摘要:介绍 list 容器,list 模拟实现
list(带头双向循环列表)
导入:list 的成员函数基本上与 vector 类似,具体内容可以查看相关文档(cplusplus.com/reference/list/list/),这里不多赘述。以下对 list 的 Operations 部分的函数进行简单讲解。
| splice | Transfer elements from list to list (public member function) |
| remove | Remove elements with specific value (public member function) |
| remove_if | Remove elements fulfilling condition (public member function template) |
| unique | Remove duplicate values (public member function) |
| merge | Merge sorted lists (public member function) |
| sort | Sort elements in container (public member function) |
| reverse | Reverse the order of elements (public member function) |
注意:list 没有扩容的概念,而是一份一份相对独立的节点串连起来的。
1)sort
- #include<list> std::list::sort 与 #include<algorithm> std::sort
 如上图,RandomAccessIterator 至少已经在名称上提示使用者,这个 sort 函数要求支持能够被随机访问的迭代器。
如上图,RandomAccessIterator 至少已经在名称上提示使用者,这个 sort 函数要求支持能够被随机访问的迭代器。
首先,list 的迭代器是双向迭代器;其次,从底层实现来看,std::sort 函数用到了迭代器相减,而 list 的地址是不连续的。所以 list 不支持使用 std::sort 函数。
-
std::list::sort 的使用:该函数默认升序排列(底层是归并排序)
如果要降序排序有如下代码以供参考:(std::greater<int>() 是一个 greater 类型的匿名对象,这种写法更常用)#include<functional> #include<list>int main() {std::list<int> lt;//在 lt 中插入一些数据之后std::greater<int> gt;lt.sort(gt);//or:lt.sort(std::greater<int>());return 0; }
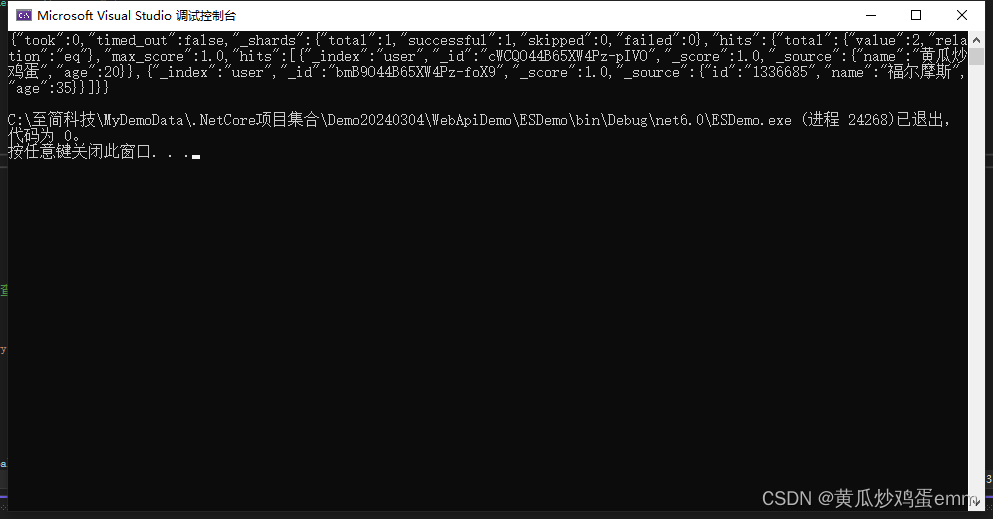
- std::list::sort 的性能测试
测试结果:
①在 Rlease 模式下, std::vector::sort 效率大约是 list 的 2 倍,并且数据量越大效率差距越大。(tip.性能测试要在 Rlease 模式下进行,Debug 模式下优化没有全开)
②通过 vector 给 list 排序:把 list 对象 → 拷贝数据到 vector 对象中 →对 vector 对象 sort → 把排序好的数据拷贝到 list 。这样对 list 排序,在数据量较大的情况下效率甚至比 list 直接排序要高。
sum. list 的 sort 在性能上没有什么优势,list 中的 sort 函数在对于数据量小的情况下可以使用,但平时能不用尽量不要频繁使用。
2)merge
归并两个 list 到一个 list(要先 sort 才可以 merge,实践中很少用)。
3)unique
去重,但也有要求——只能去除连续相同的,所以要先 sort 再 unique 才可以真正“去重”。
4)splice
转移(移动指针),如下图。

以上就是对 list 一些函数的简单介绍。
list 的模拟实现
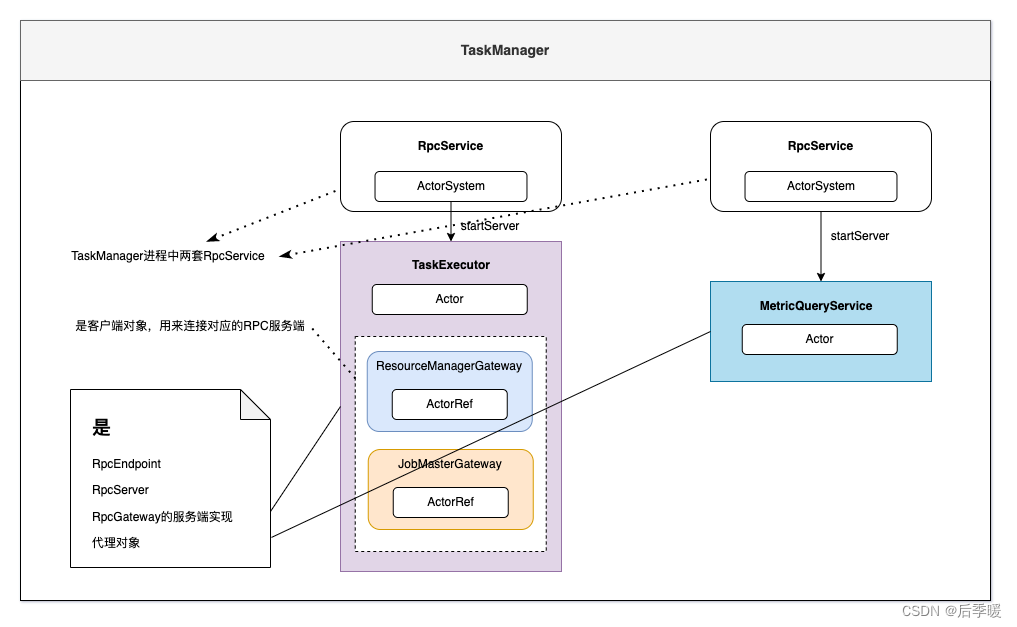
1)结构

如上图,list 中的每个节点是一个自定义类型 Node,对于双向链表,每个节点内包括自身储存的数据、前节点指针和后节点指针。
对于由一个一个节点组成的 list,通过头节点来管理整个 list。
代码示例
// List的节点类template<class T>struct ListNode{ListNode<T>* _pPre;ListNode<T>* _pNext;T _val;};//List类template<class T>class list{PNode _pHead;//注意:这里是一个内置类型(指针) };2)初始化_Constructor
对 list 的初始化首先是对头节点的初始化。
// List的节点类template<class T>struct ListNode{ListNode(const T& val = T()): _val(val), _pPre(nullptr), _pNext(nullptr){}ListNode<T>* _pPre;ListNode<T>* _pNext;T _val;};//List类template<class T>class list{typedef ListNode<T> Node;typedef Node* PNode;public:///// List的构造list(){CreateHead();}private:void CreateHead()//对头结点进行初始化{_pHead = new Node;//这里会去调用struct ListNode的构造函数_pHead->_pNext = _pHead;_pHead->_pPre = _pHead;}PNode _pHead;//注意:这里是一个内置类型(指针) };3)Iterator
class Iterator——Iterator类
- 成员变量:Node* _pNode
- 成员函数:operator* 、operator++ 、operator-- 、operator!= 、operator==(模拟指针的行为)——这里体现了“封装”。封装屏蔽底层差异和实现细节,提供统一的访问修改遍历方式。
代码示例
//List的迭代器类template<class T>class ListIterator{typedef ListNode<T>* PNode;typedef ListIterator<T> Self;public://constructorListIterator(PNode pNode = nullptr):_pNode(pNode){}ListIterator(const Self& l)//copy constructor{_pNode = l._pNode;}//operationsT& operator*(){return _pNode->_val;}T* operator->(){return &_pNode->_val;}Self& operator++(){_pNode = _pNode->_pNext;return *this;}Self operator++(int){Self tmp = _pNode;_pNode = _pNode->_pNext;return tmp;}Self& operator--(){_pNode = _pNode->_pPre;return *this;}Self operator--(int){Self tmp = _pNode;_pNode = _pNode->_pPre;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const Self& l){return _pNode != l._pNode;}bool operator==(const Self& l){return _pNode == l._pNode;}PNode _pNode;};
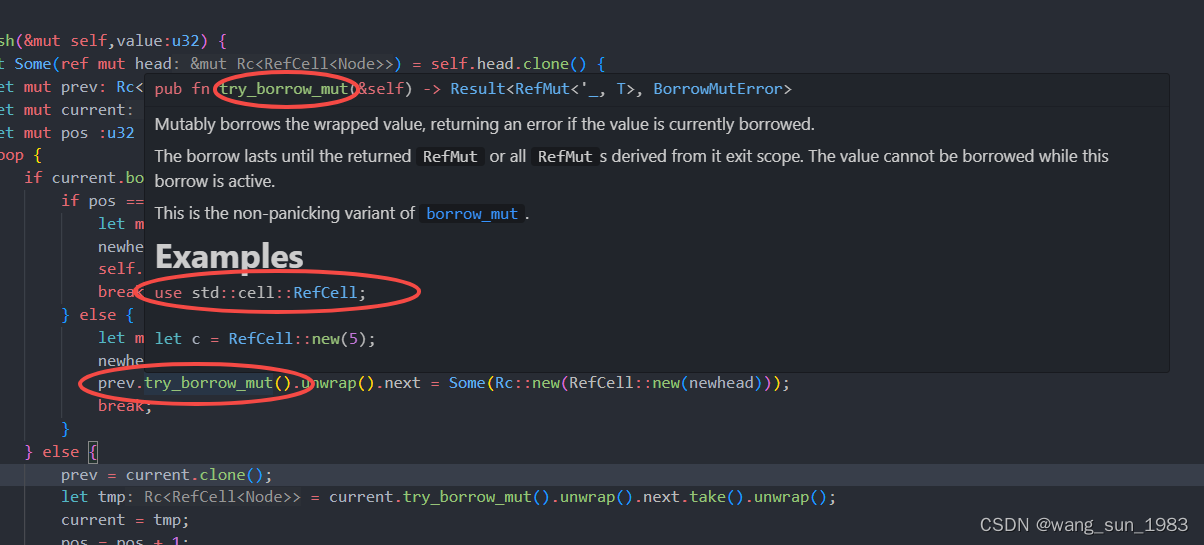
对 operator-> 的补充说明
我们知道,对于自定义类型,可以通过对其指针解引用 " *(pointer). " 和 " (pointer)-> " 来访问其成员。而 iterator 实际上是在模拟指针的行为,对于 operator-> 的使用编译器做出了优化。如下图。

3)Const_Iterator
注意!const_iterator 不是用 const 修饰 iterator,如上 iterator 中的模拟实现可以看出,iterator 底层是原生指针,用 const 修饰 iterator 是使得指针本身不可修改,const_iterator 本身是要能被进行 ++ 和 -- 操作的,否则无法实现遍历;而 const_iterator 针对的是被 const 修饰的 list 的对象,即 const 修饰的是 list 的实例化对象本身。(ps. list 对象是 const 的,那储存在节点中的数据肯定也是 const 的,即为 const T)
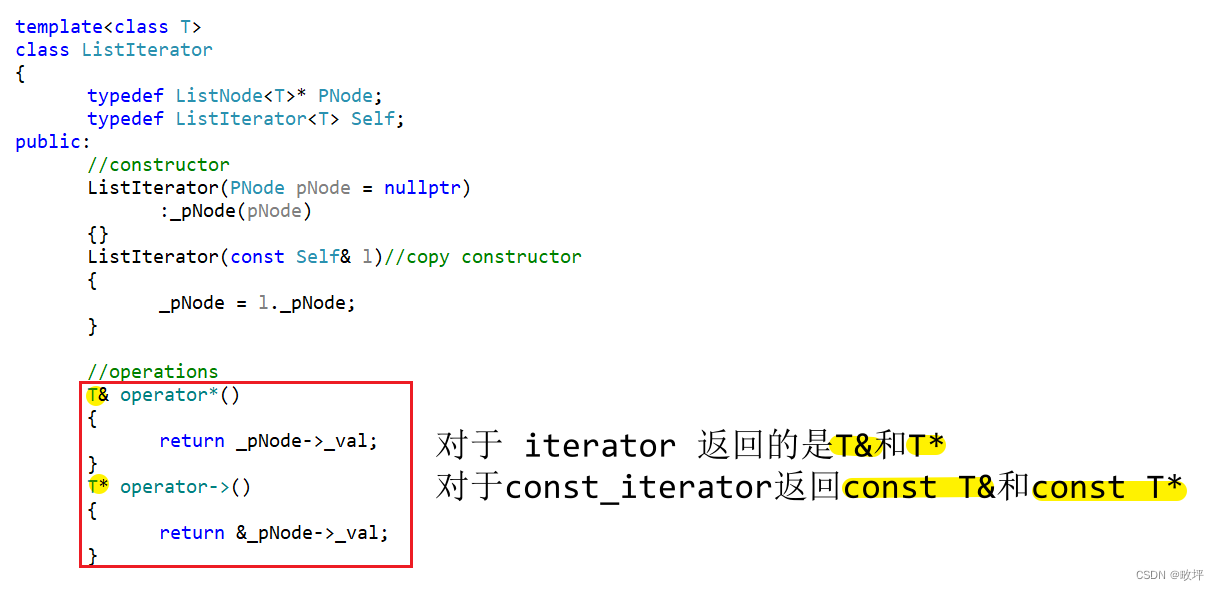
如上图,实际上我们需要实现两个不同的 iterator —— class ListIterator 和 class ListConst_Iterator ,而对于 const 对象,begin 和 end 函数将会返回 const_iterator。
优化:使用类模板实现 List 的 Iterator 类
代码示例
//List的迭代器类template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>class ListIterator{typedef ListNode<T>* PNode;typedef ListIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;public://constructorListIterator(PNode pNode = nullptr):_pNode(pNode){}ListIterator(const Self& l)//copy constructor{_pNode = l._pNode;}//operationsRef operator*(){return _pNode->_val;}Ptr operator->(){return &_pNode->_val;}Self& operator++(){_pNode = _pNode->_pNext;return *this;}Self operator++(int){Self tmp = _pNode;_pNode = _pNode->_pNext;return tmp;}Self& operator--(){_pNode = _pNode->_pPre;return *this;}Self operator--(int){Self tmp = _pNode;_pNode = _pNode->_pPre;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const Self& l){return _pNode != l._pNode;}bool operator==(const Self& l){return _pNode == l._pNode;}PNode _pNode;};//list类template<class T>class list{typedef ListNode<T> Node;typedef Node* PNode;public:typedef ListIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef ListIterator<T, const T&, const T&> const_iterator;public:///// List的构造list(){CreateHead();}///// List Iteratoriterator begin(){return _pHead->_pNext;}iterator end(){return _pHead;}const_iterator begin() const{return _pHead->_pNext;}const_iterator end()const{return _pHead;}}注意:同一个类模板,实例化参数不同,就是完全不同的类型,即对于 ListIterator<T, T&, T*> 和 ListIterator<T, const T&, const T&> 是两个不同的类型。(ps. iterator 和 const_iterator 都实现之后才可以支持使用范围 for)
4)其他成员函数
这些成员函数实现起来思路很简单,有问题建议去看数据结构的文章回顾一下。以下简略说明。
①insert
insert 之后 iterator 不失效,因为没有扩容的影响。
// 在pos位置前插入值为val的节点iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& val){PNode cur = pos._pNode;PNode newnode = new Node(val);newnode->_pNext = cur;newnode->_pPre = cur->_pPre;cur->_pPre = newnode;newnode->_pPre->_pNext = newnode;return pos;}②erase
erase 之后 iterator 失效,因为这个被 erase 的节点被释放了,那么指向它的 iterator 也就失效了。
// 删除pos位置的节点,返回该节点的下一个位置iterator erase(iterator pos){if (!empty()){PNode next = pos._pNode->_pNext;pos._pNode->_pPre->_pNext = next;next->_pPre = pos._pNode->_pPre;delete pos._pNode;--_size;return next;}return _pHead;}③push_back and push_front
复用 insert。
// List Modifyvoid push_back(const T& val) { insert(end(), val); }void push_front(const T& val) { insert(begin(), val); } ④pup_back and pop_front
复用 erase。
// List Modifyvoid pop_back() { erase(--end()); }void pop_front() { erase(begin()); }⑤clear
用 iterator 遍历,依次 erase 每个节点。
void clear(){iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){it = erase(it);}}⑥Destructor
clear → delete → nullptr,即清理 list,释放头节点,头结点指针指针置空。
//destructor~list(){clear();delete _pHead;_pHead = nullptr;}⑦Copy Constructor
范围 for 循环 push_back。(注意:使用范围 for 需要把 const_iterator 也实现了才能用)
list(const list<T>& l)//copy constructor{CreateHead();for (auto e : l){push_back(e);}}⑧赋值重载
//assignlist<T>& operator=(list<T> l){if (_pHead != l._pHead){swap(l);return *this;}}void swap(list<T>& l){std::swap(_pHead, l._pHead);std::swap(_size, l._size);}⑨其他构造函数重载
list(int n, const T& value = T()){CreateHead();while (n--){push_back(value);}}template <class Iterator>list(Iterator first, Iterator last){CreateHead();Iterator it = first;while (it != last){push_back(*it);++it;}}补充:list 的成员变量中可以加一个 size_t 类型的变量来记录节点个数,因为如果没有这个成员变量就需要遍历来获取有效数据个数,效率比较低。(提醒:如果增加了 size_t 类型的成员变量记得在 insert 和 erase 的函数实现中相应地做出调整)
5)补充:Print
针对于 list<int> / list<char> 等类型的打印函数很好实现,以下我们尝试写出更通用的打印函数。
打印 list<T> 而不只是针对某个具体的 T 类型
因为语法编译之前要先对模板进行实例化,对于 Btl::list<T>::const_iterator 由于模板没有被实例化,所以编译器不知道 const_iterator 是 list<T> 中的一个内嵌类型还是静态成员变量,这样的行为对于编译器是未知的。
所以,Btl::list<T>::const_iterator 前加 typename 来声明这是一个内嵌类型。代码如下。
template<typename T>
void print_l(const Btl::list<T>& _list)
{typename Btl::list<T>::const_iterator it = _list.begin();while (it != _list.end()){std::cout << *it;++it;}std::cout << std::endl;
}打印任意容器
提醒:下列代码中要求 *it 支持流插入。
template<typename Container>
void print_l(const Container& _con)
{typename Container::const_iterator it = _con.begin();while (it != _con.end()){std::cout << *it;++it;}std::cout << std::endl;
}回顾:vector模拟实现中涉及的深浅拷贝的问题
对于类似 vector<string> 而出现的深浅拷贝问题,因为 list 不涉及扩容的概念,所以不会出现深浅拷贝的问题。
附:完整代码链接My_List/My_List/My_List.h · fantansy-13-07/Cpp - 码云 - 开源中国 (gitee.com)
END