使用C++无锁编程实现多线程下的单例模式
贺志国
2023.8.1
在多线程环境下创建一个类的单例对象,要比单线程环境下要复杂很多。下面介绍在多线程环境下实现单例模式的几种方法。
一、尺寸较小的类单例对象创建
如果待创建的单例类SingletonForMultithread内包含的成员变量较少,整个类占用的内存空间较小,则可使用局部静态变量来创建单例对象。C++ 11标准保证在进入多线程前,已完成静态类对象的构建。如果类的尺寸较大,静态变量存储栈区无法容纳该类的单例对象,则禁止使用该方法。例如:64位Linux系统默认栈的最大空间为8 MB,64位Windows系统默认栈的最大空间为1 MB,当待创建的单例对象尺寸接近或超过上述栈的默认存储空间时,如使用该方法创建则会导致程序崩溃。示例代码如下所示:
class SmallSingletonForMultithread {public:static SmallSingletonForMultithread& GetInstance() {static SmallSingletonForMultithread instance;return instance;}private:SmallSingletonForMultithread() = default;~SmallSingletonForMultithread() = default;SmallSingletonForMultithread(const SmallSingletonForMultithread&) = delete;SmallSingletonForMultithread& operator=(const SmallSingletonForMultithread&) = delete;SmallSingletonForMultithread(SmallSingletonForMultithread&&) = delete;SmallSingletonForMultithread& operator=(SmallSingletonForMultithread&&) = delete;
};
二、尺寸较大的类单例对象创建(要求显式调用销毁函数来避免内存泄漏)
在实际工作中,由于某些单例类的尺寸较大,静态变量存储栈区无法容纳该单例对象,因此无法使用上述方法来创建单例对象,这时需要使用new在堆区动态创建单例对象。为了避免多线程环境下对于单例对象的抢夺,可使用C++无锁编程来实现。需要付出的代价就是,最后一个调用者需要显式地调用销毁函数DestoryInstance来避免内存泄漏,示例代码如下所示:
#include <atomic>
#include <cassert>
#include <mutex>class SingletonForMultithread {public:static SingletonForMultithread* GetInstance() {if (!instance_.load(std::memory_order_acquire)) {auto* new_ptr = new SingletonForMultithread;SingletonForMultithread* old_ptr = nullptr;if (!instance_.compare_exchange_strong(old_ptr, new_ptr,std::memory_order_release,std::memory_order_relaxed)) {// If the CAS operation fails, another thread has created a singleton// object, and it's necessary to delete the temporary object created by// the current thread.delete new_ptr;new_ptr = nullptr;}}return instance_.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);}static void DestoryInstance() {if (instance_.load(std::memory_order_acquire)) {auto* old_ptr = instance_.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);SingletonForMultithread* new_ptr = nullptr;if (instance_.compare_exchange_strong(old_ptr, new_ptr,std::memory_order_release,std::memory_order_relaxed)) {// If the CAS operation succeeds, the current thread obtains the// original object and can safely delete it.delete old_ptr;old_ptr = nullptr;}}}private:SingletonForMultithread() = default;~SingletonForMultithread() = default;SingletonForMultithread(const SingletonForMultithread&) = delete;SingletonForMultithread& operator=(const SingletonForMultithread&) = delete;SingletonForMultithread(SingletonForMultithread&&) = delete;SingletonForMultithread& operator=(SingletonForMultithread&&) = delete;private:static std::atomic<SingletonForMultithread*> instance_;
};// Static member variable initialization
std::atomic<SingletonForMultithread*> SingletonForMultithread::instance_;int main() {auto* singleton = SingletonForMultithread::GetInstance();assert(singleton != nullptr);singleton->DestoryInstance();return 0;
}
三、尺寸较大的类单例对象创建(使用std::unique_ptr<T>和std::call_once实现)
很多时候,我们无法显式地调用销毁函数来避免内存泄漏,这时就可借助std::unique_ptr<T>和std::call_once来实现,示例代码如下:
#include <cassert>
#include <memory>
#include <mutex>class SingletonForMultithread {public:~SingletonForMultithread() = default;static SingletonForMultithread* GetInstance() {static std::unique_ptr<SingletonForMultithread> instance;static std::once_flag only_once;std::call_once(only_once,[]() { instance.reset(new (std::nothrow) SingletonForMultithread); });return instance.get();}private:SingletonForMultithread() = default;SingletonForMultithread(const SingletonForMultithread&) = delete;SingletonForMultithread& operator=(const SingletonForMultithread&) = delete;SingletonForMultithread(SingletonForMultithread&&) = delete;SingletonForMultithread& operator=(SingletonForMultithread&&) = delete;
};int main() {auto* singleton = SingletonForMultithread::GetInstance();assert(singleton != nullptr);return 0;
}
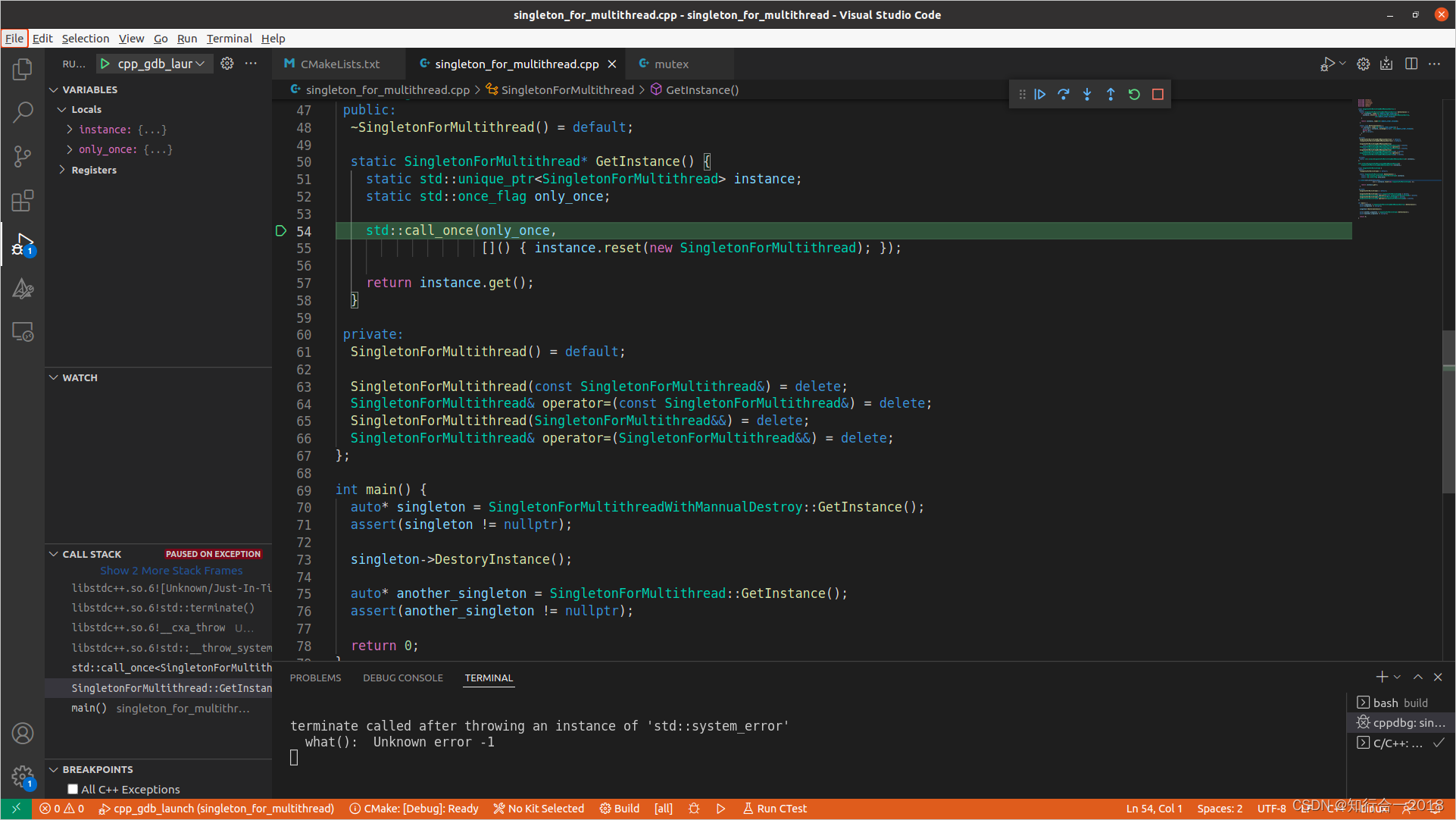
但我在Ubuntu 20.04系统上使用GCC 9.4.0似乎无法正常完成任务,会抛出异常,产生core dump,原因暂不详。
四、尺寸较大的类单例对象创建(使用std::unique_ptr<T>和std::atomic_flag实现)
第三节借助std::unique_ptr<T>和std::call_once来实现单例对象的创建,同时避免显式地调用销毁函数来避免内存泄漏。这种方法在Ubuntu 20.04系统上使用GCC 9.4.0实现时似乎会导致程序core dump。于是我们使用std::atomic_flag替换std::call_once来完成任务。基本思想如下:首先定义一个静态的无锁标志变量std::atomic_flag start_flag,并将其初始值设置为ATOMIC_FLAG_INIT。第一次调用start_flag.test_and_set(std::memory_order_relaxed)函数时,由于start_flag的状态是ATOMIC_FLAG_INIT,该函数返回false,于是可调用instance.reset(new SingletonForMultithread)创建单例对象。第二次直至第N次调用start_flag.test_and_set(std::memory_order_relaxed)函数时,因为start_flag的状态已被设置,该函数返回true,创建单例对象的语句instance.reset(new SingletonForMultithread)永远不会被再次执行,这就达到了只创建一次的目的。同时,因为使用静态的智能指针变量std::unique_ptr<SingletonForMultithread> instance来管理单例对象,于是不再需要显式地回收内存,只要程序结束,静态变量自动清除,智能指针对象instance会在其析构函数中释放内存。
由于new运算符创建单例对象可能耗时较长,为了避免其他线程在单例对象创建到一半的过程中读取到不完整的对象,导致未定义的行为,我们使用另一个原子变量std::atomic<bool> finished来确保创建动作已正确完成,不选用另一个无锁标志变量std::atomic_flag的原因是,该类在C++ 20标准前未提供单独的测试函数test。finished.store(true, std::memory_order_release);与while (!finished.load(std::memory_order_acquire))的内存顺序,实现了synchronizes-with与happens-before关系,保证在while (!finished.load(std::memory_order_acquire))成功时,instance.reset(new SingletonForMultithread);必定执行完毕,单例对象的创建是完整的。
完整的示例代码如下:
#include <atomic>
#include <cassert>
#include <memory>
#include <mutex>
#include <thread>
#include <vector>using namespace std::chrono_literals;namespace {
constexpr size_t kThreadNum = 2000;
}class SingletonForMultithread {public:~SingletonForMultithread() = default;static SingletonForMultithread* GetInstance() {static std::unique_ptr<SingletonForMultithread> instance;static std::atomic_flag start_flag = ATOMIC_FLAG_INIT;static std::atomic<bool> finished(false);if (!start_flag.test_and_set(std::memory_order_relaxed)) {// The object created by the `new` operator may be relatively large and// time-consuming, therefore another atomic variable 'finished' is used to// ensure that other threads read a fully constructed singleton object. Do// not consider using another `std::atomic_flag`. Because it doesn't// provide a separate `test` function before the C++ 20 standard.instance.reset(new (std::nothrow) SingletonForMultithread);finished.store(true, std::memory_order_release);}// Wait in a loop until the singleton object is fully created, using// `std::this_thread::yield()` to save CPU resources.while (!finished.load(std::memory_order_acquire)) {std::this_thread::yield();}return instance.get();}private:SingletonForMultithread() {// Simulate a constructor that takes a relative long time.std::this_thread::sleep_for(10ms);}SingletonForMultithread(const SingletonForMultithread&) = delete;SingletonForMultithread& operator=(const SingletonForMultithread&) = delete;SingletonForMultithread(SingletonForMultithread&&) = delete;SingletonForMultithread& operator=(SingletonForMultithread&&) = delete;
};int main() {std::vector<std::thread> customers;for (size_t i = 0; i < kThreadNum; ++i) {customers.emplace_back(&SingletonForMultithread::GetInstance);}for (size_t i = 0; i < kThreadNum; ++i) {customers[i].join();}auto* singleton = SingletonForMultithread::GetInstance();assert(singleton != nullptr);return 0;
}