前言
- 今天要刷的是图论,还没学过,先看看《代码随想录》这部分的基础
深搜DFS理论基础
-
深搜三部曲
- 确认递归函数、参数
- 确认终止条件
- 处理目前搜索节点出发的路径
-
代码框架
-
void dfs(参数) {if (终止条件) {存放结果;return;}for (选择:本节点所连接的其他节点) {处理节点;dfs(图,选择的节点); // 递归回溯,撤销处理结果} }
-
797. 所有可能的路径 - 力扣(LeetCode)
-
DFS
-
class Solution:def allPathsSourceTarget(self, graph: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:res = [] # 存放结果path = [0] # 当前路径def dfs(root: int):if root == len(graph) - 1: # 如果到达最后节点存入结果,res.append(path[:]) # path[:]避免使用引用,deep copyreturnfor node in graph[root]: # 遍历root所有节点path.append(node) # path加上当前遍历节点dfs(node) # 下一层继续搜索path.pop() # 回溯,撤销节点dfs(0)return res
-
广搜BFS理论基础
- 适用于解决两个点之间的最短路径问题
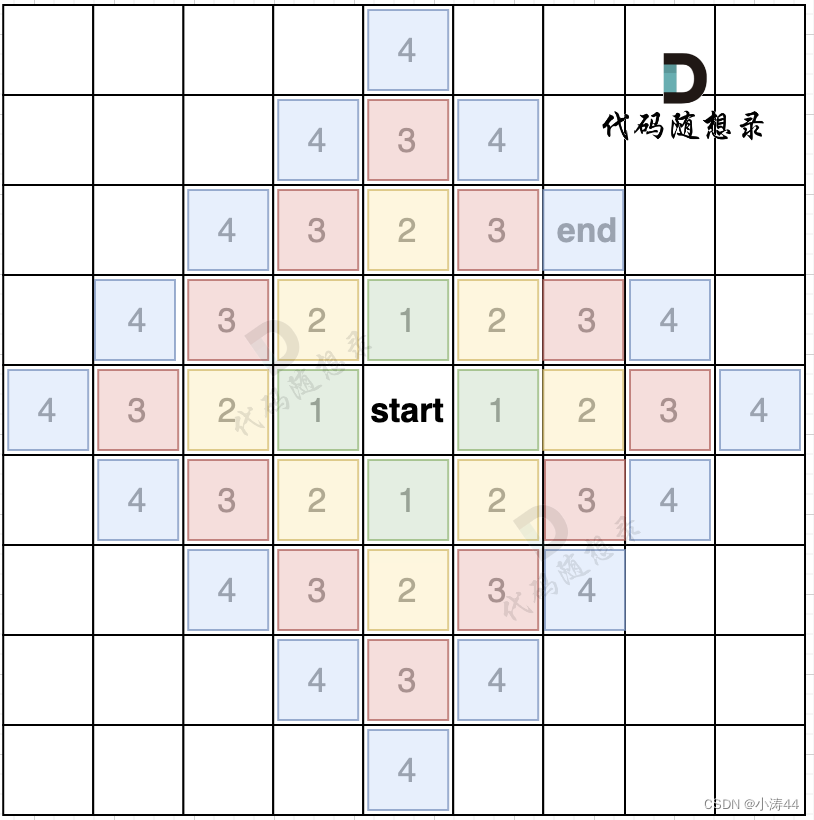
-
from collections import deque dir = [(0, 1), (1, 0), (-1, 0), (0, -1)] # 创建方向元素def bfs(grid, visited, x, y):queue = deque() # 初始化队列queue.append((x, y)) # 放入第一个元素/起点visited[x][y] = True # 标记为访问过的节点while queue: # 遍历队列里的元素curx, cury = queue.popleft() # 取出第一个元素for dx, dy in dir: # 遍历四个方向nextx, nexty = curx + dx, cury + dyif nextx < 0 or nextx >= len(grid) or nexty < 0 or nexty >= len(grid[0]): continue # 越界了,直接跳过if not visited[nextx][nexty]: # 如果节点没被访问过 queue.append((nextx, nexty)) # 加入队列visited[nextx][nexty] = True # 标记为访问过的节点
200. 岛屿数量 - 力扣(LeetCode)
-
DFS
-
class Solution:def numIslands(self, grid: List[List[str]]) -> int:m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])# visited = [[False] * n for _ in range(m)] # 如果不能修改用标记grid# 深搜当前陆地部分def dfs(x, y): # x表示行,y表示列grid[x][y] = "0" # 遍历到的节点就置为0以防重复,用visited则删除此句for nx, ny in [(x-1,y), (x+1,y), (x,y-1), (x,y+1)]:if 0 <= nx < m and 0 <= ny < n and grid[nx][ny] == "1":# if 0 <= nx < m and 0 <= ny < n and grid[nx][ny] == "1" and not visited[nx][ny]:# visited[nx][ny] = Truedfs(nx,ny)# 依次遍历每个节点搜索大陆res = 0for i in range(m):for j in range(n):if grid[i][j] == "1":# if not visited[i][j] and grid[i][j] == '1':# visited[i][j] = Trueres += 1 # 遇到没访问过的陆地,+1dfs(i, j)# 返回总陆地数return res
-
-
BFS
-
class Solution:def numIslands(self, grid: List[List[str]]) -> int:m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])# visited = [[False] * n for _ in range(m)] # 如果不能修改用visited标记grid中已访问节点# 广搜当前陆地部分def bfs(x, y): # x表示行,y表示列q = deque()q.append((x,y))grid[x][y] = "0" # 遍历到的节点就置为0以防重复,用visited则删除此句# visited[x][y] = True # 用visitedwhile q:x0, y0 = q.popleft() # 当前遍历节点加入队列for nx, ny in [(x0-1,y0), (x0+1,y0), (x0,y0-1), (x0,y0+1)]:if 0 <= nx < m and 0 <= ny < n and grid[nx][ny] == "1": # 用visited则删除此句# if 0 <= nx < m and 0 <= ny < n and grid[nx][ny] == "1" and not visited[nx][ny]:q.append((nx, ny))grid[nx][ny] = "0" # 加入列表就标记为访问过,用visited则删除此句# visited[nx][ny] = True # 用visited # 依次遍历每个节点搜索大陆res = 0for i in range(m):for j in range(n):if grid[i][j] == "1":# if not visited[i][j] and grid[i][j] == '1':res += 1 # 遇到没访问过的陆地,+1bfs(i, j)# 返回总陆地数return res
-
-
并查集
- 没接触过并查集,依据这道题在B站大学找了相关视频和文章学习一下
-
## 解法三:UnionFind 并查集经典解法 class UnionFind: ## 定义为一个类。后面类似的题目,也可以直接搬去使用def __init__(self, grid): ## 初始化m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])self.count = 0 ## count 是最终结果,初始化为0self.parent = [-1] * (m * n) ## 初始化 parent 数组取值全部为 -1## rank 秩,表示树的高度,在连接的时候要规定秩小的指向秩大的元素self.rank = [0] * (m * n) ## rank 用来实现上下左右的合并;初始化全部为 0 ## 计算陆地的总数 count;修改 parent 数组陆地元素的取值for i in range(m):for j in range(n):if grid[i][j] == "1": ## 对于陆地元素,把它的parent初始化为它的一维化的位置self.parent[i * n + j] = i * n + j ## parent初始化为元素本身的一维化的(位置)索引self.count += 1 ## 陆地总数## find 方法给union 方法调用def find(self, i):if self.parent[i] != i: ## 对于索引不等于自身的元素self.parent[i] = self.find(self.parent[i]) ## 路径优化。把所有链式关系,简化为一层的父子关系return self.parent[i] ## 返回父亲的索引(也等于该索引对应的取值)## 最关键是 union 方法,用来处理目标元素并计算岛屿数量def union(self, x, y):rootx = self.find(x) ## 找到自己的 root 索引rooty = self.find(y) ## 找到自己的 root 索引if rootx != rooty: ## 如果不等,则进行合并if self.rank[rootx] <= self.rank[rooty]: ## 如果 rank 更小self.parent[rootx] = rooty ## 秩小的指向秩大的元素else:self.parent[rooty] = rootx ## 秩小的指向秩大的元素if self.rank[rootx] == self.rank[rooty]: ## 如果秩相等self.rank[rootx] += 1 ## 如果深度相同,新节点的 rank + 1self.count -= 1 ## 合并一次,则陆地数量减一(岛屿数量=陆地数量-总的合并次数)## 主类 + 主函数 class Solution:def numIslands(self, grid: List[List[str]]) -> int: ## 主函数nr = len(grid) ## number of rowif nr == 0:return 0nc = len(grid[0]) ## number of columnuf = UnionFind(grid) ## 调用并查集函数## 遍历每一个位置for r in range(nr):for c in range(nc):if grid[r][c] == "1": ## 碰到陆地 1grid[r][c] = "0" ## 先修改为 0for x, y in [(r - 1, c), (r + 1, c), (r, c - 1), (r, c + 1)]: ## 遍历上下左右if 0 <= x < nr and 0 <= y < nc and grid[x][y] == "1": ## 碰到新的 1uf.union(r * nc + c, x * nc + y) ## 调用并查集函数return uf.count
后言
- 并查集这个学得我好累,这就是缺乏基础吧,路漫漫啊