文章目录
- 前言
- 一、环境
- 实验所需的库
- 终端指令
- 二、实现过程
- Version 1 起源
- Version 2 list
- Version 3 array
- Version 4 结构化数组
- Version 5 区分单元且打乱顺序
- Version 6 可视化
- 三、txt文件
前言
缘起自懒得考小孩儿单词,最终效果如图:
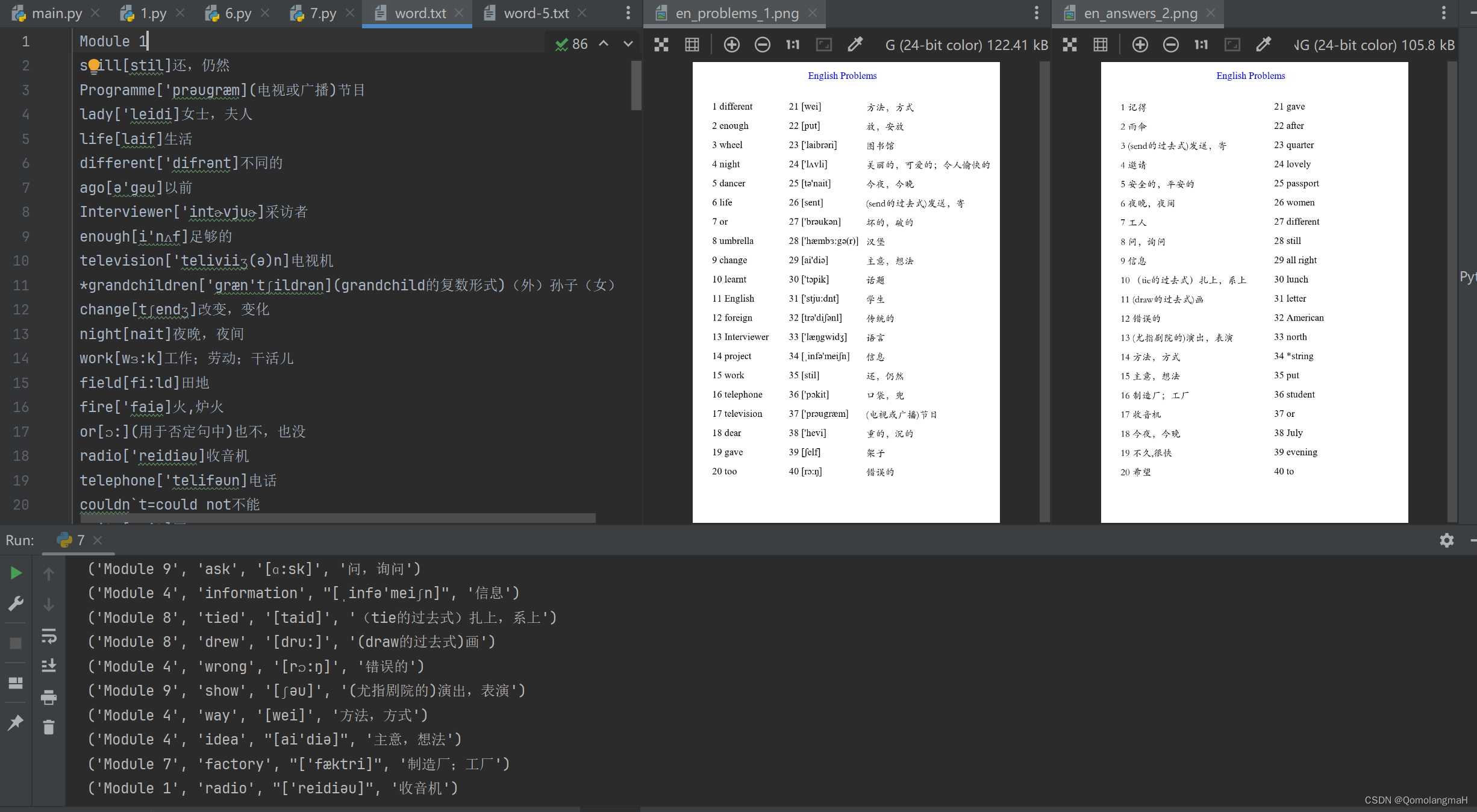
本文记录了英语单词文本处理过程,生成“试卷”
PS:单词docx文件来源于百度文库高校版(单词txt文本附文末)
一、环境
实验所需的库
import re
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
终端指令
conda create -n DL python==3.11
conda activate DL
conda install numpy pillow
或
pip install numpy pillow
二、实现过程
大过年的,暂不对代码进行详细介绍,其进化过程如下:
Version 1 起源
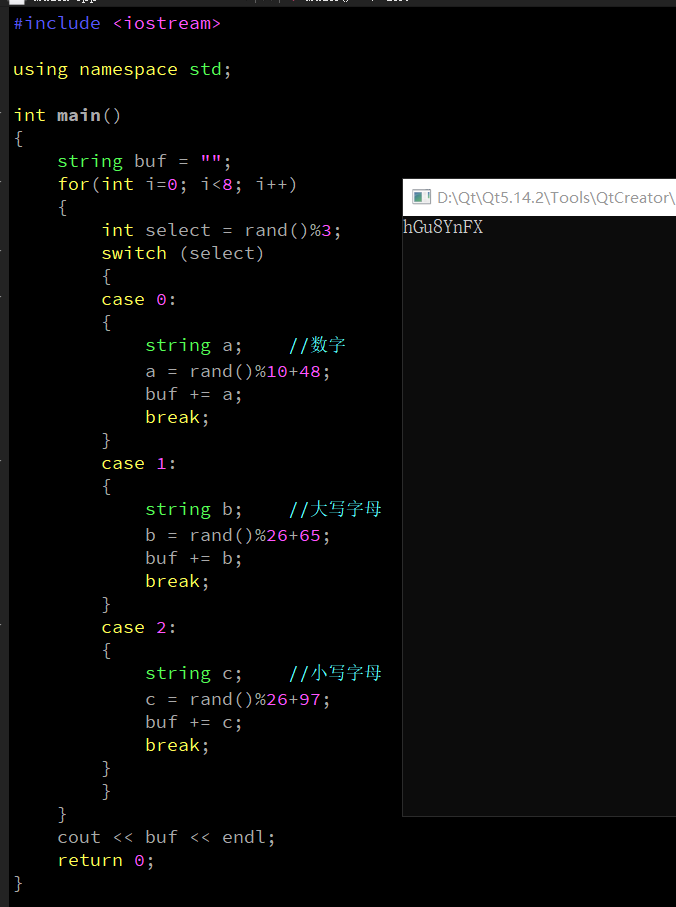
import rewith open('./word.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:for line in file:if re.match(r'^[A-Za-z*]', line): # 使用正则表达式匹配以英文字母开头的行if 'Module' in line:continueif '[' not in line: # 如果行中没有 [print("无法解析的行:", line) # 直接输出行的内容continueword, pro_chinese = line.strip().split('[')pronunciation, meaning = pro_chinese.strip().split(']')pronunciation = '[' + pronunciation + ']' # 将括号加回去meaning = meaning.rstrip() # 去掉末尾的换行符print("单词:", word)print("音标:", pronunciation)print("中文:", meaning)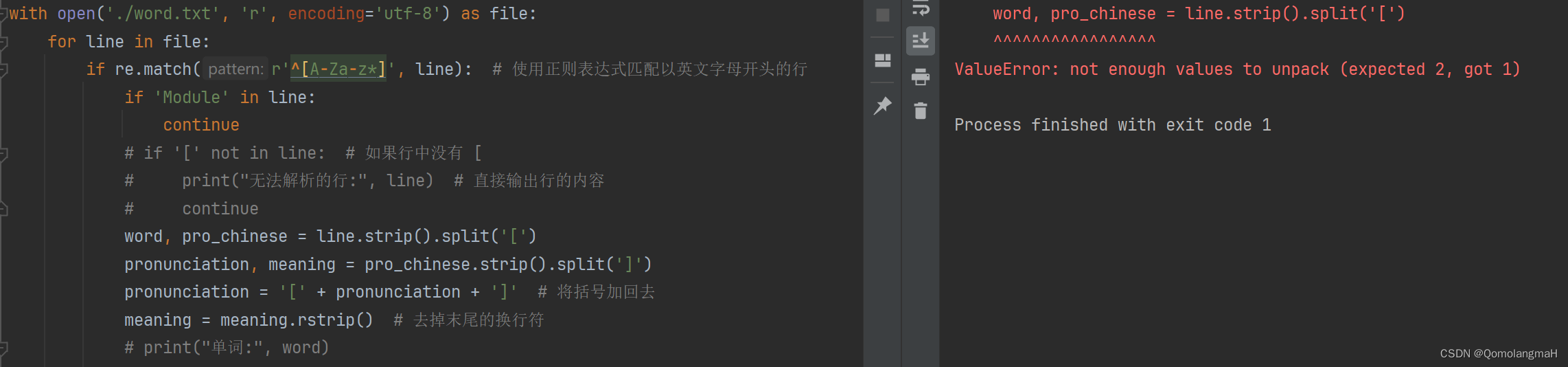
Version 2 list
存储为列表
import rewords, pronunciations, meanings, modules = [], [], [], []
with open('./word.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:current_module = ""for line in file:if re.match(r'^[A-Za-z*]', line): # 使用正则表达式匹配以英文字母开头的行if 'Module' in line:current_module = line.strip()# print(current_module)continueif '[' not in line: # 如果行中没有 [# print("无法解析的行:", line) # 直接输出行的内容continueword, pro_chinese = line.strip().split('[')pronunciation, meaning = pro_chinese.strip().split(']')pronunciation = '[' + pronunciation + ']' # 将括号加回去meaning = meaning.rstrip() # 去掉末尾的换行符# print("单词:", word)# print("音标:", pronunciation)# print("中文:", meaning)words.append(word)pronunciations.append(pronunciation)meanings.append(meaning)modules.append(current_module)for i in range(len(words)):print(modules[i], words[i], pronunciations[i], meanings[i])
Version 3 array
存储为array数组
import re
import numpy as npwords, pronunciations, meanings = np.array([]), np.array([]), np.array([])with open('./word.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:current_module = ""for line in file:if re.match(r'^[A-Za-z*]', line): # 使用正则表达式匹配以英文字母开头的行if 'Module' in line:current_module = line.strip()print(current_module)continueif '[' not in line: # 如果行中没有 [print("无法解析的行:", line) # 直接输出行的内容continueword, pro_chinese = line.strip().split('[')pronunciation, meaning = pro_chinese.strip().split(']')pronunciation = '[' + pronunciation + ']' # 将括号加回去meaning = meaning.rstrip() # 去掉末尾的换行符words = np.append(words, word)pronunciations = np.append(pronunciations, pronunciation)meanings = np.append(meanings, meaning)for i in range(len(words)):print("单词:", words[i])print("音标:", pronunciations[i])print("中文:", meanings[i])
Version 4 结构化数组
进化为结构化数组
import re
import numpy as np# 定义结构化数组的数据类型
dt = np.dtype([('word', 'U50'), ('pronunciation', 'U50'), ('meaning', 'U50')])# 创建空的结构化数组
data = np.array([], dtype=dt)with open('./word.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:for line in file:if re.match(r'^[A-Za-z*]', line): # 使用正则表达式匹配以英文字母开头的行if 'Module' in line:continueif '[' not in line: # 如果行中没有 [# print("无法解析的行:", line) # 直接输出行的内容continueword, pro_chinese = line.strip().split('[')pronunciation, meaning = pro_chinese.strip().split(']')pronunciation = '[' + pronunciation + ']' # 将括号加回去meaning = meaning.rstrip() # 去掉末尾的换行符new_data = np.array([(word, pronunciation, meaning)], dtype=dt) # 创建包含当前单词数据的结构化数组data = np.append(data, new_data) # 将当前单词数据添加到总的结构化数组中for i in data:print(i)
Version 5 区分单元且打乱顺序
区分单元且打乱顺序
import re
import numpy as np# 定义结构化数组的数据类型
dt = np.dtype([('module', 'U50'), ('word', 'U50'), ('pronunciation', 'U50'), ('meaning', 'U50')])# 创建空的结构化数组
data = np.array([], dtype=dt)with open('./word.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:current_module = ""for line in file:if re.match(r'^[A-Za-z*]', line): # 使用正则表达式匹配以英文字母开头的行if 'Module' in line:current_module = line.strip()# print(current_module)continueif '[' not in line: # 如果行中没有 [# print("无法解析的行:", line) # 直接输出行的内容continueword, pro_chinese = line.strip().split('[')pronunciation, meaning = pro_chinese.strip().split(']')pronunciation = '[' + pronunciation + ']' # 将括号加回去meaning = meaning.rstrip() # 去掉末尾的换行符new_data = np.array([(current_module, word, pronunciation, meaning)], dtype=dt) # 创建包含当前单词数据的结构化数组data = np.append(data, new_data) # 将当前单词数据添加到总的结构化数组中np.random.shuffle(data)
# 打印打乱顺序后的数组
print(data[0]['word'])
print(len(data))
for d in data:print(d)
for d in data:if d['module'] == 'Module 1':print(d)
Version 6 可视化
可视化
import re
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont# 定义结构化数组的数据类型
dt = np.dtype([('module', 'U50'), ('word', 'U50'), ('pronunciation', 'U50'), ('meaning', 'U50')])# 创建空的结构化数组
data = np.array([], dtype=dt)with open('./word.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:current_module = ""for line in file:if re.match(r'^[A-Za-z*]', line): # 使用正则表达式匹配以英文字母开头的行if 'Module' in line:current_module = line.strip()print(current_module)continueif '[' not in line: # 如果行中没有 [print("无法解析的行:", line) # 直接输出行的内容continueword, pro_chinese = line.strip().split('[')pronunciation, meaning = pro_chinese.strip().split(']')pronunciation = '[' + pronunciation + ']' # 将括号加回去meaning = meaning.rstrip() # 去掉末尾的换行符new_data = np.array([(current_module, word, pronunciation, meaning)], dtype=dt) # 创建包含当前单词数据的结构化数组data = np.append(data, new_data) # 将当前单词数据添加到总的结构化数组中# 打印数组
print(data[0]['word'])
print(len(data))
for d in data:if d['module'] == 'Module 1':print(d)np.random.shuffle(data)
# 打印打乱顺序后的数组
print(data)
# dt = np.dtype([('module', 'U50'), ('word', 'U50'), ('pronunciation', 'U50'), ('meaning', 'U50')])problem_image = Image.new('RGB', (800, 1200), color='white')
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(problem_image)
# font = ImageFont.truetype("arial.ttf", 25)
c_font = ImageFont.truetype("STKAITI.TTF", 25) # 华文楷体
e_font = ImageFont.truetype("times.ttf", 25) # times new Romantext_y = 100
draw.text((300, 20), 'English Problems', fill='blue', font=e_font)
for i in range(20):draw.text((50, text_y), str(i+1)+' '+data[i]['word'], fill='black', font=e_font)draw.text((350, text_y), str(i + 21) + ' ' + data[i+20]['meaning'], fill='black', font=c_font)text_y += 50problem_image.save('en_problems_3.png')# Generate a combined image of the answers
answer_image = Image.new('RGB', (800, 1200), color='white')
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(answer_image)text_y = 100
draw.text((300, 20), 'English Problems', fill='blue', font=e_font)
for i in range(20):draw.text((50, text_y), str(i+1)+' '+data[i]['meaning'], fill='black', font=c_font)draw.text((450, text_y), str(i + 21) + ' ' + data[i+20]['word'], fill='black', font=e_font)text_y += 50answer_image.save('en_answers_3.png')
问题:左侧前20英译汉,右侧汉译英:

答案:

三、txt文件
外研社小学英语五年级下册(三年级起点)单词表(带音标):
Module 1
still[stil]还,仍然
Programme’prəugræm节目
lady['leidi]女士,夫人
life[laif]生活
different['difrənt]不同的
ago[ə’gəu]以前
Interviewer['intɚvjuɚ]采访者
enough[i’nʌf]足够的
television['teliviiʒ(ə)n]电视机
*grandchildren’græn’tʃildrən(外)孙子(女)
change[tʃendʒ]改变,变化
night[nait]夜晚,夜间
work[wɜ:k]工作;劳动;干活儿
field[fi:ld]田地
fire['faiə]火,炉火
orɔ:也不,也没
radio['reidiəu]收音机
telephone['telifəun]电话
couldn`t=could not不能
write[rait]写
hope[həup]希望
Module 2
learnt[lɜ:nt](learn的过去式)学习
taughttɔ:t教,讲授
language['læŋgwidʒ]语言
wroterəut写
dancer['dɑ:nsə®] 舞蹈演员
foreign['fɔrən]外国的
studied’stʌdid学习
hard[hɑ:d]努力地
Module 3
hamburger['hæmbɜ:gə®]汉堡
English['iŋgliʃ]英国(式)的
breakfast['brekfəst]早餐,早饭
lunch[lʌntʃ]午餐,午饭
sandwich['sænwitʃ]三明治
fish and chips炸鱼加炸薯条
traditional[trə’diʃənl]传统的
dish[diʃ]食品;菜肴
very much['veri mʌtʃ]很,非常
gave[geiv](give的过去式)给
tonight[tə’nait]今夜,今晚
Module 4
library['laibrəri]图书馆
student['stju:dnt]学生
sentsent发送,寄
*CD 激光唱片,光盘
idea[ai’diə]主意,想法
put[put]放,安放
*shelf[ʃelf]架子
heavy['hevi]重的,沉的
dictionary['dikʃənri]词典;字典
card[kɑ:d]卡片
library card图书卡,借书证
ask[ɑ:sk]邀请
wrong[rɔ:ŋ]错误的
dear[diə®]哎呀
information[ˌinfə’meiʃn]信息
*e-book电子书
project['prɔdʒekt]项目
guide[gaid]介绍,指南,手册
film[film]电影
as well又,还,也
way[wei]方法,方式
on[ɔn]关于
*topic['tɔpik]话题
Module 5
light[lait]轻的
hard[hɑ:d]困难的,费力的
*broken['brəukən]坏的,破的
department store[di’pɑ:tmənt stɔ:]百货商店
pocket['pɔkit]口袋,兜
umbrella[ʌm’brelə]雨伞
sales assistant[seilz ə’sistənt]售货员,营业员
wheel[wi:l]轮子
easy['i:zi]容易的,不费力的
take[teik]选择要,选择购买
too[tu:]太,过于
try[trai]试,尝试
lovely['lʌvli]美丽的,可爱的;令人愉快的
Module 6
moon[mu:n]月亮,月球
get[ɡet]到达
west[west]西,西部,西方;向西方
parent['peərənt]母亲;父亲;家长
stay[stei]停留
July[dʒu’lai]七月
south[sauθ]南,南部,南方;向南方
remember[ri’membə®]记得
June[dʒu:n]六月
east[i:st]东,东部,东方;向东方
best[best]最好的
north[nɔ:θ]北,北部,北方;向北方
rest[rest]休息
have a rest休息一下
rode[rəud](ride的过去式)骑
Module 7
evening['i:vniŋ]傍晚,晚上
late[leit]近日暮的;近深夜的;时间不早的
worker['wɜ:kə®]工人
factory['fæktri]制造厂;工厂
early['ɜ:li]早的
taxi['tæksi]出租车,计程车
quarter['kwɔ:tə®]一刻钟
to[tu,tə](距整点)差…
worry['wʌri]焦虑,担心
Module 8
paper['peipə®]纸
Chinese[ˌtʃai’ni:z]中国人的
so[səʊ]如此,这样
word[wɜ:d]词,字
drewdru:画
cutkʌt剪,切,割
piece[pi:s]张,片,块
paint[peint](用颜料)绘画,着色
putput放,安放
stick[stik]小木棍,小木条
tied[taid](tie的过去式)扎上,系上
*string[striŋ]线,绳子
Module 9
laugh[lɑ:f]笑
worewɔ:®穿
letter['letə®]信,书信
theatre['θiətə]剧院
women’wimin女性,妇女
actor['æktə®]演员
toldtəuld口述,讲(故事等)
joke[dʒəuk]笑话
after['ɑ:ftə®]在……以后
showʃəu演出,表演
restaurant['restrɔnt]饭店,餐馆
readri:d读
at all[æt ɔ:l]一点都
in[in]在(将来一段时间)之后
another[ə’nʌðə®]另一个
history['histri]历史
ask[ɑ:sk]问,询问
question['kwestʃən]问题
forget[fə’get]忘,忘记
bring[briŋ]带来,拿来
soon[su:n]不久,很快
Module 10
when[wen]在什么时候
end[end]结束,终止
nervous['nɜ:vəs]紧张的,情绪不安的
all right[ɔ:l rait]没事,没问题
airport['eəpɔ:t]机场
ticket['tikit]票
passport['pɑ:spɔ:t]护照
safe[seif]安全的,平安的
pet[pet]宠物
speak[spi:k]说,讲
building['bildiŋ]建筑物
American[ə’merikən]美国的;美国人的;美国人
find out[faind aut]发现,弄清
more[mɔ:®]更多的(量),较多的(量)