MYSQL笔记:简单的SQL操作和select查询
文章目录
- MYSQL笔记:简单的SQL操作和select查询
- 结构化查询语句SQL
- 库操作
- 表操作
- CRUD操作
- 单表查询
- select 查询
- 例子
- 分页查询与limit
- limit 只是对结果条数有限制还是会提高查询效率?
- order by
- group by
- 多表连接查询
- 内连接查询
- 外连接
- 左连接
- 右连接
结构化查询语句SQL
SQL主要分为3个类别:
- DDL 数据库定义语义
creat drop alter - -DML 数据库操作语义
insert delete update select - DCL 数据控制语句
控制用户访问权限等:grant revoke
库操作
查看,创建,删除,选择数据库
show databases;
create database db;
drop database db;
use db;
表操作
创建表:六个约束: primary key unique not null default auto_increment
create table user(
id int unsigned primary key not null auto_increment,
name varchar(50) unique not null ,
age tinyint default '18'
)engine=INNODB default charset=utf8;
查看表结构:
desc user;
删除表:
drop table user;
查看表的创建语句:
show create table user\G;
mysql> use test;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -ADatabase changed
mysql> show table;
ERROR 1064 (42000): You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near '' at line 1
mysql> show tables;
+----------------+
| Tables_in_test |
+----------------+
| user |
+----------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> show create table user\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************Table: user
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `user` (`id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT ' 用户id',`nickname` varchar(50) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户名称',`age` tinyint(3) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT '18',`sex` enum('male','famale') DEFAULT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`id`),UNIQUE KEY `nickname` (`nickname`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
CRUD操作
insert 增加
insert into user(name,age,sex) values('a',20,'M');
mysql> insert into user(nickname,age,sex) values('a',20,'male');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.03 sec)
mysql> select * from user;
+----+----------+-----+------+
| id | nickname | age | sex |
+----+----------+-----+------+
| 1 | a | 20 | male |
+----+----------+-----+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
update 更新
update user set age=age+1;
连续插入的两种方法:

区别:
首先mysql处理的过程:
 第一种会进行5次tcp握手挥手过程。
第一种会进行5次tcp握手挥手过程。
第二次只进行1次tcp握手挥手,会更省网络资源提升性能。
联想数据库连接池项目
单表查询
select 查询
select * from user;
select name,age from user where age>=21 and sex='male';
select name,age from user where age>=21 and sex='male';
select name,age from user where age beteen 10 and 22;
select name,age from user where name like "zhang%";
between and-》包含起始和末尾
去重
distinct
空值查询
select * from user where name is null;
union 合并查询
union 默认去重不用修饰distinct。union all 表示显示所有重复值
带in的子查询
select * from user where id in (10,20);
例子
mysql> select nickname from user where nickname is not null;
+-----------+
| nickname |
+-----------+
| a |
| zhangsan |
| zhangsass |
| zhangww |
+-----------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> select nickname from user where age in (20,21);
+-----------+
| nickname |
+-----------+
| a |
| zhangsan |
| zhangsass |
| zhangww |
+-----------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> select nickname from user where age in (20);
+-----------+
| nickname |
+-----------+
| zhangsan |
| zhangsass |
| zhangww |
+-----------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> select nickname from user where age not in (20);
+----------+
| nickname |
+----------+
| a |
+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> select age from user;
+-----+
| age |
+-----+
| 21 |
| 20 |
| 20 |
| 20 |
+-----+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> select distinct age from user;
+-----+
| age |
+-----+
| 21 |
| 20 |
+-----+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> select nickname from user where age in (20) union all select sex from user where sex='male';
+-----------+
| nickname |
+-----------+
| zhangsan |
| zhangsass |
| zhangww |
| male |
| male |
| male |
| male |
+-----------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> select nickname from user where age in (20) union select sex from
user where sex='male';
+-----------+
| nickname |
+-----------+
| zhangsan |
| zhangsass |
| zhangww |
| male |
+-----------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)分页查询与limit
select id from user limit 10;
相当于limit 0,10

为了兼容postgresql
select id from user limit 1,3;
也可以写成:
select id from user limit 3 offset 1;mysql> select id from user limit 3;
+----+
| id |
+----+
| 1 |
| 2 |
| 3 |
+----+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> select id from user limit 1,3;
+----+
| id |
+----+
| 2 |
| 3 |
| 4 |
+----+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
limit 只是对结果条数有限制还是会提高查询效率?
用 explain 查看SQL的执行计划:
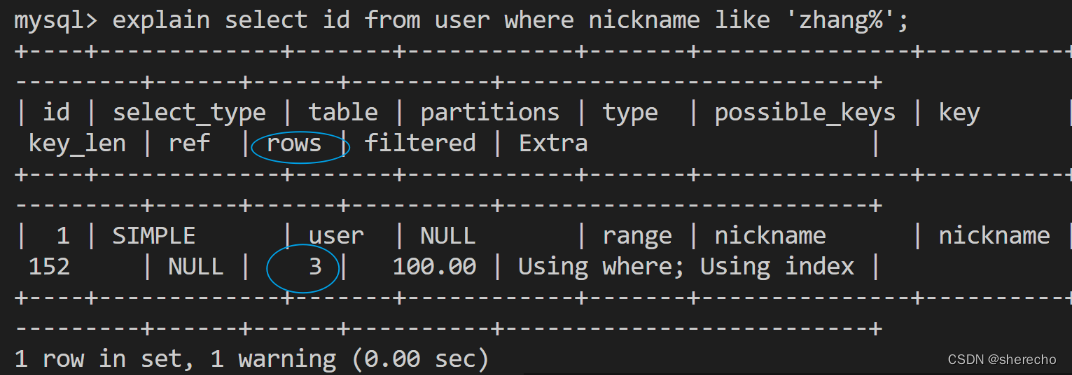
对于添加了索引的,每次扫都是直接扫1行
对于没有索引且没有limit的查找,是全表的查询
如果加了limit,就不会进行全表查询。
存储过程
create table t_user(id int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,email varchar(255) default NULL,password varchar(255) default NULL,PRIMARY KEY (id))engine =InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
delimiter $
create procedure add_t_user( IN n INT)
BEGIN
DECLARE i INT;
SET i=0;
WHILE i<n DO
INSERT INTO t_user(email,password) values(CONCAT(i+1,'@qq.com'),i+1);
SET i=i+1;
END WHILE;
END$
delimiter ;
call add_t_user(1000000);
常用聚合函数:count()
select count(*) from t_user;
分页
想设置分页怎么select:
如何降低偏移量大对性能的影响:
可以使用
select * from t_user where id>20001 limit 20;
代替
select * from t_user limit 20000,20;
因为id是有索引的,过滤会更快,是常量时间

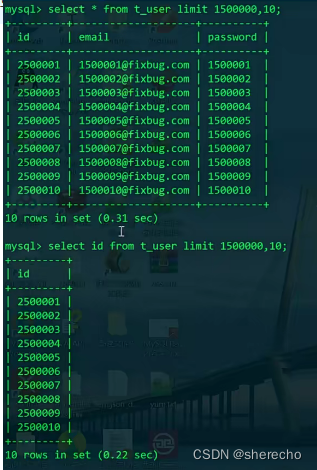
select 多与少也是影响效率的
解决方法1:
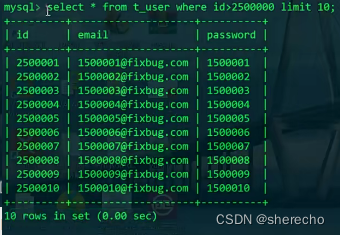
如何查询更多的类型:
解决方法2:利用内连接优化分页
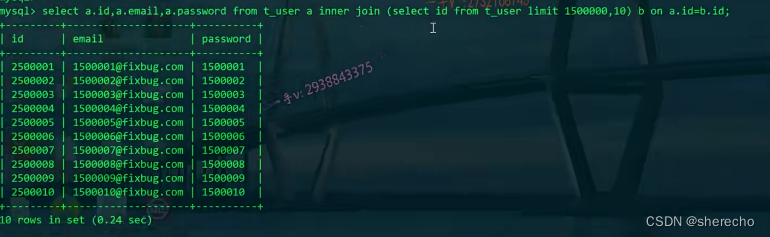
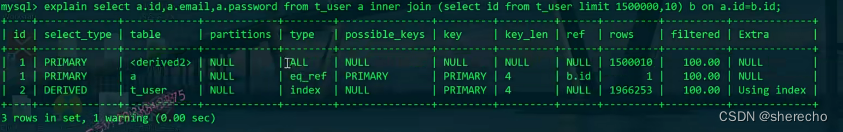
这样生成临时表是小表整表扫描
order by
select * from uer order by age ;select * order from user by age desc;
order by explain发现extra有 using filesort 外排序,放到磁盘里面是比较慢的,可以加索引变成using index可以提升效率
group by
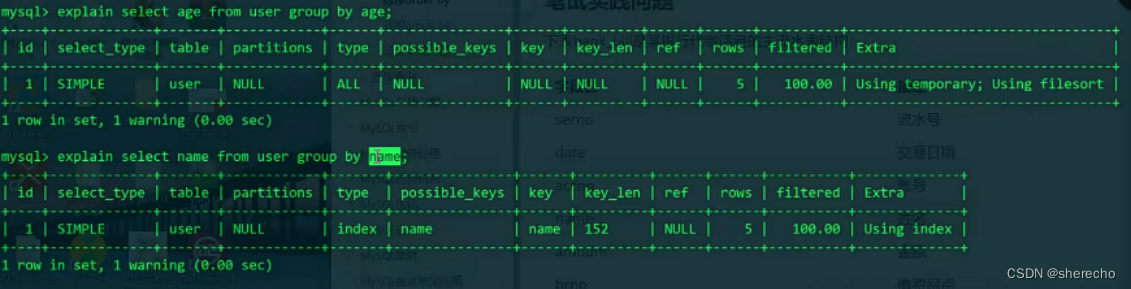
select name,age from user group by age;
上述语句将age相同的分为一组,一般是结合统计函数,distinct没有这个功能
select name,sum(age) from user group by age;
分组后过滤:
select name,sum(age) from user group by age having age>20;
先过滤在分组:
select name,sum(age) from user where age>20 group by age;
group by加索引后可以提升性能,如下图所示,age字段本身没有索引。所以一开始是group by 生成临时表以后使用的是外排序。外排序有较大的磁盘IO容易降低性能。name有索引,所以using index的排序。性能会提升。order by 和group by都是这样。
例子
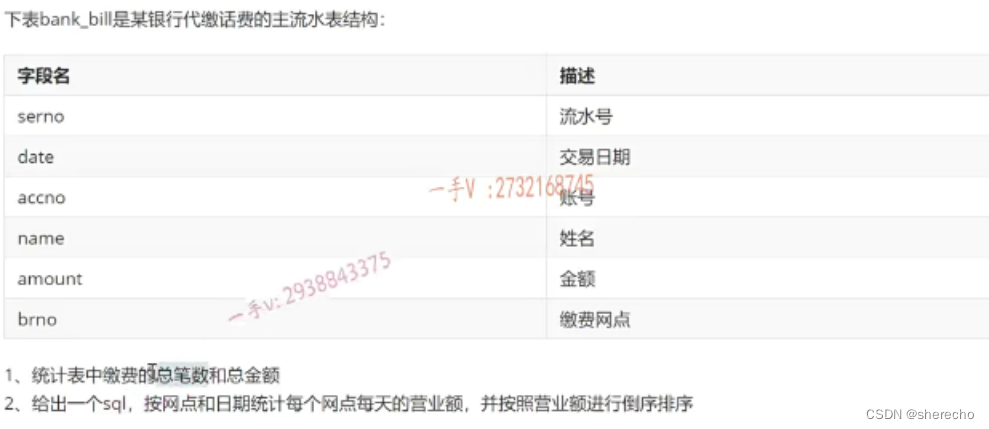
select count(serno) ,sum(amount) from bank_bill;
select brno,date,sum(amount) as money from bank_bill group by brno,date order by brno money desc;
多表连接查询
内连接查询
create table student(
uid int unsigned PRIMARY KEY not null auto_increment,
name varchar(50) not null,
age Tinyint unsigned not null,
sex enum('M','W') NOT NULL
);
create table course (
cid int unsigned PRIMARY KEY not null auto_increment,
cname varchar(50) not null,
credit TINYINT unsigned not null
);
create table exame(
uid int unsigned,
cid int unsigned not null ,
time date not null,
score float not null,
primary key (uid,cid)
);
insert into course (cname ,credit) values
('C++高级课程',5),
('操作系统',6),
('移动互联网',3),
('体系结构',5);insert into student (name ,age,sex) values
('zjam',15,'M'),
('CAOjam',18,'M'),
('lijam',25,'W'),
('wangam',25,'W'),
('kakaxijam',20,'M');
insert into exame(uid,cid,time,score) values
(1,1,'2022-04-01',99.0),
(1,2,'2022-04-02',89.0),
(1,3,'2022-04-10',90.0),
(1,4,'2022-04-15',90.0),
(2,1,'2022-04-01',99.0),
(2,2,'2022-04-02',79.0),
(2,3,'2022-04-10',95.0),
(3,1,'2022-04-01',98.0),
(3,2,'2022-04-02',59.0),
(3,3,'2022-04-10',92.0),
(3,4,'2022-04-15',60.0),
(4,1,'2022-04-01',99.0),
(4,2,'2022-04-02',79.0),
(4,3,'2022-04-10',63.0),
(4,4,'2022-04-15',94.0),
(5,1,'2022-04-01',49.0),
(5,2,'2022-04-02',69.0),
(5,3,'2022-04-10',92.0),
(5,4,'2022-04-15',97.0);
查看某人某门课的成绩:
预置条件 uid:1 cid :2
select score from exame where uid=1 and cid=2;
select uid .name,age,sex from student where uid=1 ;
合并上述两句:
首先先给表命名:
select c.score from exame c where c.uid=1 and c.cid=2;
select a.uid ,a.name,a.age,a.sex from student a where a.uid=1 ;
合并:(区分大表和小表,按照数据量区分小表永远是整表扫描,然后去大表搜索
因为小表一直都是整表搜索,所以给大表建索引才有优化效果,小表建索引没用
select a.uid ,a.name,a.age,a.sex ,c.score from student a inner join exame c on a.uid=c.uid;
+-----+-----------+-----+-----+-------+
| uid | name | age | sex | score |
+-----+-----------+-----+-----+-------+
| 1 | zjam | 15 | M | 99 |
| 1 | zjam | 15 | M | 89 |
| 1 | zjam | 15 | M | 90 |
| 1 | zjam | 15 | M | 90 |
| 2 | CAOjam | 18 | M | 99 |
| 2 | CAOjam | 18 | M | 79 |
| 2 | CAOjam | 18 | M | 95 |
| 3 | lijam | 25 | W | 98 |
| 3 | lijam | 25 | W | 59 |
| 3 | lijam | 25 | W | 92 |
| 3 | lijam | 25 | W | 60 |
| 4 | wangam | 25 | W | 99 |
| 4 | wangam | 25 | W | 79 |
| 4 | wangam | 25 | W | 63 |
| 4 | wangam | 25 | W | 94 |
| 5 | kakaxijam | 20 | M | 49 |
| 5 | kakaxijam | 20 | M | 69 |
| 5 | kakaxijam | 20 | M | 92 |
| 5 | kakaxijam | 20 | M | 97 |
+-----+-----------+-----+-----+-------+
19 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql>
上述连接语句,从小表student中取出所有的a.uid然后拿着uid去exame大表中搜索
连接三个表:
select a.uid ,a.name,a.age,a.sex,b.cid,b.cname,b.credit,c.score from exame c
inner join student a on c.uid=a.uid
inner join course b on c.cid=b.cid
where c.uid=1 and c.cid=2;+-----+------+-----+-----+-----+--------------+--------+-------+
| uid | name | age | sex | cid | cname | credit | score |
+-----+------+-----+-----+-----+--------------+--------+-------+
| 1 | zjam | 15 | M | 2 | 操作系统 | 6 | 89 |
+-----+------+-----+-----+-----+--------------+--------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)外连接
select a.*,b.* from student a inner join exame b on a.uid=b.uid;
如果加了where语句,先进行where条件的过滤
对于内连接,过滤条件写在where语句后面和写在on连接条件里面效果是一样的
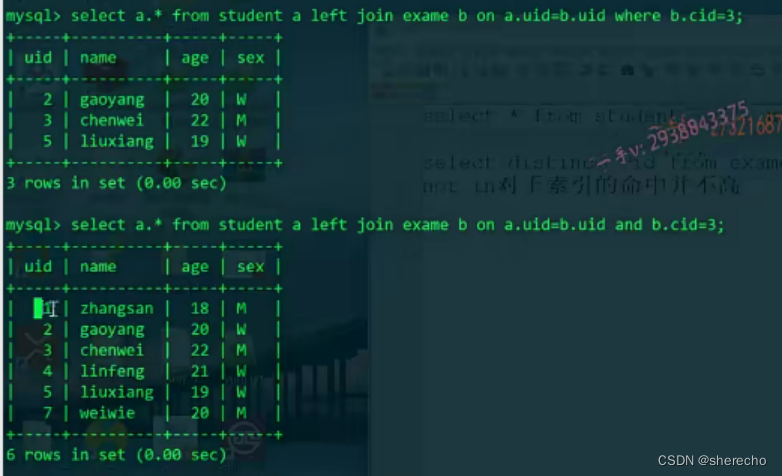
对于外连接是不同的
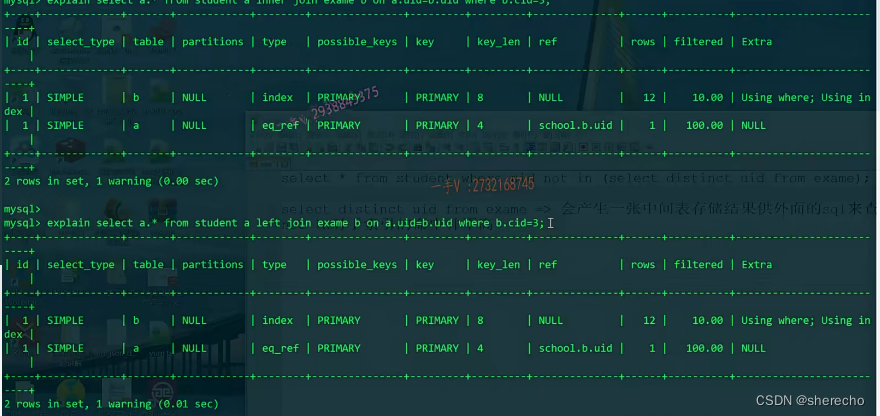
在外连接如果加了where条件,效果会变得和内连接一样,所以外连接一般过滤条件都写在on的连接条件里面
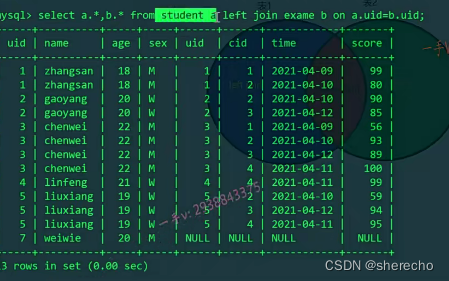
左连接
把左边的表的所有数据显示出来,若在右表中不存在相应数据,则显示NULL
右连接
把right右边的表的所有数据显示出来,若在左表中不存在相应数据,则显示NULL
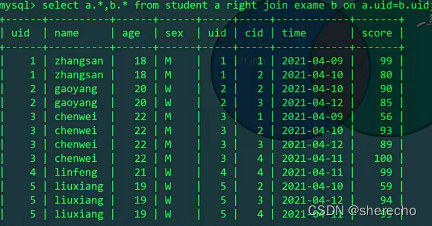
区别:
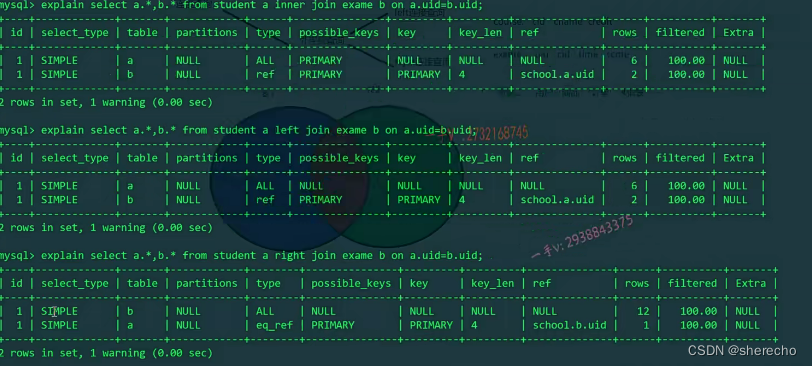
右连接先对右边的表进行整表的搜索,left连接先对左边的表进行整表搜索
小应用
如何查询那些人没有参加考试
select * from student where uid not in (select distinct uid from exame);
带in子查询的缺点:
in 可用到索引,而not in在没有sql优化的时候一般都是不能用索引的
子查询一般会产生一张中间表存储结果供外面的sql查询
用外连接实现:
select a.* from studenta a left join exame b on a.uid=b.uid where b.cid is null;