看着算法书看到了这一题,想着不能只看不做,就想着做了一下
算法书上的描述太抽象了,就网上找了其他的描述

当然去看英文描述是最准确的,算法书上说是哪一个oj网来着?我给忘了
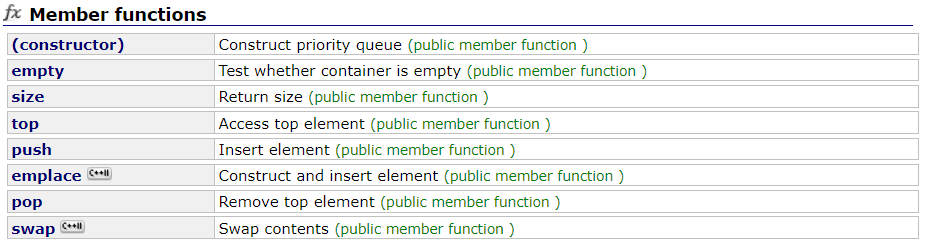
STL还是很好用的
代码如下:
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void search_num(int a, int &x, int &y);//找到a的位置
void homing(const int &x, const int &y);//第x堆,第y高的木块上方的木块归位
void move(const int &x, const int &y, const int &z);//第x堆,第y高的木块和上方的木块放在第z堆上方
vector<vector<int>> blocks;
int N;int main(void)
{cin >> N, blocks.resize(N);for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)blocks[i].push_back(i);string str1, str2;while(true){cin >> str1;if(str1 == "quit") break;int a, b, xa, ya, xb, yb;cin >> a >> str2 >> b;search_num(a, xa, ya), search_num(b, xb, yb);if(xa == xb) continue;if(str1 == "move"){homing(xa, ya);if(str2 == "onto") homing(xb, yb);blocks[xa].pop_back(), blocks[xb].push_back(a);}else{if(str2 == "onto") homing(xb, yb);move(xa, ya, xb);}}for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){cout << i << ':';for(auto it = blocks[i].begin(); it != blocks[i].end(); it++)cout << ' ' << *it;cout << endl;}return 0;
}
void search_num(int a, int &x, int &y)
{for(x = 0; x < N; x++)for(y = 0; y < blocks[x].size(); y++)if(blocks[x][y] == a)return;return;
}
void homing(const int &x, const int &y)
{int n_tmp = y;while(++n_tmp < blocks[x].size())blocks[blocks[x][n_tmp]].push_back(n_tmp);blocks[x].resize(y + 1);return;
}
void move(const int &x, const int &y, const int &z)//第x堆,第y高的木块和上方的木块放在第z堆上方
{int n_tmp = y - 1;while(++n_tmp < blocks[x].size())blocks[z].push_back(blocks[x][n_tmp]);blocks[x].resize(y);return;
}
![[ai笔记12] chatGPT技术体系梳理+本质探寻](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/cbf42387b2df0c76b16b4f7ac2416fa0.png)