前言:
最近的开发中遇到了寻路这个知识点,然后去了解了一下最常见的A算法,本会会结合我的理解,用最通俗易懂的话语讲解A算法的原理,下面会给出代码示例。
说到寻路算法,就涉及到了图的遍历,然后又分为深度优先和广度优先等等,这些知识点大家随便一搜就能查到,为了方便这里给个链接,里面有介绍算法的发展史。
在A出来之前,遍历算法要不就是效率不高,要不就是不是最优路径,A的出现,是结合了前面的有点,所以说A*只是相对来说效率很高的一种算法。
A*算法
A*算法通过下面这个函数来计算每个节点的优先级。
算法表示:
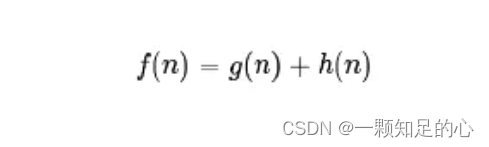
其中:
- f(n)是节点n的综合优先级。当我们选择下一个要遍历的节点时,我们总会选取综合优先级最高(值最小)的节点。
- g(n) 是节点n距离起点的代价。本文中,会以父子节点距离相加来算距离起点的距离。
- h(n)是节点n距离终点的预计代价,这也就是A*算法的启发函数。关于启发函数我们在下面详细讲解。
一句话来解释就是:比如从A到C,中间有个点B,A算法会计算B离A的距离和B离C的距离的综合值来判定,顾前又顾后。
A算法在运算过程中,每次从优先队列中选取f(n)值最小(优先级最高)的节点作为下一个待遍历的节点。
关键集合: 有两个集合openList和closeList,openList存放待遍历的坐标点,closeList存放遍历过的坐标点,closeList最后也用来表示路径。
如果用文字来描述A*算法:
- 将起始点加入openList。
- while循环,只要openList不包含目标点(如果包含了说明已经找到路径了),从opelist取出一个f(n)最小值(第一次是起始点)的点A,然后将点A周围的点,计算好f(n),放入openList。
- openList删除点A。
- closeList加入点A。
- 输入路径。
为了便于第二步取f(n)最小的点,openList和closeList,我都用的PriorityQueue优先级队列,里面规则就是f(n)最小的在最顶端。
然后简单说一下启发函数,对于网格形式的图,有以下这些启发函数可以使用:
- 如果图形中只允许朝上下左右四个方向移动,则可以使用曼哈顿距离(Manhattan distance)。
- 如果图形中允许朝八个方向移动,则可以使用对角距离。
- 如果图形中允许朝任何方向移动,则可以使用欧几里得距离(Euclidean distance)。
本文中使用的欧几里得距离,也就是我们上学学的,两点坐标相减的平方,再开根号
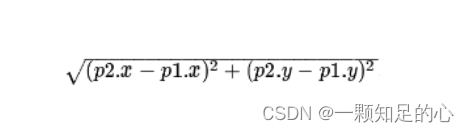
代码部分:
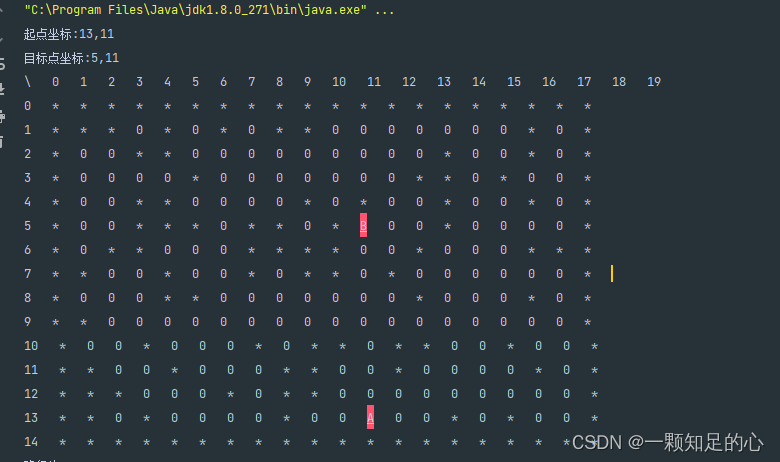
我们先看看效果图:
我们随机生成一个20x15的地图,其中0表示可走,* 代表是障碍物不可走,起点A和终点B都是随机生成的。
然后看看算法给出的路径:这里路径用红色底色标出了。
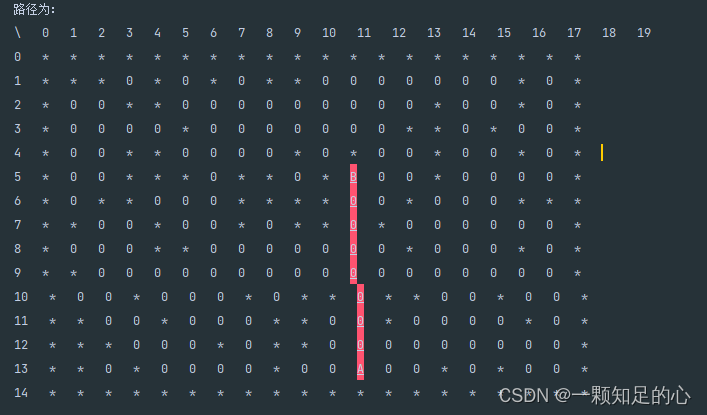
其实这样一看,A*算法的步数少,时间也用的少,效率高。
下面就开始说下代码部分的思路,首先我们约定几点关键内容:
- 约定每一个格子的距离是1,这样算,如果A和B是平行的、挨着的两个点,那么他们距离相距1,如果A和B是斜对角的点,那么就是根号2,约定于1.4几,我们取1.4,为了没有小数,我们代码中在计算的时候都乘以10,所以就是10和14(代码中有这样的计算方式)。
- 我们用Node类来表示地图上每一个坐标点,每个Node都有parentNode,parentNode的用处就是用来计算g(n),通过累加来计算出当前点离起始点的g(n)值
代码主要有3个类,
- Map.java,地图生成类,主要用来生成地图坐标和起始点。
- Node.java,地图坐标的包装类,里面存了一些信息。
- AStar.java,寻路算法类,里面是寻路算法的实现。
下面贴上所有类的代码,里面有关键注释。我们先从入口代码开始看:
public class MainTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Map map = new Map();map.ShowMap(null);AStar aStar = new AStar();aStar.search(map);}
}
Node.java
/*** 地图节点类*/
@Data
public class Node {//坐标的x和yprivate int x;private int y;//value:0表示可通过,*表示障碍物private String value;//这三个参数就是f(n)=g(n)+h(n)private double fValue = 0;private double gValue = 0;private double hValue = 0;//标注当前节点是否走过private boolean reachable;private Node parentNode;public Node(int x, int y, String value, boolean reachable) {this.x = x;this.y = y;this.value = value;this.reachable = reachable;}public Node() {}
}
Map.java
/*** 地图类*/
@Data
public class Map {public static final int Length = 15;public static final int Weight = 20;private Node[][] map;private Node start;private Node end;public Map() {map = new Node[Length][Weight];Random random = new Random();int startX = random.nextInt(Length - 2) + 1;int startY = random.nextInt(Weight - 2) + 1;int endX = random.nextInt(Length - 2) + 1;int endY = random.nextInt(Weight - 2) + 1;System.out.println("起点坐标:" + startX + "," + startY);System.out.println("目标点坐标:" + endX + "," + endY);for (int i = 0; i < Length; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < Weight; j++) {Node node = new Node(i, j, "0", true);if (i == 0 || j == 0 || i == Length - 1 || j == Weight - 1) {node.setValue("*");node.setReachable(false);} else {int num = random.nextInt(10);if (num < 3) {node.setValue("*");node.setReachable(false);}if (i == startX && j == startY) {node.setValue("A");node.setReachable(true);start = node;}if (i == endX && j == endY) {node.setValue("B");node.setReachable(true);end = node;}}map[i][j] = node;}}}public void ShowMap(PriorityQueue<Node> nodeList) {System.out.print("\\" + " ");for (int i = 0; i < Weight; i++) {System.out.print(i + " ");}System.out.println();for (int i = 0; i < Length; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < Weight; j++) {Node node = map[i][j];String value = map[i][j].getValue();if (nodeList == null) {if ("A".equals(value) || "B".equals(value)) {System.out.format("\33[41;4m" + value + "\33[0m" + " ");} else {if (j == 0) {System.out.print(i + " ");System.out.print(value + " ");} else {System.out.print(value + " ");}}} else {if (j == 0) {System.out.print(i + " ");}if (nodeList.contains(node)) {System.out.format("\33[41;4m" + value + "\33[0m" + " ");} else {System.out.print(value + " ");}}}System.out.println();}}
}
Astar,java
public class AStar {private final PriorityQueue<Node> openList = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> (int) (o1.getFValue() - o2.getFValue()));private final PriorityQueue<Node> closeList = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> (int) (o1.getFValue() - o2.getFValue()));private Map map;public void search(Map mapData) {this.map = mapData;Node start = map.getStart();openList.add(start);while (!openList.contains(mapData.getEnd())) {Node node = openList.peek();assert node != null;selectNearByNode(node);node.setReachable(false);openList.remove(node);closeList.add(node);}closeList.add(mapData.getEnd());showPath(closeList, map);}/*** 将选中节点周围的节点添加进“开启列表”*/public void selectNearByNode(Node currentNode) {int x = currentNode.getX();int y = currentNode.getY();for (int dx = (x > 0 ? -1 : 0); dx <= (x < Map.Length ? 1 : 0); ++dx) {for (int dy = (y > 0 ? -1 : 0); dy <= (y < Map.Weight ? 1 : 0); ++dy) {if (dx != 0 || dy != 0) {Node node = map.getMap()[x + dx][y + dy];if (node.isReachable() && !openList.contains(node)) {node.setParentNode(currentNode);node.setGValue(getGValue(node));node.setHValue(getHValue(node, map.getEnd()));node.setFValue(getFValue(node));openList.add(node);}}}}}/*** 获取H值** @param currentNode:当前节点* @param endNode:终点*/public double getHValue(Node currentNode, Node endNode) {return (Math.abs(currentNode.getX() - endNode.getX()) + Math.abs(currentNode.getY() - endNode.getY())) * 10;}/*** 获取G值** @param currentNode:当前节点*/public double getGValue(Node currentNode) {if (currentNode.getParentNode() != null) {if (currentNode.getX() == currentNode.getParentNode().getX() || currentNode.getY() == currentNode.getParentNode().getY()) {//判断当前节点与其父节点之间的位置关系(水平?对角线)return currentNode.getParentNode().getGValue() + 10;}return currentNode.getParentNode().getGValue() + 14;}return currentNode.getGValue();}/*** 获取F值 : G + H*/public double getFValue(Node currentNode) {return currentNode.getGValue() + currentNode.getHValue();}/*** 将路径标记出来*/public void showPath(PriorityQueue<Node> closeList, Map map) {if (closeList.size() > 0) {System.out.println("路径为:");map.ShowMap(closeList);}}
}
总的来说,A*算法还是很简单的,如果有啥疑问欢迎在评论区询问,如果有错误也欢迎指出。