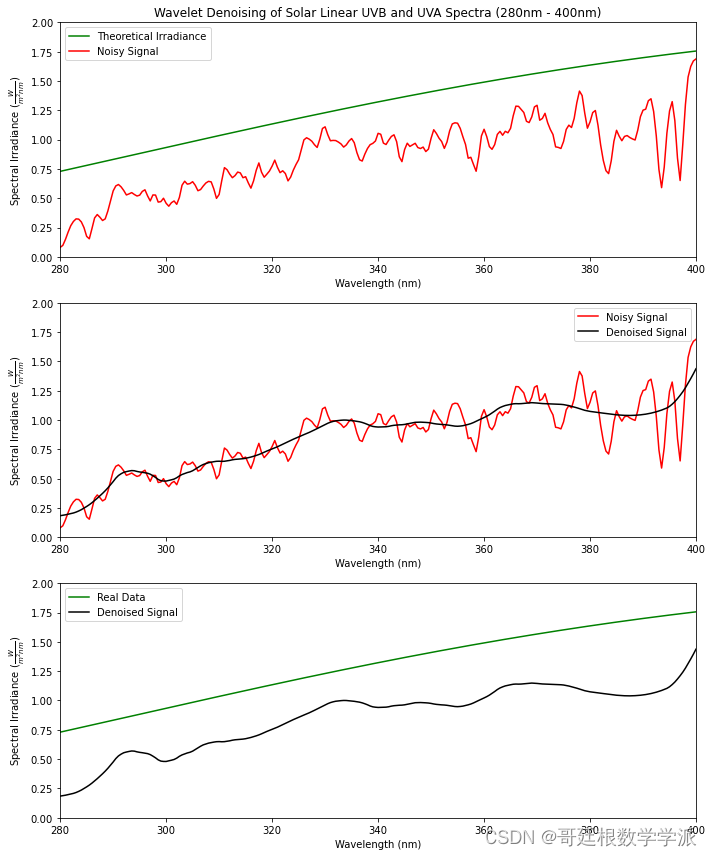
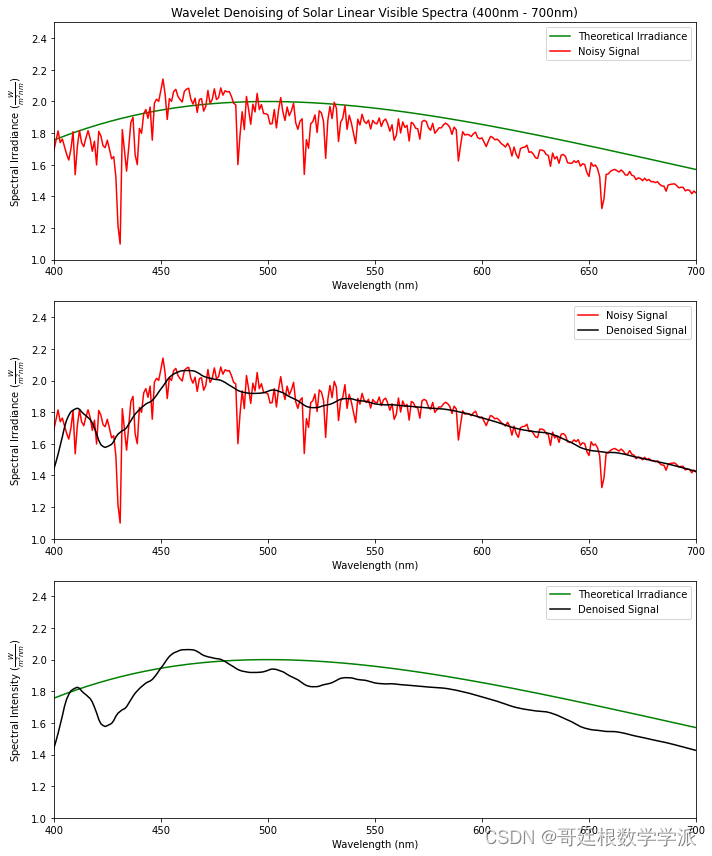
小波变换以其良好的时频局部化特性,成功地解决了保护信号局部性和抑制噪声之间的矛盾,因此小波技术在信号降噪中得到了广泛的研究,并获得了非常好的应用效果。小波降噪中最常用的方法是小波阈值降噪。基于小波变换的阈值降噪关键是要解决两个问题:阈值的选取和阈值函数的确定,目前常用的阈值选取原则有以下四种:通用阈值(sqtwolog原则)、Stein无偏似然估计阈值(rigrsure原则)、启发式阈值(heursure原则)、极大极小阈值(minimaxi原则)。
鉴于此,采用小波分析对电磁谱信号进行降噪,完整代码如下:
import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport pywtfrom scipy import constants as consdata = open('Data.txt', 'r')wl = []intensity = []for line in data:rows = [i for i in line.split()]wl.append(float(rows[0]))intensity.append(float(rows[1]))h = 6.626e-34 # Planck's constant (J·s)c = 3e8 # Speed of light (m/s)k = 1.381e-23 # Boltzmann constant (J/K)temperature = 5800 # Temperature (K)wien_constant = 2.897e-3 # Wien's displacement constant (m/K)desired_peak = 2# Wavelength range (in meters)wavelengths = np.linspace(280, 1100, 941) * 1e-9# Planck's law for spectral radiancedef planck_law(wavelength, temperature):return (8 * np.pi * h * c) / (wavelength**5) / (np.exp((h * c) / (wavelength * k * temperature)) - 1)# Calculate spectral radiance for the Sunspectral_irradiance = planck_law(wavelengths, temperature)# Normalize to have the peak value equal to the desired valuescaling_factor = desired_peak / np.max(spectral_irradiance)spectral_irradiance *= scaling_factorpeak_wavelength = 1e9*wien_constant / temperaturepeak_wavelengthDWTcoeffs = pywt.wavedec(intensity, 'db4')DWTcoeffs[-1] = np.zeros_like(DWTcoeffs[-1])DWTcoeffs[-2] = np.zeros_like(DWTcoeffs[-2])DWTcoeffs[-3] = np.zeros_like(DWTcoeffs[-3])DWTcoeffs[-4] = np.zeros_like(DWTcoeffs[-4])#DWTcoeffs[-5] = np.zeros_like(DWTcoeffs[-5])#DWTcoeffs[-6] = np.zeros_like(DWTcoeffs[-6])#DWTcoeffs[-7] = np.zeros_like(DWTcoeffs[-7])#DWTcoeffs[-8] = np.zeros_like(DWTcoeffs[-8])#DWTcoeffs[-9] = np.zeros_like(DWTcoeffs[-9])filtered_data=pywt.waverec(DWTcoeffs,'db4')filtered_data = filtered_data[:len(wl)]plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))plt.plot(wavelengths * 1e9, spectral_irradiance, color='green', label='Theoretical Irradiance')plt.plot(wl, intensity, color='red', label='Noisy Signal')plt.plot(wl, filtered_data, markerfacecolor='none',color='black', label='Denoised Signal')plt.annotate(str(temperature)+' K BlackBody Spectrum',ha = 'center', va = 'bottom',xytext = (900,1.75),xy = (700,1.60),arrowprops = { 'facecolor' : 'black', 'shrink' : 0.05 })plt.legend()plt.title('Wavelet Denoising of Solar Linear Spectra (280nm - 1100nm)')plt.xlabel(r'Wavelength (nm)')plt.ylabel(r'Spectral Irradiance $(\frac{W}{m^2nm})$')plt.axis([280, 1100, 0, 2.5])plt.show()plt.figure(figsize=(10, 12)) # Set the figure size for both subplots# Subplot 1plt.subplot(3, 1, 1) # Three rows, one column, index 1plt.plot(wavelengths * 1e9, spectral_irradiance, color='green', label='Theoretical Irradiance')plt.plot(wl, intensity, color='red', label='Noisy Signal')plt.legend()plt.title('Wavelet Denoising of Solar Linear UVB and UVA Spectra (280nm - 400nm)')plt.xlabel(r'Wavelength (nm)')plt.ylabel(r'Spectral Irradiance $(\frac{W}{m^2nm})$')plt.axis([280, 400, 0, 2])# Subplot 2plt.subplot(3, 1, 2) # Three rows, one column, index 2plt.plot(wl, intensity, color='red', label='Noisy Signal')plt.plot(wl, filtered_data, markerfacecolor='none', color='black', label='Denoised Signal')plt.legend()plt.xlabel(r'Wavelength (nm)')plt.ylabel(r'Spectral Irradiance $(\frac{W}{m^2nm})$')plt.axis([280, 400, 0, 2])# Subplot 2plt.subplot(3, 1, 3) # Three rows, one column, index 3plt.plot(wavelengths * 1e9, spectral_irradiance, color='green', label='Real Data')plt.plot(wl, filtered_data, markerfacecolor='none', color='black', label='Denoised Signal')plt.legend()plt.xlabel(r'Wavelength (nm)')plt.ylabel(r'Spectral Irradiance $(\frac{W}{m^2nm})$')plt.axis([280, 400, 0, 2])plt.tight_layout() # Adjust layout to prevent overlappingplt.show()plt.figure(figsize=(10, 12)) # Set the figure size for both subplots# Subplot 1plt.subplot(3, 1, 1) # Three rows, one column, index 1plt.plot(wavelengths * 1e9, spectral_irradiance, color='green', label='Theoretical Irradiance')plt.plot(wl, intensity, color='red', label='Noisy Signal')plt.legend()plt.title('Wavelet Denoising of Solar Linear Visible Spectra (400nm - 700nm)')plt.xlabel(r'Wavelength (nm)')plt.ylabel(r'Spectral Irradiance $(\frac{W}{m^2nm})$')plt.axis([400, 700, 1, 2.5])# Subplot 2plt.subplot(3, 1, 2) # Three rows, one column, index 2plt.plot(wl, intensity, color='red', label='Noisy Signal')plt.plot(wl, filtered_data, markerfacecolor='none', color='black', label='Denoised Signal')plt.legend()plt.xlabel(r'Wavelength (nm)')plt.ylabel(r'Spectral Irradiance $(\frac{W}{m^2nm})$')plt.axis([400, 700, 1, 2.5])# Subplot 2plt.subplot(3, 1, 3) # Three rows, one column, index 3plt.plot(wavelengths * 1e9, spectral_irradiance, color='green', label='Theoretical Irradiance')plt.plot(wl, filtered_data, markerfacecolor='none', color='black', label='Denoised Signal')plt.legend()plt.xlabel(r'Wavelength (nm)')plt.ylabel(r'Spectral Intensity $(\frac{W}{m^2nm})$')plt.axis([400, 700, 1, 2.5])plt.tight_layout() # Adjust layout to prevent overlappingplt.show()plt.figure(figsize=(10, 12)) # Set the figure size for both subplots# Subplot 1plt.subplot(3, 1, 1) # Three rows, one column, index 1plt.plot(wavelengths * 1e9, spectral_irradiance, color='green', label='Theoretical Irradiance')plt.plot(wl, intensity, color='red', label='Noisy Signal')plt.legend()plt.title('Wavelet Denoising of Solar Linear Visible Spectra (400nm - 700nm)')plt.xlabel(r'Wavelength (nm)')plt.ylabel(r'Spectral Irradiance $(\frac{W}{m^2nm})$')plt.axis([700, 1100, 0, 2.5])# Subplot 2plt.subplot(3, 1, 2) # Three rows, one column, index 2plt.plot(wl, intensity, color='red', label='Noisy Signal')plt.plot(wl, filtered_data, markerfacecolor='none', color='black', label='Denoised Signal')plt.legend()plt.xlabel(r'Wavelength (nm)')plt.ylabel(r'Spectral Irradiance $(\frac{W}{m^2nm})$')plt.axis([700, 1100, 0, 2.5])# Subplot 2plt.subplot(3, 1, 3) # Three rows, one column, index 3plt.plot(wavelengths * 1e9, spectral_irradiance, color='green', label='Theoretical Irradiance')plt.plot(wl, filtered_data, markerfacecolor='none', color='black', label='Denoised Signal')plt.legend()plt.xlabel(r'Wavelength (nm)')plt.ylabel(r'Spectral Irradiance $(\frac{W}{m^2nm})$')plt.axis([700, 1100, 0, 2.5])plt.tight_layout() # Adjust layout to prevent overlappingplt.show()def calculate_mse(original, denoised):mse = np.mean(np.square(np.subtract(original, denoised)))return msedef calculate_rmse(original, denoised):mse = calculate_mse(original, denoised)rmse = np.sqrt(mse)return rmsedef calculate_psnr(original, denoised):max_pixel_value = 255.0 # Assuming pixel values are in the range [0, 255]mse_value = calculate_mse(original, denoised)psnr = 10 * np.log10((max_pixel_value ** 2) / mse_value)return psnr# Assuming 'original_signal' and 'denoised_signal' are your original and denoised signals as lists or arraysmse_value = calculate_mse(spectral_irradiance, filtered_data)rmse_value = calculate_rmse(spectral_irradiance, filtered_data)psnr_value = calculate_psnr(spectral_irradiance, filtered_data)print(f"MSE: {mse_value}")print(f"RMSE: {rmse_value}")print(f"PSNR: {psnr_value} dB")

工学博士,担任《Mechanical System and Signal Processing》审稿专家,担任《中国电机工程学报》优秀审稿专家,《控制与决策》,《系统工程与电子技术》,《电力系统保护与控制》,《宇航学报》等EI期刊审稿专家。
擅长领域:现代信号处理,机器学习,深度学习,数字孪生,时间序列分析,设备缺陷检测、设备异常检测、设备智能故障诊断与健康管理PHM等。