1> 将互斥机制的代码实现重新敲一遍
#include<myhead.h>
int num=520;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;//创建互斥锁
void*task1(void*arg)
{pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);sleep(3);num++;printf("%d\n",num);pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);pthread_exit(NULL);
}void*task2(void*arg)
{pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);sleep(1);num=1314;printf("%d\n",num);pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{pthread_t tid1=-1,tid2=1;pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);//初始化if(pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,task1,NULL)!=0){puts("tid1 create error");return -1;}if(pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,task2,NULL)!=0){puts("tid2 create error");return -1;}pthread_join(tid1,NULL);pthread_join(tid2,NULL);pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);return 0;
}
2> 将无名信号量的代码实现重新敲一遍
#include<myhead.h>
//创建无名信号量
sem_t sem1,sem2,sem3;
void*task1(void*arg)
{while(1){//申请资源sem_wait(&sem1);sleep(1);printf("A");fflush(stdout);sem_post(&sem2);} pthread_exit(NULL);}
void*task2(void*arg)
{while(1){sem_wait(&sem2);sleep(1);printf("B");fflush(stdout);sem_post(&sem3);}pthread_exit(NULL);}
void*task3(void*arg)
{while(1){sem_wait(&sem3);sleep(1);printf("C");fflush(stdout);sem_post(&sem1);} pthread_exit(NULL);}int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{pthread_t tid1=-1,tid2=-1,tid3=-1;//初始化无名信号量sem_init(&sem1,0,1);sem_init(&sem2,0,0);sem_init(&sem3,0,0);if(pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,task1,NULL)!=0){puts("tid1 reate error");return -1;}if(pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,task2,NULL)!=0){puts("tid2 reate error");return -1;}if(pthread_create(&tid3,NULL,task3,NULL)!=0){puts("tid3 reate error");return -1;}pthread_join(tid1,NULL);pthread_join(tid2,NULL);pthread_join(tid3,NULL);sem_destroy(&sem1);sem_destroy(&sem2);sem_destroy(&sem3);return 0;
}
3> 将条件变量的代码实现重新敲一遍
#include<myhead.h>
pthread_cond_t cond;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;//创建互斥锁
void*task1(void*arg)
{int num=5;while(num--){sleep(1);printf("%#lx的生产了一辆特斯拉\n",pthread_self());pthread_cond_signal(&cond);}pthread_exit(NULL);
}void*task2(void*arg)
{int num=5;while(num--){sleep(1);pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&mutex); printf("%#lx的消费了一辆特斯拉\n",pthread_self());pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);}pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{pthread_t tid1=-1,tid2=1,tid3=-1,tid4=-1,tid5=-1,tid6=-1;pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);//初始化pthread_cond_init(&cond,NULL);if(pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,task1,NULL)!=0){puts("tid1 create error");return -1;}if(pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,task2,NULL)!=0){puts("tid2 create error");return -1;} if(pthread_create(&tid3,NULL,task2,NULL)!=0){puts("tid3 create error");return -1;}if(pthread_create(&tid4,NULL,task2,NULL)!=0){puts("tid4 create error");return -1;}if(pthread_create(&tid5,NULL,task2,NULL)!=0){puts("tid5 create error");return -1;}if(pthread_create(&tid6,NULL,task2,NULL)!=0){puts("tid6 create error");return -1;}pthread_join(tid1,NULL);pthread_join(tid2,NULL);pthread_join(tid3,NULL);pthread_join(tid4,NULL);pthread_join(tid5,NULL);pthread_join(tid6,NULL);pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);return 0;
}
4> 将无名管道的代码实现重新敲一遍
#include<myhead.h>
void*task(void*arg)
{int pipefd[2]=*((int*)arg);close(pipefd[1]);char buf[128];while(1){bzero(buf,sizeof(buf));read(pipefd[0],buf,sizeof(buf));if(strcmp(buf,"quit")==0){break;}printf("收到:%s\n",buf);}}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{int pipefd[2]={0};if(pipe(pipefd)==-1){perror("pipe error");return -1;}pthread_t tid=-1;if(pthread_create(&tid,NULL,task,pipefd)!=0){puts("create error");return -1;}close(pipefd[0]);char buf[128];while(1){puts("请输入数据");bzero(buf,sizeof(buf));fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),stdin);buf[strlen(buf)-1]=0;write(pipefd[1],buf,strlen(buf));if(strcmp(buf,"quit")==0){break;}close(pipefd[1]);}pthread_join(&tid,NULL);return 0;
}
5> 将有名管道的代码实现重新敲一遍
p.c管道文件
#include<myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{if(mkfifo("./myfifo",0664)==-1){perror("mkfifo error");return -1;}getchar();system( "rm myfifo");return 0;
}
写端
#include<myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{int fd=-1;if((fd=open("./myfifo",O_WRONLY))==-1){perror("open error");return -1;}char buf[128];while(1){bzero(buf,sizeof(buf));printf("请输入>>>");fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),stdin);buf[strlen(buf)-1]=0;write(fd,buf,sizeof(buf));if(strcmp(buf,"quit")==0){break;}}close(fd);return 0;
}
读端
#include<myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{int fd=-1;if((fd=open("./myfifo",O_RDONLY))==-1){perror("error open");return -1;}char buf[128];while(1){bzero(buf,sizeof(buf));read(fd,buf,sizeof(buf));if(strcmp(buf,"quit")==0){break;}printf("b:%s\n",buf);}return 0;
}
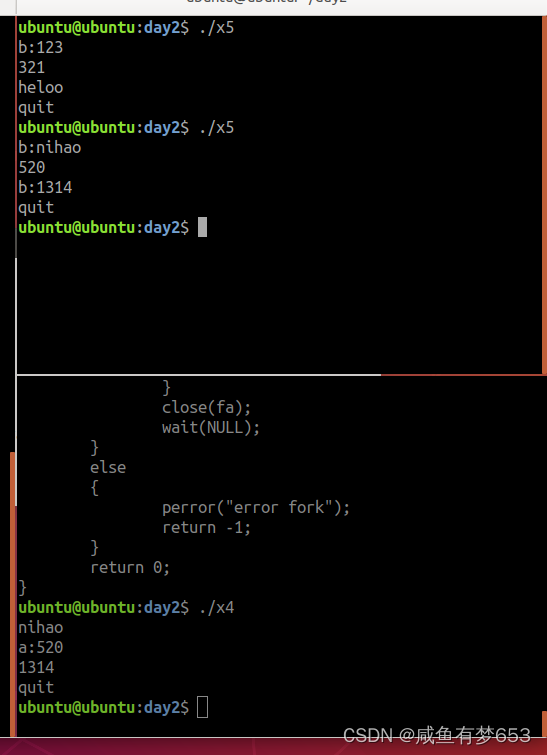
6> 使用有名管道完成两个进程的相互通信(提示:可以使用多进程或多线程完成)
管道文件
#include<myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{if(mkfifo("./myfifo",0664)==-1){perror("mkfifo error");return -1;}if(mkfifo("./myfifo1",0664)==-1){perror("mkfifo error");return -1;}getchar();system( "rm myfifo");system( "rm myfifo1");return 0;
}a:
#include<myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{pid_t pid=-1;pid=fork();if(pid==0){int fd=-1;if((fd=open("./myfifo",O_RDONLY))==-1){perror("error open");return -1;}char buf[128];while(1){bzero(buf,sizeof(buf));read(fd,buf,sizeof(buf));if(strcmp(buf,"quit")==0){break;}printf("b:%s\n",buf);}close(fd);exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);}else if(pid>0){int fa=-1;if((fa=open("./myfifo1",O_WRONLY))==-1){perror("open error");return -1;}char buf[128];while(1){bzero(buf,sizeof(buf));fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),stdin);buf[strlen(buf)-1]=0;write(fa,buf,sizeof(buf));if(strcmp(buf,"quit")==0){break;}}close(fa);}else{perror("fork error");return -1;}return 0;
}
b:
#include<myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{pid_t pid=-1;pid=fork();if(pid==0){int fd=-1;if((fd=open("./myfifo",O_WRONLY))==-1){perror("open error");return -1;}char buf[128];while(1){bzero(buf,sizeof(buf));fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),stdin);buf[strlen(buf)-1]=0;write(fd,buf,sizeof(buf));if(strcmp(buf,"quit")==0){break;}}close(fd);exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);}else if(pid>0){int fa=-1;if((fa=open("./myfifo1",O_RDONLY))==-1){perror("open error");return -1;}char buf[128];while(1){bzero(buf,sizeof(buf));read(fa,buf,sizeof(buf));if(strcmp(buf,"quit")==0){break;}printf("a:%s\n",buf);}close(fa);wait(NULL);}else{perror("error fork");return -1;}return 0;
}
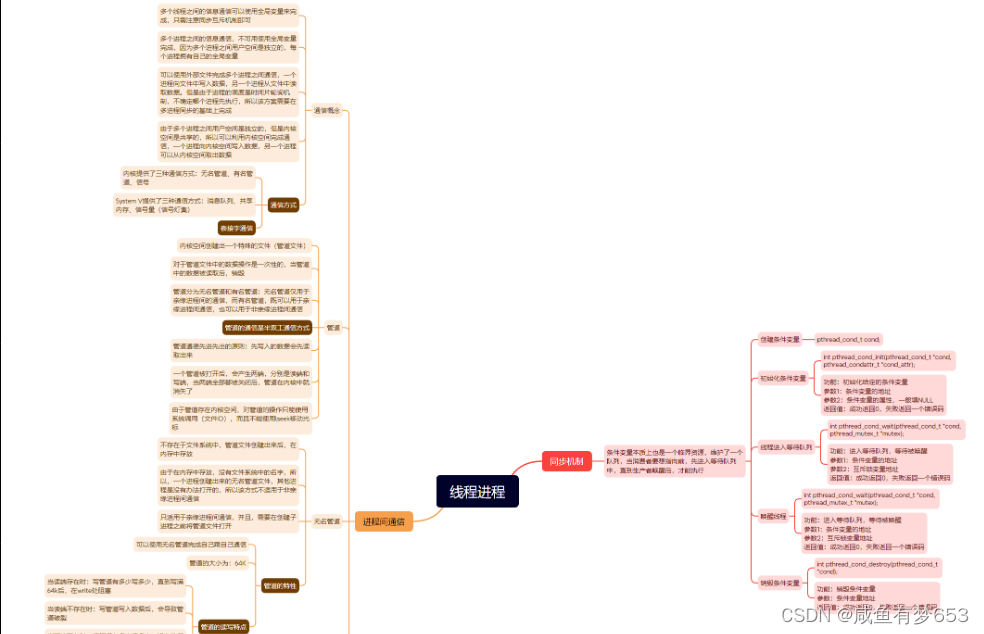
7>思维导图



![[力扣 Hot100]Day31 K 个一组翻转链表](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/2704474325d04beaab2db2da6c41d20a.png)