简介
PyInstaller 是一个用于将 Python 程序打包成可执行文件(可执行程序)的工具。它能够将 Python 代码和其相关的依赖项(包括 Python 解释器、依赖的模块、库文件等)打包成一个独立的可执行文件,方便在不同环境中运行,而无需安装 Python 环境和相关依赖。
使用 PyInstaller,你可以将 Python 程序打包成 Windows 的可执行文件(.exe)、Mac OS 的应用程序(.app)以及 Linux 下的可执行文件。打包后的可执行文件可以在原始操作系统之外的其他操作系统上运行(如将 Windows 上的 Python 程序打包成 Mac OS 或 Linux 下的可执行文件)。
问题
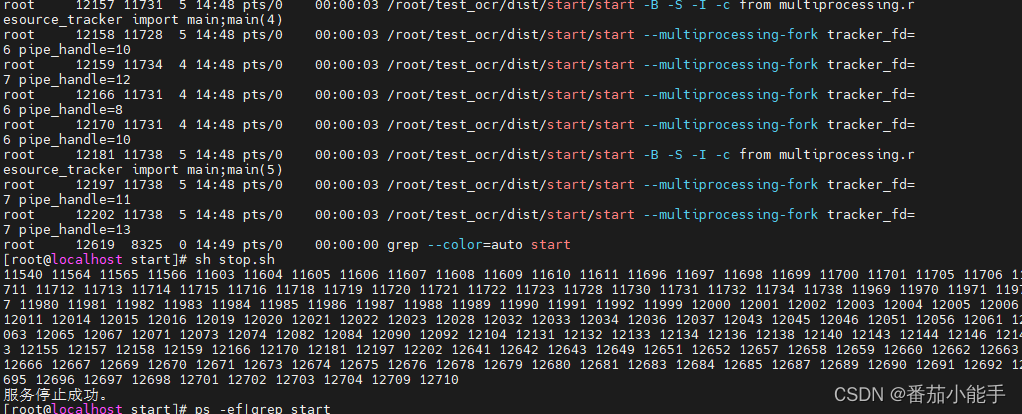
在编写python程序的时候,或多或少会用到多进程,但是使用多进程后,再使用pyinstaller打包我们的程序后,代码会陷入死循环。如Windows中,运行exe时,程序出现多个窗口,关闭以后又出现新的窗口。linux系统中,可以看到启动非常多的进程,如下图:
解决方案
在你的主程序前添加一行代码:
import multiprocessingif __name__=='__main__':# 在此处添加multiprocessing.freeze_support()# 这里是你的代码# ......
有关更多信息,请阅读有关multiprocessing.freeze_support的 Python 库手册。
PyInstaller < 3.3 和 Windows 的其他代码
从 PyInstaller 3.3 开始。添加此代码不再是必需的,它已经由运行时钩子添加。
在 Windows 上,使用 --onefile 可执行文件时,多处理代码失败。此问题特定于 Windows,它不支持 。使用默认 (--onedir) 模式时不会发生这种情况,也不会发生在其他 (Posix) 平台(如所有 Unix 和 Mac OS X 版本)上。spawn()
要在 Windows 上使用 python 模块,您需要扩展多处理代码,如下所示。有关详细信息,请参阅有关背景和票证 https://github.com/pyinstaller/pyinstaller/issues/182 的此主题。_multiprocess_
此配方需要 PyInstaller 3.0 < 3.3。
import os
import sys# Module multiprocessing is organized differently in Python 3.4+
try:# Python 3.4+if sys.platform.startswith('win'):import multiprocessing.popen_spawn_win32 as forkingelse:import multiprocessing.popen_fork as forking
except ImportError:import multiprocessing.forking as forkingif sys.platform.startswith('win'):# First define a modified version of Popen.class _Popen(forking.Popen):def __init__(self, *args, **kw):if hasattr(sys, 'frozen'):# We have to set original _MEIPASS2 value from sys._MEIPASS# to get --onefile mode working.os.putenv('_MEIPASS2', sys._MEIPASS)try:super(_Popen, self).__init__(*args, **kw)finally:if hasattr(sys, 'frozen'):# On some platforms (e.g. AIX) 'os.unsetenv()' is not# available. In those cases we cannot delete the variable# but only set it to the empty string. The bootloader# can handle this case.if hasattr(os, 'unsetenv'):os.unsetenv('_MEIPASS2')else:os.putenv('_MEIPASS2', '')# Second override 'Popen' class with our modified version.forking.Popen = _Popen测试多处理示例:
import multiprocessingclass SendeventProcess(multiprocessing.Process):def __init__(self, resultQueue):self.resultQueue = resultQueuemultiprocessing.Process.__init__(self)self.start()def run(self):print 'SendeventProcess'self.resultQueue.put((1, 2))print 'SendeventProcess'if __name__ == '__main__':# On Windows calling this function is necessary.# On Linux/OSX it does nothing.multiprocessing.freeze_support()print 'main'resultQueue = multiprocessing.Queue()SendeventProcess(resultQueue)print 'main'此代码片段的控制台输出应类似于
main
main
SendeventProcess
SendeventProcess