组合总和
39. 组合总和 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给你一个 无重复元素 的整数数组 candidates 和一个目标整数 target ,找出 candidates 中可以使数字和为目标数 target 的 所有 不同组合 ,并以列表形式返回。你可以按 任意顺序 返回这些组合。
candidates 中的 同一个 数字可以 无限制重复被选取 。如果至少一个数字的被选数量不同,则两种组合是不同的。
对于给定的输入,保证和为 target 的不同组合数少于 150 个。
示例 1:
输入:candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7
输出:[[2,2,3],[7]]
解释:
2 和 3 可以形成一组候选,2 + 2 + 3 = 7 。注意 2 可以使用多次。
7 也是一个候选, 7 = 7 。
仅有这两种组合。
提示:
1 <= candidates.length <= 302 <= candidates[i] <= 40candidates的所有元素 互不相同1 <= target <= 40
解
数字组合问题:递归纵向遍历,横向 for 遍历

List<List<Integer>> combinations = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayDeque<Integer> path = new ArrayDeque<>();public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target)
{dfs(candidates, target, 0);return combinations;
}public void dfs(int[] candidates, int target, int startIndex)
{//组合的和大于 targetif (target < 0)return;//组合的和等于 targetif (target == 0){combinations.add(new ArrayList<>(path));return;}//纵向递归,横向遍历for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length; i++){if (candidates[i] <= target){path.addLast(candidates[i]);dfs(candidates, target - candidates[i], i); //candidates[i]可以重复使用,所以 startIndex 还是 i 。path.removeLast(); //回溯}}
}
分割回文串
131. 分割回文串 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给你一个字符串 s,请你将 s 分割成一些子串,使每个子串都是 回文串 。返回 s 所有可能的分割方案。
回文串 是正着读和反着读都一样的字符串。
示例 1:
输入:s = "aab"
输出:[["a","a","b"],["aa","b"]]
解
参考题解:131. 分割回文串 - 力扣(LeetCode)
List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> path = new ArrayList<>();
String s;public List<List<String>> partition(String s)
{this.s = s; //将题目输入的字符串变为全局变量dfs(0);return res;
}/*** @param startIndex 子串的起始索引 */
public void dfs(int startIndex)
{//当子串的起始索引超出范围时,说明分割结束。记录此次分割方案if(startIndex == s.length()){res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));return;}//递归更新起始点,for循环延伸子串//起始点的更新优先于子串的延伸for (int i = startIndex; i < s.length(); i++){if (isPalindrome(startIndex, i)){//记录一个回文子串。从startIndex(包括)提取子字符串,直到i + 1(不包括)path.add(s.substring(startIndex, i + 1));//以下一个字符为新的起始点dfs(i +1);//恢复现场,接下来以startIndex为起始,延长一下子串再试试path.remove(path.size() - 1);}}
}/*** @param left 子串的起始索引* @param right 子串的末尾索引*/
public boolean isPalindrome(int left, int right)
{while (left < right){if (s.charAt(left) != s.charAt(right))return false;left++;right--;}return true;
}
时间复杂度:O(n * n ^ 2)。O(n)为判断回文串的开销,O(n ^ 2)为枚举所有子串的开销(一个集合的所有子集个数)。
空间复杂度:O(n)。
子集
78. 子集 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给你一个整数数组 nums ,数组中的元素 互不相同 。返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
解集 不能 包含重复的子集。你可以按 任意顺序 返回解集。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,3]
输出:[[],[1],[2],[1,2],[3],[1,3],[2,3],[1,2,3]]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0]
输出:[[],[0]]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 10-10 <= nums[i] <= 10nums中的所有元素 互不相同
解
与上一题略有不同
List<List<Integer>> subsetList = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> subset = new ArrayList<>();
int[] nums;public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums)
{this.nums = nums;dfs(0);return subsetList;
}public void dfs(int startIndex)
{//收集每一个子集subsetList.add(new ArrayList<>(subset));if (startIndex > nums.length - 1)return;//for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++){subset.add(nums[i]);dfs(i + 1);subset.remove(subset.size() - 1);}
}
全排列
46. 全排列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个不含重复数字的数组 nums ,返回其 所有可能的全排列 。你可以 按任意顺序 返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,3]
输出:[[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 6-10 <= nums[i] <= 10nums中的所有整数 互不相同
解
全排列中,[1,2]和[2,1]是不同的,所以不能用startIndex,而是改用used数组来标记已经选择过的元素,回溯时一并撤销。

List<List<Integer>> permutationList = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> permutation = new ArrayList<>();
int[] nums;
boolean[] used;public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums)
{this.nums = nums;used = new boolean[nums.length];backTracing();return permutationList;
}public void backTracing()
{if (permutation.size() == nums.length){permutationList.add(new ArrayList<>(permutation));return;}for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){if (used[i] == false){used[i] = true;permutation.add(nums[i]);backTracing();permutation.remove(permutation.size() - 1);used[i] = false;}}
}
字母大小写全排列
784. 字母大小写全排列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个字符串 s ,通过将字符串 s 中的每个字母转变大小写,我们可以获得一个新的字符串。
返回 所有可能得到的字符串集合 。以 任意顺序 返回输出。
示例 1:
输入:s = "a1b2"
输出:["a1b2", "a1B2", "A1b2", "A1B2"]
示例 2:
输入: s = "3z4"
输出: ["3z4","3Z4"]
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 12s由小写英文字母、大写英文字母和数字组成
思路
这一类搜索问题是在一个隐式的树上进行的搜索问题,即「树形问题」。解决这一类问题, 先画出递归树是十分重要的,可以帮助打开思路 ,然后看着图形把代码写出来。






如何便捷地转换大小写
让我们看看当一个字符的ASCII码值与32(二进制中的00100000)进行异或操作时会发生什么:
-
对于小写字符,其ASCII码值比对应的大写字符的值大32。当我们用小写字符的ASCII码值与32进行异或操作时,第五位(从右向左数,起始位为第零位)会翻转,因为32的二进制表示中只有第五位是1。这样,我们就得到了对应的大写字符的ASCII码值。
例如,小写的’a’的ASCII码值是97,其二进制表示为
01100001。与32(00100000)异或后得到01000001,即大写的’A’的ASCII码值。 -
对于大写字符,其ASCII码值比对应的小写字符的值小32。当我们用大写字符的ASCII码值与32进行异或操作时,同样地,第五位会翻转,我们就得到了对应的小写字符的ASCII码值。
例如,大写的’A’的ASCII码值是65,其二进制表示为
01000001。与32(00100000)异或后得到01100001,即小写的’a’的ASCII码值。
因此,无论是大写字符还是小写字符,与32进行异或操作都会导致第五位翻转,从而实现大小写之间的转换。
代码实现
List<String> stringList = new ArrayList<>();
char[] charArr;public List<String> letterCasePermutation(String s)
{charArr = s.toCharArray();backTracing(0);return stringList;
}public void backTracing(int pos)
{//排除数字的干扰while (pos < charArr.length && Character.isDigit(charArr[pos]))pos++;//记录一种字母大小写全排列if (pos == charArr.length){stringList.add(new String(charArr));return;}charArr[pos] ^= 32; //大小写转换backTracing(pos + 1);charArr[pos] ^= 32; //换回来,又是一种字母大小写全排列backTracing(pos + 1); //在换回来的情况下继续探索
}
单词搜索
79. 单词搜索 - 力扣(LeetCode)
给定一个 m x n 二维字符网格 board 和一个字符串单词 word 。如果 word 存在于网格中,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
单词必须按照字母顺序,通过相邻的单元格内的字母构成,其中“相邻”单元格是那些水平相邻或垂直相邻的单元格。同一个单元格内的字母不允许被重复使用。
示例 1:
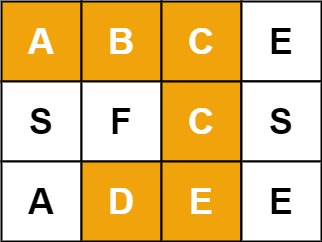
输入:board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCCED"
输出:true
示例 2:
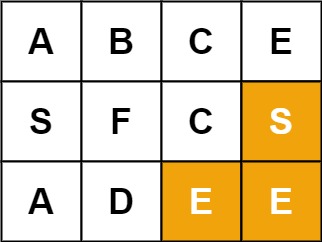
输入:board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "SEE"
输出:true
示例 3:
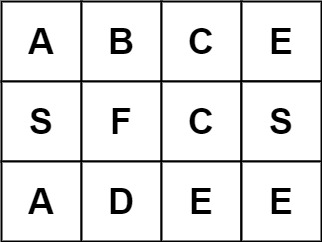
输入:board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCB"
输出:false
提示:
m == board.lengthn = board[i].length1 <= m, n <= 61 <= word.length <= 15board和word仅由大小写英文字母组成
解
char[][] board;
String word;public boolean exist(char[][] board, String word)
{this.board = board;this.word = word;int charIndex = 0; // word 中字符的索引//依次选择起始点开始深搜for (int row = 0; row < board.length; row++)for (int col = 0; col < board[row].length; col++)if (dfs(row, col, charIndex))return true;return false;
}public boolean dfs(int row, int col, int charIndex)
{//超出网格的范围,或当前网格的单词与 word 中 charIndex 位置的字符不同,返回搜索结果 falseif (row < 0 || row > board.length - 1 || col < 0 || col > board[0].length - 1|| board[row][col] != word.charAt(charIndex) )return false;//在网格中确认存在 word 后,返回搜索结果 true 。之后向上传递搜索结果的过程不会再用到这条语句if (charIndex == word.length() - 1)return true;//将当前网格单元标记为已访问(同一个单元格内的字母不允许被重复使用。)board[row][col] = ' ';//顺时针探索。//由于 || 的性质,只要某个方向的探索结果为 true,res 便会被赋值为 true,后面的 dfs 便不会再执行,大大提高了效率boolean res = dfs(row - 1, col, charIndex + 1)|| dfs(row, col + 1, charIndex + 1)|| dfs(row + 1, col, charIndex + 1)|| dfs(row, col - 1, charIndex + 1);//从这个网格单元开始的所有路径都走过了,该向上传递搜索结果了//向上传递搜索结果前,需要将这个网格单元恢复,使上层的 dfs 能以新的起点或从新的方向重新探索board[row][col] = word.charAt(charIndex);return res;
}