搜索与图论
- 一、DFS
- ① 排列数字
- ② n-皇后问题(还没写)
- 二、BFS
- ① 走迷宫
- ② 八数码(还没写)
- 三、树与图的深度优先遍历(树的重心)
- 四、树与图的广度优先遍历(图中点的层次)
- 五、有向图的拓扑序列
| 比较 | 空间 | 特点 | 数据结构 |
|---|---|---|---|
| DFS | 0(h) | 第一次搜到的答案不具有最短性 | stack |
| BFS | 0(2^h) | 第一次搜索到的答案一定是最短路 | queue |
一、DFS
① 排列数字
算法
两个重要概念:回溯和剪枝
想好搜索顺序,构建一颗搜索树
回溯时一定要注意恢复现场
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>using namespace std;const int N = 10;int n;
int path[N];
bool st[N];void dfs(int u)
{//当填充位置为n时,说明已经有n个数了,将路径上的n个数输出if (u == n){for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) cout << path[i] << " ";cout << endl;return ;}//从1~n中顺次判断,如果该数没有被遍历过,则取这个数for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){if (!st[i]){st[i] = true; //修改状态path[u] = i;dfs(u + 1); //填充下一位数字st[i] = false; //还原状态}}
}int main()
{cin >> n;dfs(0); //从path的0号位置开始填充return 0;
}
② n-皇后问题(还没写)
算法
代码
二、BFS
① 走迷宫
算法

代码
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>using namespace std;
const int N = 110;typedef pair <int, int> PII;int n, m;
int g[N][N];
int st[N][N]; //记录当前节点最少需要几步走到,并且防止每个节点被遍历两次void bfs()
{queue <PII> q;q.push({0, 0});st[0][0] = 0;while (!q.empty()) //可以遍历到所有的0,仅且只有一遍{auto cur = q.front();q.pop();int dx[4] = {-1, 1, 0, 0};int dy[4] = {0, 0, -1, 1};for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++){int a = cur.first + dx[i], b = cur.second + dy[i];if (a >= 0 && a < n && b >= 0 && b < m && g[a][b] == 0 && st[a][b] == -1){q.push({a, b});st[a][b] = st[cur.first][cur.second] + 1; //该节点的出边节点所需步数加一}}}cout << st[n - 1][m - 1]; //出口处那个点记录的步数一定是最少的
}int main()
{cin >> n >> m;for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++)for (int j = 0; j < m; j ++)cin >> g[i][j];memset(st, -1, sizeof(st));bfs();return 0;
}
② 八数码(还没写)
算法
代码
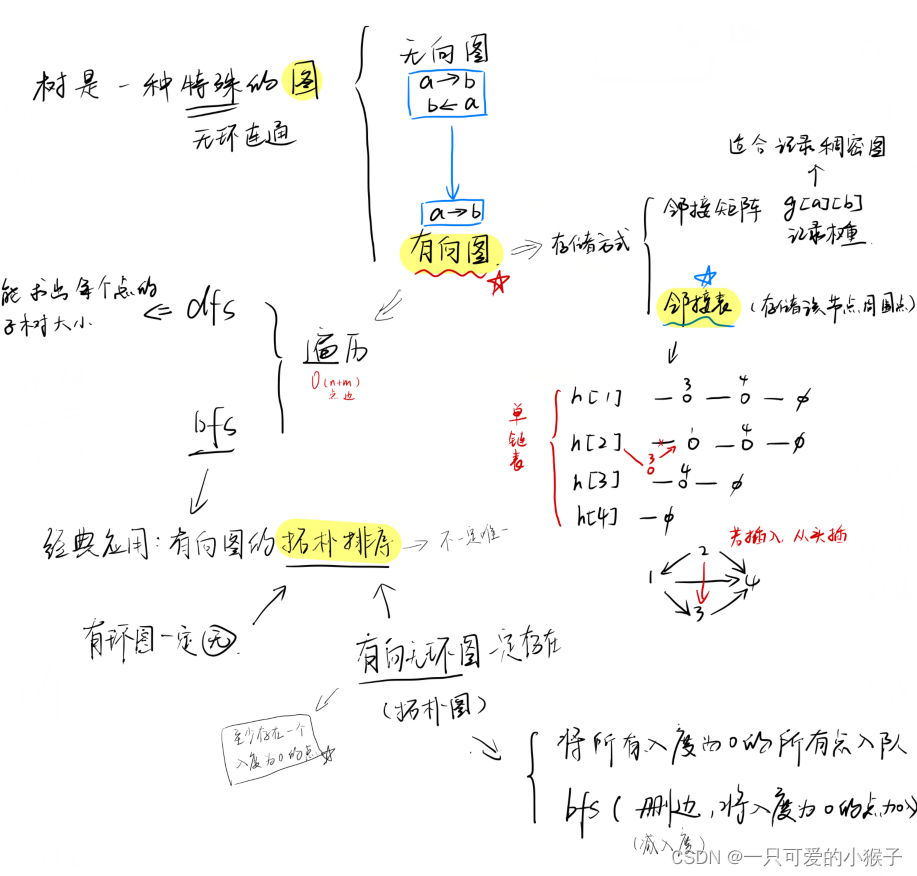
三、树与图的深度优先遍历(树的重心)
代码
const int N = 100010, M = N * 2; //N条边,开2 * N 个点
int h[N], e[M], ne[M], idx; // h存储每个节点的存放位置,e存放每个节点的值,ne存放下一个节点的位置,idx指向当前使用的数组下标
bool st[M]; //记录每个节点是否被遍历过//初始化
memset(h, -1, sizeof(h));//将y节点接入以x为头的单链表中
//读入边使用add函数构建图,例如无向图x - y :add(x, y), add(y, x),需要双向连接
void add(int x, int y)
{e[idx] = y;ne[idx] = h[x];h[x] = idx ++;
}//遍历以u为头的单链表
for (int i = h[u]; i != -1; i = ne[i]){}//树的深搜,可以返回以u为根节点的子节点数目
int dfs(int u)
{st[u] = true;int sum = 1;for (int i = h[u]; i != -1; i = ne[i]){int cur = e[i]; //当前访问节点的内容if (!st[cur]){int s = dfs(cur);sum += s;}}return sum;
}//树的宽搜就是套用普通宽搜模板即可
四、树与图的广度优先遍历(图中点的层次)
算法
代码
五、有向图的拓扑序列
算法
使用邻接表存储有向图,并记录每个点的入度
使用bfs得到拓扑序列,并且可以判断该图中是否有环
每次将入度为0的点放入队列,该点弹出时,将其相连的点入度-1,并将入度为0的点入队
若存在环,整个过程中所有入度为0的点的个数小于总点数
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>using namespace std;const int N = 100010;int n, m, R[N];
int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;void add(int x, int y)
{e[idx] = y;ne[idx] = h[x];h[x] = idx ++;
}void bfs()
{queue <int> q, res;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){if (!R[i]){q.push(i);res.push(i);}}while (!q.empty()){auto t = q.front();q.pop();for (int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i]){int j = e[i];R[j] --;if (R[j] == 0){q.push(j);res.push(j);}}}if (res.size() < n) cout << -1;else{while (!res.empty()){auto x = res.front();res.pop();cout << x << " ";}}
}int main()
{memset(h, -1, sizeof(h));cin >> n >> m;bool flag = false;for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++){int x, y;cin >> x >> y;if (x == y){flag = true;}R[y] ++;add(x, y);}if (flag) cout << -1;else bfs();return 0;
}
![[Angular 基础] - Angular 渲染过程 组件的创建](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/ae6669b1941641fdb35724349183c360.png)