论文网址:Graph Neural Networks in Network Neuroscience | IEEE Journals & Magazine | IEEE Xplore
英文是纯手打的!论文原文的summarizing and paraphrasing。可能会出现难以避免的拼写错误和语法错误,若有发现欢迎评论指正!文章偏向于笔记,谨慎食用
目录
1. 省流版
1.1. 心得
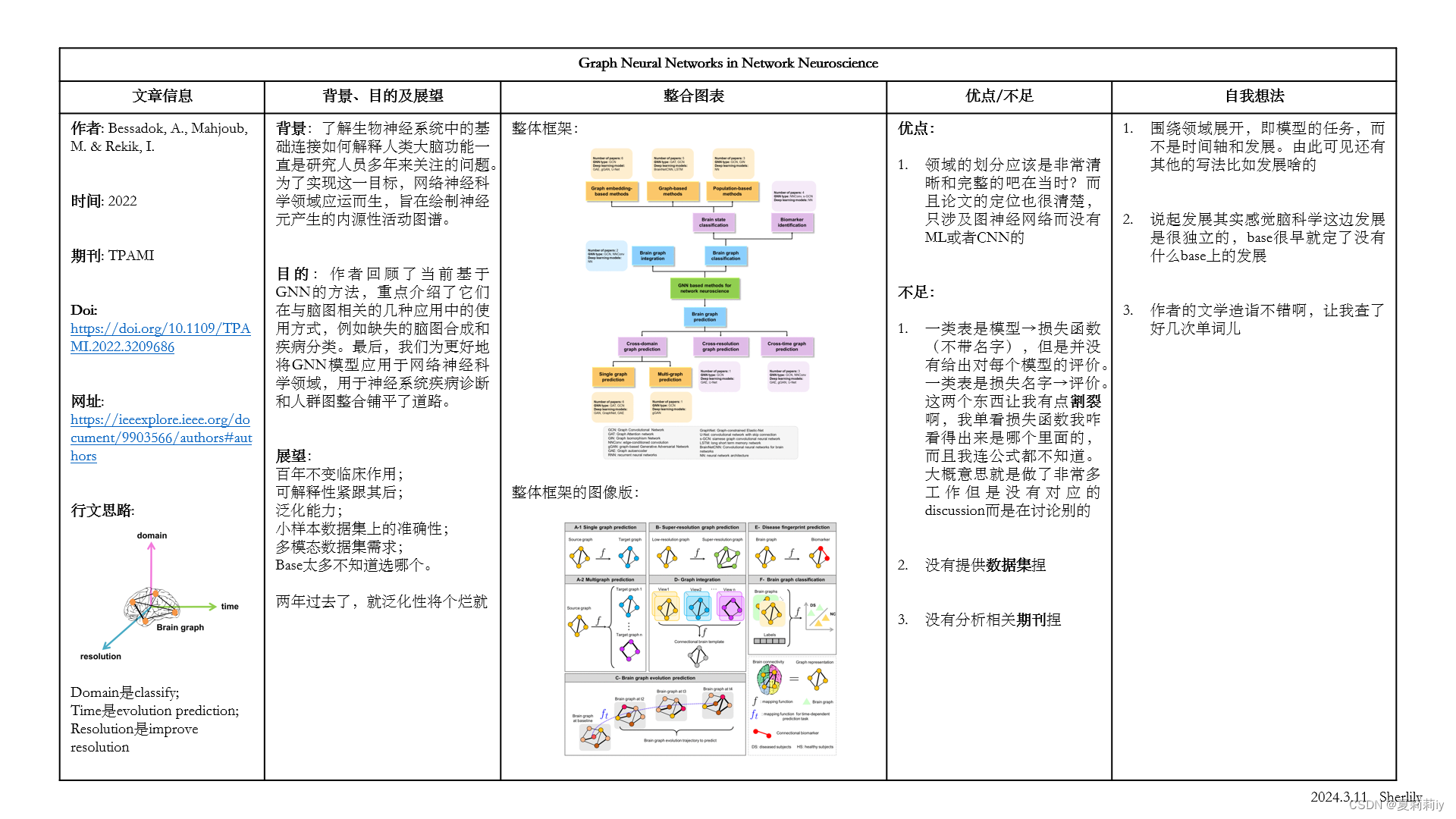
1.2. 论文总结图
2. 论文逐段精读
2.1. Abstract
2.2. Introduction
2.3. What Do Graph Neural Networks Offer to Network Neuroscience?
2.3.1. GNN Overview
2.3.2. Brain Graph Overview
2.3.3.Literature Search and Taxonomy Definition
2.3.4. Brain Graph Prediction
2.3.5. Brain Graph Integration
2.3.6. Brain Graph Classification
2.4. Discussion and Outlook
2.4.1. Toward Clinical Translation
2.4.2. Outlook
3. 知识补充
3.1. Structural and anatomical images
3.2. Brain images
3.3. Dichotomized learning-based models
3.4. Isomeric and heterogeneous
3.5. Mesh and grid
4. Reference List
1. 省流版
1.1. 心得
(1)一看时间2022,哥们儿你真是错过了2022的GNN盛世
(2)妈妈,感觉看综述被生僻英文单词输出了
(3)这Intro是真长啊一口气读下去差点没噎死我
(4)第二次challenge2.3.2. 脑图一般是无向图,能不能发展一点有向啊,虽然是作为外行人的发言
(5)挑战与见解写得有点紧密联系了最好还是分开吧而且那个见解有点vague
1.2. 论文总结图
2. 论文逐段精读
2.1. Abstract
①Medical neuroimaging now can present the morphology, structure, and function of brain
②Their citations list: GitHub - basiralab/GNNs-in-Network-Neuroscience: A review of papers proposing novel GNN methods with application to brain connectivity published in 2017-2020.
morphological n.同 morphologic adj.形态学(上)的;【语】词法的
2.2. Introduction
①The three representations of brains bring time, resolution and domain information of brain:
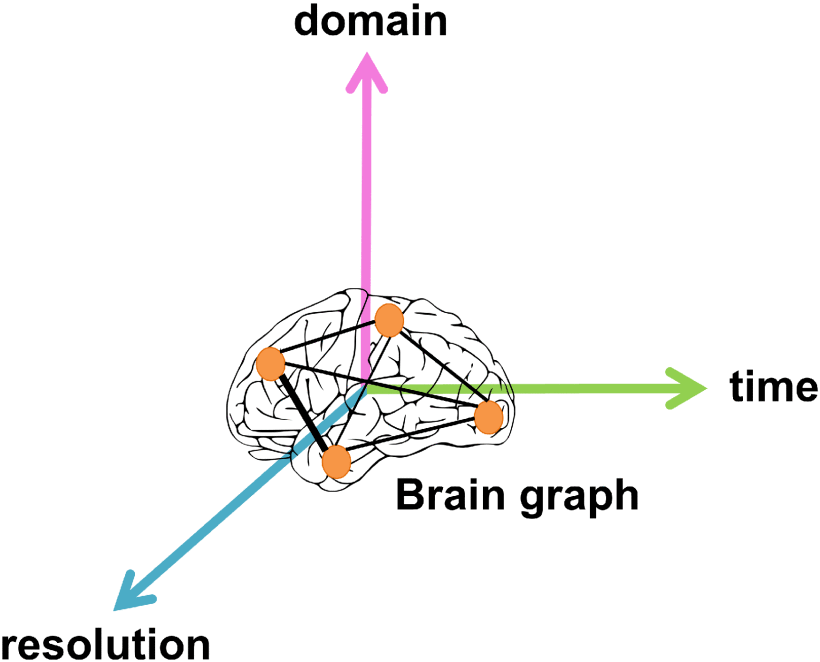
②Multi-modality data will bring different information of brain. Human Connectome Project (HCP), the Baby Connectome Project (BCP) and the Connectome Related to Human Disease (CRHD) datasets focus to collect such data.
③Functional connectivity (FC) matrix can be generated by CONN toolbox or groupwise whole-brain parcellation methods and structural and morphological connectivity (SC/MC) matrices can be measured by FSL toolbox and Desikan-Killiany atlas via FreeSurfer software(应该只列了一部分啦)
④There are methods that can predict images with other modalities by a single imaging modality
⑤Moreover, mapping brain graph from non Euclidean domains to other domains such as geometric and hyperbolic domains
⑥Citing other surveys and list the differences
underpinning v.基础;加强;巩固;构成(…的基础等) underpin的现在分词 n.(学说、理论等的)基础;基础结构;基础材料;(人的)腿
endogenous adj.内源性的;内生的
holistic adj.整体的;全面的;功能整体性的
coalescent adj.合并的;接合的 n.联合;合并
internodal adj.节间的
nascent adj.新生的;萌芽的;未成熟的
taxonomy n.分类法;分类学;分类系统
2.3. What Do Graph Neural Networks Offer to Network Neuroscience?
2.3.1. GNN Overview
①GNNs can be categorized into three main types: Graph Convolutional Network (GCN), Graph Attention Network (GAT) and message-passing mechanism(为什么消息传递机制不被包含在GCN里啊?)
②GNN usually defines graph as , where
denotes the pairwise correlation,
denotes feature matrix,
denotes the nodes set and
denotes the edges set.
③If there is no feature of node, setting
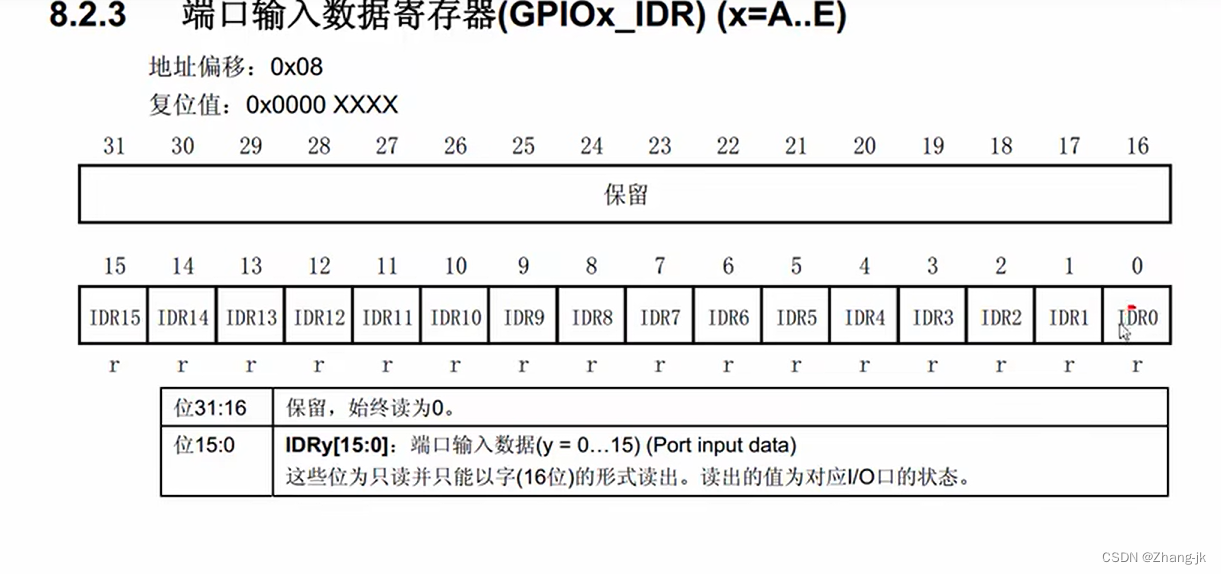
④The aggregation method of GCN:
where denotes the activate function,
denotes the filter that presents the graph convolutional weights,
dentoes the GCN function,
and
⑤Graph-based model and population based model:
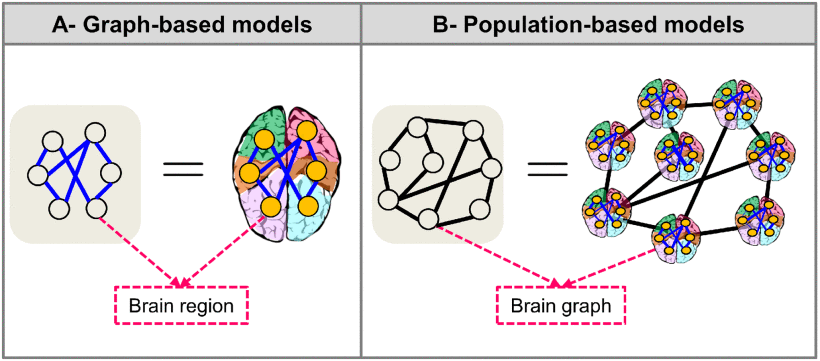
2.3.2. Brain Graph Overview
①Basically, regarding neurons as nodes and corresponding synapses as edges is a method of constructing brain graph. However, it is relevant expensive in computing(嘻嘻,文心了一下大脑中大概有120亿到140亿个神经元,往死里算!所以后来的ROI划分(一组神经元!)也算是迈出了很大一步呢!)
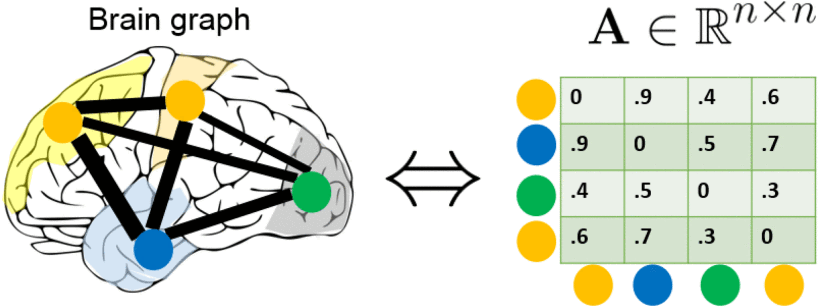
②Traditionally, brain graphs are undirected graphs.
③Common method of brain graph construction:
(1)Morphological brain graphs
①Method: cortical measures of detecting the sulcal depth and cortical thickness
②Extraction: from T1-weighted images
③Main preprocessing: "skull stripping, motion correction, T1-w intensity normalization, topology correction, segmentation of the sub-cortical white matter and deep grey matter volumetric structures and cortical hemisphere construction"
④Dividing regions by specific atlas, such as Desikan-Killiany Atlas. The weighted edges of ROIs are absolute difference
(2)Functional brain graphs
①Method: constructed by fMRI, namely blood-oxygen-level-dependent (BOLD) signal
②Edges: correlations between ROI
③Node: with no feature
(3)Structural brain graphs
①Method: constructed by diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) or diffusion spectrum imaging (DSI), which measured by diffusion of water molecules. It can distinguish gray matter and white matter
②Edges: absolute difference of number of fibers in different ROIs
2.3.3.Literature Search and Taxonomy Definition
①Data focused: 2017.1.1 - 2020.12.31
②Databases: IEEExplore, PubMed, Research Gate, Arxiv Sanity and Google Scholar using
③Keywords: “brain graph”, “brain network”, “connectome”, “GNN”, “graph representation learning”, “network neuroscience”, “graph neural networks”
④Journals/Conferences: Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention conference (MICCAI), the Information Processing in Medical Imaging (IPMI) conference, Journal of Neuroscience Methods, IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging journal, Frontiers in Neuroscience, Neuroimage, Cerebral Cortex journals and bioRxiv
⑤Ignore: CNN/ML in brain
⑥Three domains in brain graph: prediction, integration and classification
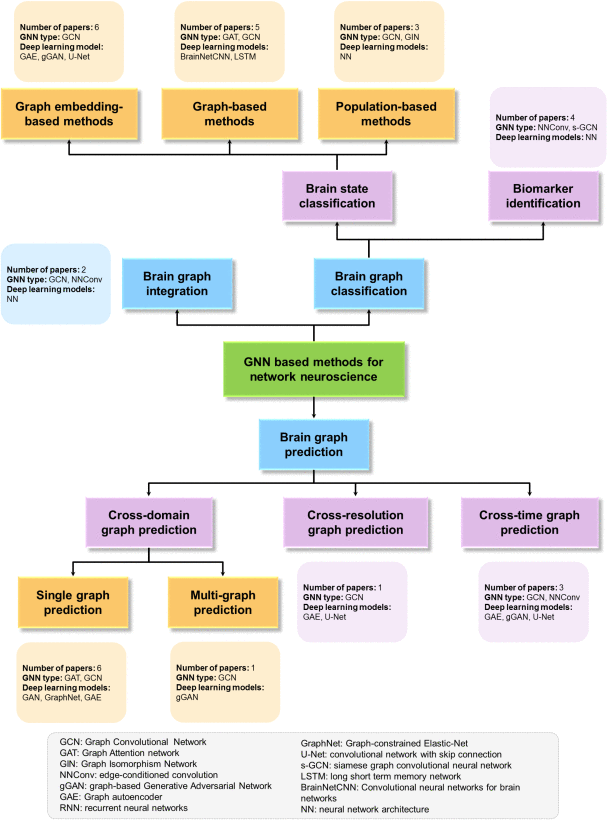
⑦Specific types in brain domain:
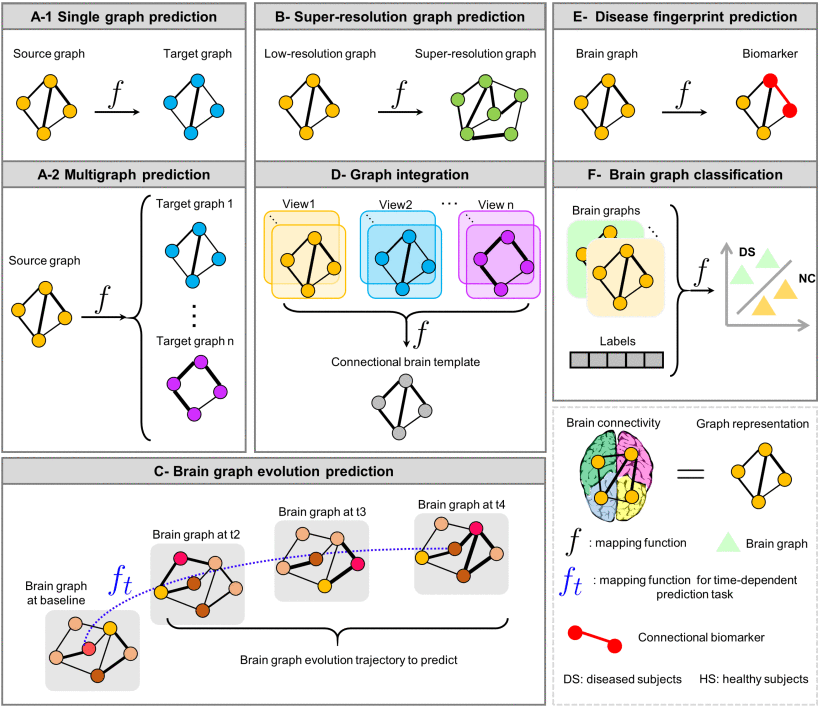
primer n.底漆;初级读本;底层涂料;入门书;启蒙读本;识字课本
2.3.4. Brain Graph Prediction
①⭐Patients may lack multi-times scans over time or multi-modality scan images
②The data of brain image is too little
③Brain Graph Prediction Publications
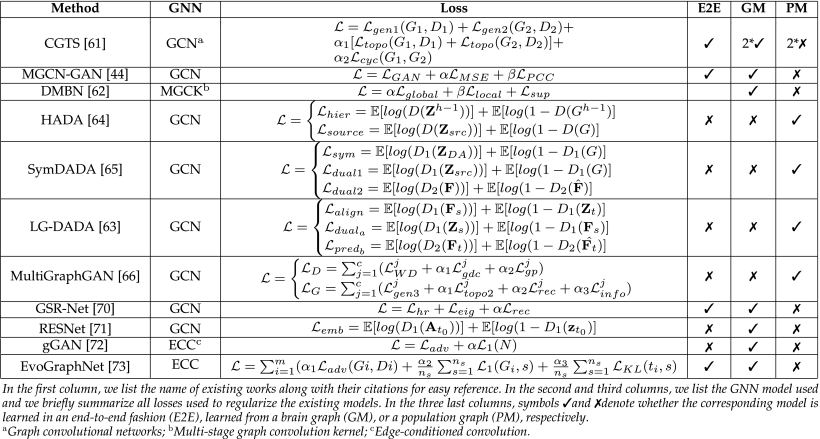
④Brain Graph Integration Publications
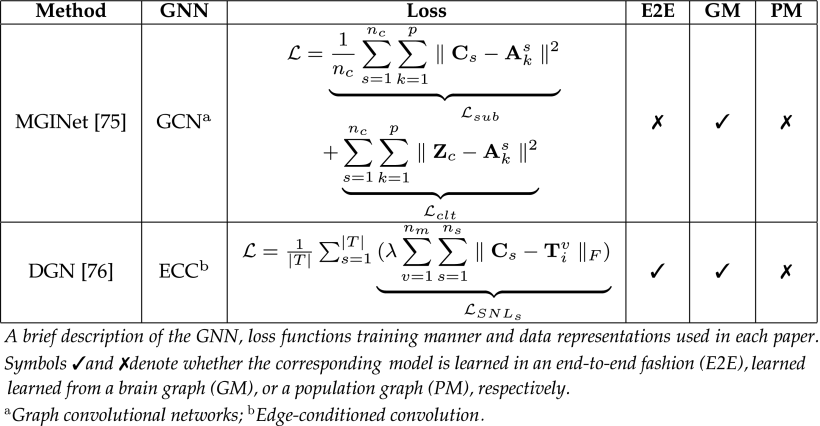
⑤Disease Classification Publications
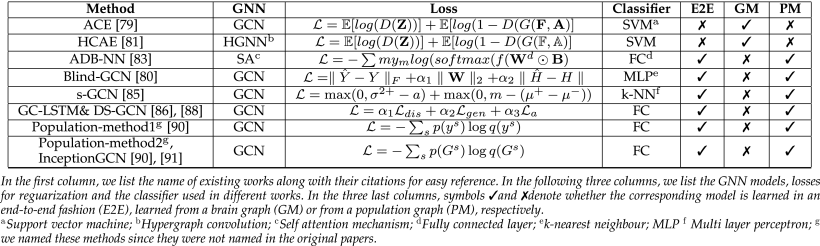
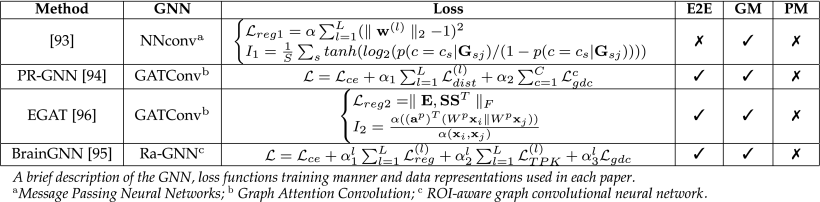
⑥Biomarker Identification Publications
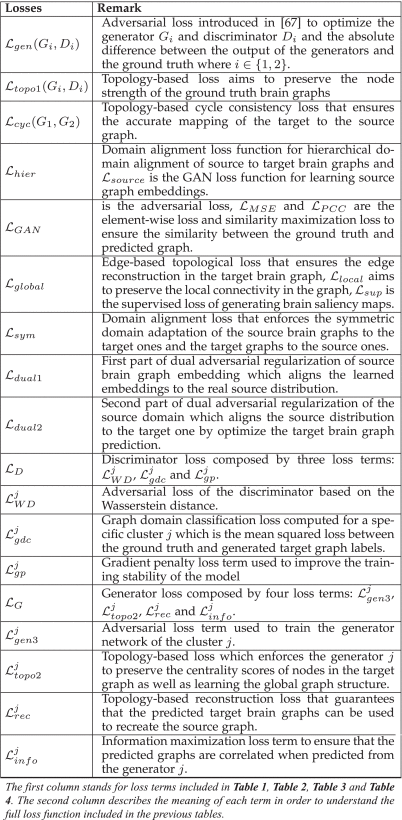
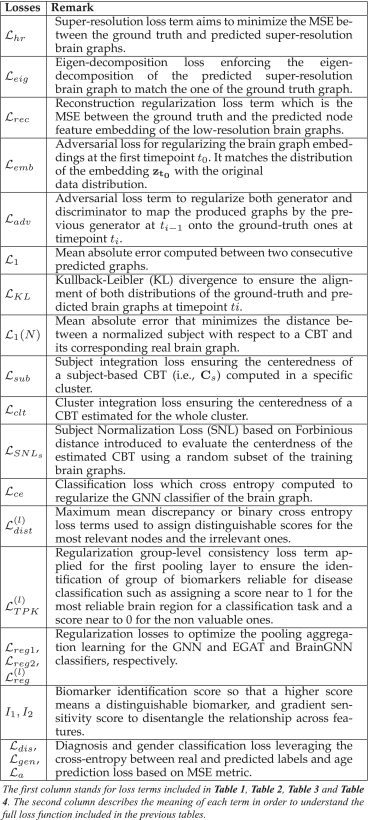
⑦Summary of lost functions:
(1)Cross-Domain Graph Prediction
①Problem statement: for original graph , learning a manpping function
. After that,
②Categories: single/multi graph prediction
③Single graph prediction: such as GAN based models, they predict brain graph with another modality from one source modality. It requires different training when predict different modalities of brain graph
④Multi graph prediction: such as GCN based autoencoder methods
⑤Challenges: a) not all of them are end-to-end, which may accumulates errors, b) GAN based models are possible face mode collapse, c) few topological structured considered
(2)Cross-Resolution Graph Prediction
①Problem statement: for low-resolution brain graph , learning a mapping function
to map
②Example: U-autoencoder constructed by GCN layers, which inspired by U-Net
③Future challenges: better GNN framework, computing efficiency, higher accuracy. What is more, people can fucos on multi-resolution graph synthesis in the future
(3)Cross-Time Graph Prediction
①Problem statement: to learn a mapping function , which turns
to a evolution trajectory
②Categories: dichotomized learning-based/end-to-end learning based GNN model
③Briefly introducing GCN-based graph autoencoder (dichotomized) and GAN-based graph autoencoder with edge-conditioned convolution (ECC) (end-to-end)(不是我的领域捏,介绍了这俩东西的进化预测实现方法)
④Challenges: a) dichotomized learning strategy might limit joint prediction(为啥捏), b) edge convolution in end-to-end method limits the scalability of training time on large-scale graphs(作者后面紧跟了说边缘卷积已被证明是耗时间的)
⑤Prospect: combining multi-modalities to predict
dichotomize v.二分法;对分,二分
2.3.5. Brain Graph Integration
①Problem statement: to learn a mapping function , where
denotes all the modalities of one subject,
denotes a brain graph in one of the modality,
denotes the number of modalities,
and
denotes a shared common connectivity patterns (connectional brain template (CBT))(呃呃说白了就是HC一个fingerprint图,患病一个fingerprint吗)
②Introducing corresponding models such as MGINet, Deep Graph Normalizer (DGN)
③Challenges: ⭐ the existing models do not possess an ability that integrate isomeric graphs of different subjects
2.3.6. Brain Graph Classification
Categories: brain state classification and biomarker identification
(1)Brain State Classification
①Graph Embedding-Based classification
| Problem statement | To learn a mapping function |
| Examples | 没给模型名不想多说,都只给了引用标号 |
| Challenge | Interpretability(哈哈哈哈哈哈哈哈哈) |
②Graph-Based Classification
| Problem statement | This method does not squeez graph presentation, using the whole brain to predict |
| Prediction direction | Classifying sex, age or typical |
| Challenge | Interpretability(怎么一到了我的领域就是这,这啊...) |
③Population-Based Classification
| Problem statement | To learn a mapping function |
| Examples | ———— |
| Challenges | This model fits for large dataset, but now the brain data is scarce, which may cause over-fitting |
calibration n.校准;标定;(温度计或其他仪表上的)刻度
(2)Biomarker Identification
①Problem statement: identifying influential biomarkers
②Challenges: reproducibility (难道不能重复吗?应该也不会差很远吧) and explainability
2.4. Discussion and Outlook
2.4.1. Toward Clinical Translation
(1)Strengths and Limitations
①Morphological brain graph (MBG) is the most common modality in brain image analysis
②因为MBGs是融合了皮质厚度和脑沟深度的图像...所以它本身也带有多模态性质...6
③MBG presents special characters which can not be presented in structural or functional images
④More modalities recorded helps a dataset to complete the task which a model applied in it to predict the other modalities
(2)Reproducibility and Explainability
①作者认为不同的GNN框架会导致不同的分类结果和不同的生物标志物。但这不是很正常吗?又不是所有的模型都是完美的
②Construction methods of atlas: a) voxel, b) anatomical sulcal and gyral boundries parcellation, c) random
rationale n.基本原理;根本原因 delineate vt.勾画;(详细地)描述,描画,解释
disentangle vt.使解脱;使摆脱;分清,清理出(混乱的论据、想法等);理顺;解开…的结;使脱出
(3)GNN Selection and Learning Improvement
①In existing works, 50% are GCN based and 50% are other model based, such as ECC, NNConv or GATConv
②⭐作者说这些base太多了,不知道如何选择基础模型。好的,两年后的我仍旧无法回答这个问题
betweenness n.介数;中间性,介于
(4)Few-Shot Learning
①The accuracy on few-shot dataset for models are essential problem
②The existing work often treats the brain images of manifolds as graphics, i.e. mesh. But the mesh cannot represent the relationships between regions
2.4.2. Outlook
①The "holy grail" in brain region is clinical utility, the authors stated. But all I wanna say is that all the works above for clinical are b*ll sh*t.
②Hhh, don't be too pessimistic
③The generalization ability, accuracy in small dataset, graph presentation are vital
frugal adj.节俭的;(对金钱、食物等)节约的;简单廉价的
3. 知识补充
3.1. Structural and anatomical images
大脑的解剖像和结构像在描述大脑时各有侧重,两者之间存在一些差异。
解剖像:主要关注大脑的形态和外观。它显示大脑的各个部分,如左脑、右脑、大脑皮质、大脑髓质等,并详细描述这些部分的形状、位置和相互关系。解剖像通常通过医学成像技术(如CT扫描、MRI等)获得,可以显示大脑的宏观结构。
结构像:则更侧重于大脑的内部结构和组织。它关注大脑的微观层面,包括神经元的排列、突触的连接、神经纤维的走向等。结构像通过更精细的成像技术(如电子显微镜、高分辨率MRI等)获得,能够揭示大脑的复杂结构和功能。
简而言之,解剖像提供了大脑的整体外观和宏观结构,而结构像则提供了大脑的微观结构和组织细节。两者结合使用可以更全面地了解大脑的形态和功能。
3.2. Brain images
(1)Functional images: always named "FunRaw", obtained by fMRI
(2)Anatomical images: always named "T1Raw", obtained by sMRI
(3)Structural images: always named "T2Raw", obtained by sMRI
(4)但是作者在文章中说morphological images是T1像,而structural images来自DTI。暂时持保留意见
3.3. Dichotomized learning-based models
作者提到的二分法模型,不知道啥意思,不是我领域的吧?以下是作者给的引用:
(1)[71]基于残差嵌入相似性的网络选择预测脑网络演化轨迹 |施普林格链接 (springer.com)
(2)[72]使用深度对抗网络归一化器预测脑图随时间推移的演变 |施普林格链接 (springer.com)
3.4. Isomeric and heterogeneous
在脑科学文章里面都出现过诶,但是我盲猜分子的异构是isomeric,然后heterogeneous就是表示多种多样的
3.5. Mesh and grid
Mesh和Grid都涉及网格的概念,但它们在结构和应用上存在一些关键的区别。
结构特点:Grid通常指的是具有良好结构的网格,其元素往往以典型的正方形或矩形对齐,呈现出一种规则且有序的排列方式。相对而言,Mesh则更为通用,其结构可能非结构化,并可能使用各种形状的元素,有时甚至在同一网格中混合使用不同类型的元素。因此,Mesh在形状和结构上具有更大的灵活性和多样性。
应用场景:Grid因其结构化特性,在某些需要规则网格的应用中表现出色,如数值计算、图像处理等领域。而Mesh则因其非结构化和灵活性,在需要适应复杂形状或不规则空间的应用中更具优势,如三维建模、流体动力学模拟等。
4. Reference List
Bessadok, A., Mahjoub, M. & Rekik, I. (2022) 'Graph Neural Networks in Network Neuroscience', IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 45 (5), pp. 5833-5848. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3209686
![[RoarCTF 2019]Easy Java -不会编程的崽](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/c30290a9ed854ab4a2ab07f053fd9a32.png)