JDK版本:jdk17
IDEA版本:IntelliJ IDEA 2022.1.3
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、异步任务的交互
- 1.1 applyToEither
- 1.2 acceptEither
- 1.3 runAfterEither
- 二、get() 和 join() 区别
- 三、ParallelStream VS CompletableFuture
- 3.1 使用串行流执行并统计总耗时
- 3.2 使用并行流执行并统计总耗时
- 3.3 使用串行流和CompletableFutre组合执行并统计总耗时
- 3.4 使用串行流和CompletableFutre组合执行并统计总耗时(优化:指定线程数量)
- 3.5 注意合理配置线程池中的线程数
- 四、大数据商品比价Demo(实践)
- 4.1 需求描述和分析
- 4.2 构建工具类和实体类
- 4.3 构建 HttpRequest
- 4.4 使用串行的方式操作商品比价
- 4.5 使用Future+线程池增加并行
- 4.6 使用CompletableFuture进一步增强并行
- 4.7 需求变更:同一个平台比较同款产品(iPhone15)不同色系的价格
前言
在前面入门篇中的内容中,我们详细介绍了异步编程Completablefuture的基本用法等相关知识;接下来,在本文进阶篇我们将详细探讨Completablefuture与stream API 相结合的具体用法,以及进一步增强并行处理的相关知识和案例用法
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考
一、异步任务的交互
释义
异步任务的交互是指在异步任务获取结果的速度相比较中,按一定的规则(先到先得)进行下一步处理
1.1 applyToEither
说明
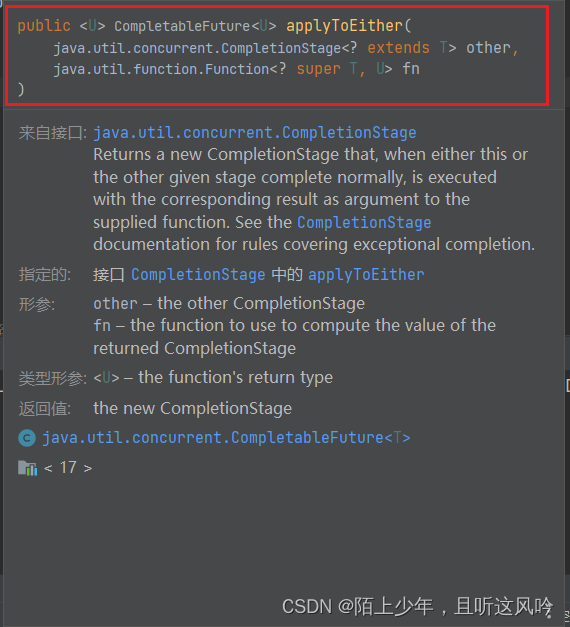
applyToEither()把两个异步任务做比较,异步任务先得到结果的,就对其获得的结果进行下一步操作。
案例
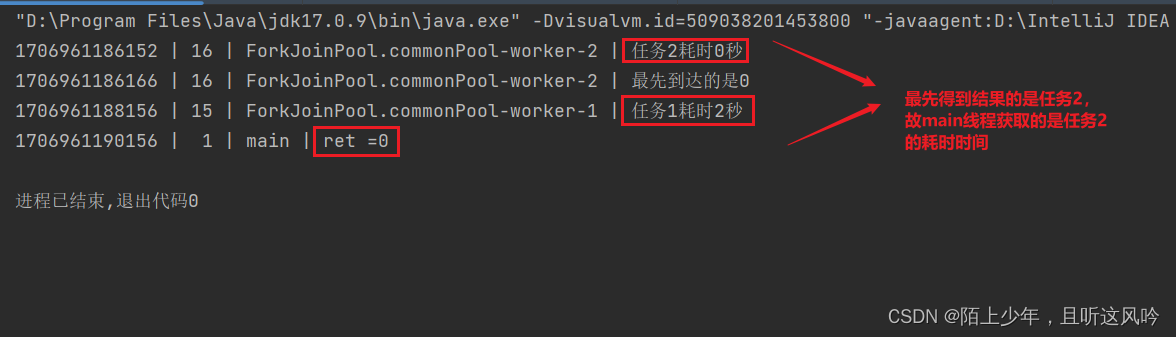
演示使用最先完成的异步任务的结果
示例代码如下
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {//异步任务1CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {int x = new Random().nextInt(3);CommonUtils.sleepSecond(x);CommonUtils.printTheadLog("任务1耗时" + x + "秒");return x;});//异步任务2CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {int y = new Random().nextInt(3);CommonUtils.sleepSecond(y);CommonUtils.printTheadLog("任务2耗时" + y + "秒");return y;});//哪个异步任务结果先到达,使用哪个异步任务的结果CompletableFuture<Integer> future3 = future1.applyToEither(future2, result -> {CommonUtils.printTheadLog("最先到达的是" + result);return result;});CommonUtils.sleepSecond(4);Integer ret = future3.get();CommonUtils.printTheadLog("ret ="+ret);//异步任务交互指两个异步任务,哪个结果先到,就使用哪个结果(先到先用)}
运行如下
以下是applyToEither 和其对应的异步回调版本
CompletableFuture<U> applyToEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Function<? super T, U> fn)
CompletableFuture<U> applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Function<? super T, U> fn)
CompletableFuture<U> applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Function<? super T, U> fn,Executor executor)1.2 acceptEither
说明
acceptEither()把两个异步任务做比较,异步任务先到结果的,就对先到的结果进行下一步操作(消费使用)
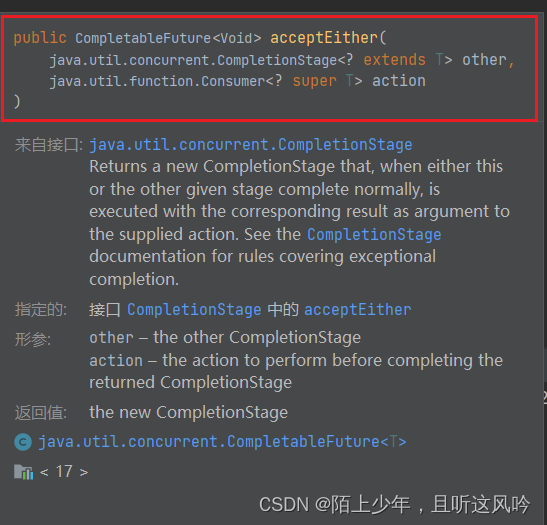
以下是acceptEither和其对应的异步回调版本
CompletableFuture<Void> acceptEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Consumer<? super T> action)
CompletableFuture<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Consumer<? super T> action)
CompletableFuture<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Consumer<? super T> action,Executor executor)
案例
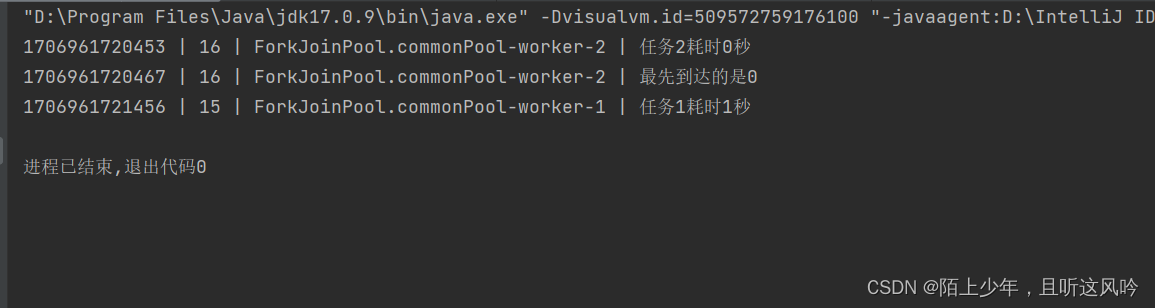
演示使用最先完成的异步任务的结果
示例代码如下
public static void main(String[] args) {//异步任务1CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {int x = new Random().nextInt(3);CommonUtils.sleepSecond(x);CommonUtils.printTheadLog("任务1耗时" + x + "秒");return x;});//异步任务2CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {int y = new Random().nextInt(3);CommonUtils.sleepSecond(y);CommonUtils.printTheadLog("任务2耗时" + y + "秒");return y;});//哪个异步任务结果先到达,使用哪个异步任务的结果future1.acceptEither(future2,result-> {CommonUtils.printTheadLog("最先到达的是"+result);});CommonUtils.sleepSecond(4);}
运行如下
1.3 runAfterEither
说明
如果不关心最先到达的结果,只想在有一个异步任务完成时得到完成的通知,可以使用 runAfterEither()
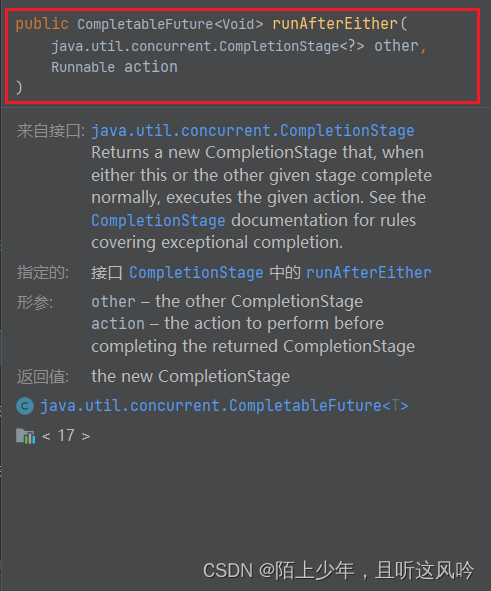
以下是它的相关方法
CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterEither(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action)
CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action)
CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action,Executor executor)案例
演示在最先完成的异步任务时得到它完成的通知
示例代码如下
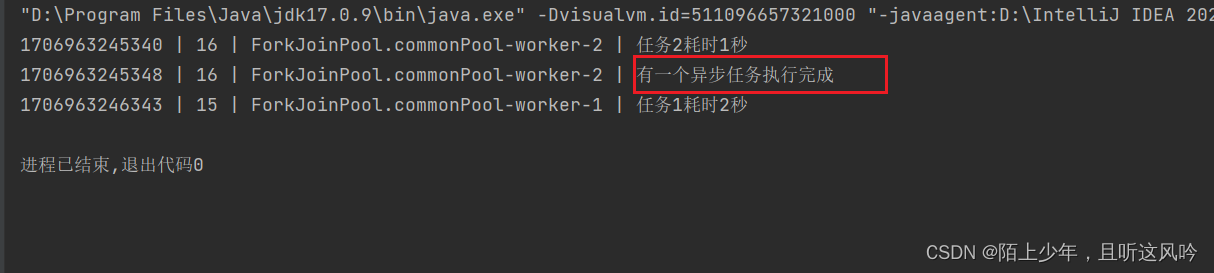
public static void main(String[] args) {//异步任务1CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {int x = new Random().nextInt(3);CommonUtils.sleepSecond(x);CommonUtils.printTheadLog("任务1耗时" + x + "秒");return x;});//异步任务2CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {int y = new Random().nextInt(3);CommonUtils.sleepSecond(y);CommonUtils.printTheadLog("任务2耗时" + y + "秒");return y;});future1.runAfterEither(future2, () -> {CommonUtils.printTheadLog("有一个异步任务执行完成");});CommonUtils.sleepSecond(4);/*** thenApply thenAccept thenRun* 对上一个异步任务的结果进行操作(转换、消费使用等)**applyToEither acceptEither runAfterEither* 对两个异步任务先到的结果进行燥作(转换,消费使用)*/}
运行如下
Trips
在之前入门篇的文章中,我们学习了CompletableFuture的thenApply
,thenAccept与thenRun()的使用,它们和以上的applyToEither ,acceptEither与
runAfterEither看似都在对异步任务的结果进行燥作(转换,消费使用),而实则针对操作对象的结果存在不同
thenApply() ,thenAccept() ,thenRun():对上一个异步任务的结果进行操作(转换、消费使用等)applyToEither() ,acceptEither(),runAfterEither():对两个异步任务先到的结果进行燥作(转换,消费使用)
二、get() 和 join() 区别
说明
get() 和 join() 都是CompletableFuture提供的以阻塞方式获取结果的方法
那么该如何选用呢? 请看如下案例:
public class GetOrJoinDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// get or joinCompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return "hello";});String ret = null;// 抛出检查时异常,必须处理try {String ret = future.get();} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (ExecutionException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}System.out.println(("ret = " + ret);// 抛出运行时异常,可以不处理String ret = future.join();System.out.println(("ret = " + ret);}
}
结论
使用时,我们发现,get() 抛出检查时异常,需要程序必须处理;而join() 方法抛出运行时异常,程序可以不处理。所以, join()更适合用在流式编程中
三、ParallelStream VS CompletableFuture
思考
- CompletableFuture 虽然提高了任务并行处理能力,如果它和 Stream API 结合使用,能否进一步多个任务的并行处理能力呢?
- Stream API 本身就提供了并行流 ParallelStream,CompletableFuture和它之间有什么不同呢?
我们将通过一个耗时的任务来体现它们的不同, 更重要地是,我们能进一步加强 CompletableFuture 和 Stream API的结合使用,同时搞清楚 CompletableFuture 在流式操作的优势
案例
创建10个 MyTask 耗时的任务, 统计它们执行完的总耗时
准备工作
定义一个 MyTask 类,来模拟耗时的长任务
示例代码如下
public class MyTask {private int duration;public MyTask(int duration) {this.duration = duration;}// 模拟耗时的长任务public int doWork() {CommonUtils.printTheadLog("doWork");CommonUtils.sleepSecond(duration);return duration;}
}
3.1 使用串行流执行并统计总耗时
方案1
在主线程中使用串行流执行
示例代码如下
public static void main(String[] args) {//需求:创建10个MyTask耗时的任务,统计它们执行完的总耗时//方案一:在主线程中使用串行执行//step 1: 创建1日个MyTask对象,每个任务持续1s,存入List集合IntStream intStream = IntStream.range(0, 10);List<MyTask> tasks = intStream.mapToObj(item -> {return new MyTask(1);}).collect(Collectors.toList());//step 2: 执行10个MyTask,统计总耗时long start = System.currentTimeMillis();List<Integer> results = tasks.stream().map(myTask -> {return myTask.doWork();}).collect(Collectors.toList());long end = System.currentTimeMillis();double costTime = (end - start) / 1000.0;System.out.printf("processed %d tasks %.2f second", tasks.size(), costTime);}
运行如下
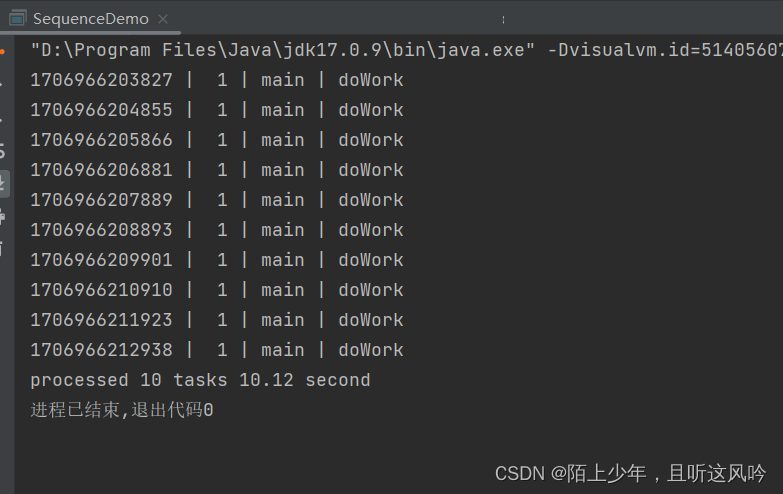
统计总耗时
10.12 second
3.2 使用并行流执行并统计总耗时
方案2
使用并行流执行统计
示例代码如下
public static void main(String[] args) {//需求:创建10个MyTask耗时的任务,统计它们执行完的总耗时//方案二:使用并行流//step 1: 创建1日个MyTask对象,每个任务持续1s,存入List集合IntStream intStream = IntStream.range(0, 10);List<MyTask> tasks = intStream.mapToObj(item -> {return new MyTask(1);}).collect(Collectors.toList());//step 2: 执行10个MyTask,统计总耗时long start = System.currentTimeMillis();List<Integer> results = tasks.parallelStream().map(myTask -> {return myTask.doWork();}).collect(Collectors.toList());long end = System.currentTimeMillis();double costTime = (end - start) / 1000.0;System.out.printf("processed %d tasks %.2f second", tasks.size(), costTime);}
运行如下
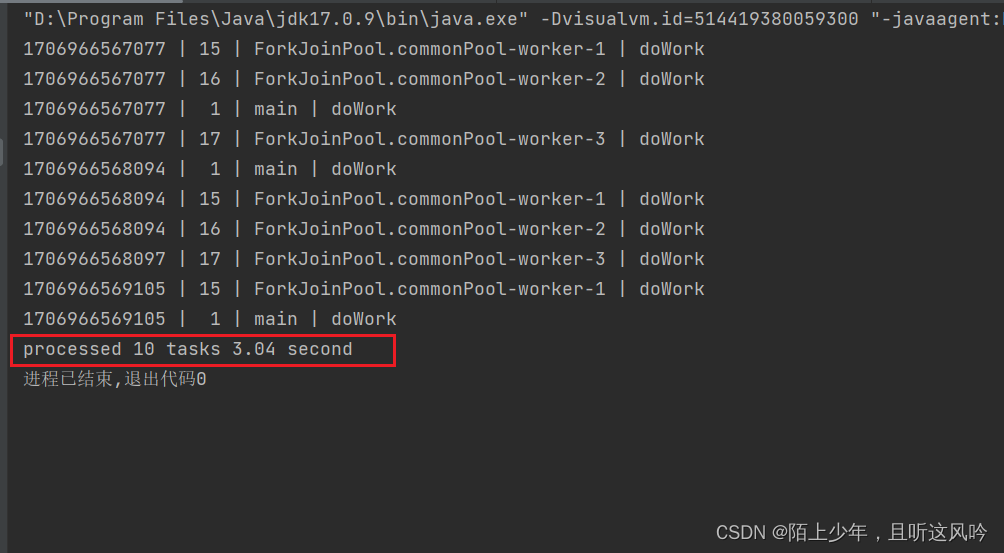
统计总耗时
3.04 second
3.3 使用串行流和CompletableFutre组合执行并统计总耗时
方案3
用并行流和CompletableFutre组合使用
示例代码如下
public static void main(String[] args) {//需求:创建10个MyTask耗时的任务,统计它们执行完的总耗时//方案三:使用并行流和CompletableFutre组合使用//step 1: 创建1日个MyTask对象,每个任务持续1s,存入List集合IntStream intStream = IntStream.range(0, 10);List<MyTask> tasks = intStream.mapToObj(item -> {return new MyTask(1);}).collect(Collectors.toList());//step 2: 根据MyTask对象构建10个耗时的异步任务long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// List<CompletableFuture<Integer>> futures = tasks.parallelStream().map(myTask -> {
// return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// return myTask.doWork();
// });
// }).collect(Collectors.toList());List<CompletableFuture<Integer>> futures = tasks.stream().map(myTask -> {return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return myTask.doWork();});}).collect(Collectors.toList());//step 3: 当所有任务完成时,获取每个异步任务的执行结果,存入L1st集合中List<Integer> results = futures.stream().map(future -> {return future.join();}).collect(Collectors.toList());long end = System.currentTimeMillis();double costTime = (end - start) / 1000.0;System.out.printf("processed %d tasks %.2f second", tasks.size(), costTime);}
运行如下
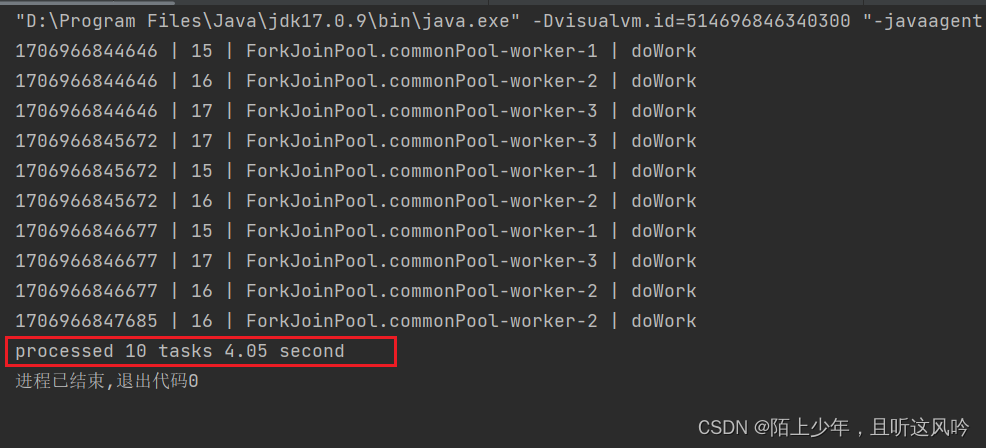
统计总耗时
4.05 second
发现
本人使用CompletableFutre执行比之前使用并行流多花了约
1.01秒的时间
本机CPU相关的核数配置如下
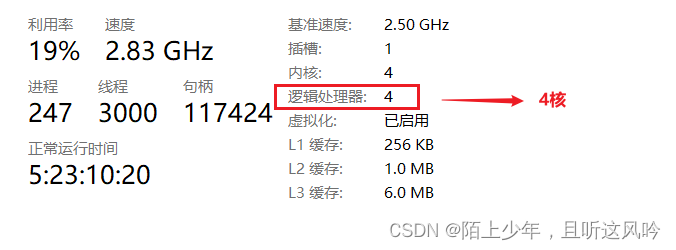
根据上述运行对比,CompletableFutre与并行流二者使用的时间大致一样,能否进一步优化呢?
CompletableFuture 比 ParallelSteam 优点之一是你可以指定Excutor去处理任务。你能选择更合适数量的线程。我们可以选择大于Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()
数量的线程, 如下所示
3.4 使用串行流和CompletableFutre组合执行并统计总耗时(优化:指定线程数量)
示例代码如下
public static void main(String[] args) {// CompletableFuture 在流式操作中的优势// 需求: 创建10个 MyTask 耗时的任务, 统计它们执行完的总耗时// 方案四:使用CompletableFuture(指定线程数量)// step 1: 创建10个MyTask对象,每个任务持续1s, 存入List集合IntStream intStream = IntStream.range(0, 10);List<MyTask> tasks = intStream.mapToObj(item -> {return new MyTask(1);}).collect(Collectors.toList());// 准备线程池int N_CPU = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();// 设置线程池中的线程的数量至少为10ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(Math.min(tasks.size(),N_CPU * 2));// step 2: 根据MyTask对象构建10个异步任务List<CompletableFuture<Integer>> futures = tasks.stream().map(myTask -> {return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()-> {return myTask.doWork();},executor);}).collect(Collectors.toList());// step 3: 执行异步任务,执行完成后,获取异步任务的结果,存入List集合中,统计总耗时long start = System.currentTimeMillis();List<Integer> results = futures.stream().map(CompletableFuture::join).collect(Collectors.toList());long end = System.currentTimeMillis();double costTime = (end - start) / 1000.0;System.out.printf("processed %d tasks %.2f second", tasks.size(), costTime);// 关闭线程池executor.shutdown();/*** 总结* CompLetabLeFuture可以控制更多的线程数量,而ParalLelstream不能*/}
运行如下
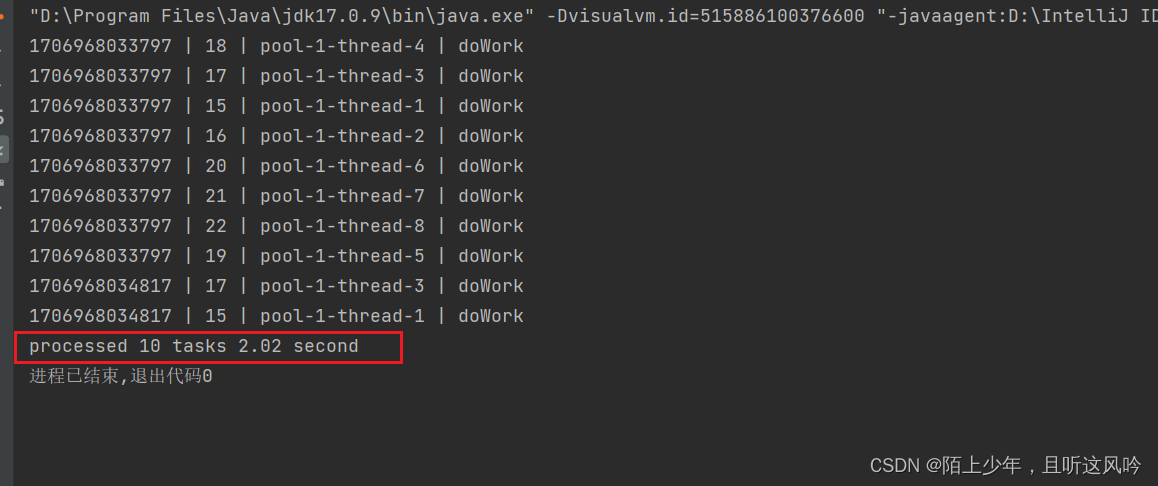
统计总耗时
2.02 second
Trips
测试运行时,本机电脑配置是4核4线程,而我们创建的线程池中线程数最少也是10个,所以每个线程负责一个任务(耗时1s)总体来说, 处理10个任务就得分成这样执行(第一次先分4个线程并行处理四个任务;第二次也分4个线程并行处理四个任务;第三次分两个线程并行处理剩下的l两个任务),故总共需要2.02秒
3.5 注意合理配置线程池中的线程数
正如我们看到的,CompletableFuture 可以更好的控制线程池的数量,而 parallelStream 不能
问题1:如何选用 CompletableFuture 和 ParallelStream?
- 如果你的任务是IO密集型,你应该使用 CompletableFuture;
- 如果你的任务是CPU密集型,使用比处理器更多的线程是没有意义的,所以选择 ParallelSteam,因为它不需要创建线程池,更容易使用。
问题2:IO密集型任务和CPU密集型任务的区别?
CPU密集型也叫计算密集型,此时,系统运行时大部分的状况是CPU占用率近乎100%,I/O在很短的时间可以完成,而CPU还有许多运算要处理,CPU使用率很高。比如计算1+2+3…+10万亿、天文计算、圆周率后几十位等,都属于CPU密集型程序。
CPU密集型任务的特点:大量计算,CPU占用率一般都很高,I/O时间很短
IO密集型指大部分的状况是CPU在等I/O(硬盘/内存)的读写操作,但CPU的使用率不高。
简单的说,就是需要大量的输入输出,例如读写文件、传输文件,网络请求。 IO密集型任务的特点:大量网络请求,文件操作,CPU运算少,很多时候CPU在等待资源才能进一步操作。
问题3:既然要控制线程池的数量,多少合适呢?
- 如果是CPU密集型任务,就需要尽量压榨CPU,参数值可以设为 Ncpu + 1
- 如果是IO密集型任务,参考值可以设置为 2 * Ncpu,其中 Ncpu 表示核心数
注意
以上给的是业界认为的参考值, 详细配置的问题以后再行讨论,故不在赘述
四、大数据商品比价Demo(实践)
4.1 需求描述和分析
实现一个大数据比价服务,价格数据可以从京东、天猫、拼多多等平台去获取指定商品的价格、优惠金额,然后计算出实际付款金额(商品价格 -优惠金额),最终返回价格最优的平台与价格信息

4.2 构建工具类和实体类
①定义价格实体类 PriceResult
示例代码如下
public class PriceResult {private int price;private int discount;private int realPrice;private String platform;public PriceResult() {}public PriceResult(String platform) {this.platform = platform;}public PriceResult(int price, int discount, int realPrice, String platform) {this.price = price;this.discount = discount;this.realPrice = realPrice;this.platform = platform;}public int getPrice() {return price;}public void setPrice(int price) {this.price = price;}public int getDiscount() {return discount;}public void setDiscount(int discount) {this.discount = discount;}public int getRealPrice() {return realPrice;}public void setRealPrice(int realPrice) {this.realPrice = realPrice;}public String getPlatform() {return platform;}public void setPlatform(String platform) {this.platform = platform;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "PriceResult{" +"平台='" + platform + '\'' +", 平台价=" + price +", 优惠价=" + discount +", 最终价=" + realPrice +'}';}
}
②修改工具类CommonUtils, 添加getCurrenTime()方法获取当前时间并格式化,添加 printThreadLog1()方法,在原先printThreadLog()方法的基础上把时间戳换成当前时间
示例代码如下
public class CommonUtils {// 读取文件路径的文件public static String readFile(String pathToFile) {try {return Files.readString(Paths.get(pathToFile));} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();return "";}}// 休眠指定的毫秒数public static void sleepMillis(long millis) {try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(millis);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}// 休眠指定的秒数public static void sleepSecond(long second) {try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(second);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}//获取当前时间private static String getCurrentTime() {LocalTime now = LocalTime.now();return now.format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("[HH:mm::ss.SS"));}// 打印输出带线程信息的日志public static void printTheadLog(String message) {// 时间戳 | 线程id | 线程名 | 日志信息String result = new StringJoiner(" | ").add(String.valueOf(System.currentTimeMillis())).add(String.format("%2d", Thread.currentThread().getId())).add(Thread.currentThread().getName()).add(message).toString();System.out.println(result);}// 打印输出带线程信息的日志public static void printTheadLog1(String message) {// 当前时间 | 线程id | 线程名 | 日志信息String result = new StringJoiner(" | ").add(getCurrentTime()).add(String.format("%2d", Thread.currentThread().getId())).add(Thread.currentThread().getName()).add(message).toString();System.out.println(result);}}
4.3 构建 HttpRequest
HttpRequest 用于模拟网络请求(耗时的操作)
示例代码如下
public class HttpRequest {private static void mockCostTimeOperation() {CommonUtils.sleepSecond(1);}// 获取淘宝平台的商品价格public static PriceResult getTaobaoPrice(String productName) {CommonUtils.printTheadLog("获取淘宝上" + productName + "价格");mockCostTimeOperation();PriceResult priceResult = new PriceResult("淘宝");priceResult.setPrice(5199);CommonUtils.printTheadLog("获取淘宝上" + productName + "价格完成:5199");return priceResult;}// 获取淘宝平台的优惠public static int getTaoBaoDiscount(String productName) {CommonUtils.printTheadLog("获取淘宝上" + productName + "优惠");mockCostTimeOperation();CommonUtils.printTheadLog("获取淘宝上" + productName + "优惠完成:-200");return 200;}// 获取京东平台的商品价格public static PriceResult getJDongPrice(String productName) {CommonUtils.printTheadLog1("获取京东上" + productName + "价格");mockCostTimeOperation();PriceResult priceResult = new PriceResult("淘宝");priceResult.setPrice(5299);CommonUtils.printTheadLog1("获取京东上" + productName + "价格完成:5299");return priceResult;}// 获取京东平台的优惠public static int getJDongDiscount(String productName) {CommonUtils.printTheadLog1("获取京东上" + productName + "优惠");mockCostTimeOperation();CommonUtils.printTheadLog1("获取京东上" + productName + "优惠完成:-150");return 150;}// 获取拼多多平台的商品价格public static PriceResult getPDDPrice(String productName) {CommonUtils.printTheadLog1("获取拼多多上" + productName + "价格");mockCostTimeOperation();PriceResult priceResult = new PriceResult("拼多多");priceResult.setPrice(5399);CommonUtils.printTheadLog1("获取拼多多上" + productName + "价格完成:5399");return priceResult;}// 获取拼多多平台的优惠public static int getPDDDiscount(String productName) {CommonUtils.printTheadLog1("获取拼多多上" + productName + "优惠");mockCostTimeOperation();CommonUtils.printTheadLog1("获取拼多多上" + productName + "优惠完成:-5300");return 5300;}}
4.4 使用串行的方式操作商品比价
①ComparePriceService类代码如下
public class ComparePriceService {// 方案一:串行方式操作商品比价public PriceResult getCheapestPlatformPrice(String productName) {PriceResult priceResult;int discount;// 获取淘宝平台的商品价格和优惠priceResult = HttpRequest.getTaobaoPrice(productName);discount = HttpRequest.getTaoBaoDiscount(productName);PriceResult taoBaoPriceResult = this.computeRealPrice(priceResult, discount);// 获取京东平台的商品价格和优惠priceResult = HttpRequest.getJDongPrice(productName);discount = HttpRequest.getJDongDiscount(productName);PriceResult jDongPriceResult = this.computeRealPrice(priceResult, discount);// 获取拼多多平台的商品价格和优惠priceResult = HttpRequest.getPDDPrice(productName);discount = HttpRequest.getPDDDiscount(productName);PriceResult pddPriceResult = this.computeRealPrice(priceResult, discount);// 计算最优的平台和价格Stream<PriceResult> stream = Stream.of(taoBaoPriceResult, jDongPriceResult, pddPriceResult);Optional<PriceResult> minOpt = stream.min(Comparator.comparing(priceRes -> {return priceRes.getRealPrice();}));PriceResult result = minOpt.get();return result;
// return Stream.of(taoBaoPriceResult, jDongPriceResult, pddPriceResult)
// .min(Comparator.comparing(PriceResult::getRealPrice))
// .get();}// 计算商品的最终价格 = 平台价格 - 优惠价public PriceResult computeRealPrice(PriceResult priceResult, int discount) {priceResult.setRealPrice(priceResult.getPrice() - discount);priceResult.setDiscount(discount);CommonUtils.printTheadLog(priceResult.getPlatform() + "最终价格计算完成" + priceResult.getRealPrice());return priceResult;}}
②main方法中执行
示例代码如下
public static void main(String[] args) {//1. 使用串行方式操作商品比价ComparePriceService service = new ComparePriceService();long start = System.currentTimeMillis();PriceResult priceResult = service.getCheapestPlatformPrice("iphone16");long end = System.currentTimeMillis();double costTime = (end - start)/1000.0;System.out.printf("cost %.2f second processed\n",costTime);System.out.println("priceResult = " + priceResult);}
运行如下
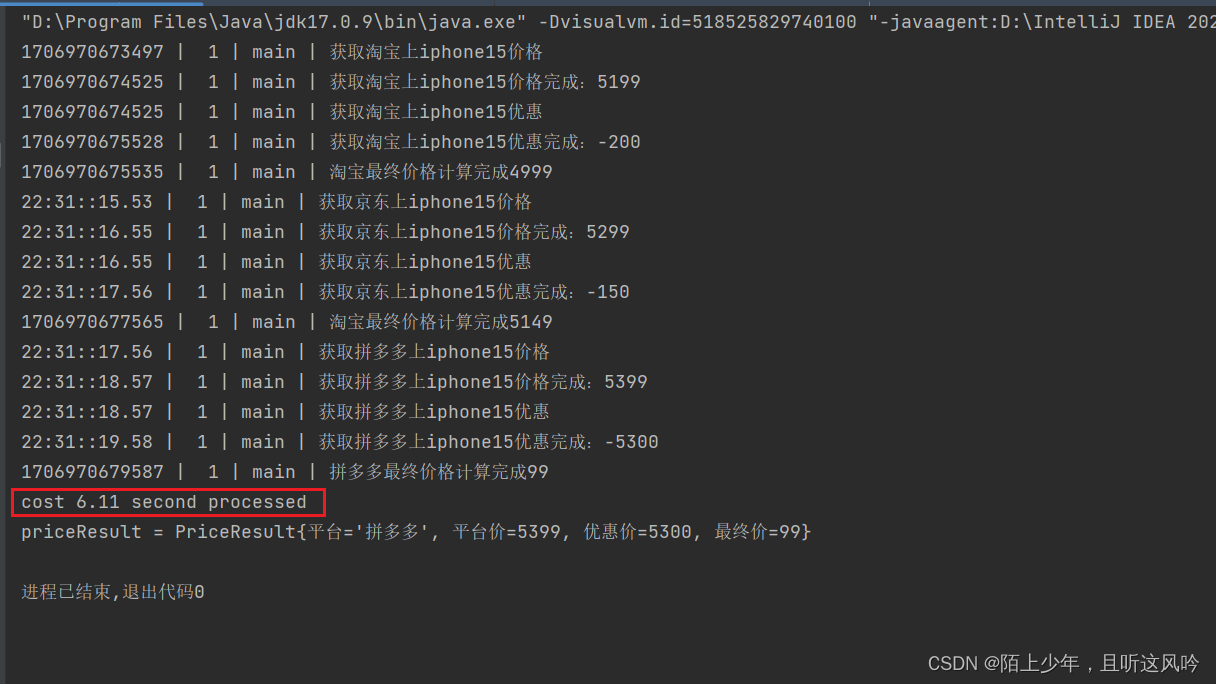
统计总耗时
6.11 second
4.5 使用Future+线程池增加并行
①ComparePriceService类代码如下
public class ComparePriceService {//方案二:使用Future + 线程池 操作商品比价public PriceResult getCheapestPlatformPrice2(String productName) {// 线程池ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4);// 获取淘宝平台的商品价格和优惠Future<PriceResult> taobaoFuture = executor.submit(() -> {PriceResult priceResult = HttpRequest.getTaobaoPrice(productName);int discount = HttpRequest.getTaoBaoDiscount(productName);return this.computeRealPrice(priceResult, discount);});// 获取京东平台的商品价格和优惠Future<PriceResult> jdFuture = executor.submit(() -> {PriceResult priceResult = HttpRequest.getJDongPrice(productName);int discount = HttpRequest.getJDongDiscount(productName);return this.computeRealPrice(priceResult, discount);});// 获取拼多多平台的商品价格和优惠Future<PriceResult> pddFuture = executor.submit(() -> {PriceResult priceResult = HttpRequest.getPDDPrice(productName);int discount = HttpRequest.getPDDDiscount(productName);return this.computeRealPrice(priceResult, discount);});// 计算最优的平台和价格PriceResult priceResult = Stream.of(taobaoFuture, jdFuture, pddFuture).map(item -> {try {//假设延时5s后,就不要它的结果,所以返回一个空return item.get(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();return null;}finally {executor.shutdown();}}).filter(Objects::nonNull).min(Comparator.comparing(PriceResult::getRealPrice)).get();return priceResult;}// 计算商品的最终价格 = 平台价格 - 优惠价public PriceResult computeRealPrice(PriceResult priceResult, int discount) {priceResult.setRealPrice(priceResult.getPrice() - discount);priceResult.setDiscount(discount);CommonUtils.printTheadLog(priceResult.getPlatform() + "最终价格计算完成" + priceResult.getRealPrice());return priceResult;}}
②main方法中执行
示例代码如下
public static void main(String[] args) {//2.使用Future + 线程池 操作商品比价ComparePriceService service = new ComparePriceService();long start = System.currentTimeMillis();PriceResult priceResult = service.getCheapestPlatformPrice2("iphone16");long end = System.currentTimeMillis();double costTime = (end - start)/1000.0;System.out.printf("cost %.2f second processed\n",costTime);System.out.println("priceResult = " + priceResult);
}
运行如下
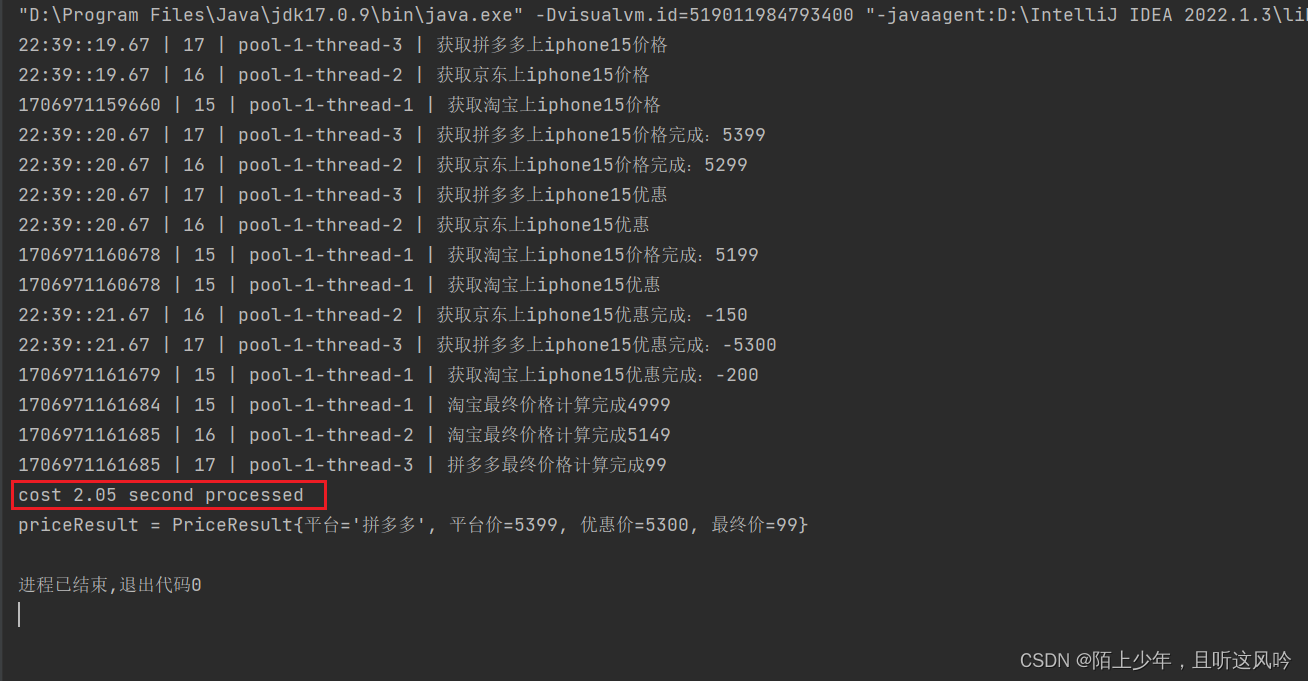
统计总耗时
2.05 second
4.6 使用CompletableFuture进一步增强并行
①ComparePriceService类代码如下
public class ComparePriceService {//方案三:使用CompletableFuture 操作商品比价public PriceResult getCheapestPlatformPrice3(String productName) {// 获取淘宝平台的商品价格和优惠CompletableFuture<PriceResult> taobaofuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> HttpRequest.getTaobaoPrice(productName)).thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> HttpRequest.getTaoBaoDiscount(productName)), (priceRsult, discount) -> {return this.computeRealPrice(priceRsult, discount);});// 获取京东平台的商品价格和优惠CompletableFuture<PriceResult> jdfuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> HttpRequest.getJDongPrice(productName)).thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> HttpRequest.getJDongDiscount(productName)), (priceRsult, discount) -> {return this.computeRealPrice(priceRsult, discount);});// 获取拼多多平台的商品价格和优惠CompletableFuture<PriceResult> pddfuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> HttpRequest.getPDDPrice(productName)).thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> HttpRequest.getPDDDiscount(productName)), (priceRsult, discount) -> {return this.computeRealPrice(priceRsult, discount);});// 计算最优的平台和价格PriceResult priceResult = Stream.of(taobaofuture, jdfuture, pddfuture).map(future -> future.join()).min(Comparator.comparing(item -> item.getRealPrice())).get();return priceResult;}// 计算商品的最终价格 = 平台价格 - 优惠价public PriceResult computeRealPrice(PriceResult priceResult, int discount) {priceResult.setRealPrice(priceResult.getPrice() - discount);priceResult.setDiscount(discount);CommonUtils.printTheadLog(priceResult.getPlatform() + "最终价格计算完成" + priceResult.getRealPrice());return priceResult;}
}
②main方法中执行
示例代码如下
public static void main(String[] args) {//3.使用CompletableFuture 操作商品比价ComparePriceService service = new ComparePriceService();long start = System.currentTimeMillis();PriceResult priceResult = service.getCheapestPlatformPrice3("iphone15");long end = System.currentTimeMillis();double costTime = (end - start)/1000.0;System.out.printf("cost %.2f second processed\n",costTime);System.out.println("priceResult = " + priceResult);}
运行如下
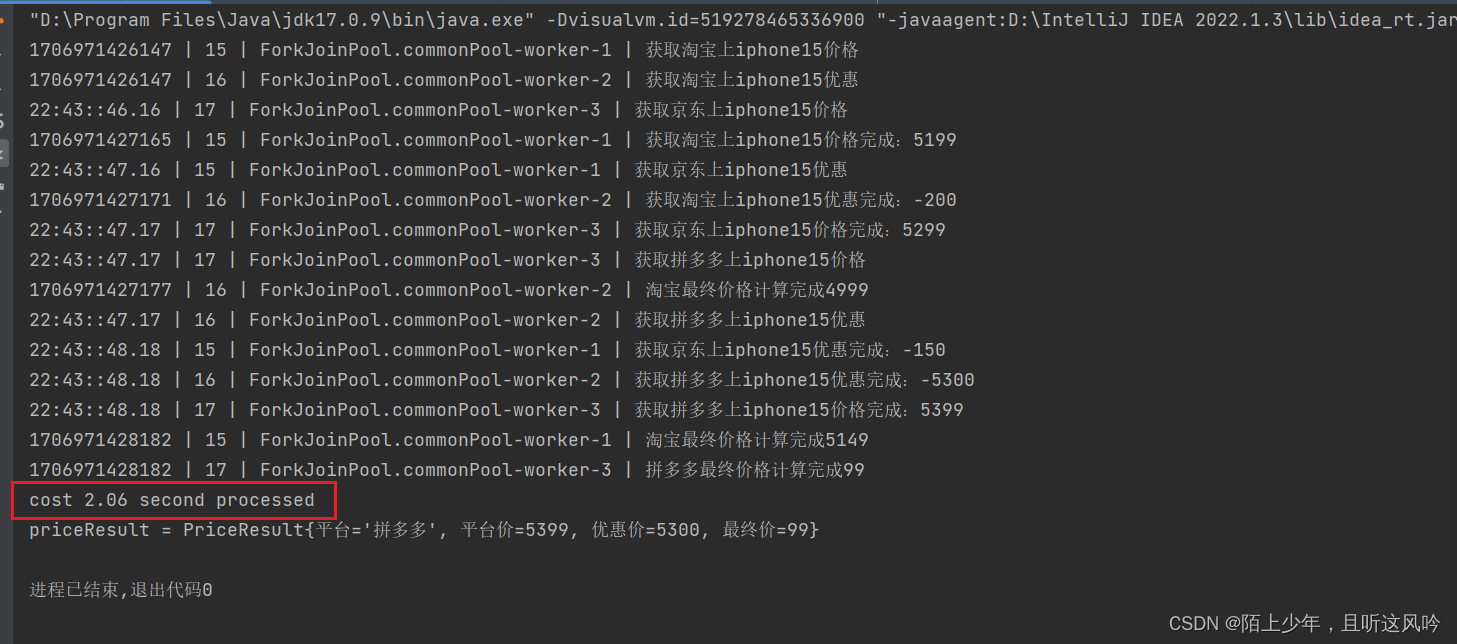
统计总耗时
2.06 second
4.7 需求变更:同一个平台比较同款产品(iPhone15)不同色系的价格
说明
使用异步任务的批量操作实现
①ComparePriceService类代码如下
public class ComparePriceService {// 计算商品的最终价格 = 平台价格 - 优惠价public PriceResult computeRealPrice(PriceResult priceResult, int discount) {priceResult.setRealPrice(priceResult.getPrice() - discount);priceResult.setDiscount(discount);CommonUtils.printTheadLog(priceResult.getPlatform() + "最终价格计算完成" + priceResult.getRealPrice());return priceResult;}public PriceResult batchComparePrice(List<String> products) {// step 1:遍历每个商品的名字, 根据商品名称开启异步任务获取最终价, 归集到List集合中List<CompletableFuture<PriceResult>> futureList = products.stream().map(productName -> {return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> HttpRequest.getTaobaoPrice(productName)).thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> HttpRequest.getTaoBaoDiscount(productName)), (priceRsult, discount) -> {return this.computeRealPrice(priceRsult, discount);});}).collect(Collectors.toList());// step 2: 把多个商品的最终价进行排序获取最小值PriceResult priceResult = futureList.stream().map(future -> future.join()).sorted(Comparator.comparing(item -> item.getRealPrice())).findFirst().get();return priceResult;}}
②main方法中执行
示例代码如下
public static void main(String[] args) {// 异步任务的批量操作// 测试在一个平台比较同款产品(iPhone15)不同色系的价格ComparePriceService service = new ComparePriceService();long start = System.currentTimeMillis();PriceResult priceResult = service.batchComparePrice(Arrays.asList("iphone15午夜黑","iphone15白色","iphone15淡青"));long end = System.currentTimeMillis();double costTime = (end - start)/1000.0;System.out.printf("cost %.2f second processed\n",costTime);System.out.println("priceResult = " + priceResult);
}
运行如下
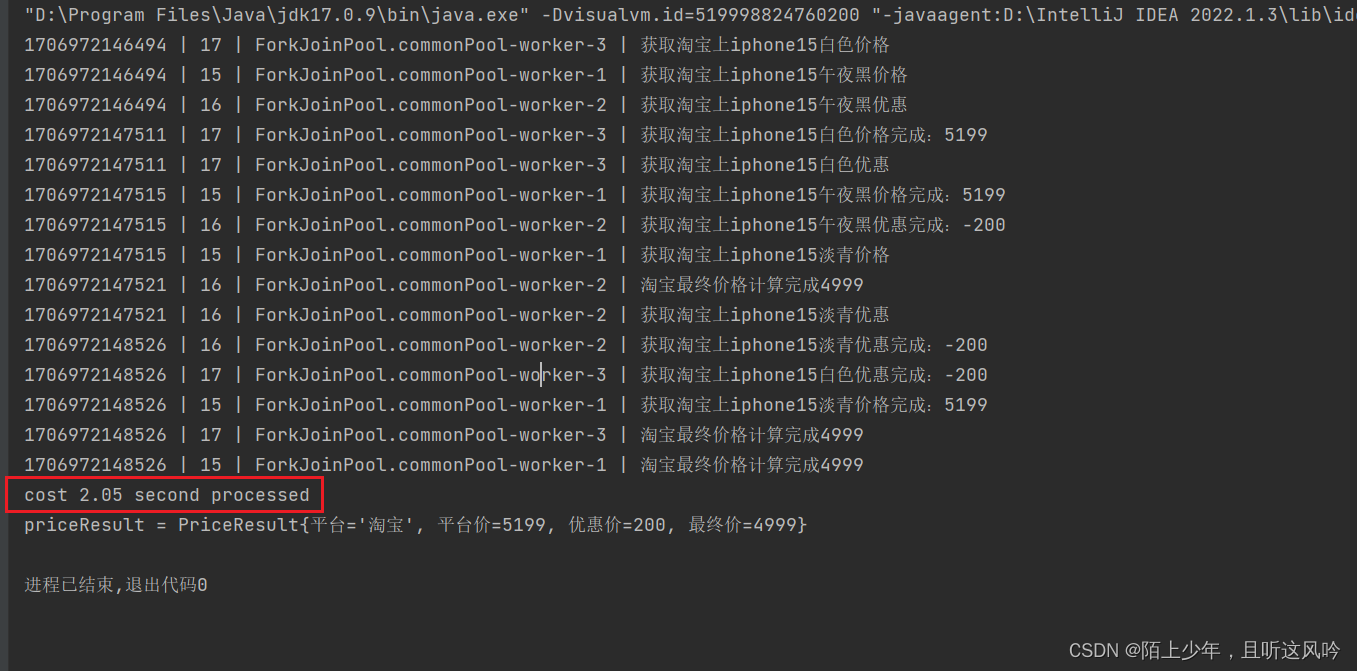
统计总耗时
2.05 second