前言:
本章会讲解二叉树及其一些相关练习题,和堆是什么。
二叉树:
二叉树的一些概念:
一棵二叉树是有限节点的集合,该集合可能为空。二叉树的特点是每一个节点最多有两个子树,即二叉树不存在度大于2的节点。且二叉树子树有左右之分,子树顺序不能颠倒。
还有两种特殊的二叉树,完全二叉树和满二叉树。
满二叉树是就是没有度为1的节点。所以当有k层时,它有2^k -1个节点。
完全二叉树有度为1的节点且是连续的。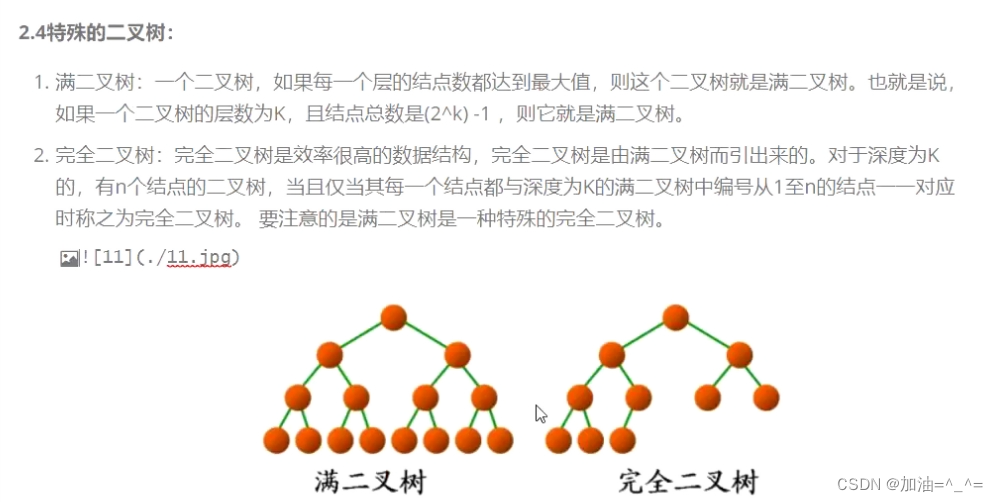
所以我们可以根据节点的个数计算树的高度。
二叉树的性质:
若规定根节点层数是1,则一颗非空二叉树第i层上最多有2^(i-1)个节点。
若规定根节点层数是1,则深度为h的二叉树的最大节点数为2^h-1个节点。
对任何一颗二叉树如果度为0的节点数是n0,度为2的节点数是n2,则有n0=n2+1。
若规定根节点层数为1,则有n个节点的满二叉树深度为h=LogN。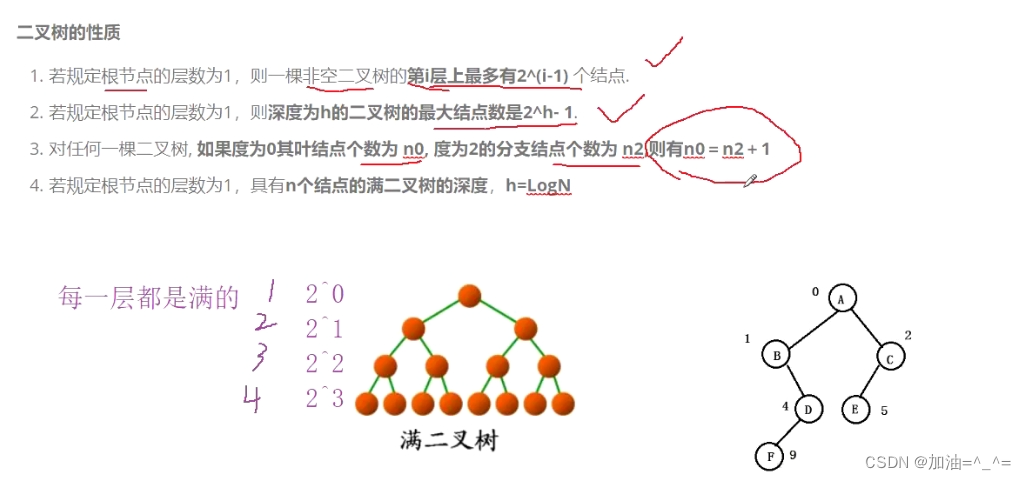
在具有2n个节点的完全二叉树中,叶子结点个数为n。
练习题:
二叉树的最大深度:
OJ链接:力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
思路:整棵树的高度 = (左子树的高度 + 右子树的高度)的最大值 + 1。
其实也就是求树的高度,这里我们利用递归来实现:
class Solution {public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return 0;}return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;}
}判断是否为平衡二叉树:
OJ链接:力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
这里需要用到二叉树的最大深度来完成:
class Solution {public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return true;}return treeHeigth(root) >= 0;//时间复杂度:O(n)}public int treeHeigth(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return 0;}int leftHeigth = treeHeigth(root.left);if (leftHeigth < 0) {return -1;}int rightHeigth = treeHeigth(root.right);if (leftHeigth >= 0 && rightHeigth >= 0&& Math.abs(leftHeigth - rightHeigth) <= 1) {return Math.max(leftHeigth, rightHeigth) + 1;} else {return -1;}}
}相同的树:
OJ链接:力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
class Solution {public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (p == null && q != null || p != null && q == null) {return false;}//此时,要么两个都为空 要么两个都不为空if (p == null && q == null) {return true;}//此时两个都不为空if (p.val != q.val) {return false;}//p != null && q != null && p.val == q.valreturn isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);//时间复杂度为min(n,m)}
}另一棵树的子树:
OJ链接:力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
这里我们需要用到判断两树是否相同的代码:
class Solution {public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode root, TreeNode subRoot) {//可能会有空的情况if (root == null || subRoot == null) {return false;}//类似于BF算法//1.是不是和根节点相同if (isSameTree(root, subRoot)) {return true;}//2.判断是不是root的左子树if (isSubtree(root.left, subRoot)){return true;}//3.右子树if (isSubtree(root.right, subRoot)) {return true;}//4.返回return false;//时间复杂度 O(M * N)}public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (p == null && q != null || p != null && q == null) {return false;}//此时,要么两个都为空 要么两个都不为空if (p == null && q == null) {return true;}//此时两个都不为空if (p.val != q.val) {return false;}//p != null && q != null && p.val == q.valreturn isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);//时间复杂度为min(n,m)}
}翻转二叉树:
OJ链接:力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
class Solution {public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return null;}TreeNode tmp = root.left;root.left = root.right;root.right = tmp;invertTree(root.left);invertTree(root.right);return root;}
}对称二叉树:
OJ链接:力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
class Solution {public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {//根的值一样//1.左树的左 和 右树的右//2.左树的右 和 右树的左if (root == null) {return true;}return isSymmetricChild(root.left, root.right);}private boolean isSymmetricChild(TreeNode leftTree, TreeNode rightTree) {if (leftTree == null && rightTree != null || leftTree != null && rightTree == null) {return false;}if (leftTree == null && rightTree == null) {return true;}if (leftTree.val != rightTree.val) {return false;}return isSymmetricChild(leftTree.left, rightTree.right) && isSymmetricChild(leftTree.right, rightTree.left);}
}最近公共祖先:
OJ链接:力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
class Solution {public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (root == null) {return null;}//利用链表相交的道理//之后利用栈来完成Stack<TreeNode> stack1 = new Stack<>();Stack<TreeNode> stack2 = new Stack<>();getPath(root, p, stack1);getPath(root, q, stack2);while (stack1.size() != stack2.size()) {if (stack1.size() > stack2.size()) {stack1.pop();} else {stack2.pop();}}while (stack1.peek() != stack2.peek()) {stack1.pop();stack2.pop();}return stack1.peek();}private boolean getPath(TreeNode root, TreeNode node, Stack<TreeNode> stack) {if (root == null || node == null) {return false;}stack.push(root);if (root == node) {return true;}boolean flag1 = getPath(root.left, node, stack);if (flag1 == true) {return true;}boolean flag2 = getPath(root.right, node, stack);if (flag2 == true) {return true;}stack.pop();return false;}
}求树的第K层节点个数:
求树的第k层节点个数,如果不用层序遍历,我们可以使用递归。
思路:整棵树第k层多少个节点 = 左子树的第k-1层节点 + 右子树的第k-1层节点。
A的第3层 = A左树的第2层 + A右树的第2层
int CountLevel(TreeNode root, int k) {if (root == null) {return 0;}if (k == 1) {return 1;}return CountLevel(root.left, k - 1) + CountLevel(root.right, k - 1);
} 找节点:
我们要找一个节点的位置,找到返回它的地址,否则返回null。
TreeNode find(TreeNode root, char val) {if (root == null) {return null;}if (root.val = val) {return root;}TreeNode ret1 = find(root.left, val);if (ret1 != null) {return ret1;//不去右边了,因为找到了}TreeNode ret2 = find(root.right, val);if (ret2 != null) {return ret2;}return null;
}根据树的前序遍历构建一棵树:
oj链接:二叉树遍历__牛客网
class TreeNode {public char val;public TreeNode left;public TreeNode right;public TreeNode(char val) {this.val = val;}
}// 注意类名必须为 Main, 不要有任何 package xxx 信息
public class Main {public static int i = 0;public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);// 注意 hasNext 和 hasNextLine 的区别while (in.hasNextLine()) { // 注意 while 处理多个 caseString str = in.nextLine();TreeNode root = creatNode(str);inorder(root);}}public static TreeNode creatNode(String str) {//1.遍历str// for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {// char ch = str.charAt(i);// }TreeNode root = null;if (str.charAt(i) != '#') {root = new TreeNode(str.charAt(i));i++;root.left = creatNode(str);root.right = creatNode(str);} else {i++;}//2.根据字符串创建二叉树//3.返回根节点return root;}public static void inorder(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return ;}inorder(root.left);System.out.print(root.val + " ");inorder(root.right);}}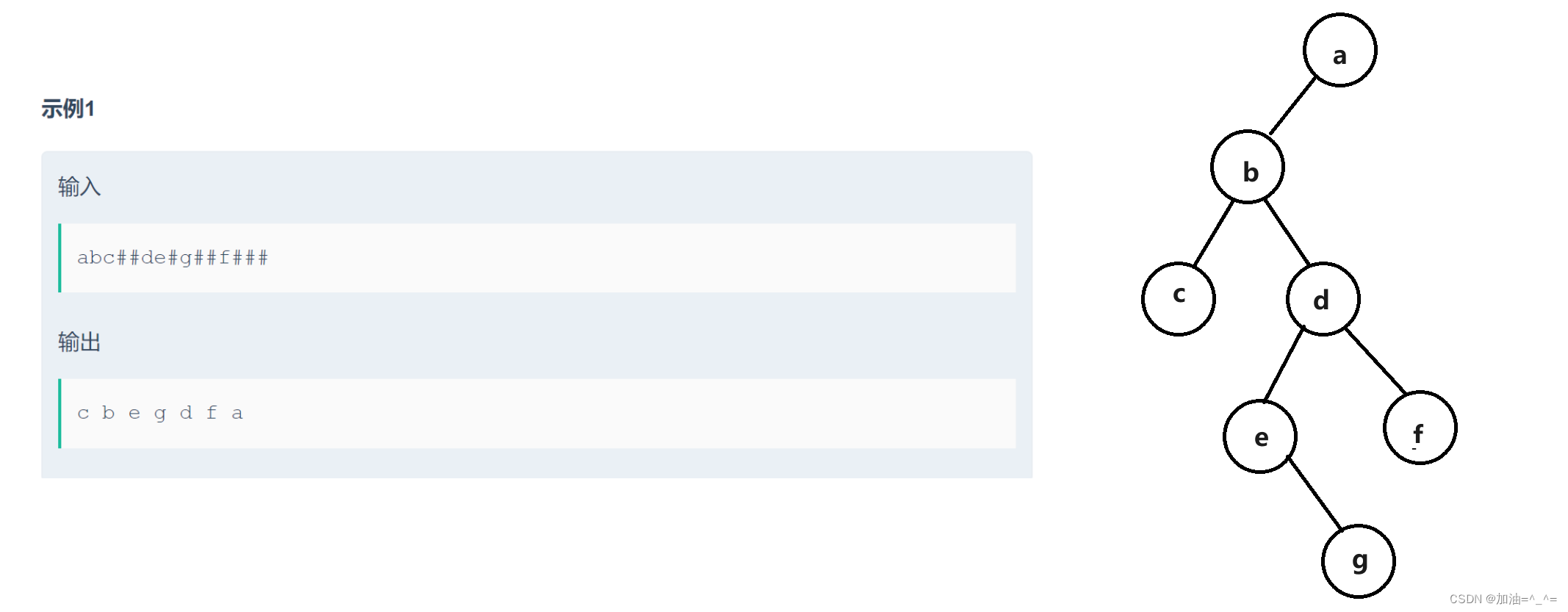
判断是否为完全二叉树:
12节(2:44)。
我们利用层序遍历,每次都把所有节点加入队列,包括null。之后遇到null就跳出,之后再判断(此时如果是完全二叉树,则队列中所有元素为null;否则则不是完全二叉树)。
boolean isCompleteTree(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return true;}Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);while (!queue.isEmpty()) {TreeNode cur = queue.poll();if (cur != null) {queue.offer(cur.left);queue.offer(cur.right);} else {break;}}//判断队列中是否有非空元素while (!queue.isEmpty()) {TreeNode cur = queue.peek();if (cur == null) {queue.poll();} else {return false;}}return true;
}这里我们使用队列的性质来完成。
层序遍历:
OJ链接:力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {//利用队列List<List<Integer>> link = new ArrayList<>();Queue<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();if (root != null) {queue.offer(root);}while(!queue.isEmpty()) {int n = queue.size();List<Integer> level = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {TreeNode node = queue.poll();level.add(node.val);if (node.left != null) {queue.add(node.left);}if (node.right != null) {queue.add(node.right);}}link.add(level);}return link;}
}根据前序遍历和中序遍历构建二叉树:
OJ链接:力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
class Solution {public int preIndex;public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {return buildTreeChild(preorder, inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1);}private TreeNode buildTreeChild(int[] preorder, int [] inorder, int inbegin, int inend) {if (inbegin > inend) {return null;}TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[preIndex]);int rootIndex = findIndexRoot(inorder, inbegin, inend, preorder[preIndex]);if (rootIndex == -1) {return null;}preIndex++;root.left = buildTreeChild(preorder, inorder, inbegin, rootIndex - 1);root.right = buildTreeChild(preorder, inorder, rootIndex + 1, inend);return root;}private int findIndexRoot(int[] inorder, int inbegin, int inend, int target) {while (inbegin <= inend) {if (inorder[inbegin] == target) {return inbegin;}inbegin++;}return -1;}
}根据中序遍历和后序遍历构建二叉树:
OJ链接:力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
class Solution {public int endIndex;public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {endIndex = postorder.length - 1;return buildTreeChild(inorder, postorder, 0, postorder.length - 1);}private TreeNode buildTreeChild(int[] inorder, int[] postorder, int begin, int end) {if (begin > end) {return null;}TreeNode root = new TreeNode(postorder[endIndex]);int rootIndex = findTreeNode(inorder, begin, end, postorder[endIndex]);if (rootIndex < 0) {return null;}endIndex--;//这里要先创建右树root.right = buildTreeChild(inorder, postorder, rootIndex + 1, end);root.left = buildTreeChild(inorder, postorder, begin, rootIndex - 1);return root;}private int findTreeNode(int[] inorder, int begin, int end, int key) {while (begin <= end) {if (inorder[begin] == key) {return begin;}begin++;}return -1;}
}前序遍历非递归:
此时我们借助栈来完成。
void preOrderNor(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return;}Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();TreeNode cur = root;while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {while (cur != null) {stack.push(cur);System.out.print(cur.val + " ");cur = cur.left;}TreeNode top = stack.pop();cur = top.right;}
}后序遍历非递归:
void postOrderNor(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return;}Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();TreeNode cur = root;while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {while (cur != null) {stack.push(cur);cur = cur.left;}TreeNode top = stack.peek();TreeNode prev = null;//方便记录if (top.right == null || top.right == prev) {System.out.print(top.val + " ");stack.pop();prev = top;} else {cur = top.right;}}
}堆(优先级队列):
堆的概念:
我们可以将数组想成一个二叉树,堆的逻辑结构是一颗完全二叉树,物理结构是一个数组。我们可以得出左右孩子和父节点的数学关系。
建立堆,可以分为两种,一种建立小堆,一种建立大堆。我们利用向下调整算法来建立堆。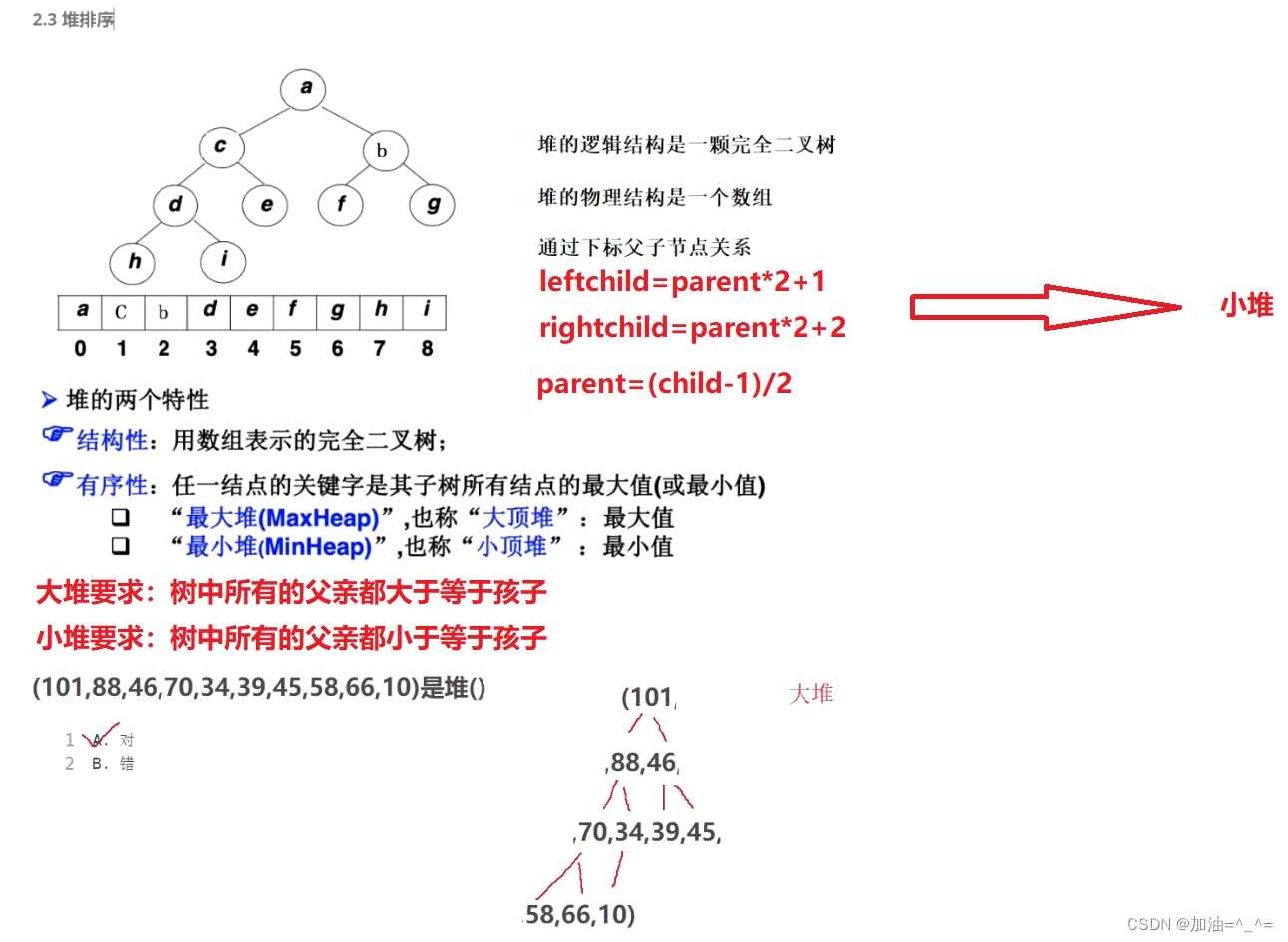
向下调整算法:
我们可以将数组想象成二叉树,但是向下调整算法必须保证左右树必须已经建好堆,所以我们从数组的最后开始建堆,也就是从最后一颗子树开始,根据公式,最后一棵树的位置(下标)就是(n - 1 - 1) / 2,之后逐个向下调整并建好堆。接下来给出该算法:
public class TestHeap {public int[] elem;public int usedSize;public TestHeap() {this.elem = new int[10];}public void initElem(int[] array) {for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {elem[i] = array[i];usedSize++;}}public void createHeap() {for (int parent = (usedSize - 1 - 1) / 2; parent >= 0; parent--) {AdjustDown(parent, usedSize);}}private void AdjustDown(int parent, int len) {int child = parent * 2 + 1;//建大堆while (child < len) {if (elem[child] < elem[child + 1] && child + 1 < len) {child++;}if (elem[parent] < elem[child]) {//交换swap(parent, child);parent = child;child = parent * 2 + 1;} else {break;}}}private void swap(int a, int b) {int tmp = elem[a];elem[a] = elem[b];elem[b] = tmp;}}优先级队列(PriorityQueue):
其实就是堆,但是我们还是要先了解一下什么是优先级队列。
优先级队列,有些情况下,操作的数据可能带有优先级,一般出队列时,可能需要优先级高的元素先出队列。此时一般的队列显然不合适。比如玩手机时,有人打来电话,系统就应该优先处理打来的电话。
这种数据结构应该提供两个最基本的操作,一个是返回最高优先级对象,一个是添加新的对象。这就被称为优先级队列,优先级队列底层是一个完全二叉树。
这里优先级队列底层是使用数组实现的,操作规则是使用队列来完成的。
不能插入null对象,可以插入任意多个元素,内部可以实现自动扩容。
当我们进行删除优先级队列元素时,需要从队列头部开始删除,如果从尾部开始删除,则相当于向上建堆,向上调整建堆时间复杂度会很大,所以我们进行头删。
public static void main(String[] args) {PriorityQueue<Integer> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();//堆priorityQueue.offer(10);priorityQueue.offer(5);priorityQueue.offer(6);System.out.println(priorityQueue.peek());//当我们实例化一个 priorityQueue 之后,默认是一个小根堆
}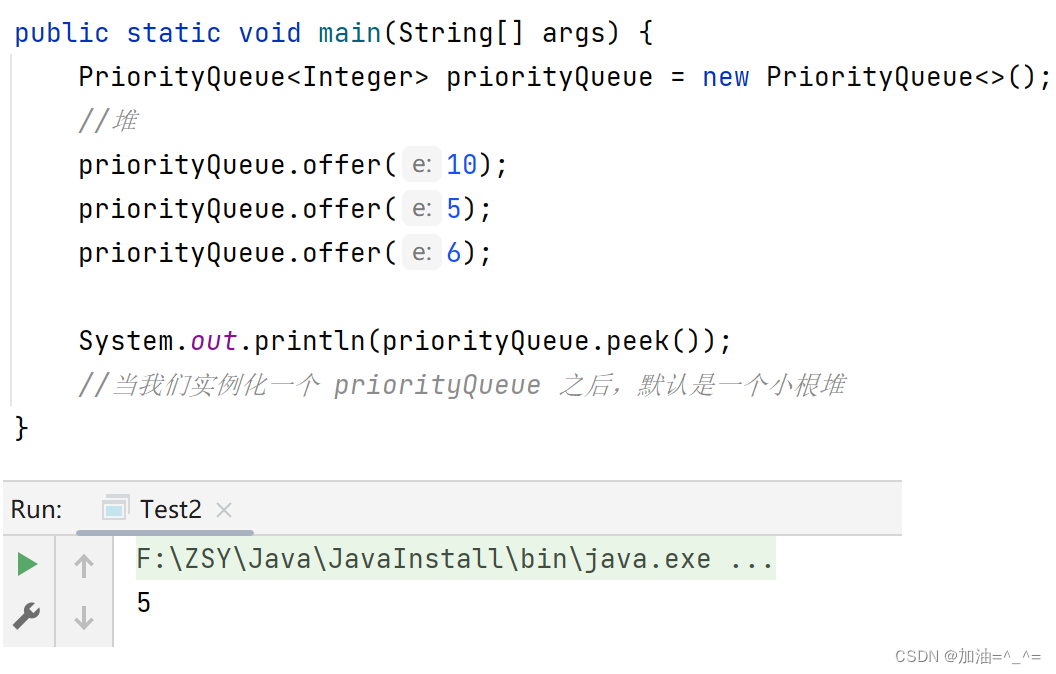
此时队头元素为5,可以发现默认是小堆。 所以我们如何将其改为大堆呢?
构建大堆(Comparable接口):
我们不能随意向其中插入数据,因为我们其实会进行比较。举个例子:
class Student {public int age;public String name;public Student(int age, String name) {this.age = age;this.name = name;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student{" +"age=" + age +", name='" + name + '\'' +'}';}
}public class Test2 {public static void main(String[] args) {PriorityQueue<Student> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();priorityQueue.offer(new Student(22, "wowo"));priorityQueue.offer(new Student(21, "wda"));}
}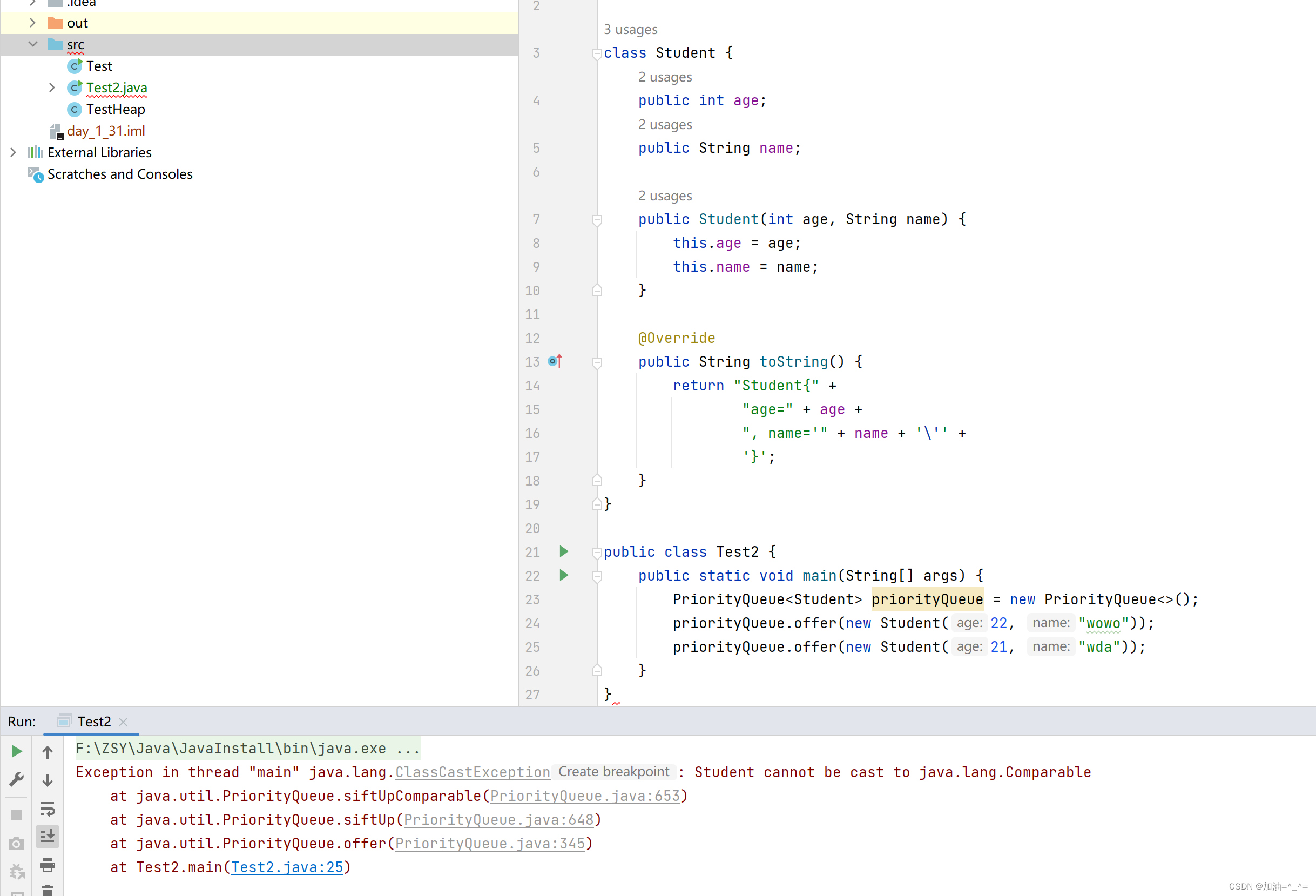
此时报错,因为没有指定类型去建堆。 所以我们其实可以想到可能其中使用了Comparable接口。
所以可以发现当我们使用无参构造器时,默认优先队列的容量是11。而且可以发现其使用了比较器。
看一看出,里面重载了构造方法,所以我们可以传入比较器来完成效果。比如此时我们是一个小堆,第一个元素是10,之后插入5: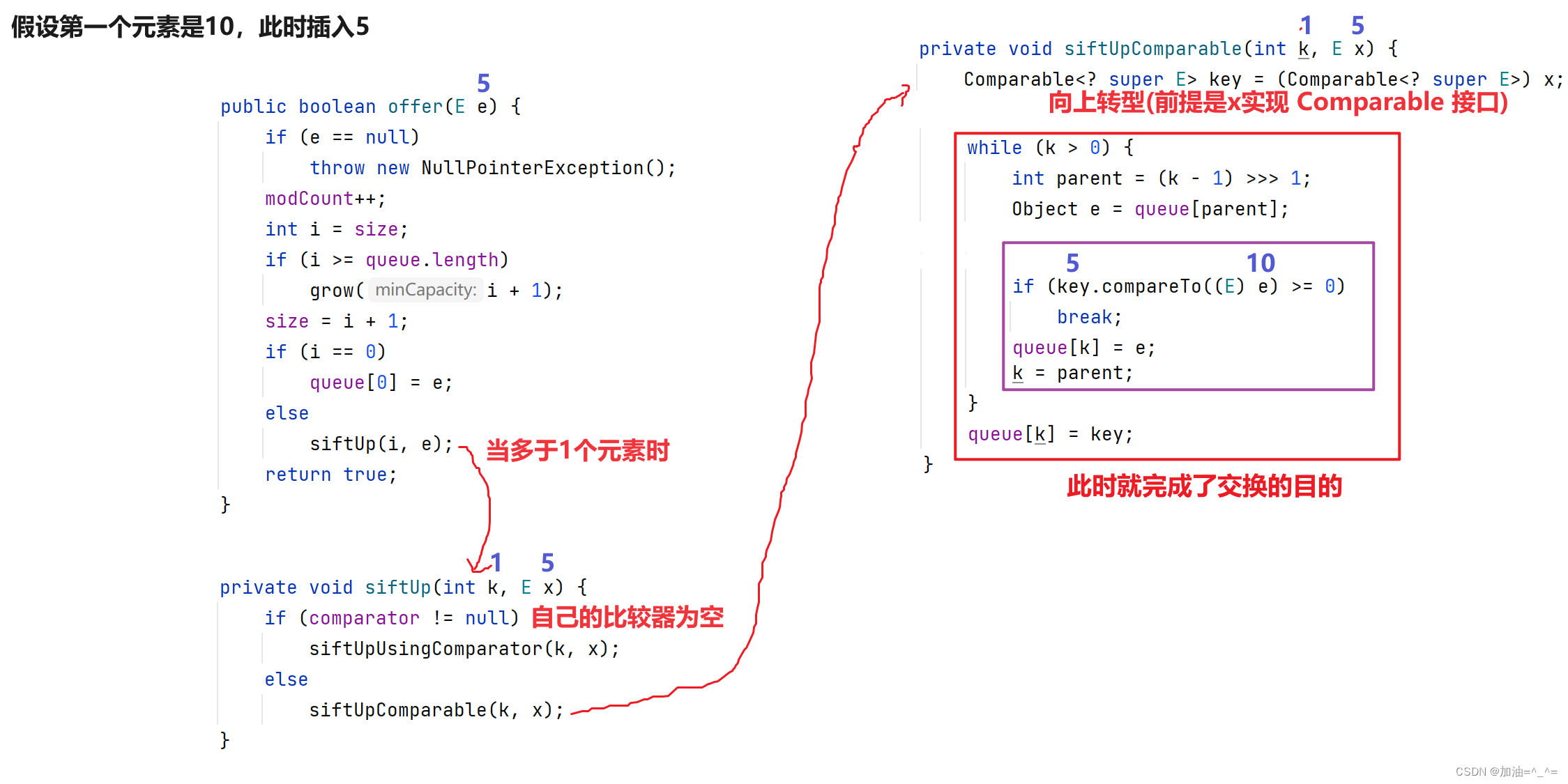
我们再观察Integer中的Comparable接口中的compareTo方法。 
也就是说,此时我们将返回值改变即可将小根堆改为大根堆。
public static void main(String[] args) {Imp imp = new Imp();PriorityQueue<Integer> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(imp);//使用自己的比较器//堆priorityQueue.offer(10);priorityQueue.offer(5);
}class Imp implements Comparator<Integer> {@Overridepublic int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {return o1.compareTo(o2);}
}所以我们可以通过自己实现的比较器来构建大根堆。
观察源码:
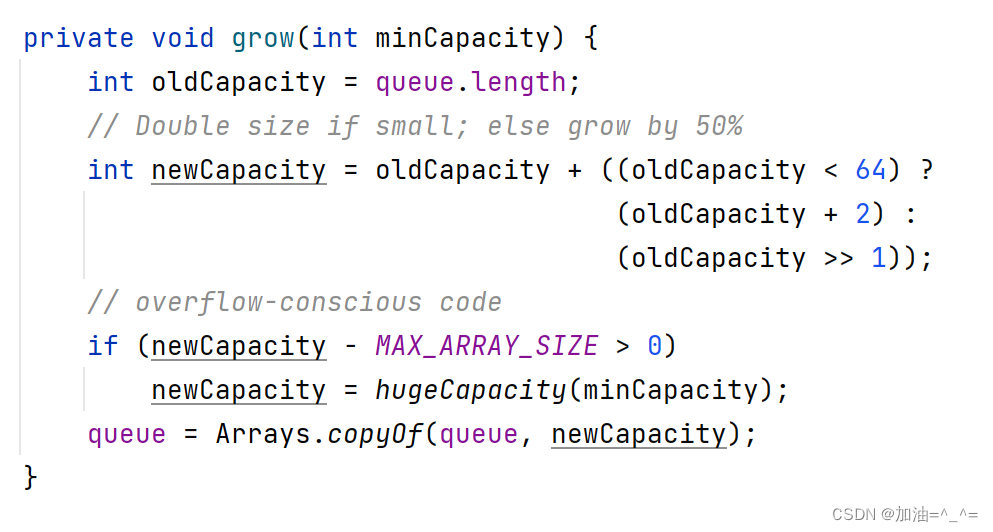
可以看到,当数组容量小于64时,每次增加2;当容量大于64时,每次扩容1.5倍。