。