DIV CSS基础
- 一、DIV和CSS样式
- 二、样式表类型
- 2.1 嵌入样式表
- 2.2 外部样式
- 2.3 内联样式
- 三、注释
- 四、样式选择器
- 组合选择器
- 五、背景
- 六、边框
- 七、文字属性
- 八、文本属性
- 九、列表
- 十、超链接
- 十一、盒子模型
- 十二、Border 边框
- margin padding
- 十三、float 脱离文档流浮动
- 十四、块级元素、行内元素
- 十五、溢出
- 十六、定位
一、DIV和CSS样式
层叠样式表 (英文全称:Cascading Style Sheets)是一种用来表现HTML(标准通用标记语言的一个应用)或XML(标准通用标记语言的一个子集)等文件样式的计算机语言。CSS不仅可以静态地修饰网页,还可以配合各种脚本语言动态地对网页各元素进行格式化。
CSS 能够对网页中元素位置的排版进行像素级精确控制,支持几乎所有的字体字号样式,拥有对网页对象和模型样式编辑的能力。
DIV是html的一个标签 css是一个样式表
二、样式表类型
2.1 嵌入样式表
实现代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title></title><style>.demo1{color: red;width: 100px;height: 100px;background: blue;}</style></head><body><div class="demo1">demo1</div></body>
</html>输出结果:

2.2 外部样式
创建一个g.css后缀的文件并输入:
body{background: black;
}再次创建一个css.css后缀的文件并输入:
@import url("g.css");
.demo1{color: red;width: 100px;height: 100px;background: blue;}输出结果:
@import url("g.css");
.demo1{color: red;width: 100px;height: 100px;background: blue;}2.3 内联样式
实现代码:
<div style="color: blue;width: 100px;height: 100px; background: black;">demo2</div>
对其进行使用:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title></title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/css.css" /></head><body><div class="demo1">demo1</div><div style="color: blue;width: 100px;height: 100px; background: black;">demo2</div></body>
</html>并将css.css中的引用去掉,也就是:
.demo1{color: red;width: 100px;height: 100px;background: blue;}输出结果:

三、注释
/* */ 注释内容
四、样式选择器
| 选择器 | 代码格式 |
|---|---|
| 元素选择器 | div{属性:值} |
| ID选择器 | #id{属性:值} |
| class选择器 | .类名{属性:值} |
| 通配符选择器 | *{属性:值} |
| 群组选择器 |
- 元素选择器
div{
color:gold;
}
/*设置所有p标签的属性*/
- id选择器
#id{
color:gold;
}
<p id="first">ZY技术分享</p>
/*需要使用id引入才能使属性生效
(通常用于描述一个标签具有唯一的样式)*/
- class选择器
.class{
color:blue;
}
<p class="blue">ZY技术分享</p>
/*必须使用class引入才能使属性生效
(通常用于修饰一组或者一系列具有相同样式的标签)*/
- 通配符选择器
一般情况下在css页面刚开始的时候 ,描述通用属性使用
*{
pading:0;
margin:0;
list-style: none;
}
/*对页面中所有的标签都起作用*/
选择器的优先级:行内 > Id > class>标签
导入方式的优先级:行内样式>内嵌样式>外链样式>导入样式
注意事项: 他们的优先级不是固定的,以哪种方式举例修饰的目标最近,那么谁的优先级就越高 — 就近原则
案例使用:
实现代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title></title><style>*{margin: 0px;padding: 0px;}.demo1{color: yellow;width: 200px;height: 200px;background: red;}#id1{color: yellow;width: 200px;height: 200px;background:black;}</style></head><body><div class="demo1">demo1</div><div id="id1">id1</div></body>
</html>输出结果:

这里我们同时可以设置整体边框大小以及颜色:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title></title><style>*{margin: 0px;padding: 0px;}div{border: 10px solid blue;}.demo1{color: yellow;width: 200px;height: 200px;background: red;}#id1{color: yellow;width: 200px;height: 200px;background:black;}</style></head><body><div class="demo1">demo1</div><div id="id1">id1</div></body>
</html>输出结果:

组合选择器
| 选择器 | 代码格式 |
|---|---|
| 子选择器 | 元数 空格 元素{属性:值} |
| 后代选择器 | 元数 > 元数{属性:值} |
| 属性选择器 | 元素[属性]{} |
选择 <div> 元素内的所有 <p> 元素
div p {
background-color: red;
}
选择class为red的<div>
div.red{
font-size: 30px;
color: red;
}
同时选中h1标签和p标签
h1,p{
text-align: center;
font-size: 30px;
}
选择div下所有为p的子元素
div > p {
background-color: yellow;
}
选择p下面含有title属性的元素
p[title]{
color: red;
}
选择ul下中的li的第一个子元素
ul>li:first-child{
color: red;
}
选择ul下中的li的最后一个子元素
ul>li:last-child{
color: red;
}
选择ul下中的li的第二个子元素(括号里的数字可以改变比如写3就表示选中第三个元素,写n就表示全选中)
ul>li:nth-child(2){
color: red;
}
选择ul下中的li中的所有子元素除了第二个子元素
ul>li:not(:nth-child(2)){
color: red;
}
实例使用:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title></title><style>*{margin: 0px;padding: 0px;}/*div{border: 10px solid blue;}*/.demo1,#id1{width: 200px;height: 200px;}.demo1{color: yellow;background: red;}#id1{color: yellow;background:black;}.demo2 p{color: red;}</style></head><body><div class="demo1">demo1</div><div id="id1">id1</div><div class="demo2"><p>这是一个段落</p><p>测试</p>测试</div></body>
</html>输出结果:

五、背景
background-color 规定要使用的背景颜色。
background-position 规定背景图像的位置。
background-size 规定背景图片的尺寸。
background-repeat 规定如何重复背景图像。
background-origin 规定背景图片的定位区域。
background-clip 规定背景的绘制区域。
常见属性:
| 功能 | 语法 |
|---|---|
| 背景 | background:颜色 图片 平铺方式 固定方式 位置 |
| 背景颜色 | background-color:#ccc; |
| 背景图像 | background-image:url(背景图像的位置及全称) |
| 背景图像的重复方式 | background-repeat:[repeat、no-repeat、repeat-x、repeat-y] |
| 背景图像的位置 | background-position:top[left center right]center[left center right] bottom[left center right],坐标 y坐标[第一个值是水平位置,第二个值是垂直位置。左上角是0 0.单位是像素(0px 0px) |
| m背景图像的依附方式 | background-attachment;[scroll、fixed] |
repeat 默认。背景图像将在垂直方向和水平方向重复。
repeat-x 背景图像将在水平方向重复。
repeat-y 背景图像将在垂直方向重复。
no-repeat 背景图像将仅显示一次。
inherit 规定应该从父元素继承 background-repeat 属性的设置。
background-attachment 规定背景图像是否固定或者随着页面的其余部分滚动。
background-image 规定要使用的背景图像。
inherit 规定应该从父元素继承 background 属性的设置。
left top
left center
left bottom
right top
right center
right bottom
center top
center center
center bottom
简写
background: url(images/bg.gif) no-repeat top right
背景图片的滚动
背景图片是否随着内容的滚动而滚动由background-attachment设置
background-attachment:fixed; 固定,不随内容的滚动而滚动
background-attachment:scroll; 滚动,随内容的滚动而滚动
案例讲解:
实现代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title></title><style>body{/*background-color: #FFFF00;*/background-image: url(img/1.jpg);background-repeat: no-repeat;background-attachment: fixed;/*background-repeat:repeat-y;background-repeat:repeat-x;*/}</style></head><body><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p><p>xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx</p></body>
</html>输出结果:

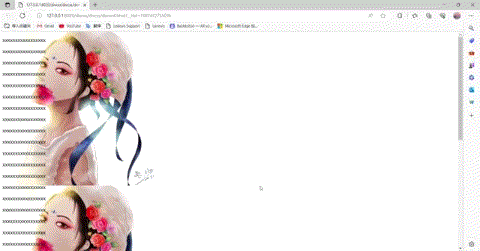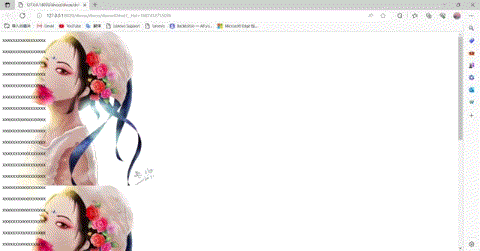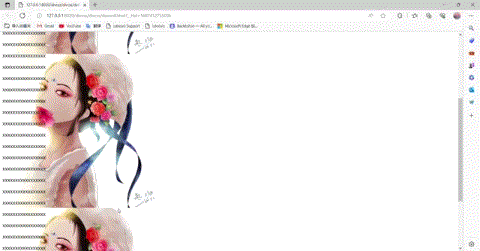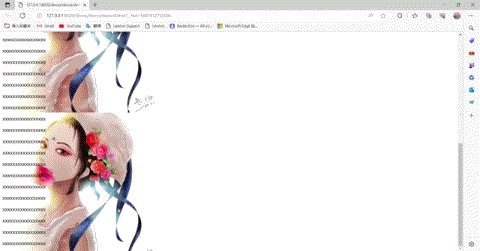
这里可以看到图片是不随着滑动的。,当然我们也可以将fixed改为scorll,并垂直方向重复
实现代码:
body{/*background-color: #FFFF00;*/background-image: url(img/1.jpg);background-attachment: scroll;background-repeat:repeat-y;/*background-repeat:repeat-x;*/}
输出结果:
同时,我们也可以进行简写:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title></title><style>body{/*background-color: #FFFF00;background-image: url(img/1.jpg);background-repeat: no-repeat;background-attachment: fixed;/*background-repeat:repeat-y;background-repeat:repeat-x;*/background: url(img/1.jpg) no-repeat fixed;}</style></head><body></body>
</html>输出结果:

六、边框
边框颜色 border-color:#000
边框宽度 border-width:1px;
border-left 设置左边框,一般单独设置左边框样式使用
border-right 设置右边框,一般单独设置右边框样式使用
border-top 设置上边框,一般单独设置上边框样式使用
border-bottom 设置下边框,一般单独设置下边框样式使用,有时可将下边框样式作为css下划线效果应用。
边框样式值如下:
none : 无边框。与任何指定的border-width值无关
hidden : 隐藏边框。IE不支持
dotted: 在MAC平台上IE4+与WINDOWS和UNIX平台上IE5.5+为点线。否则为实线(常用)
dashed : 在MAC平台上IE4+与WINDOWS和UNIX平台上IE5.5+为虚线。否则为实线(常用)
solid : 实线边框(常用)
double : 双线边框。两条单线与其间隔的和等于指定的border-width值
上 右 下左
groove : 根据border-color的值画3D凹槽
ridge : 根据border-color的值画菱形边框
inset: 根据border-color的值画3D凹边
outset : 根据border-color的值画3D凸边
上 右 下左
简写
border:5px solid red;
案例配合使用:
实现代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title></title><style>.demo6{/*width: 400px;height: 400px;border-width: 10px;border-style: solid;border-color: red;*/border: 1px solid red;height: 400px;width: 400px;}.demo7{margin-top:10px;width: 500px;height: 500px;border-width: 20px;border-color: red;border-top: solid;border-left:double;border-right: dotted ;border-bottom: groove;}</style></head><body><div class="demo6"></div><div class="demo7"></div></body>
</html>输出结果:
 /
/
七、文字属性
color:red; 文字颜色 #ffeeees
font-size:12px; 文字大小
font-weight:bolds 文字粗细(bold/normal)
font-family:”宋体”文字字体
font-variant:small-caps小写字母以大写字母显示
| 功能 | 语法 |
|---|---|
| 设置字号 | font-size:12px |
| 设置字色 | color:#000000 |
| 设置字体 | font-family:Arial,‘宋体’ |
| 设置行高 | line-height:150% line-height:1.5em |
| 设置字体的粗细 | font-weight:normal[正常]bold[粗体] |
| 设置对象中文本的缩进 | text-indent:2em 可以为负值 |
| 文本水平对齐方式 | text-align:left[左]center[中]right[右] |
| 设置文本划线 | text-decoration: none; [没有下划线]underline [下划线]overline [上划线]line-througn [贯穿线] |
| 文本大小写控制 | text-transform:none[正常大小]capitalize[每个单词的第一个字母转换成大写]uppercase[转换成大写]lowercase[转换成小写] |
浏览器默认字体大小为: 16px.
常用单位: px 像素 em当前字体尺寸
- 1、继承:
网页中子元素,将继承父元素的样式
例如:要控制段落p中的文字大小,可以直接给body标记加样式。 - 2、层叠:
网页中子元素定义了与父元素相同的样式,则子元素的样式将覆盖掉父元素的样式
后面定义的样式,会覆盖前面定义的样式
八、文本属性
text-align:center; 文本对齐(right/left/center)
line-height:10px; 行间距(可通过它实现文本的垂直居中)
text-indent:20px; 首行缩进
text-decoration:none;
文本线(none/underline/overline/line-through) underline/overline/line-through; 定义文本上的下划线/上划线/中划线
letter-spacing: 字间距
字体文本以及文本属性的案例使用:
实现代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>文字 文本的属性</title><style>body{color:red;font-family: "微软雅黑";font-size: 14px;}.demo7{font-variant:small-caps;border: 1px solid red;text-align: center;}.p1{line-height: 30px;text-indent:20px;}</style></head><body><div class="demo7">HCIP</div>
<p class="p1">高级网络工程师<span style="font-weight:bold;">HCIP笔记</span> 如果该设备是这个FEC的出站LSR时,LDP才会主动为这个FEC分配标签。
例如,R4是4.0网段的出站LSR,则R4会主动为4.0网段分配一个标签。但是R1,R2,R3均不是出站LSR,则都不会主动分配标签。
但是,构建LSP时也都需要有4.0网段的标签。所以,当R4将自己的标签信息传递到R3时,R3收到后,将进行检查环节
看本地路由表中是否存在到达4.0网段的路由信息,且路由表中的下一跳是否和通告者相同,
如果检查成功,则R3也会为4.0网段分配一个标签,依次类推。
<a href="https://www.baidu.com">点击了解</a></p></body>
</html>输出结果:

九、列表
list-style-type 设置列表项标记的类型。
参阅:list-style-type 中可能的值。
list-style-position 设置在何处放置列表项标记。
参阅:list-style-position 中可能的值。
list-style-image 使用图像来替换列表项的标记。
参阅: list-style-image 中可能的值。
inherit 规定应该从父元素继承 list-style 属性的值
取值:disc | circle | square | decimal | decimal-leading-zero | lower-roman | upper-roman | lower-greek | lower-latin | upper-latin | armenian | georgian | lower-alpha | upper-alpha | none | inherit
disc: 点
circle: 圆圈
square: 正方形
decimal: 数字
decimal-leading-zero: 十进制数,不足两位的补齐前导0,例如: 01, 02, 03, ..., 98, 99
lower-roman: 小写罗马文字,例如: i, ii, iii, iv, v, ...
upper-roman: 大写罗马文字,例如: I, II, III, IV, V, ...
lower-greek: 小写希腊字母,例如: α(alpha), β(beta), γ(gamma), ...
lower-latin: 小写拉丁文,例如: a, b, c, ... z
upper-latin: 大写拉丁文,例如: A, B, C, ... Z
armenian: 亚美尼亚数字
georgian: 乔治亚数字,例如: an, ban, gan, ..., he, tan, in, in-an, ...
lower-alpha: 小写拉丁文,例如: a, b, c, ... z
upper-alpha: 大写拉丁文,例如: A, B, C, ... Z
none: 无(取消所有的list样式)
inherit: 继承
list-style-position
inside
列表项目标记放置在文本以内,且环绕文本根据标记对齐。
outside
默认值。保持标记位于文本的左侧。列表项目标记放置在文本以外,且环绕文本不根据标记对齐。
简写
list-style:square inside url('/i/arrow.gif');
十、超链接
a{text-decoration: none;}
a:link {color:#FF0000;} /* 未访问的链接 */
a:visited {color:#00FF00;} /* 已访问的链接 */
a:hover {color:#FF00FF;} /* 鼠标划过链接 */
a:active {color:#0000FF;} /* 已选中的链接 */
列表及超链接的案例使用:
实现代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>ZY技术分享</title><style>.demo8{/*list-style: decimal;list-style-position:outside;list-style-image:url(img/e.gif);*/list-style: url(img/e.gif) outside;}.demo8 a{text-decoration: none;}.demo8 a:hover{color: red;}.demo8 a:visited {color: yellow;}.demo8 a:link{color: brown;}.demo8 a:active{color: blue;}</style></head><body><ul class="demo8"><li><a href="http://blog.csdn.net/weixin_63172698">TCP四次握手讲解及抓包分析</a></li><li><a href="http://blog.csdn.net/weixin_63172698">DHCP协议讲解及抓包分析</a></li><li><a href="http://blog.csdn.net/weixin_63172698">RIP路由信息协议</a></li><li><a href="http://blog.csdn.net/weixin_63172698">动态路由协议讲解</a></li><li><a href="https://www.google.com">NAT技术讲解</a></li></ul></body>
</html>输出结果:

十一、盒子模型

盒子模型的组成部分
外边距(margin)、边框(border)、内边距(padding)、内容(content)四个属性
自身的身高 width height
内边距 padding
盒子边框 border
与其他盒子的距离 margin 外边距
常见属性:
| 功能 | 语法 |
|---|---|
| 设置元素的宽度 | width:100px; |
| 设置元素的高度 | height:100px; |
| 设置元素的某一个方向外边距 | margin-top/right/bottom/left:10px; |
| 设置外边距 | margin:10px;上下左右4个方向 margin:10px 20px;上下 左右 margin:10px 20px 30px;上 左右 下 margin:10px 20px 30px 上 右 下 左 |
| 设置内边距 | padding:10px;上下左右四个方向(跟margin的用法一样) |
| 设置边框粗细 | border-top-width:12px; |
| 设置边框样式 | border-top-style:solid[实线]、dashed[虚线] |
| 设置边框颜色 | border-top-color:#000000 |
| 设置某一边框属性的简捷方式 | border-边框位置:线框 线型 颜色; |
| 设置某一个元素四条边框的简捷方式 | border:线框 线型 颜色; |
案例使用:
实现代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>ZY技术分享</title><style>.demo10{width: 400px;height: 400px;border-width: 10px;/*border-style: dotted ;*/border-top: solid;border-bottom: dashed;border-left: dotted ;border-right: double;border-color: red;}</style></head><body><div class="demo10">demo10</div></body>
</html>输出结果:


十二、Border 边框
常见的写法 border:1px solid #foo;
单独属性:
border-widh:
border-style:
dotted 点状虚线
dashed(虚线)
solid(实线)
double(双实线)
border-color(颜色)
设置外边距的使用:
实现代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title></title><style>.demo12{width: 400px;height: 400px;border: 1px solid red;margin: 20px 30px 10px 40px;}</style></head><body><div class="demo12">demo12</div><div class="demo12">demo12</div></body>
</html>输出结果:

margin padding
padding:内边距值:像素/厘米等长度单位、百分比
padding:10px; 上下左右
padding:10px 10px; 上下 左右
padding:10px 10px 10px; 上 左右 下
padding:10px 10px 10px 10px; 上 右 下 左(设置4个点–>顺时针方向)
单独属性
padding-top:
padding-right:
padding-bottom:
padding-left:
当设置内边距的时候会把盒子撑大,为了保持盒子原来的大小,应该高度和宽度进行减小,根据width和height减小
margin
外边距值:与padding相同
单独属性:与padding相同
案例使用:
实现代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title></title><style>.demo12{width: 400px;height: 400px;border: 1px solid red;/*margin: 20px 30px 10px 40px;*/padding-top: 10px;padding-bottom: 20px;margin-top:20px;}</style></head><body><div class="demo12">demo12</div><div class="demo12">demo12</div></body>
</html>输出结果:


外边距合并: 两个盒子同时设置了外边距,会进行一个外边距合并
margin
margin:10px 上下左右都会腾出10px出来
margin:0px auto; 居中
案例使用:
实现代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title></title><style>.demo13{width: 400px;height: 400px;border: 1px solid red;/*margin: 20px 30px 10px 40px;*/margin: 0px auto;text-align: center;}</style></head><body><div class="demo13">demo12</div></body>
</html>输出结果:

十三、float 脱离文档流浮动
left 元素向左浮动。
right 元素向右浮动
清除浮动
clear: both;
left
right
案例使用:
实现代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title></title><style>div{width: 200px;height: 200px;border: 1px solid red;}.div1,.div2{float: left;}.div3 {float: right;}.div4{width: 400px;height: 400px;border: 1px solid blue;clear: both;}</style></head><body><div class="div1">div1</div><div class="div2">div2</div><div class="div3">div3</div><div class="div4">div4</div></body>
</html>输出结果:

十四、块级元素、行内元素
块级元素:
他会独占一行,在默认情况下,其宽度自动填满其父元素的宽度;
块级元素可以设置width、height属性;
块级元素即使设置了宽度也是独占一行,块级元素可以设置margin、padding属性;
display:block; 块状元素的默认属性,具有宽度和高度属性 width height,比较霸道,不允许其他元素和它同行显示,常见块状元素为div、p、body、h1-h6 等
案例学习:
实现代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>ZY技术分享</title><style>.demo15,h1,form{border: 1px solid red;height: 100px;width: 400px;}</style></head><body><div class="demo15">demo15</div><h1>h1</h1><form>表单</form><a href="https://www.baidu.com">baidu</a><label>标签</label><input type="text" value="输入的内容"></body>
</html>输出结果:

行内元素:
行内元素不会独占一行,相邻的行内元素会排列在同一行里,直到行排不下,就自动换行,其宽度随内容而变化;
行内元素的width、height属性则无效;
行内元素的margin、padding属性很奇怪,水平方向的padding-left、padding-rigtht、margin-left、padding-right都会产生边距效果,但是竖直方向的padding-top、padding-bottom、margin-top、margin-bottom却不产生边距效果。
display:inline 内联元素的属性,不具有 高度和宽度 这两个属性,允许其他元素和它同行显示,常见内联元素为a、em、span 等
案例学习:
实现代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title></title><style>.demo16,.demo17{border: 1px solid red;height: 100px;width: 400px;display: block;}.s1,.s2{border: 1px solid red;display:inline-block;height: 100px;width: 100px;}</style></head><body><div class="demo16">demo16</div><div class="demo17">demo17</div><span class="s1">sss</span><span class="s2">sss</span></body>
</html>输出结果:

行内元素转换
display:none; 不显示
display:block;变成块级元素
display:inline; 变成行内元素
display:inline-block;以块级元素样式展示,以行级元素样式排列
块级元素(block element)
address 地址
center 举中对齐块
div- 常用块级容易
dl 定义列表
form 交互表单 (只能用来容纳其它块元素)
h标签
hr 水平分隔线
ol 无需列表
ul有序列表
p 段落
pre 格式化文本
行内元素:
a - 锚点
b - 粗体(不推荐)
br- 换行
code - 计算机代码(在引用源码的时候需要)
em - 强调
i - 斜体
img - 图片(特殊的内联元素,同时是内联替换元素,替换元素可以设置宽高)
<font color=darkblue>当图片和DIV在一起时,图片周围会出现margin现象,即元素不重合贴在一起,为了解决这个问题,设置img的css为{margin:0;display:block;border:0px}
input - 输入框
label - 表格标签
select - 项目选择
strong - 粗体强调
textarea - 多行文本输入框
u - 下划线
var - 定义变量
替换元素有如下:(和img一样的设置方法)
<img>、<input>、<textarea>、<select><object>都是替换元素,这些元素都没有实际的内容
十五、溢出
overflow 属性规定当内容溢出元素框时发生的事情。
visible 默认值。内容不会被修剪,会呈现在元素框之外。
hidden 内容会被修剪,并且其余内容是不可见的。
scroll 内容会被修剪,但是浏览器会显示滚动条以便查看其余的内容。
auto 如果内容被修剪,则浏览器会显示滚动条以便查看其余的内容。
inherit 规定应该从父元素继承 overflow 属性的值。
案例使用:
实现代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title></title><style>.demo17{width: 200px;height: 200px;border: 1px solid red;overflow:hidden;}</style></head><body><div class="demo17">ssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssss</div></body>
</html>输出结果:

十六、定位
position
static静态定位(不对它的位置进行改变,在哪里就在那里)
position:static(默认值)只有设置了除了static(默认值)的定位才能设置(偏移量)top,bottom,left,right
默认值。没有定位,元素出现在正常的流中(忽略 top,bottom, left, right 或者z-index 声明)。
fixed固定定位(参照物–浏览器窗口)— 做弹窗广告用到
position: fixed;(固定定位)固定定位也是一种绝对定位,所以固定定位的特点绝大部分和绝对定位一样,唯一不用的是固定定位永远参照浏览器的视口进行定位
生成固定定位的元素,相对于浏览器窗口进行定位。 元素的位置通过 "left", "top", "right"以及 "bottom"属性进行规定。
relative(相对定位 )(参照物以他本身)
position: sticky;(粘滞定位)粘滞定位的特点和我们的相对定位的特点基本一致,但是不同的时粘滞定位可以在元素到达某个位置的时候将其固定。
生成相对定位的元素,相对于其正常位置进行定位。
absolute(绝对定位)(除了static都可以,找到参照物–>与它最近的已经有定位的父元素进行定位)
position:relative(相对定位)
1.元素开启定位以后,如果不设置偏移量元素不会发生任何变化
2.相对定位是参照于元素在文档流中的位置进行定位的
3.相对定位会提升元素的层级
4.相对定位不会使元素脱离文档流
5.相对定位不会改变元素的性质块还是块,行内还是行内
生成绝对定位的元素,相对于 static定位以外的第一个父元素进行定位。
元素的位置通过 "left", "top", "right" 以及"bottom" 属性进行规定
z-index,z-index 属性设置元素的堆叠顺序。拥有更高堆叠顺序的元素总是会处于堆叠顺序较低的元素的前面。
position: absolute;(绝对定位)
1.开启绝对定位后,如果不设置偏移量元素不会发生任何变化
2.开启绝对定位后,元素会从文档中脱离
3.绝对定位会改变元素的性质,行内变成块,块的宽高被内容撑开
4.绝对定位会提升元素一个层级
5.绝对定位元素是相对于其包含块进行定位的
定位的基本思想: 它允许你定义元素框相对于其正常位置应该出现的位置,或者相对于父元素、另一个元素甚至浏览器窗口本身的位置。
案例学习:
实现代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title></title><style>div{width: 300px;height: 300px;}.div1{background: red;}.div2{width: 500px;height: 500px;background: blue;position: relative;left: 40px;top:50px;}.div3{background: green;}.div4{width: 150px;height: 150px;background: yellow;position: absolute;top: 100px;left: 100px;z-index: -1;}.div5{width: 150px;height: 150px;background: black;position: absolute;top: 120px;left: 120px;z-index: 1;}</style></head><body><div class="div1"></div><div class="div2"><div class="div4"></div><div class="div5"></div></div><div class="div3"></div></body>
</html>输出结果: