双向链表
单链表结点中只有一个指向其后继的指针,使得单链表只能从前往后依次遍历,要访问某个结点的前驱(插入、删除操作时),只能从头开始遍历,访问前驱的时间复杂度为O(N)。为了克服这个缺点,引入了双链表。
循环链表
循环单链表和单链表的区别在于,表中最后一个结点的指针不是NULL,而改为指向头结点,从而整个链表形成一个环,如图所示。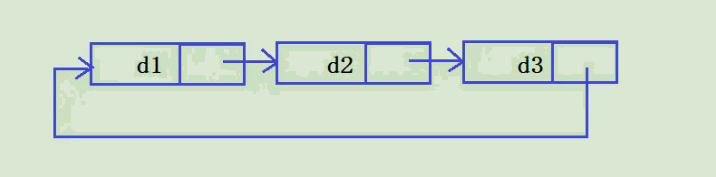
在循环单链表中,表尾结点d3的next域指向d1,故表中没有指针域为NULL的结点,因此,循环单链表的判空条件不是头结点的指针是否为空,而是它是否等于头指针d1。
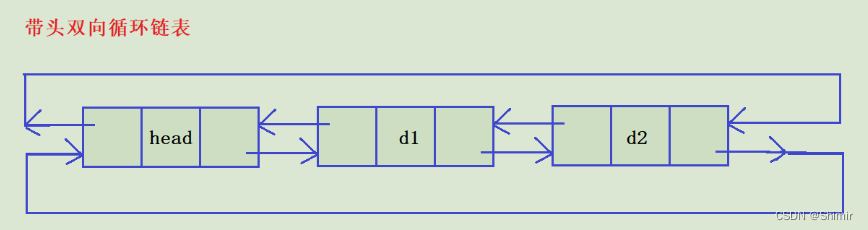
带头双向循环链表的增删查改
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>typedef int LTDataType;typedef struct ListNode
{LTDataType data;struct ListNode* next;struct ListNode* prev;
}ListNode;//创建返回链表的头结点
ListNode* BuyLTNode(LTDataType x);//初始化双向链表
ListNode* ListInit();//销毁双向链表
void ListDestory(ListNode* phead);//打印双向链表
void ListPrint(ListNode* phead);//判断链表是否为空
bool LTEmpty(ListNode* phead);//查找双向链表
ListNode* LTFind(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x);//双向链表的头插
void ListPushFront(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x);//双向链表的尾插
void ListPushBack(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x);//双向链表的头删
void ListPopFront(ListNode* phead);//双向链表的尾删
void ListPopBack(ListNode* phead);//双向链表在pos位置之前的插入
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x);//双向链表删除pos位置的结点
void ListErase(ListNode* pos);
双向链表的头插
#include "list.h"//创建返回链表的头结点
ListNode* BuyLTNode(LTDataType x)
{ListNode* newnode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("newnode malloc fail");return NULL;}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;newnode->prev = NULL;return newnode;
}//初始化双向链表
ListNode* ListInit()
{ListNode* phead = BuyLTNode(-1);phead->next = phead;phead->prev = phead;return phead;
}//销毁双向链表
void ListDestory(ListNode* phead)
{assert(phead);ListNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){ListNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}free(phead);
}//打印双向链表
void ListPrint(ListNode* phead)
{assert(phead);printf("sentinel《==》");ListNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){printf("%d《==》", cur->data);cur = cur->next;}printf("\n");
}//判断链表是否为空
bool LTEmpty(ListNode* phead)
{assert(phead);return phead->next == phead;//等于就是空
}//查找双向链表
ListNode* LTFind(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{assert(phead);ListNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){if (cur->data == x){return cur;}cur = cur->next;}return NULL;
}//双向链表的头插
void ListPushFront(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{assert(phead);/*ListInsert(phead->next,x);//使用 Insert 进行头插*/ListNode* newnode = BuyLTNode(x);ListNode* frist = phead->next;phead->next = newnode;newnode->prev = phead;newnode->next = frist;frist->prev = newnode;/*newnode->next = phead->next;phead->next->prev = newnode;newnode->prev = phead;phead->next = newnode;*/
}//双向链表的尾插
void ListPushBack(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{assert(phead);/*ListInsert(phead->prev,x);//使用 Insert 进行尾插*/ListNode* newnode = BuyLTNode(x);ListNode* tail = phead->prev;newnode->next = phead;phead->prev = newnode;newnode->prev = tail;tail->next = newnode;
}//双向链表的头删
void ListPopFront(ListNode* phead)
{assert(phead);assert(!LTEmpty(phead));//断言条件尽量不写在一起,不然无法判断是其中哪个条件出错/*ListErase(phead->next);//使用 Erase 进行头删*/ListNode* frist = phead->next;ListNode* fristnext = frist->next;//增加代码的可读性free(frist);phead->next = fristnext;fristnext->prev = phead;/*if (frist != phead){frist->next->prev = phead;phead->next = frist->next;free(frist);}*/
}//双向链表的尾删
void ListPopBack(ListNode* phead)
{assert(phead);assert(!LTEmpty(phead));/*ListErase(phead->prev);//使用 Erase 进行尾删*/ListNode* tail = phead->prev;ListNode* tailprev = tail->prev;free(tail);tailprev->next = phead;phead->prev = tailprev;/*if (tail != phead){phead->prev = tail->prev;tail->prev->next = phead;free(tail);}*/
}//双向链表在pos位置之前的插入
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x) {assert(pos);ListNode* prev = pos->prev;ListNode* newnode = BuyLTNode(x);prev->next = newnode;newnode->prev = prev;newnode->next = pos;pos->prev = newnode;
}//双向链表删除pos位置的结点
void ListErase(ListNode* pos) {assert(pos);//注意,当pos传递为phead的值时,即哨兵位值时,会出现错误。//可将phead传递进来,使pos!=phead,,,否则就干脆不判断,出现错误时再解决ListNode* prev = pos->prev;ListNode* next = pos->next;prev->next = next;next->prev = prev;free(pos);
}
#include "list.h"void test1()
{ListNode* plist = ListInit();ListPushFront(plist, 1);ListPushFront(plist, 1);ListPushFront(plist, 2);ListPushFront(plist, 2);ListPushFront(plist, 3);ListPushFront(plist, 3);ListPushBack(plist, 11);ListPushBack(plist, 22);ListPrint(plist);ListPopFront(plist);ListPopBack(plist);ListPrint(plist);ListNode* pos = LTFind(plist,3);ListInsert(pos, 33);pos = LTFind(plist, 1);ListErase(pos);ListPrint(plist);ListDestory(plist);plist = NULL;
}int main()
{test1();return 0;
}
顺序表和链表比较
顺序表的优点:
1.尾插尾删效率不错,
2.下标的随机访问
3.CPU高速缓存命中率会更高(物理空间时连续的)
顺序表的缺点:
1.前面部分插入删除数据,效率低O(N),需要依次挪动数据,物理空间是连续的。
2.连续的物理空间,空间不够,需要扩容。
a.扩容是需要付出代价的
b.一般伴随着空间浪费
链表的优点:
1.任意位置插入删除,O(1)。ex:带头双向循环链表
2.按需申请空间
链表的缺点:
1.不支持下标的随机访问
2.CPU高速缓存命中率会更低