哈希算法:哈希也叫散列、映射,将任意长度的输入通过散列运算转化为固定长度的输出,该输出就是哈希值(散列值)。
哈希映射是一种压缩映射,通常情况下,散列值的空间远小于输入值的空间。
哈希运算的结果称为哈希值,哈希运算是不可逆过程,即不能通过哈希值推算出原值。
哈希运算常用于加密、位图、布隆过滤,位图的作用是海量数据的标记,布隆过滤器的作用是提高海量数据查询的效率(客户端向服务端查询数据)。
一、哈希函数
HashFunc.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>// 仿函数
template<class K>
struct HashFunc
{size_t operator()(const K& key){return (size_t)key;}
};// 特化
template<>
struct HashFunc<std::string>
{size_t operator()(const std::string& str){size_t res = 0;for (const auto& ch : str){res *= 131; // 随机数取值,避免哈希冲突res += ch;}return res;}
};哈希表:将数据根据哈希运算得到哈希值(关键值),再根据哈希值将数据映射在表中,哈希表通常情况是一个vector容器。哈希表分为闭散列和开散列(哈希桶)。
哈希表的数据增删与红黑树差别不大,各有优劣,但是哈希表的数据查询效率远高于红黑树。
二、闭散列

#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#pragma
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include "HashFunc.h"enum status
{EMPTY,EXIST,DELETE
};template<class K, class V>
struct CloseHashNode
{std::pair<K, V> _kv;status _status = EMPTY;
};template<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class CloseHash
{typedef CloseHashNode<K, V> Data;
public:CloseHash(): _n(0){_table.resize(10);}bool Insert(const std::pair<K, V>& kv){if (Find(kv.first))return false;// 负载因子为0.7if (_n * 10 / _table.size() >= 7){std::vector<Data> newTable;newTable.resize(2 * _table.size());for (int i = 0; i < _table.size(); ++i){if (_table[i]._status == EXIST){size_t pos = Hash()(_table[i]._kv.first) % newTable.size();while (newTable[pos]._status != EMPTY){pos = (++pos) % newTable.size();}newTable[pos] = _table[i];}}_table.swap(newTable);}size_t pos = Hash()(kv.first) % _table.size();while (_table[pos]._status != EMPTY){pos = (++pos) % _table.size();}_table[pos]._kv = kv;_table[pos]._status = EXIST;++_n;return true;}Data* Find(const K& key){size_t pos = Hash()(key) % _table.size();int cnt = 0;while (_table[pos]._status != EMPTY && cnt != _table.size()){if (key == _table[pos]._kv.first && _table[pos]._status == EXIST)return &_table[pos];pos = (++pos) % _table.size();++cnt;}return nullptr;}bool Erase(const K& key){Data* ret = Find(key);if (ret){ret->_status = DELETE;--_n;return true;}else{return false;}}private:std::vector<Data> _table;size_t _n;
};三、开散列
开散列也称哈希桶,哈希桶的vector节点存储的是数据节点,相同哈希值的节点以链表的形式存储在同一个vector位置上,当节点数与vector容量的比值为平衡因子值(1)时,哈希桶扩容,扩容时重新遍历原表,将原表的元素重新取哈希进行映射,为了提高效率,不拷贝节点,而是改变节点的指向。
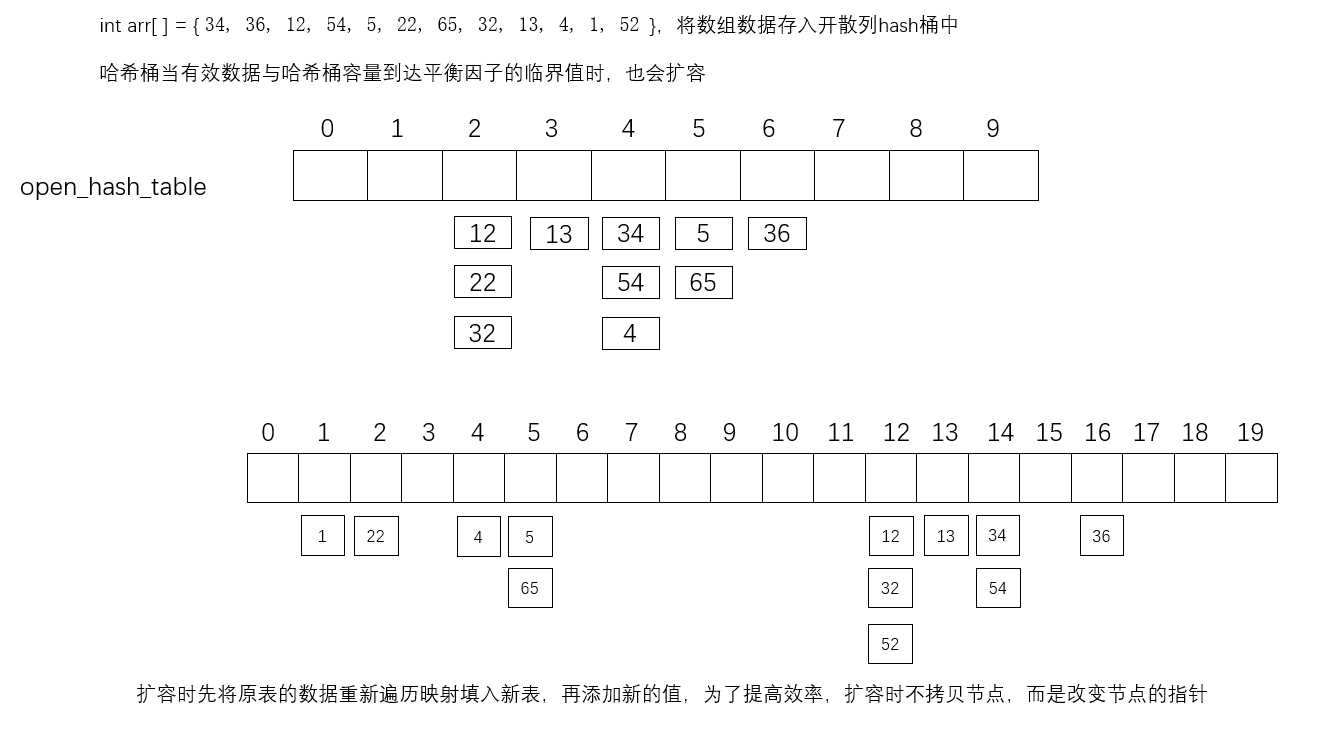
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include "HashFunc.h"template<class K, class V>
struct OpenHashNode
{std::pair<K, V> kv;OpenHashNode<K, V>* next;OpenHashNode(const std::pair<K, V>& x): kv(x), next(nullptr){}
};template<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class OpenHash
{typedef OpenHashNode<K, V> Node;
public:OpenHash(): _n(0){_table.resize(10, nullptr);}bool Insert(const std::pair<K, V>& kv){if (Find(kv.first))return false;// 检查扩容,平衡因子为 1if (_n == _table.size()){std::vector<Node*> newTable;newTable.resize(2 * _table.size(), nullptr);for (int i = 0; i < _table.size(); ++i){Node* cur = _table[i];while (cur){Node* next = cur->next;size_t pos = Hash()(cur->kv.first) % newTable.size();cur->next = newTable[pos];newTable[pos] = cur;cur = next;}}_table.swap(newTable);}// 插入新节点Node* newNode = new Node(kv);size_t pos = Hash()(newNode->kv.first) % _table.size();newNode->next = _table[pos];_table[pos] = newNode;++_n;return true;}Node* Find(const K& key){size_t pos = Hash()(key) % _table.size();Node* cur = _table[pos];while (cur){if (cur->kv.first == key)return cur;cur = cur->next;}return nullptr;}bool Erase(const K& key){Node* ret = Find(key);if (ret){size_t pos = Hash()(key) % _table.size();Node* cur = _table[pos];if (cur == ret){cur = ret->next;delete ret;ret = nullptr;}else{while (cur->next != ret){cur = cur->next;}cur->next = ret->next;delete ret;ret = nullptr;}--_n;return true;}else{return false;}}private:std::vector<Node*> _table;int _n;
};
四、测试
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include "CloseHash.h"
#include "OpenHash.h"
using namespace std;void TestCloseHash()
{cout << "CloseHash: " << endl << endl;CloseHash<int, int> hash;int arr[] = { 34, 36, 12, 54, 5, 22, 65, 32, 13, 4, 1, 52 };for (auto& e : arr){hash.Insert(make_pair(e, e));}cout << hash.Find(12) << endl;cout << hash.Find(22) << endl;cout << hash.Find(32) << endl;cout << hash.Find(42) << endl;cout << hash.Find(52) << endl;cout << endl;hash.Erase(32);cout << hash.Find(12) << endl;cout << hash.Find(22) << endl;cout << hash.Find(32) << endl;cout << hash.Find(42) << endl;cout << hash.Find(52) << endl;
}void TestOpenHash()
{cout << endl << endl << "OpenHash: " << endl << endl;OpenHash<int, int> hash;int arr[] = { 34, 36, 12, 54, 5, 22, 65, 32, 13, 4, 1, 52 };for (auto& e : arr){hash.Insert(make_pair(e, e));}cout << hash.Find(12) << endl;cout << hash.Find(22) << endl;cout << hash.Find(32) << endl;cout << hash.Find(42) << endl;cout << hash.Find(52) << endl;cout << endl;hash.Erase(32);cout << hash.Find(12) << endl;cout << hash.Find(22) << endl;cout << hash.Find(32) << endl;cout << hash.Find(42) << endl;cout << hash.Find(52) << endl;
}int main()
{TestCloseHash();TestOpenHash();return 0;
}