一、无头单向非循环链表
1.结构(两个部分):
typedef int SLTDataType;
typedef struct SListNode
{SLTDataType data;//数据域struct SListNode* next;//指针域
}SLNode;它只有一个数字域和一个指针域,里面数据域就是所存放的数据,类型是存放数据的类型,而指针域是为了找到下一个节点,存放的是下一个节点的地址,因此它的类型是一个结构体类型的指针,我们可以使用 typedef 对类型和结构体类型进行重命名,这里就体现一个好名字的重要性,变量命名的规范性是非常关键的,前面学习的时候,我命名十分随意,结果就是越写越混乱,过几天看的时候也不知道自己这个名字代表的是什么。
这里建议头结点的数据域中不要储存东西,很多人习惯里面存放链表的长度,可是我们已经使用 typedef 对类型进行重命名,就是为了方便改变其储存数据的类型,如果我们存放的数据不再是整型了,那自然是储存不了链表长度的,所以为了写出来的链表更具有普适性,还是不要在头结点中数据域中储存链表长度等数据。
还有要区分头结点和头指针,这两个东西完全就不是一个概念,我之前就把它们搞混了,还是很痛苦的。首先头结点是一个节点,本质上是一个结构体,区分数据域和指针域,头指针是一个指针,就别谈什么数据域和指针域了,它就是用来储存第一个节点的地址。这可以理解吧,你想想后面所有节点都是一个指一个,肯定需要一个头引导一下。
当然链表的每一个数据都是直接储存在一个结构体变量中,多个结构体变量共同组成一个链表,而我之前学习的顺序表它就是在一个结构体变量的基础上,通过成员申请指向动态申请的空间,顺序表中的数据并没有直接储存在结构体中,而是储存在动态申请开的空间里,所以一个顺序表只对应一个结构体变量。就是这样的结构差异导致 pList ==NULL 和 ps == NULL 所表达的含义是不同的,pList ==NULL 表示当前链表是一个空链表,当然空链表也是一个链表,只不过里面没有数据罢了,而 ps == NULL 则表示这个顺序表根本不存在,这里需要注意!!!,一个空顺序表的表示方式是:ps->size == 0 。
2.遍历链表数据:
void STLPrint(SLTNode* phead)
{SLTNode* cur = phead;while (cur != NULL){printf("%d->", cur->data);cur = cur->next;}printf("NULL\n");
}直接写一个函数,这里我们传递的是头指针,当决定用指针去遍历链表之后,接下来就该让这个指针动起来 cur = cur->next 就是通过不断把下一个节点的地址不断赋值给自己来实现遍历的,直到cur = NULL 的时候说明已经遍历完了整个链表。这里有个非常值得注意的问题:循环结束你条件的设置,我设置的是 cur != NULL ,那么需要思考的是为什么不是 cur -> next != NULL 呢!?让我们来观察这个循环,当cur -> next != NULL 时说明 cur 指向最后一个节点,并没有遍历结束。
3.创建新节点:
由于我们后面很多操作都需要创建新的节点,就把节点的创建单独封装了一个函数。
不难这就不展开说了。
SLTNode* BuySLTNode(SLTDataType x)//创建新节点
{SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc");return NULL;}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;return newnode;
}4.尾加:
void SLTPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)//尾加函数
{assert(pphead);SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTNode(x);if (*pphead == NULL){*pphead = newnode;}else{SLTNode* cur = *pphead;while (cur->next != NULL){cur = cur->next;}cur->next = newnode;}
}尾加的第一步当然是先创建一个节点来储存数据,是通过函数来实现的,对于函数来说实参的改变不会影响实参,这里就涉及到传值和传址的区别了,毫无疑问是使用传地址来实现,也就是传递头指针的地址,不然创建的节点就是一个局部变量,离开作用域后就自动销毁了。我们还需要注意的是,当链表为空时,意味着链表只有一个节点,且该节点的地址是0x00000000。当我们能不能把创建的新节点连接到此节点的后面呢?答案是不可以的!!!因为0x00000000后面的地址空间是不允许我们随意访问的,它属于操作系统严格管控的区域。正确做法是:直接将新创建的节点当做头结点,这就意味着:需要把头指针中存放的地址修改成新创建节点的地址!
既然上面说到需要传递头指针的地址,地址的地址那形参自然就需要用一个二级指针来接收,这里记作 pphead 。注意:这个二级指针不能为空!!!,因为它存的可是头指针地址的地址啊,如果这个都为空,那就说明链表不存在,我们还是要区分链表不存在和空链表各自是如何表示的,所以我们在使用 pphead 时就要对它进行检查(使用 assert 进行断言)
这里代码的实现,需要先判断头指针是不是空的,就意味着链表只有一个节点,那如果我们需要插入数据,直接将新节点赋值给头指针指向的地址,这个不难理解,这一步也不能忘记,还是很必要的,如果不为空呢?我们就需要创建一个新的指针来遍历链表,循环结束条件就是当指针走到下一个就是空时就说明到尾部了,需要赋值了。好的非常通俗易懂。
5.头加:
void SLTPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{assert(pphead);SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTNode(x);newnode->next = *pphead;*pphead = newnode;
}这个和上面同理依然要使用二级指针来实现,但是这里不需要考虑空链表的情况,已经明白,就不多说了。
6.尾删:
void SLTPopBack(SLTNode** pphead)//尾删
{assert(pphead);assert(*pphead);//检查链表是否为空if ((*pphead)->next == NULL){free(*pphead);*pphead = NULL;}else{SLTNode* prev = *pphead;SLTNode* tail = *pphead;while (tail->next != NULL){prev = tail;tail = tail->next;}free(tail);tail = NULL;prev->next = NULL;}
}才开始按自己思路写了一个,写完发现并没有我想的那么容易,它需要考虑链表是否为空,并且也需要使用二级指针来完成。尾删首先要遍历链表找到最后一个节点将其释放掉,还要找到倒数第二个节点,将它的指针域中存的地址改为 NULL 。所以定义两个指针让它们同时去遍历链表。需要注意的是空链表和只有一个节点的链表的情况,空链表无法进行尾删,而只有一个节点的链表,这意味着要改变头指针里面存放的地址,所以尾删也要传递二级指针。
7.头删:
void SLTPopFront(SLTNode** pphead)//头删
{assert(pphead);assert(*pphead);SLTNode* tail = *pphead;*pphead = (*pphead)->next;free(tail);tail = NULL;
}没什么好讲的,就是要注意链表是否为空,空链表无法进行删除,此外在进行头删的时候记得将原来的头结点释放掉,先保留,再释放。
8.单链表查找:
SLTNode* SLTFind(SLTNode* phead, SLTDataType x)//单链表查找
{SLTNode* ptr = phead;while (ptr != NULL){if (ptr->data == x){return ptr;//返回数据存放地址}else{ptr = ptr->next;}}return NULL;//说明没找到(已经遍历结束)
}其实就是遍历一遍链表,但是只能返回第一次出现的地址。查找可以当做修改使用,我们找到节点地址之后就可以通过地址去修改数据域中储存的数据。
9.在 pos 位置之前插入:
oid SLTInsert(SLTNode** pphead,SLTNode*pos,SLTDataType x)//在 pos 位置之前插入
{assert(pphead);assert(pos);if (pos == *pphead)//如果pos就是头结点{SLTPushFront(pphead, x);}else{SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTNode(x);SLTNode* prev = *pphead;while (prev->next != pos){prev = prev->next;}prev->next = newnode;newnode->next = pos;}
}需要注意的是 pos 是头结点的情况,此时就成头插了,需要改变头指针中存的地址,因此函数形参需要传递二级指针。
10.删除 pos 位置数据:
void SLTzErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos)//删除 pos 位置数据:
{assert(pphead);assert(*pphead);//空链表不能删assert(pos);if (pos == *pphead){SLTPopFront(pphead);//相当于头删}else{SLTNode* prev = *pphead;while (prev->next != pos){prev = prev->next;}prev->next = pos->next;free(pos);pos = NULL;//其实没什么用,形参不改变实参}
}pos 可能是头结点的地址,因此形参要用二级指针,其他的没什么好说的。
11.在 pos 位置的后面插入:
void SLTInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x)//在 pos 位置的后面插入:
{assert(pos);SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTNode(x);SLTNode* tmp = pos->next;pos->next = newnode;newnode->next = tmp;
}这里需要注意赋值的顺序问题,有两种方法:
- 先让 newnode 的指针域储存 pos 后一个节点的地址,再让 pos 的指针域存 newnode 的地址。
- 借助中间变量,先把 pos 后面节点的地址保存起来,再让 pos 的指针域存 newnode 的地址,最后再让 newnode 的指针域存第一步中间变量中保存的地址(这个比较容易理解,正如上面代码所表示的)。
12.删除 pos 位置后面的数据:
void SLTEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos)//删除 pos 位置后面的数据:
{arrest(pos);assert(pos->next);//后面有数据才能删SLTNode* tmp = pos->next->next;//这里保存了 pos 后面的后面的节点的地址free(pos->next);pos->next = tmp;
}注意后面不能写成: pos->next = pos->next->next 这样写虽然也达到了删除 pos 后面节点的目的,但是没有真正意义上实现删除,因为每一个节点都是通过 malloc 在堆上申请的,不使用的时候要主动的去释放掉(free),把这块空间归还给操作系统,否则会导致内存泄漏。而上面那样写,就会导致 、pos 后面的节点丢失,无法进行释放,正确做法是在执行这条语句之前把 pos 后面节点的地址先保存起来。
在自己已经完整练习过几遍后,确保已经掌握。
二、双向链表:
1.双向链表的特点:
- 每次在插入或者删除某个节点时,需要处理四个节点的使用,而不是两个,实现起来有点困难。
- 相对于单链表,占用空间内存更大。
- 既可以从头遍历到尾,也可以从尾遍历到头。
2.结构(三个部分):
typedef int E;
typedef struct SLTNode
{struct Node* pre;//指针域E data;//数据域struct Node* next;//指针域
}Node;在学习完单链表后,理解双向链表容易多了,可以很容易的观察到它比单链表多一个指针域,struct Node* pre 是指向当前节点的直接前驱。后面两个不用多做说明了。
拓展:双向链表也可以进行首尾相接,构成双向循环链表,在创建链表时只需要在最后首尾相连即可。
3.创建双向链表:
Node* CreatNode(Node* head)//创建双向链表
{head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));if (head == NULL){perror("malloc");return NULL;}head->pre = NULL;head->next = NULL;head->data = rand() % MAX;return head;
}
Node* CreatList(Node* head, int length)
{if (length == 1)//这里length指需要创建的链表长度{return(head = CreatNode(head));}else{head = CreatNode(head);Node* list = head;for (int i = 1; i = length; i++){Node* body = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));body->pre = NULL;body->next = NULL;body->data = rand() % MAX;list->next = body;body->pre = list;list = list->next;}}return head;
}同单链表相比,双链表仅是各节点多了一个用于指向直接前驱的指针域,因此可以类比学习,需要注意的是,与单链表不同,双向链表创建过程中,每创建一个新节点,都要与其前驱节点建立两次联系,分别是:
- 将新节点的 pre 指针指向直接前驱节点
- 将直接前驱节点的 next 指针指向新节点
这里我创建了两个函数,其实可以合并为一个创建函数,但是为了更容易理解,我把它分为两种情况,第一种情况是指仅仅为了创建头结点,基于单链表的学习,这里不多做阐述。最重要的是第二种情况,我函数参数引入了 length 这个变量,是指所需要创建链表的长度,我还是觉得挺新奇的,毕竟单链表的创建就只是一个节点一个节点的创建。让我们剖析一下这个代码的具体过程,length==1 的情况跳过,关于多节点的创建,讲究一个连续性,使用 for 循环来实现,然后就是建立节点与节点之间的联系,多看多打多理解。
4.插入节点:
Node* InsertList(Node* head,int add, E data)//在add位置前插入data节点
{Node* temp = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));if (temp == NULL){perror("malloc");return NULL;}else{temp->data = data;temp->pre = NULL;temp->next = NULL;}if (add == 1){temp->next = head;head->pre = temp;head = temp;}else{Node* body = head;for (int i = 1; i < add; i++){body = body->next;}if (body->next == NULL){body->next = temp;temp->pre = body;}else{body->next->pre = temp;temp->next = body->next;body->next = temp;temp->pre = body;}}return head;
}当我学到这里的时候,发现这种方法格外新颖,和我单链表的学习方法出入太大,果断放弃,另择它法。
直接重学双向链表是带头节点的,当然依然不存储有效数据,具体原因在学习单链表的时候已经详细解释过了。
1.结构设计及其初始化:
typedef int LTDataType;
typedef struct ListNode
{struct ListNode* prev;//指针域(直接前驱)LTDataType data;//数据域struct ListNode* next;//指针域(直接后继)
}LTNode;
LTNode* LTlint()//初始化
{LTNode* phead = (LTNode*)malloc(sizeof(LTNode));phead->next = NULL;phead->prev = NULL;return phead;
}只能说这个版本正常多了,这里不需要多做解释,咱们继续看。
2.创建节点:
void BuyLTNode(LTDataType x)//创建节点
{LTNode* newnode = (LTNode*)malloc(sizeof(LTNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc");return NULL;}newnode->next = NULL;newnode->data = x;newnode->prev = NULL;return newnode;
}3.尾插:
void LTPushBack(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x)//尾插
{assert(phead);LTNode* tail = phead->prev;LTNode* newnode = BuyLTNode(x);tail->next = newnode;newnode->prev = tail;newnode->next = phead;phead->prev = newnode;
}这个代码我真的思考了很久,它和单链表有个巨大的不同之处,是我所忽略的。在循环链表中我们让头结点的前驱是链表的最后一个节点!!!意识到这个问题之后,便可以不用循环遍历到尾部,也能实现尾插操作。
4.头插、尾删、头删、查找、pos位前插入、pos位删除:
void LTPushFront(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x)//头插
{assert(phead);LTNode* first = phead->next;LTNode* newnode = BuyLTNode(x);phead->next = newnode;newnode->prev = phead;newnode->next = first;first->prev = newnode;
}
void LTPopBack(LTNode* phead)//尾删
{assert(phead);assert(phead->next != phead);//防止只有一个节点LTNode* tail = phead->prev;LTNode* tailprev = tail->prev;free(tail);phead->prev = tailprev;tailprev->next = phead;
}
void LTPopFront(LTNode* phead)//头删
{assert(phead);assert(phead->next != phead);LTNode* first = phead->next;LTNode* firstnext = first->next;free(first);firstnext->prev = phead;phead->next = firstnext;
}
LTNode* LTFind(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x)//查找
{assert(phead);LTNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead)//注意此处循环条件{if (cur->data == x){return cur;}cur = cur->next;}return NULL;
}
void LTInsert(LTNode* pos, LTDataType x)//在pos之前插入
{assert(pos);LTNode* newnode = BuyLTNode(x);LTNode* posprev = pos->prev;newnode->prev = posprev;posprev->next = newnode;pos->prev = newnode;
}
void LTErase(LTNode* pos)//在pos位删除
{assert(pos);LTNode* posprev = pos->prev;LTNode* posnext = pos->next;free(pos);posprev->next = posnext;posnext->prev = posprev;
}5.判断是否为空、打印、销毁:
bool LTEmpty(LTNode* phead)//判断是否为空(可以简化代码)
{assert(phead);return phead->next == phead;
}
void LTPrint(LTNode* phead)//打印
{assert(phead);printf("guard<==>");LTNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){printf("%d<==>", cur->data);cur = cur->next;}printf("\n");
}
void LTDestroy(LTNode* phead)//销毁
{assert(phead);LTNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){LTNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}free(phead);
}三、链表练习题:
1.单向链表: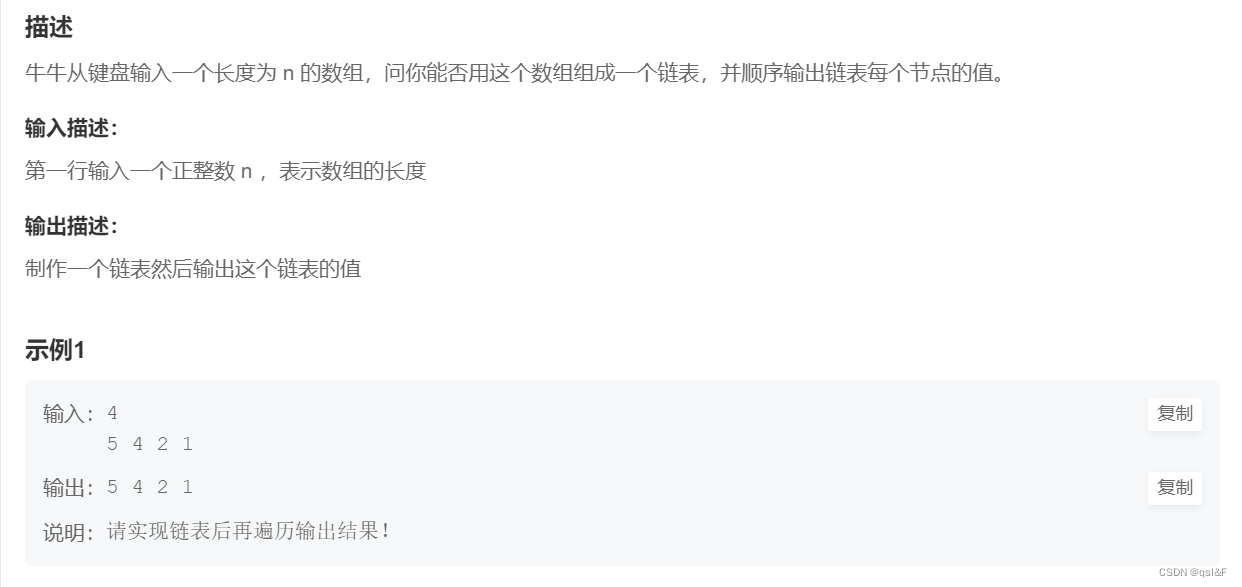
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef struct SListNode
{int data;struct SListNode* next;
}SLTNode;
SLTNode* SLTInit()
{SLTNode* phead = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));assert(phead);phead->next = NULL;phead->data = 0;return phead;
}
void SLTPush(SLTNode** pphead, int x)
{assert(pphead);SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));assert(newnode);newnode->next = NULL;newnode->data = x;SLTNode* cur = *pphead;while (cur->next != NULL){cur = cur->next;}cur->next = newnode;
}void SLTPrint(SLTNode* phead)
{assert(phead);assert(phead->next);SLTNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != NULL){printf("%d ", cur->data);cur = cur->next;}
}
int main()
{int n = 0;scanf("%d", & n);//动态数组int* arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);SLTNode* head = SLTInit();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){scanf("%d", &arr[i]);}for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){SLTPush(&head, arr[i]);}SLTPrint(head);return 0;
}刚开始第一次写出来的时候发生了几处错误:
- 第一:使用静态数组进行初始化操作,结果发现无法达到预期效果,在小方同学的提醒下知道了在这个情况下可以使用动态数组

- 第二:打印函数一直打印的是头结点(完全是粗心错误)。
2.交换链表: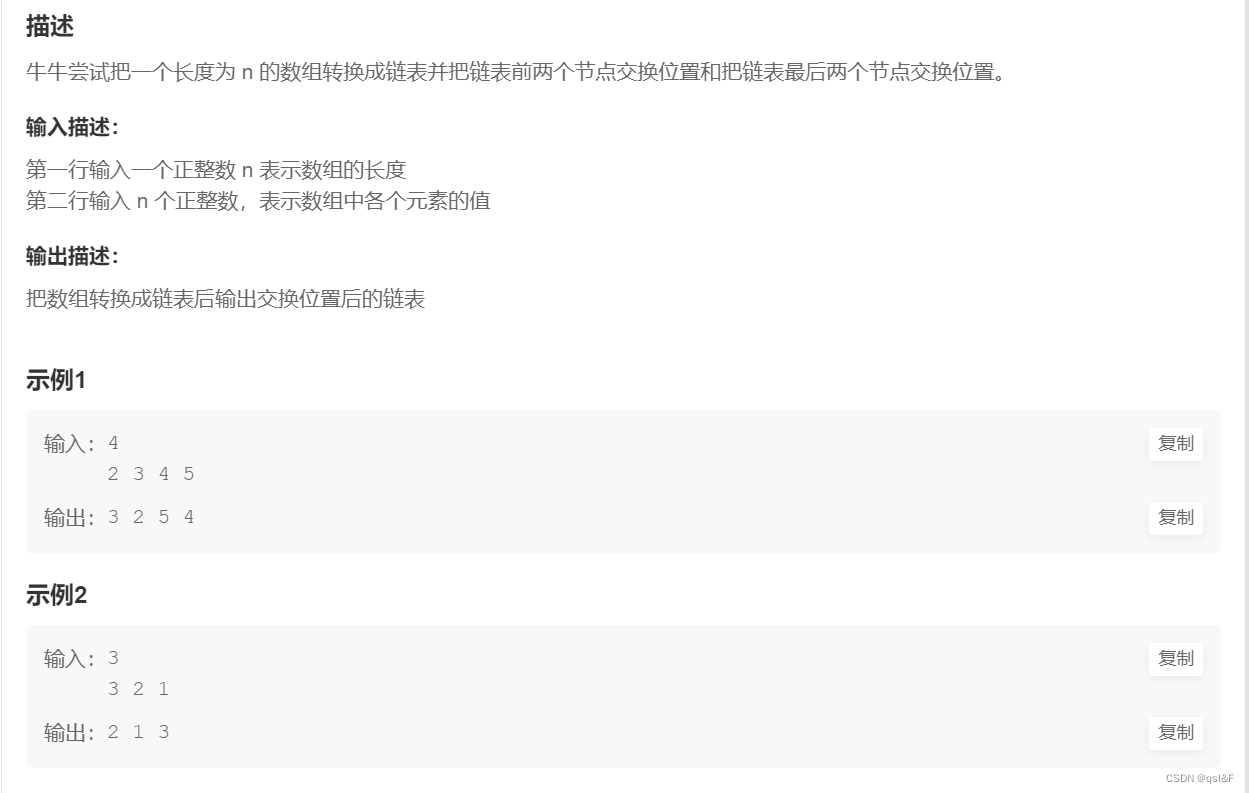
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef struct SListNode
{int data;struct SListNode* next;
}SLTNode;
SLTNode* Init()
{SLTNode* phead = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));assert(phead);phead->data = 0;phead->next = NULL;return phead;
}
void SLTPush(SLTNode** pphead, int x)
{assert(pphead);SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));newnode->next = NULL;newnode->data = x;assert(newnode);SLTNode* cur = *pphead;while (cur->next != NULL){cur = cur->next;}cur->next = newnode;
}
void SLTExchangeFront(SLTNode**pphead)
{SLTNode* cur = (*pphead)->next;SLTNode* prev = cur->next;int t = cur->data;cur->data = prev->data;prev->data = t;
}
void SLTExchangeBack(SLTNode** pphead)
{SLTNode* tail = *pphead;SLTNode* prev = *pphead;while (tail->next != NULL){prev = tail;tail = tail->next;}int t = tail->data;tail->data = prev->data;prev->data = t;
}
void SLTPrint(SLTNode* phead)
{assert(phead);assert(phead->next);SLTNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != NULL){printf("%d ", cur->data);cur = cur->next;}
}
int main()
{int n = 0;scanf("%d", &n);int* arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);int i = 0;for (i = 0; i < n; i++){scanf("%d", &arr[i]);}SLTNode* head = Init();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){SLTPush(&head, arr[i]);}SLTExchangeFront(&head);SLTExchangeBack(&head);SLTPrint(head);return 0;
}3.链表求和: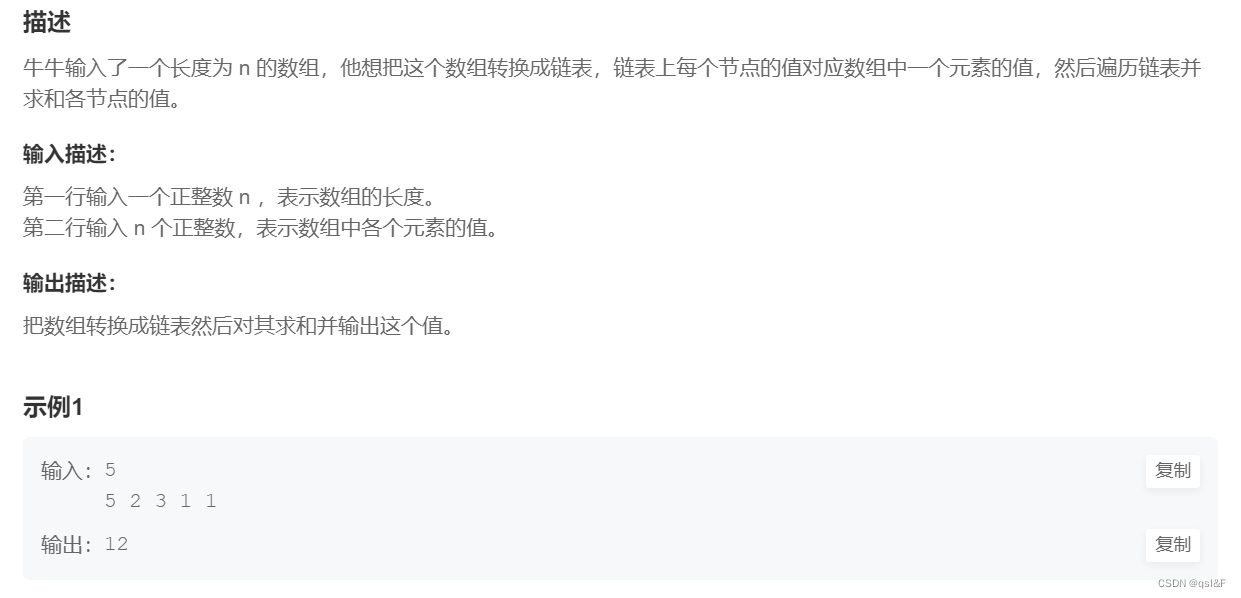
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef struct SListNode
{int data;struct SListNode* next;
}SLTNode;
SLTNode* Init()
{SLTNode* phead = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));assert(phead);phead->data = 0;phead->next = NULL;return phead;
}
void SLTPush(SLTNode** pphead, int x)
{assert(pphead);SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));newnode->next = NULL;newnode->data = x;assert(newnode);SLTNode* cur = *pphead;while (cur->next != NULL){cur = cur->next;}cur->next = newnode;
}
void SLTPrint(SLTNode* phead)
{assert(phead);assert(phead->next);int sum = 0;SLTNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != NULL){sum += cur->data;cur = cur->next;}printf("%d", sum);
}
int main()
{int n = 0;scanf("%d", &n);int* arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);int i = 0;for (i = 0; i < n; i++){scanf("%d", &arr[i]);}SLTNode* head = Init();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){SLTPush(&head, arr[i]);}SLTPrint(head);return 0;
}
4.双链表求和:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef struct SListNode1
{int data;struct SListNode1* next;
}SLTNode1;
typedef struct SListNode2
{int data;struct SListNode2* next;
}SLTNode2;
SLTNode1* Init1()
{SLTNode1* phead = (SLTNode1*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode1));assert(phead);phead->data = 0;phead->next = NULL;return phead;
}
SLTNode2* Init2()
{SLTNode2* phead = (SLTNode2*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode2));assert(phead);phead->data = 0;phead->next = NULL;return phead;
}
void SLTPush1(SLTNode1** pphead, int x)
{assert(pphead);assert(*pphead);SLTNode1* newnode = (SLTNode1*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode1));assert(newnode);newnode->next = NULL;newnode->data = x;SLTNode1* cur = *pphead;while (cur->next != NULL){cur = cur->next;}cur->next = newnode;
}
void SLTPush2(SLTNode2** pphead, int x)
{assert(pphead);assert(*pphead);SLTNode2* newnode = (SLTNode1*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode2));assert(newnode);newnode->next = NULL;newnode->data = x;SLTNode2* cur = *pphead;while (cur->next != NULL){cur = cur->next;}cur->next = newnode;
}
void SLTPrint(SLTNode1* phead1,SLTNode2*phead2)
{assert(phead1->next);assert(phead2->next);SLTNode1* cur1 = phead1->next;SLTNode2* cur2 = phead2->next;while (cur1 != NULL){cur1->data = cur1->data + cur2->data;printf("%d ", cur1->data);cur1 = cur1->next;cur2 = cur2->next;}
}
int main()
{int n = 0;scanf("%d", &n);int* arr1 = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);int* arr2 = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);int i = 0;SLTNode1* head1 = Init1();SLTNode2* head2 = Init2();for (i = 0; i < n; i++){scanf("%d", &arr1[i]);}for (i = 0; i < n; i++){scanf("%d", &arr2[i]);}for (i = 0; i < n; i++){SLTPush1(&head1, arr1[i]);}for (i = 0; i < n; i++){SLTPush2(&head2, arr2[i]);}SLTPrint(head1, head2);return 0;
}5.链表删除:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef struct SListNode
{int data;struct SListNode* next;
}SLTNode;
SLTNode* Init()
{SLTNode* phead = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));assert(phead);phead->data = 0;phead->next = NULL;return phead;
}
void SLTPush(SLTNode** pphead, int x)
{assert(pphead);SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));newnode->next = NULL;newnode->data = x;assert(newnode);SLTNode* cur = *pphead;while (cur->next != NULL){cur = cur->next;}cur->next = newnode;
}
SLTNode* SLTFind(SLTNode* phead, int x)
{assert(phead->next);SLTNode* ptr = phead->next;while (ptr != NULL){if (ptr->data == x){return ptr;}else{ptr = ptr->next;}}return NULL;
}
void SLTPopFront(SLTNode** pphead)
{assert(pphead);assert(*pphead);SLTNode* tail,*temp ;tail = (*pphead)->next;if (tail->next != NULL) {temp = tail->next;(*pphead)->next = temp;}free(tail);tail = NULL;
}
void SLTzErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos)
{assert(pphead);assert(pos);assert(*pphead);if (pos == (*pphead)->next){SLTPopFront(pphead);}else{SLTNode* prev = *pphead;while (prev->next != pos){if (prev->next == NULL)return;prev = prev->next;}if (pos->next != NULL)prev->next = pos->next;elseprev->next = NULL;free(pos);pos = NULL;}
}
void SLTPrint(SLTNode* phead)
{assert(phead);assert(phead->next);int sum = 0;SLTNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != NULL){printf("%d ", cur->data);cur = cur->next;}
}
int main()
{int n = 0;int x = 0;scanf("%d", &n);scanf("%d", &x);int* arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);int i = 0;for (i = 0; i < n; i++){scanf("%d", &arr[i]);}SLTNode* head = Init();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){SLTPush(&head, arr[i]);}for (i = 0; i < n; i++){SLTNode* pos = SLTFind(head, x);if (pos == NULL)break;SLTzErase(&head, pos);}SLTPrint(head);return 0;
}写这题的时候卡了一下,经过小方同学改错后,发现头删函数不完善,把头节点删了,而且还没有连接头节点和下一个节点,以后书写时需注意,以及循环遇空(NULL)需及时 break ,不然就会被 assert(pos)断言报错。
6.链表添加节点: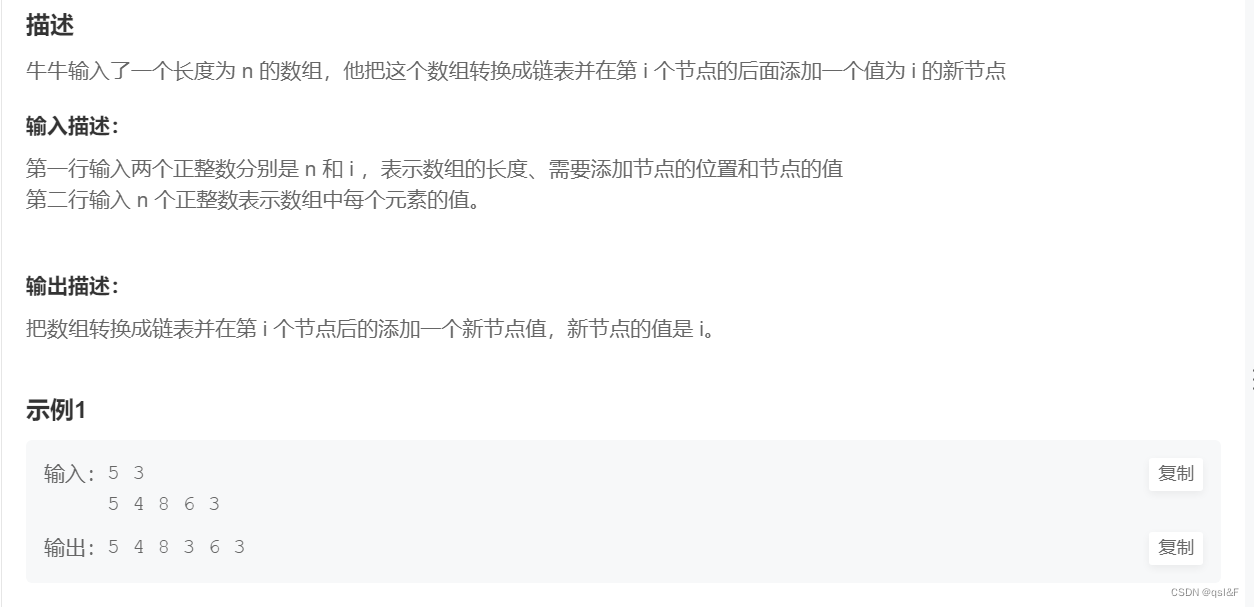
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef struct SListNode
{int data;struct SListNode* next;
}SLTNode;
SLTNode* SLTInit()
{SLTNode* phead = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));assert(phead);phead->next = NULL;phead->data = 0;return phead;
}
void SLTPush(SLTNode** pphead, int x)
{assert(pphead);SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));assert(newnode);newnode->next = NULL;newnode->data = x;SLTNode* cur = *pphead;while (cur->next != NULL){cur = cur->next;}cur->next = newnode;
}void SLTPrint(SLTNode* phead)
{assert(phead);assert(phead->next);SLTNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != NULL){printf("%d ", cur->data);cur = cur->next;}
}
void SLTAdd(SLTNode** pphead, int pos)
{assert(pphead);assert(pos);SLTNode* cur = *pphead;SLTNode* prev = *pphead;for (int i = 0; i < (pos+1); i++){prev = cur;cur = cur->next;}SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));assert(newnode);newnode->next = NULL;newnode->data = pos;newnode->next = cur;prev->next = newnode;
}
int main()
{int n = 0;scanf("%d", &n);//动态数组int i = 0;scanf("%d", &i);int* arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);SLTNode* head = SLTInit();for (int j = 0; j < n; j++){scanf("%d", &arr[j]);}for (int j = 0; j < n; j++){SLTPush(&head, arr[j]);}SLTAdd(&head, i);SLTPrint(head);return 0;
}
链表基础题目已完成,可以较为熟练使用链表来解决相关问题。



![[PHP]严格类型](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/aaf86b2bd14448d7953a6b4afb731358.png)