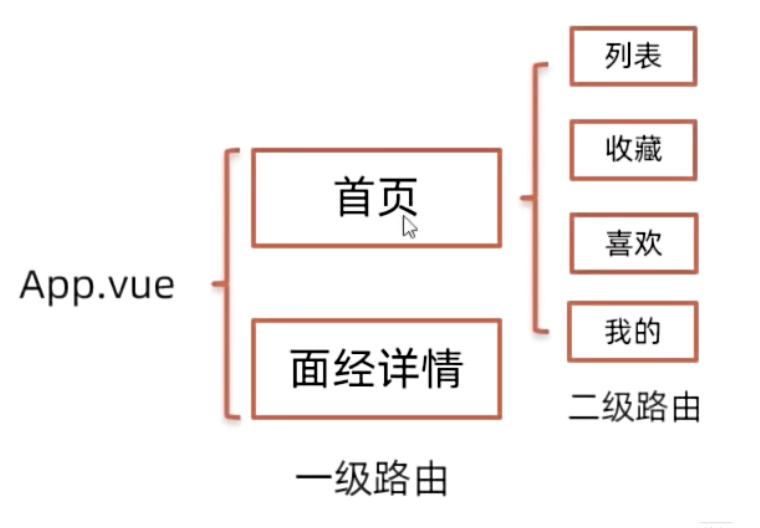
Vue2:路由
Date: May 28, 2023
Sum: vue-router基本使用、高级用法
单页面应用程序
概念:SPA【Single Page Application】是指所有的功能都在一个html页面上实现
案例:
单页应用网站: 网易云音乐 https://music.163.com/
多页应用网站:京东 https://jd.com/
**单页应用 VS 多页面应用:
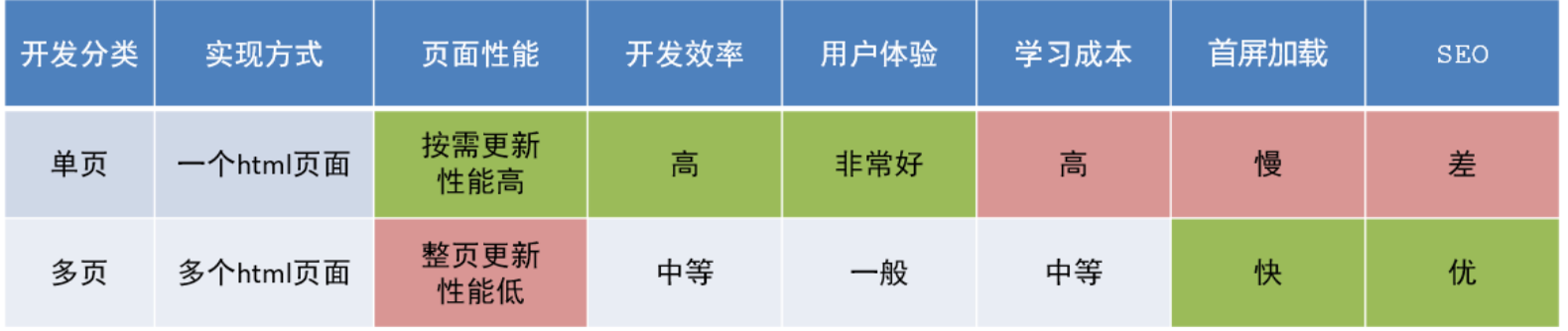
单页应用类网站:系统类网站 / 内部网站 / 文档类网站 / 移动端站点
多页应用类网站:公司官网 / 电商类网站
特点:
单页面应用程序将所有的功能局限于一个 web 页面中,仅在该 web 页面初始化时加载相应的资源( HTML、JavaScript 和 CSS)。
一旦页面加载完成了,SPA 不会因为用户的操作而进行页面的重新加载或跳转。而是利用JavaScript 动态地变换 HTML 的内容,从而实现页面与用户的交互。
注意:SPA它是按需更新的,并不是整体更新。因此,它需要更加关注访问路径与组件的对应关系
优点:
SPA 单页面应用程序最显著的 3 个优点如下:
① 良好的交互体验
单页应用的内容的改变不需要重新加载整个页面
获取数据也是通过 Ajax 异步获取
没有页面之间的跳转,不会出现“白屏现象”
② 良好的前后端工作分离模式
后端专注于提供 API 接口,更易实现 API 接口的复用
前端专注于页面的渲染,更利于前端工程化的发展
③ 减轻服务器的压力
服务器只提供数据,不负责页面的合成与逻辑的处理,吞吐能力会提高几倍
缺点:
任何一种技术都有自己的局限性,对于 SPA 单页面应用程序来说,主要的缺点有如下两个:
① 首屏加载慢
可以通过路由懒加载、代码压缩、CDN 加速、网络传输压缩处理
② 不利于 SEO
SSR 服务器端渲染
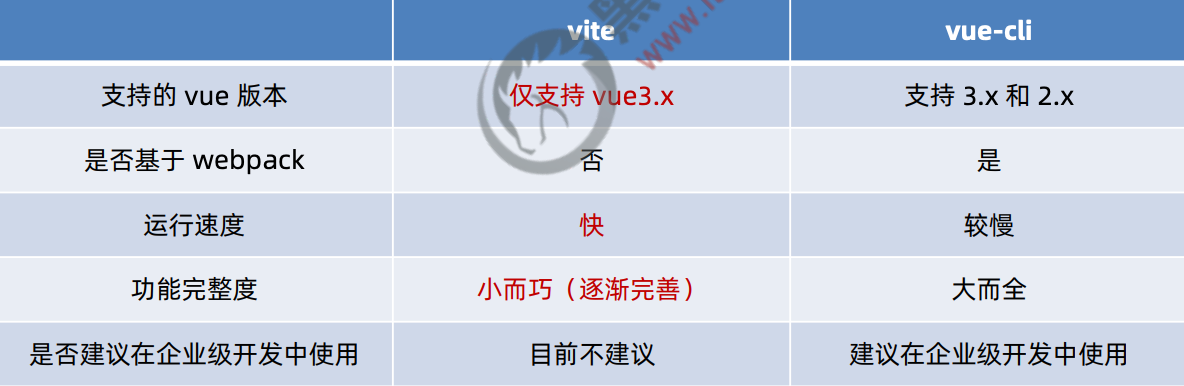
如何快速创建 vue 的 SPA 项目
vue 官方提供了两种快速创建工程化的 SPA 项目的方式:
① 基于 vite 创建 SPA 项目 ② 基于 vue-cli 创建 SPA 项目
总结:
概念:一个Web网站中只有唯一一个HTML页面,所有的功能与交互都在这唯一的一个页面内完成。
特点:
1.集中所有功能于单页面中,仅在该页面初始化时加载相应的资源。
2.通过JS动态变换页面内容,从而实现页面与用户的交互
优点:
-
良好的交互体验
没有页面跳转,不会有“白屏”现象
-
良好的前后端分离模式
前端专注页面渲染,更利于前端工程化发展;后端专注提供API接口,更易实现API接口复用
-
减轻服务端的压力
服务器只提供数据,不负责页面的合成与逻辑,吞吐能力提高几倍
缺点:
-
首屏加载慢
可以通过代码压缩、CDN加速、路由懒加载、网络传输压缩处理等
-
不利于SEO
SSR服务器端渲染
前端路由的概念与原理
思考:
单页面应用程序,之所以开发效率高,性能好,用户体验好
最大的原因就是:页面按需更新
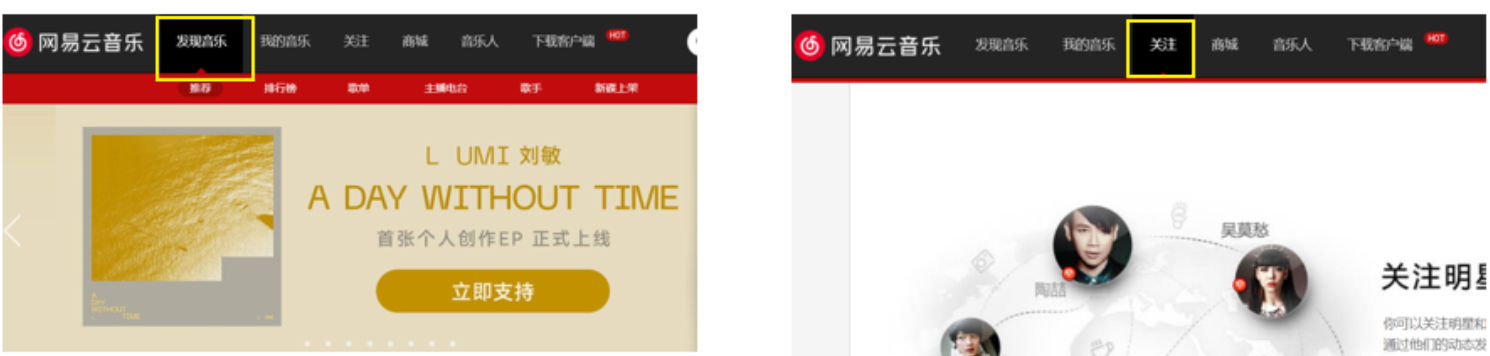
比如当点击【发现音乐】和【关注】时,只是更新下面部分内容,对于头部是不更新的
要按需更新,首先就需要明确:访问路径和 组件的对应关系!
访问路径 和 组件的对应关系如何确定呢? 路由
路由概念:
概念:路由(英文:router)就是对应关系。路由分为两大类: ① 后端路由 ② 前端路由
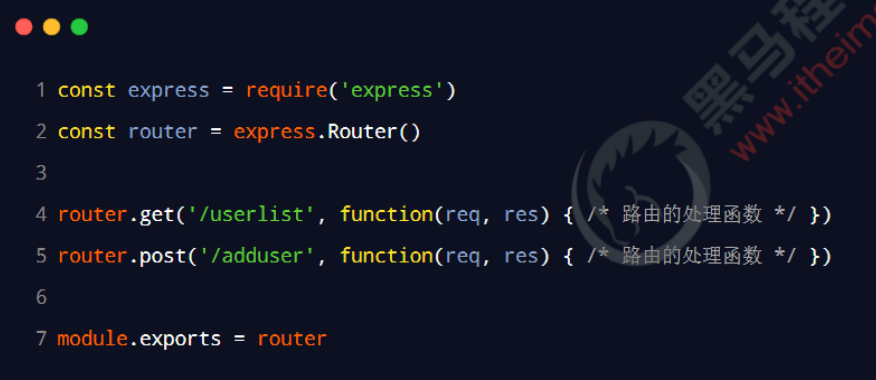
回顾:后端路由
后端路由指的是:请求方式、请求地址与 function 处理函数之间的对应关系。
在 node.js 课程中,express路由的基本用法如下:
前端路由:
SPA 与前端路由
SPA 指的是一个 web 网站只有唯一的一个 HTML 页面,所有组件的展示与切换都在这唯一的一个页面内完成。此时,不同组件之间的切换需要通过前端路由来实现。
结论:在 SPA 项目中,不同功能之间的切换,要依赖于前端路由来完成!
概念:Vue中的路由指 路径 与 组件 的映射关系,根据路由就能知道不同路径,应匹配渲染相应组件
通俗易懂的概念:Hash 地址与组件之间的对应关系。
我们点击不同的链接,会切换不同的哈希地址。当哈希地址切换,页面上就会展示对应组件。
工作方式:
① 用户点击了页面上的路由链接
② 导致了 URL 地址栏中的 Hash 值发生了变化
③ 前端路由监听了到 Hash 地址的变化
④ 前端路由把当前 Hash 地址对应的组件渲染都浏览器中

结论:前端路由,指的是 Hash 地址与组件之间的对应关系!
实现简易的前端路由:
步骤1:导入并注册 MyHome、MyMovie、MyAbout 三个组件。示例代码如下:
import MyHome from './MyHome.vue'
import MyAbout from './MyAbout.vue'
import MyMovie from './MyMovie.vue'export default {components: {MyHome, MyMovie, MyAbout,},
}
步骤2:通过 标签的 is 属性,动态切换要显示的组件。示例代码如下:
<template><div><h1>App.vue</h1><component :is="comName">This is a test</component></div>
</template>export default {data() {return {comName: 'MyName', // 要展示的组件的名称}},
}
步骤3:在组件的结构中声明如下 3 个 链接,通过点击不同的 链接,切换浏览器地址栏中的 Hash 值:
<a href="#/home">Home</a>
<a href="#/movie">Movie</a>
<a href="#/about">About</a>
步骤4:在 created 生命周期函数中监听浏览器地址栏中 Hash 地址的变化,动态切换要展示的组件的名称:
window.onhashchange = () => {switch(location.hash) {case '#/home': // 点击了“首页”的链接this.comName = 'my-home'breakcase '#/movie': // 点击了“电影”的链接this.comName = 'my-movie'breakcase '#/about': // 点击了“关于”的链接this.comName = 'my-about'break}}
},
-
Code: App.vue
<template><div><h1>App.vue</h1><a href="#/home">Home</a> <a href="#/movie">Movie</a> <a href="#/about">About</a> <hr /><component :is="comName">This is a test</component></div> </template><script> import MyHome from '../01.easy-router/MyHome.vue' import MyAbout from '../01.easy-router/MyAbout.vue' import MyMovie from '../01.easy-router/MyMovie.vue'export default {name: 'MyApp',data() {return {comName: 'MyName',}},components: {MyHome, MyMovie, MyAbout,},created() {window.onhashchange = () => {switch(location.hash) {case '#/home': // 点击了“首页”的链接this.comName = 'my-home'breakcase '#/movie': // 点击了“电影”的链接this.comName = 'my-movie'breakcase '#/about': // 点击了“关于”的链接this.comName = 'my-about'break}}},} </script><style lang="scss" scoped> </style>
vue-router 的基本使用
基础概念:
概念:
vue-router 是 vue.js 官方给出的路由解决方案。它只能结合 vue 项目进行使用,能够轻松的管理 SPA 项目中组件的切换。
作用:修改地址栏路径时,切换显示匹配的组件
版本:
vue-router 目前有 3.x 的版本和 4.x 的版本。其中:
vue-router 3.x 只能结合 vue2 进行使用
vue-router 4.x 只能结合 vue3 进行使用
vue-router 3.x 的官方文档地址:https://router.vuejs.org/zh/
vue-router 4.x 的官方文档地址:https://next.router.vuejs.org/
补充官网:https://v3.router.vuejs.org/zh/
说明:Vue 官方的一个路由插件,是一个第三方包
VueRouter 3.x的使用(5+2)
固定5个固定的步骤(不用死背,熟能生巧)
1-下载 VueRouter 模块到当前工程,版本3.6.5
yarn add vue-router@3.6.5
npm install vue-router@3.6.5
2-main.js中引入VueRouter
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
3-安装注册
Vue.use(VueRouter)
4-创建路由对象
const router = new VueRouter()
5-注入,将路由对象注入到new Vue实例中,建立关联
new Vue({render: h => h(App),router:router
}).$mount('#app')
当我们配置完以上5步之后 就可以看到浏览器地址栏中的路由 变成了 /#/的形式。表示项目的路由已经被Vue-Router管理了
案例:
main.js
// 路由的使用步骤 5 + 2
// 5个基础步骤
// 1. 下载 v3.6.5
// yarn add vue-router@3.6.5
// 2. 引入
// 3. 安装注册 Vue.use(Vue插件)
// 4. 创建路由对象
// 5. 注入到new Vue中,建立关联import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
Vue.use(VueRouter) // VueRouter插件初始化const router = new VueRouter()new Vue({render: h => h(App),router
}).$mount('#app')
**两个核心步骤:
1-创建需要的组件 (views目录),配置路由规则
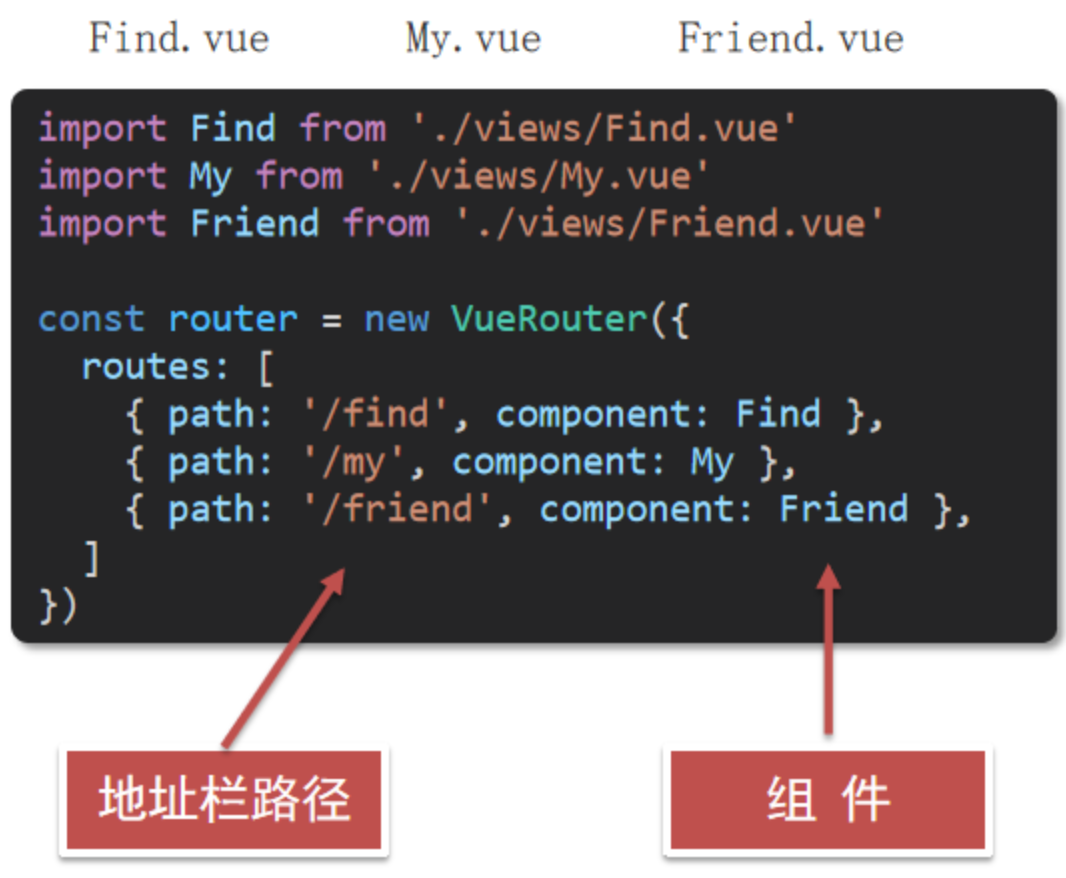
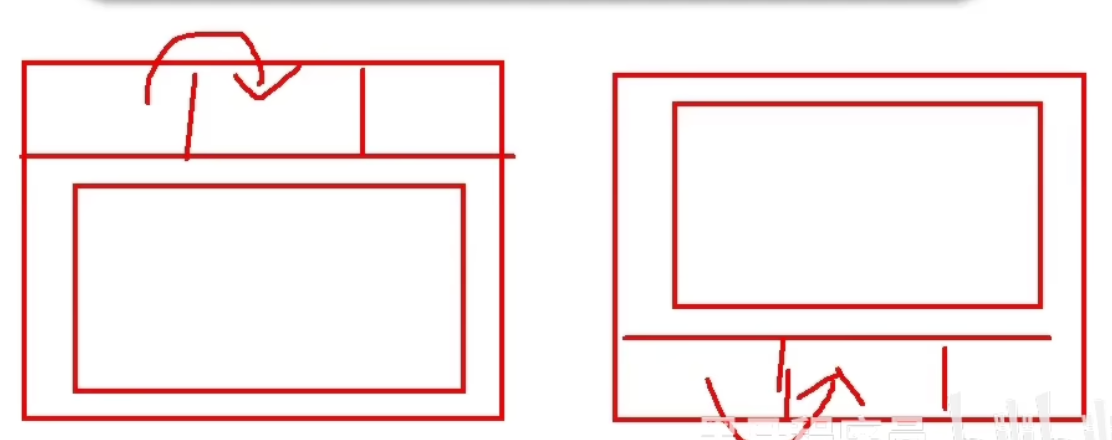
2-配置导航,配置路由出口(路径匹配的组件显示的位置)
代码中的router-view是用来匹配导航栏的位置的,如果它在代码的上/下面,那么导航栏也在上/下面
如下图所示:
App.vue
<div class="footer_wrap"><a href="#/find">发现音乐</a><a href="#/my">我的音乐</a><a href="#/friend">朋友</a>
</div>
<div class="top"><router-view></router-view>
</div>
案例:

-
Code:
main.js
import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App.vue'Vue.config.productionTip = falseimport Find from './views/Find' import My from './views/My' import Friend from './views/Friend'import VueRouter from 'vue-router' Vue.use(VueRouter) const router = new VueRouter({// routes 路由规则们// route 一条路有规则 { path: 路径, component: 组件}routes: [{ path: '/find', component: Find},{ path: '/my', component: My},{ path: '/friend', component: Friend},] })Vue.config.productionTip = falsenew Vue({render: h => h(App),router, }).$mount('#app')App.vue
<template><div><div class="footer_wrap"><a href="#/find">发现音乐</a><a href="#/my">我的音乐</a><a href="#/friend">朋友</a></div><div class="top"><!-- 路由出口:匹配的组件所展示的位置 --><router-view></router-view></div></div> </template><script> export default {}; </script><style> body {margin: 0;padding: 0; } .footer_wrap {position: relative;left: 0;top: 0;display: flex;width: 100%;text-align: center;background-color: #333;color: #ccc; } .footer_wrap a {flex: 1;text-decoration: none;padding: 20px 0;line-height: 20px;background-color: #333;color: #ccc;border: 1px solid black; } .footer_wrap a:hover {background-color: #555; } </style>
vue-router 4.x的基本使用步骤:
vue-router 4.x 的基本使用步骤
① 在项目中安装 vue-router
② 定义路由组件
③ 声明路由链接和占位符
④ 创建路由模块
⑤ 导入并挂载路由模块
3.1 在项目中安装 vue-router
在 vue3 的项目中,只能安装并使用 vue-router 4.x。安装的命令如下:
npm install vue-router@next -S
注意:包名会被注册在package.json的dependencies里面,在生产环境下这个包的依赖依然存在。
3.2 定义路由组件
在项目中定义 MyHome.vue、MyMovie.vue、MyAbout.vue 三个组件,将来要使用 vue-router 来控制它们的展示与切换:
MyAbout, 其余同理:
<template><h3>MyAbout</h3>
</template><script>
export default {name: 'MyAbout'
}
</script><style></style>
3.3 声明路由链接和占位符
可以使用 标签来声明路由链接,并使用 标签来声明路由占位符。
示例代码如下:
<template><div><h1>MyApp</h1><!-- 声明路由链接 --><router-link to="/home">首页</router-link> <router-link to="/movie">电影</router-link> <router-link to="/about">关于</router-link><hr /><!-- 路由的占位符 --><router-view></router-view></div>
</template>
注意:在声明哈希属性时,需要用to属性来声明,而且哈希地址不再需要以#开头,vue中的router会自动为我们添加#。
3.4 创建路由模块
在项目中创建 router.js 路由模块,在其中按照如下 4 个步骤创建并得到路由的实例对象:
① 从 vue-router 中按需导入两个方法
② 导入需要使用路由控制的组件
③ 创建路由实例对象
④ 向外共享路由实例对象
⑤ 在 main.js 中导入并挂载路由模块
从 vue-router 中按需导入两个方法
// 1. 从 vue-router 中按需导入两个方法
// createRouter 方法用于创建路由的实例对象
// createWebHashHistory 用于指定路由的工作模式(hash模式)
import { createRouter, createWebHashHistory } from 'vue-router'
导入需要使用路由控制的组件
//2. 导入组件,这些组件将要以路由的方式,来控制它们的切换
import MyHome from './MyHome.vue'
import MyMoive from './MyMoive.vue'
import MyAbout from './MyAbout.vue'
创建路由实例对象
// 3. 创建路由实例对象
const router = createRouter({// 3.1 通过 history 属性指定路由的工作模式history: createWebHashHistory(),// 3.2 通过 routes 数组,指定路由规则routes: [// path 是 hash 地址, component 是要展示的组件{ path: '/home', component: Home },{ path: '/movie', component: Movie },{ path: '/about', component: About },]
})
向外共享路由实例对象
// 4. 向外共享路由实例对象,
// 供其他模块导入并使用
export default router
在 main.js 中导入并挂载路由模块
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './components/App.vue'
import './index.css'// 1. 导入路由模块
import router from './components/02.start/router'
const app = createApp(App)// 2. 挂载路由模块
// app.use() 方法用来挂载“第三方的插件模块”
app.use(router)app.mount('#app')
效果:
整体流程:
当我们点击电影时,地址栏会切换成 #/movie,当哈希地址发生变化,就会被路由模块所监听到,然后进行哈希地址的匹配:
// router.js
routes: [// path 是 hash 地址, component 是要展示的组件{ path: '/home', component: MyHome },{ path: '/movie', component: MyMovie },{ path: '/about', component: MyAbout },]
当匹配到,我们就会把相应的组件比如MyMovie放到App.vue中的路由占位符中
// App.vue
<template><div><h1>MyApp</h1><!-- 声明路由链接 --><router-link to="/home">首页</router-link><router-link to="/movie">电影</router-link><router-link to="/about">关于</router-link><hr /><!-- 路由的占位符 --><router-view></router-view></div>
</template>
组件的存放目录问题
注意: .vue文件 本质无区别
组件分类:
.vue文件分为2类,都是 .vue文件(本质无区别)
- 页面组件 (配置路由规则时使用的组件)
- 复用组件(多个组件中都使用到的组件)
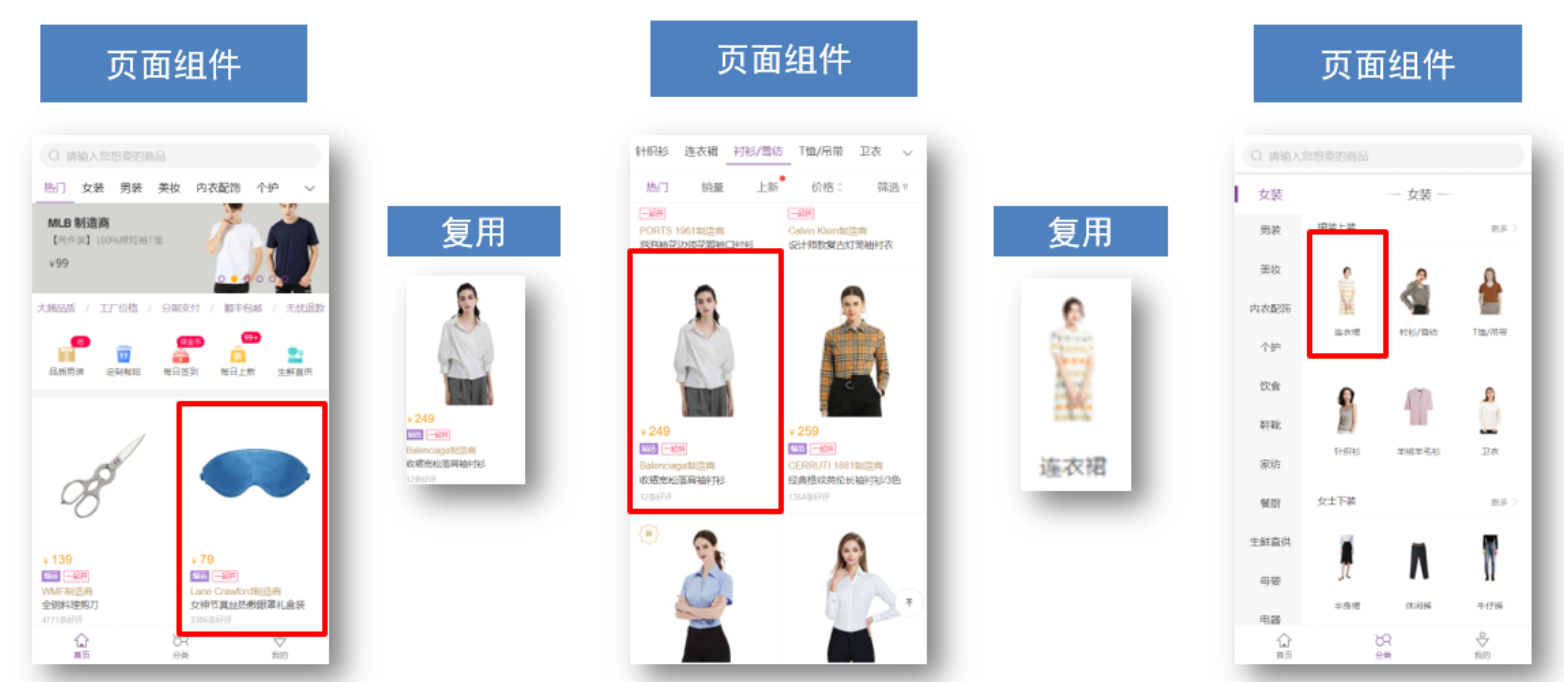
存放目录:
分类开来的目的就是为了 更易维护
-
src/views
文件夹页面组件 - 页面展示 - 配合路由用
-
src/components
文件夹复用组件 - 展示数据 - 常用于复用
路由的封装抽离
问题:所有的路由配置都在main.js中合适吗?
目标:将路由模块抽离出来。 好处:拆分模块,利于维护
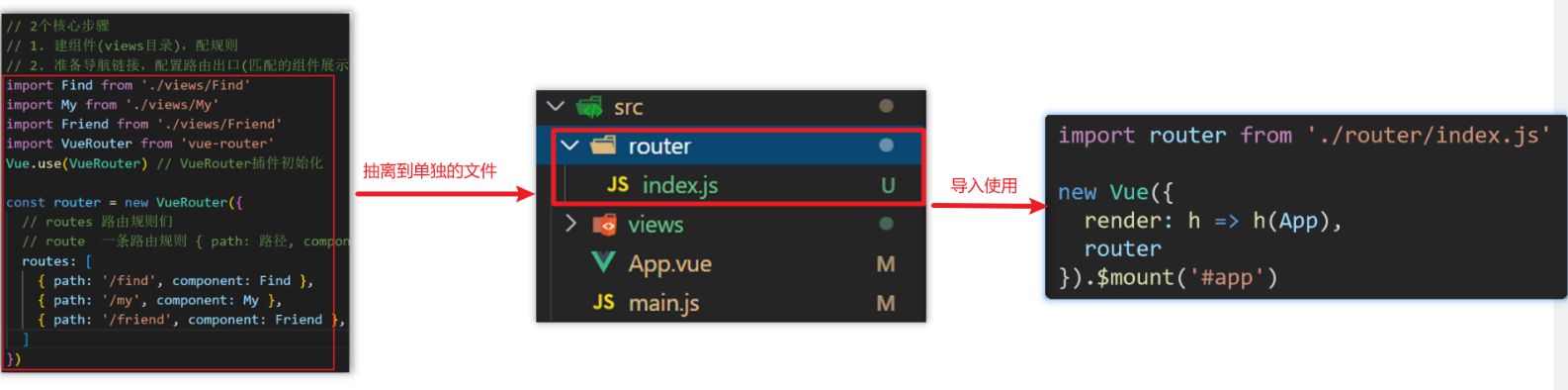
路径简写:
脚手架环境下 @指代src目录,可以用于快速引入组件
具体书写:
index.js
import Find from '@/views/Find'
import My from '@/views/My'
import Friend from '@/views/Friend'// 1. 导入Vue
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'Vue.use(VueRouter)
const router = new VueRouter({// routes 路由规则们// route 一条路有规则 { path: 路径, component: 组件}routes: [{ path: '/find', component: Find},{ path: '/my', component: My},{ path: '/friend', component: Friend},]
})// 2. 导出
export default router
main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
// 3. 导入 router
import router from './router/index'Vue.config.productionTip = falsenew Vue({render: h => h(App),router,
}).$mount('#app')
App.vue
<template><div><div class="footer_wrap"><a href="#/find">发现音乐</a><a href="#/my">我的音乐</a><a href="#/friend">朋友</a></div><div class="top"><!-- 路由出口:匹配的组件所展示的位置 --><router-view></router-view></div></div>
</template><script>
export default {};
</script><style>
body {margin: 0;padding: 0;
}
.footer_wrap {position: relative;left: 0;top: 0;display: flex;width: 100%;text-align: center;background-color: #333;color: #ccc;
}
.footer_wrap a {flex: 1;text-decoration: none;padding: 20px 0;line-height: 20px;background-color: #333;color: #ccc;border: 1px solid black;
}
.footer_wrap a:hover {background-color: #555;
}
</style>
声明式导航
导航链接
需求:实现导航高亮效果
如果使用a标签进行跳转的话,需要给当前跳转的导航加样式,同时要移除上一个a标签的样式,太麻烦!!!
**解决方案:
vue-router 提供了一个全局组件 router-link (取代 a 标签)
- 能跳转,配置 to 属性指定路径(必须) 。本质还是 a 标签 ,to 无需 #
- 能高亮,默认就会提供高亮类名,可以直接设置高亮样式
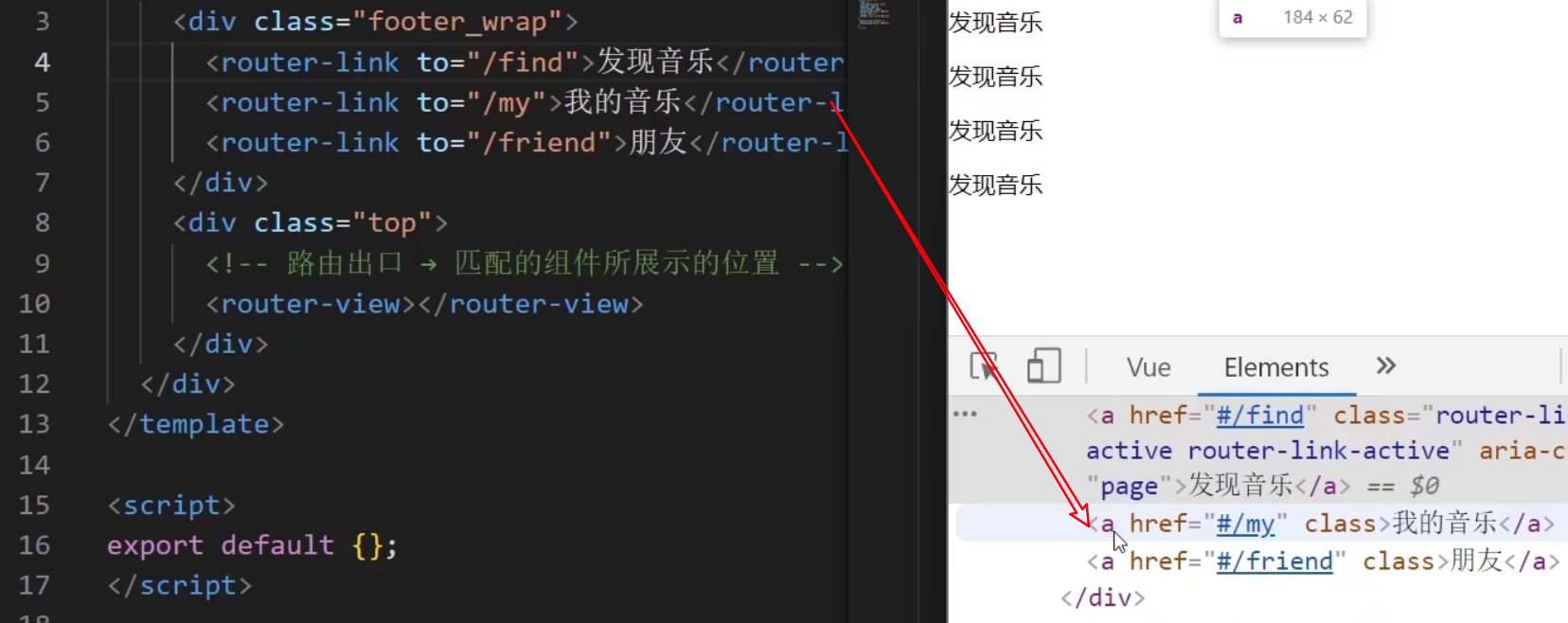
语法: 发现音乐
<div><div class="footer_wrap"><router-link to="/find">发现音乐</router-link><router-link to="/my">我的音乐</router-link><router-link to="/friend">朋友</router-link></div><div class="top"><!-- 路由出口 → 匹配的组件所展示的位置 --><router-view></router-view></div>
</div>
通过router-link自带的两个样式进行高亮:
使用router-link跳转后,我们发现。当前点击的链接默认加了两个class的值 router-link-exact-active和router-link-active
我们可以给任意一个class属性添加高亮样式即可实现功能
代码:
-
Code:
App.vue
<template><div><div class="footer_wrap"><router-link to="/find">发现音乐</router-link><router-link to="friend">我的音乐</router-link><router-link to="my">我的朋友</router-link></div><div class="top"><!-- 路由出口 → 匹配的组件所展示的位置 --><router-view></router-view></div></div> </template><script> export default {}; </script><style> body {margin: 0;padding: 0; } .footer_wrap {position: relative;left: 0;top: 0;display: flex;width: 100%;text-align: center;background-color: #333;color: #ccc; } .footer_wrap a {flex: 1;text-decoration: none;padding: 20px 0;line-height: 20px;background-color: #333;color: #ccc;border: 1px solid black; } .footer_wrap a.router-link-active {background-color: purple; } .footer_wrap a:hover {background-color: #555; } </style>
两个类名
当我们使用跳转时,自动给当前导航加了两个类名
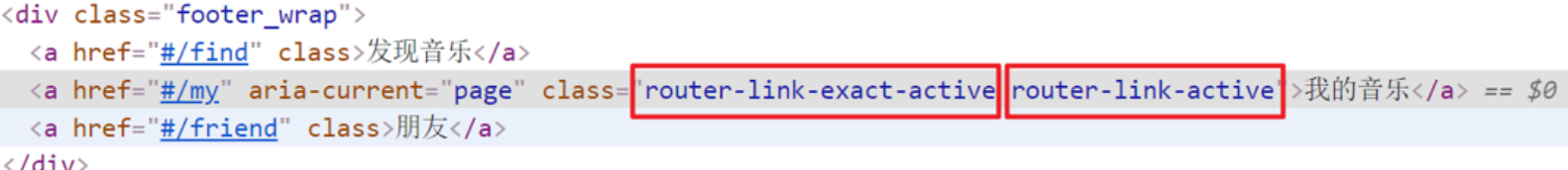
router-link-active
模糊匹配(用的多)
to=“/my” 可以匹配 /my /my/a /my/b …
只要是以/my开头的路径 都可以和 to="/my"匹配到
router-link-exact-active
精确匹配
to=“/my” 仅可以匹配 /my
在地址栏中输入二级路由查看类名的添加
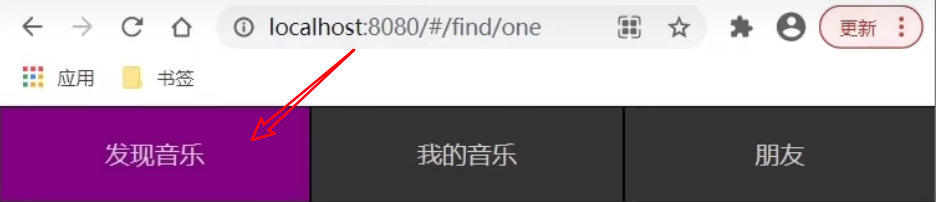
理解:即使地址栏后面加上了 /one ,也就是所谓的二级地址,我们通过模糊匹配router-link-active
也能够让他变色。
自定义类名
问题:router-link的两个高亮类名 太长了,我们希望能定制怎么办
解决方案
我们可以在创建路由对象时,额外配置两个配置项即可。 linkActiveClass和linkExactActiveClass
const router = new VueRouter({routes: [...],linkActiveClass: "类名1",linkExactActiveClass: "类名2"
})
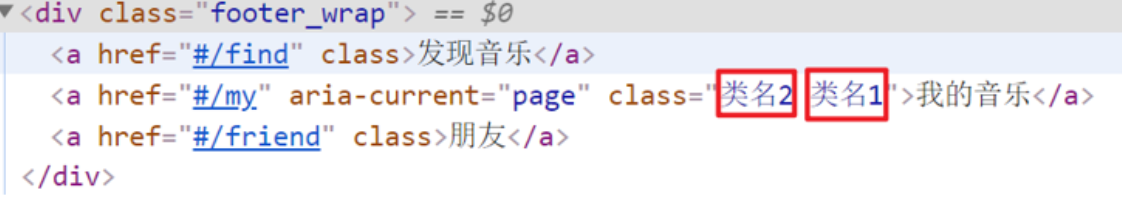
详细操作过程:
Style:
.footer_wrap a.router-link-active {background-color: purple;
}
经过main.js配置过后
const router = new VueRouter({// routes 路由规则们// route 一条路由规则 { path: 路径, component: 组件 }routes: [{ path: '/find', component: Find },{ path: '/my', component: My },{ path: '/friend', component: Friend },],// link 自定义高亮linkActiveClass: 'active',linkExactActiveClass: 'exact-active'
})
style可以简化成如下:
.footer_wrap a.active {background-color: purple;
}
跳转传参:
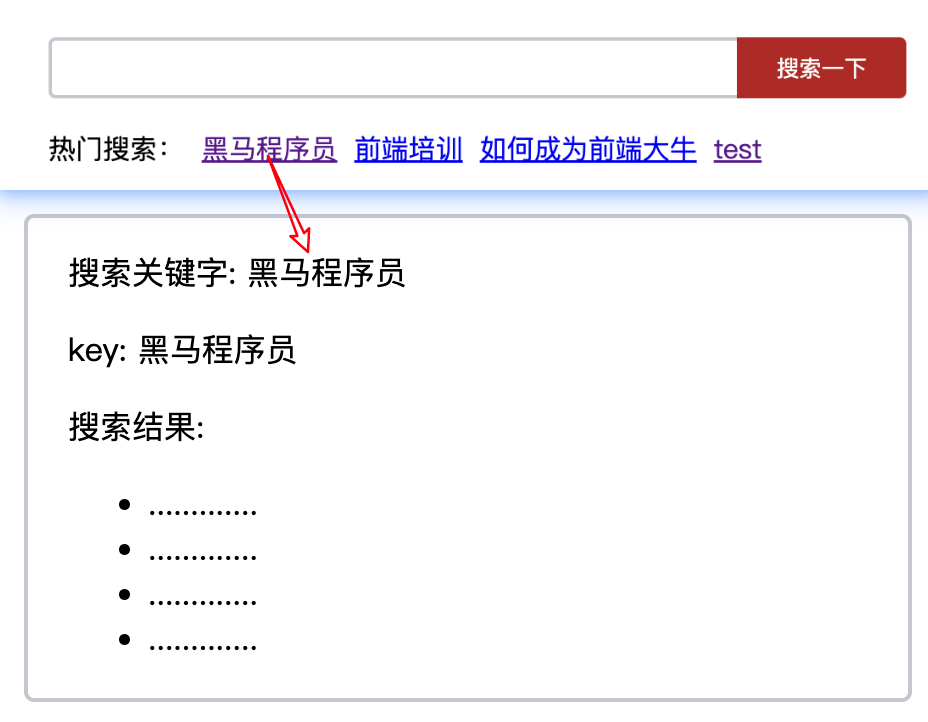
目标:在跳转路由时,进行传参

比如:当在搜索页点击了热门搜索链接,跳转到详情页,要把点击的内容带到详情页,该怎么办呢?
**跳转传参:
我们可以通过两种方式,在跳转的时候把所需要的参数传到其他页面中
- 查询参数传参
- 动态路由传参
**查询参数传参:
- 如何传参?
- 如何接受参数固定用法:
- $router.query.参数名
案例:
-
Code:
Home.vue
<template><div class="home"><div class="logo-box"></div><div class="search-box"><input v-model="inpValue" type="text"><button @click="goSearch">搜索一下</button></div><div class="hot-link">热门搜索:<router-link to="/search/黑马程序员?key=test">黑马程序员</router-link><router-link to="/search/前端培训">前端培训</router-link><router-link to="/search/如何成为前端大牛">如何成为前端大牛</router-link></div></div> </template><script> export default {name: 'FindMusic',data() {return {inpValue: '',}},methods: {goSearch() {this.$router.push(`/search${this.inpValue}`)}} } </script><style> .logo-box {height: 150px;background: url('@/assets/logo.jpeg') no-repeat center; } .search-box {display: flex;justify-content: center; } .search-box input {width: 400px;height: 30px;line-height: 30px;border: 2px solid #c4c7ce;border-radius: 4px 0 0 4px;outline: none; } .search-box input:focus {border: 2px solid #ad2a26; } .search-box button {width: 100px;height: 36px;border: none;background-color: #ad2a26;color: #fff;position: relative;left: -2px;border-radius: 0 4px 4px 0; } .hot-link {width: 508px;height: 60px;line-height: 60px;margin: 0 auto; } .hot-link a {margin: 0 5px; } </style>Search.vue
<template><div class="search"><p>搜索关键字: {{ $route.query.key }}</p><p>搜索结果: </p><ul><li>.............</li><li>.............</li><li>.............</li><li>.............</li></ul></div> </template><script> export default {name: 'MyFriend',created () {// 在created中,获取路由参数// this.$route.query.参数名 获取console.log(this.$route.query.key);} } </script><style> .search {width: 400px;height: 240px;padding: 0 20px;margin: 0 auto;border: 2px solid #c4c7ce;border-radius: 5px; } </style>
注意:如果在像created这种的js代码中,不要忘记加上this.
动态路由传参方式:
配置动态路由步骤:
1-配置动态路由
动态路由后面的参数可以随便起名,但要有语义
index.js
const router = new VueRouter({routes: [...,{ path: '/search/:words', component: Search }]
})
2-配置导航链接
Home.vue
to="/path/参数值"
3-对应页面组件接受参数
Search.vue
{{ $route.params.参数名 }}
params后面的参数名要和动态路由配置的参数保持一致
案例:
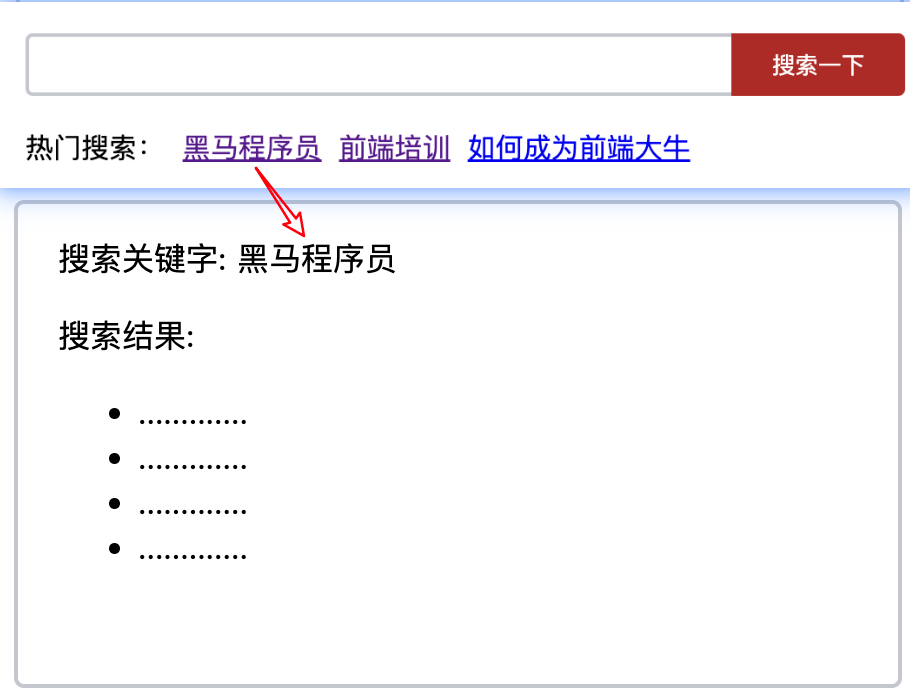
-
Code:
index.js
import Home from '@/views/Home' import Search from '@/views/Search' import Vue from 'vue' import VueRouter from 'vue-router' Vue.use(VueRouter) // VueRouter插件初始化// 创建了一个路由对象 const router = new VueRouter({routes: [{ path: '/home', component: Home },// *** 1, 配置动态路由{ path: '/search/:words', component: Search }] })export default routerHome.vue
// *** 2, 配置导航链接 <router-link to="/search/letstry">Vue-test</router-link>Search.vue
<template><div class="search"><!-- *** 3, 对应页面组件接收参数 --><p>搜索关键字: {{ $route.params.words }}</p><p>搜索结果: </p><ul><li>.............</li><li>.............</li><li>.............</li><li>.............</li></ul></div> </template><script> export default {name: 'MyFriend',created () {// 在created中,获取路由参数// this.$route.query.参数名 获取console.log(this.$route.query.key);} } </script><style> .search {width: 400px;height: 240px;padding: 0 20px;margin: 0 auto;border: 2px solid #c4c7ce;border-radius: 5px; } </style>
查询参数传参 VS 动态路由传参:
- 查询参数传参 (比较适合传多个参数)
- 跳转:to=“/path?参数名=值&参数名2=值”
- 获取:$route.query.参数名
- 动态路由传参 (优雅简洁,传单个参数比较方便)
- 配置动态路由:path: “/path/:参数名”
- 跳转:to=“/path/参数值”
- 获取:$route.params.参数名
注意:动态路由也可以传多个参数,但一般只传一个
动态路由参数的可选符(了解)
问题:配了路由 path:“/search/:words” 为什么按下面步骤操作,会未匹配到组件,显示空白?
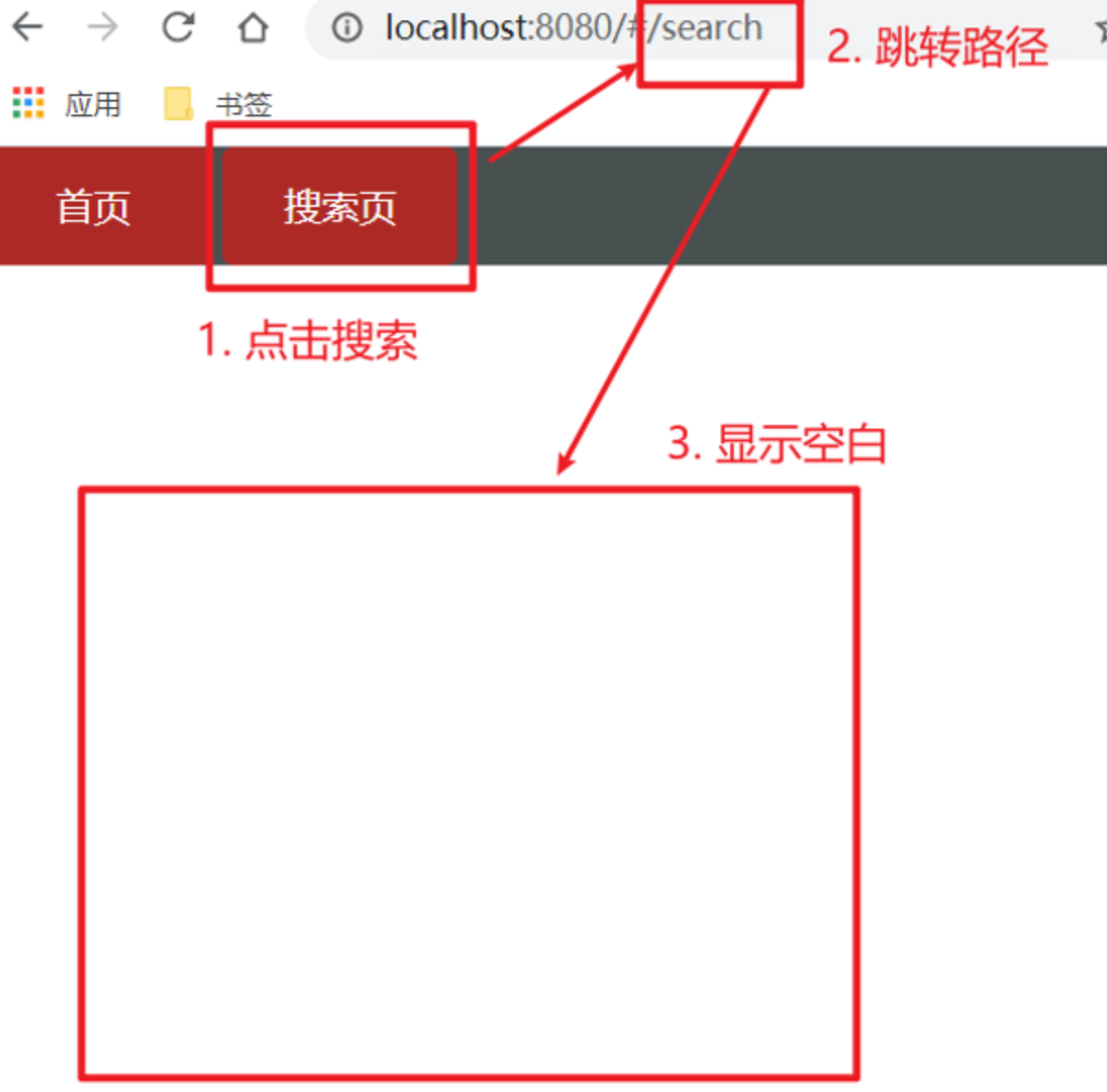
原因:/search/:words 表示,必须要传参数。如果不传参数,也希望匹配,可以加个可选符"?"
const router = new VueRouter({routes: [...{ path: '/search/:words?', component: Search }]
})
Vue路由
重定向
**问题:**网页打开时, url 默认是 / 路径,未匹配到组件时,会出现空
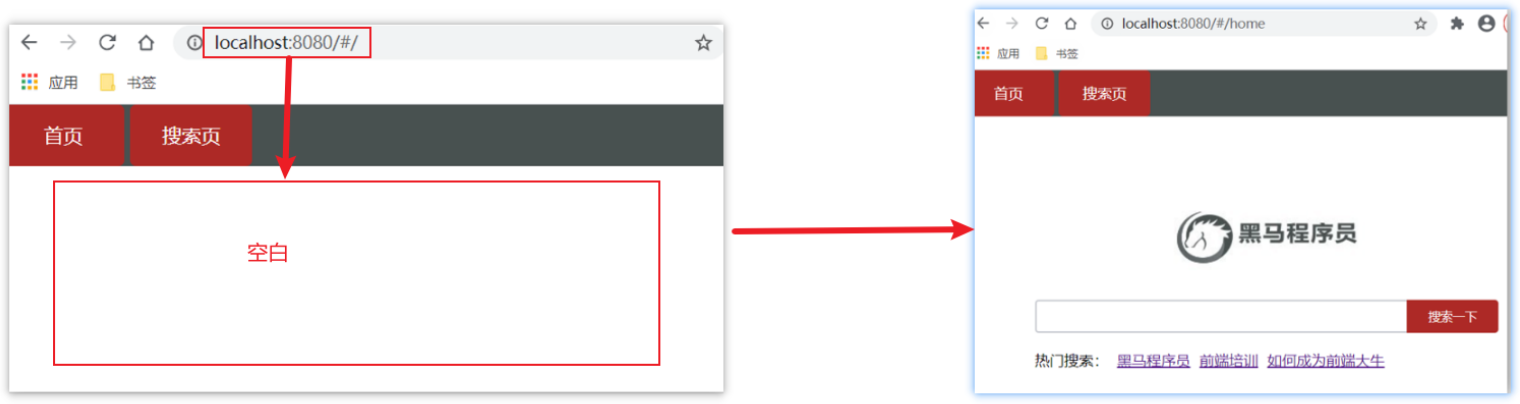
解决方案:重定向 → 匹配 / 后, 强制跳转 /home 路径
语法:
{ path: 匹配路径, redirect: 重定向到的路径 },
比如:
{ path:'/' ,redirect:'/home' }
代码:
const router = new VueRouter({routes: [{ path: '/', redirect: '/home'},...]
})
404
**作用:**当路径找不到匹配时,给个提示页面
位置:404的路由,虽然配置在任何一个位置都可以,但一般都配置在其他路由规则的最后面
**语法:**path: “*” (任意路径) – 前面不匹配就命中最后这个
import NotFind from '@/views/NotFind'const router = new VueRouter({routes: [...{ path: '*', component: NotFind } //最后一个]
})
模式设置
问题:
路由的路径看起来不自然, 有#,能否切成真正路径形式?
- hash路由(默认) 例如: http://localhost:8080/#/home
- history路由(常用) 例如: http://localhost:8080/home (以后上线需要服务器端支持,开发环境webpack给规避掉了history模式的问题)
理解:
1-hash模式:底层是由a标签,锚链接实现的
2-history模式:由新增的HTML5中的historyAPI实现
语法:
const router = new VueRouter({mode:'histroy', //默认是hashroutes:[]
})
注意:一旦采用了 histroy 模式,地址栏就没有 # ,需要后台配置访问规则
两种路由跳转方式
两种路径直接跳转
**问题:**点击按钮跳转如何实现?
**方案:**编程式导航:用JS代码来进行跳转
语法:
两种语法:
- path 路径跳转 (简易方便)
- name 命名路由跳转 (适合 path 路径长的场景)
path路径跳转语法:
特点:简易方便
Home.vue
//简单写法
this.$router.push('路由路径')
//eg
this.$router.push(`/search${this.inpValue}`)//完整写法
this.$router.push({path: '路由路径'
})
代码:
-
Code:
Home.vue中的script
export default {name: 'FindMusic',methods: {goSearch() {// Plan1: 简易写法// this.$router.push('/search')// Plan2: 完整写法this.$router.push({path: '/search'})}} }
**name命名路由跳转:
特点:适合 path 路径长的场景
语法:
- 路由规则,必须配置name配置项
index.js
{ name: '路由名', path: '/path/xxx', component: XXX },
- 通过name来进行跳转
Home.vue
this.$router.push({name: '路由名'
})
理解:给routes下的route起别名,方便自己之后push路径
代码演示通过name命名路由跳转:
-
Code:
index.js
{ name: 'test', path: '/search', component: Search}Home.vue
export default {name: 'FindMusic',methods: {goSearch() {this.$router.push({name: 'search',})}} }
问题:点击搜索按钮,跳转需要把文本框中输入的内容传到下一个页面如何实现?
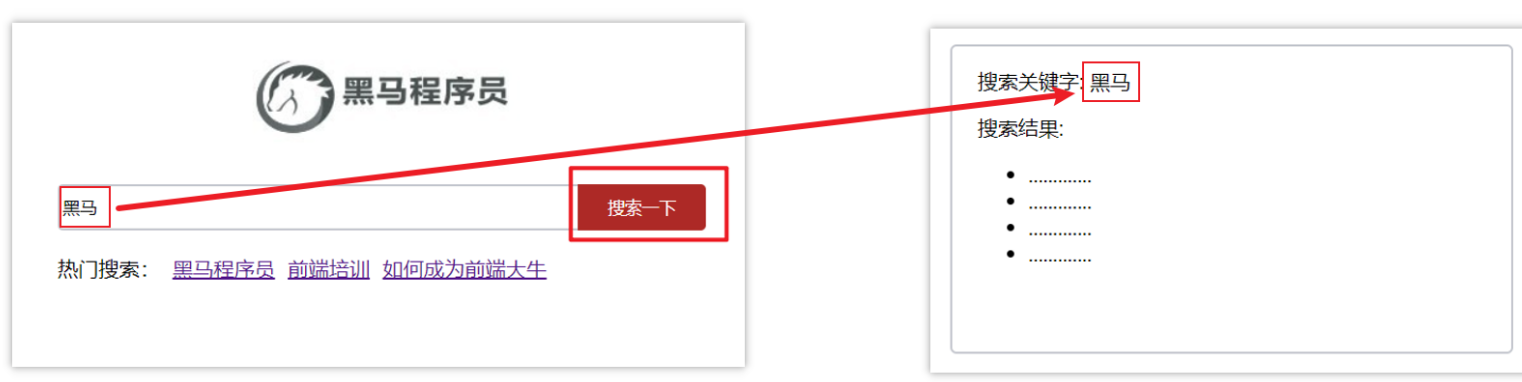
**两种传参方式:
1.查询参数
2.动态路由传参
path路径跳转传参
传参:
两种跳转方式,对于两种传参方式都支持:① path 路径跳转传参 ② name 命名路由跳转传参
**path路径跳转传参(query传参):
//简单写法
this.$router.push('/路径?参数名1=参数值1&参数2=参数值2')
//完整写法
this.$router.push({path: '/路径',query: {参数名1: '参数值1',参数名2: '参数值2'}
})
接受参数的方式依然是:$route.query.参数名
举例:
Home.vue
goSearch() {this.$router.push({path: '/search',query: {p1: this.inpValue,}})
}
Search.vue
<p>搜索关键字: {{ $route.query.p1 }}</p>
**path路径跳转传参(动态路由传参):
index.js 先在index中写出动态路由
{ path: '/search/:words', component: Search },
Home.vue
//简单写法
this.$router.push('/路径/参数值')
//完整写法
this.$router.push({path: '/路径/参数值'
})
Search.vue 接受参数的方式依然是:$route.params.参数值
<p>搜索关键字: {{ $route.params.words }}</p>
**注意:**path不能配合params使用
name命名路由传参
1.name 命名路由跳转传参 (query传参)
this.$router.push({name: '路由名字',query: {参数名1: '参数值1',参数名2: '参数值2'}
})
案例:
index.js
{ name: 'test', path: '/search', component: Search}
Home.vue
goSearch() {this.$router.push({name: 'test',query: {key: this.inpValue}})
}
Search.vue
<p>搜索关键字: {{ $route.query.key }}</p>
2.name 命名路由跳转传参 (动态路由传参)
this.$router.push({name: '路由名字',params: {参数名: '参数值',}
})
案例:
index.js
{ name: 'test', path: '/search/:words', component: Search}
Home.vue
goSearch() {this.$router.push({name: 'test',params: {words: this.inpValue}})
}
Search.vue
<p>搜索关键字: {{ $route.params.words }}</p>
总结
编程式导航,如何跳转传参?
1.path路径跳转
—query传参
this.$router.push('/路径?参数名1=参数值1&参数2=参数值2')
this.$router.push({path: '/路径',query: {参数名1: '参数值1',参数名2: '参数值2'}
})
—动态路由传参
this.$router.push('/路径/参数值')
this.$router.push({path: '/路径/参数值'
})
query与动态路由的区别:前者适合传多个参数,后者适合传入单个参数
2.name命名路由跳转
query传参
this.$router.push({name: '路由名字',query: {参数名1: '参数值1',参数名2: '参数值2'}
})
动态路由传参 (需要配动态路由)
this.$router.push({name: '路由名字',params: {参数名: '参数值',}
})
path路径跳转和name命名路由跳转区别:前者简易方便,后者适合path路径长的场景
面经基础版本-案例效果分析
效果与功能分析:
面经效果演示
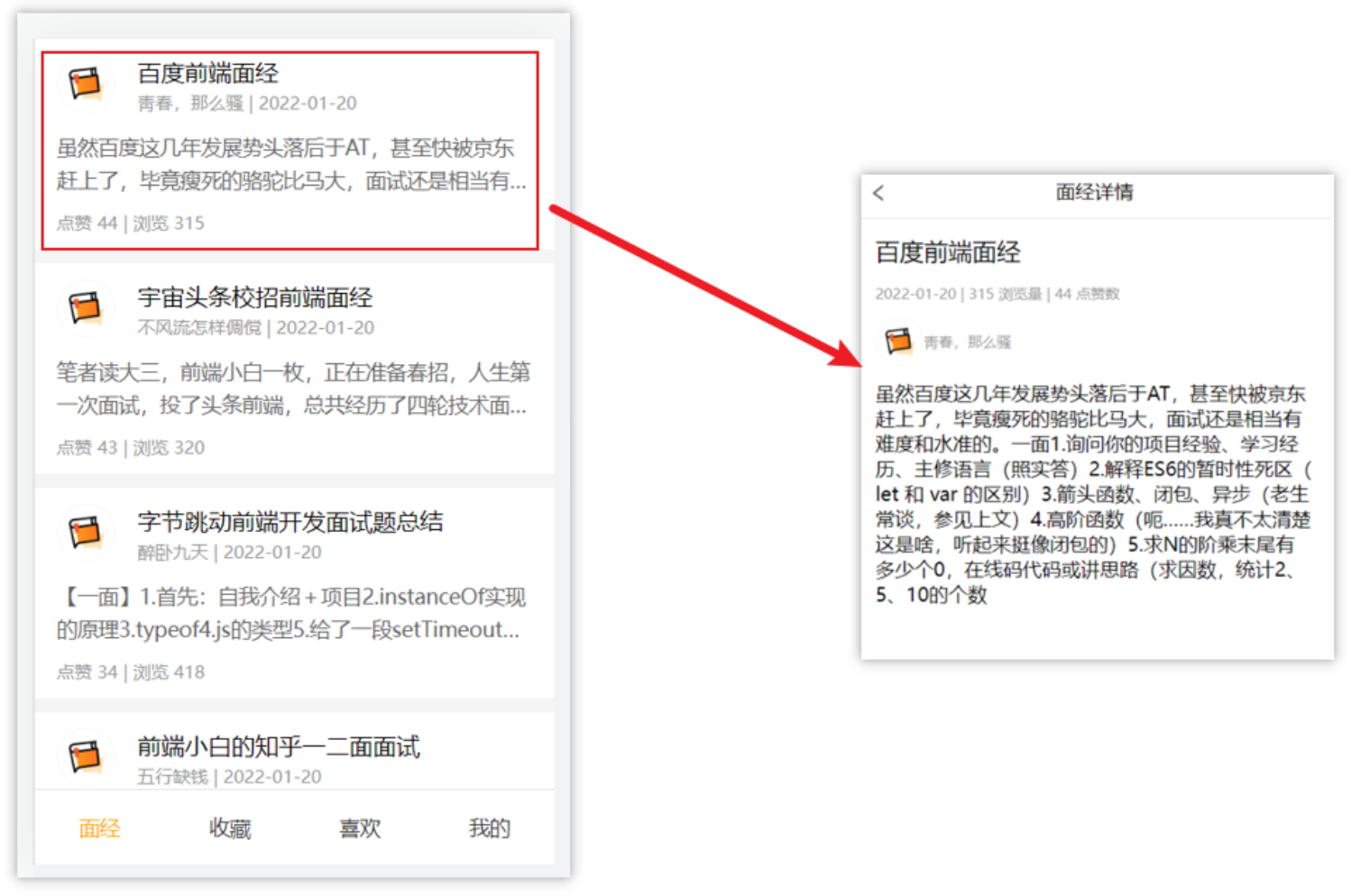
功能分析
1-配路由
首页 和 面经 详情,两个一级路由
首页内嵌四个可切换页面(嵌套二级路由)
2-实现功能
首页请求渲染
跳转传参 到 详情页,详情页渲染
组件缓存,优化性能
一级路由配置:
1.把文档中准备的素材拷贝到项目中
2.针对router/index.js文件 进行一级路由配置
...
import Layout from '@/views/Layout.vue'
import ArticleDetail from '@/views/ArticleDetail.vue'
...const router = new VueRouter({routes: [{path: '/',component: Layout},{path: '/detail',component: ArticleDetail}]
})
二级路由配置
二级路由也叫嵌套路由,当然也可以嵌套三级、四级…
1.使用场景
当在页面中点击链接跳转,只是部分内容切换时,我们可以使用嵌套路由
2.语法
- 在一级路由下,配置children属性即可
- 配置二级路由的出口
1.在一级路由下,配置children属性
注意:一级的路由path 需要加 /
const router = new VueRouter({routes: [{path: '/',component: Layout,children:[//children中的配置项 跟一级路由中的配置项一模一样 {path:'xxxx',component:xxxx.vue},{path:'xxxx',component:xxxx.vue},]}]
})
技巧:二级路由应该配置到哪个一级路由下呢?
这些二级路由对应的组件渲染到哪个一级路由下,children就配置到哪个路由下边
2.配置二级路由的出口
注意: 配置了嵌套路由,一定配置对应的路由出口,否则不会渲染出对应的组件
Layout.vue
<template><div class="h5-wrapper"><div class="content"><router-view></router-view></div>....</div>
</template>
-
Code:
index.js
import Vue from 'vue' import VueRouter from "vue-router"; import Layout from '@/views/Layout' import Article from '@/views/Article' import Collect from '@/views/Collect' import Like from '@/views/Like' import User from '@/views/User' import ArticleDetail from '@/views/ArticleDetail' Vue.use(VueRouter)const router = new VueRouter({// article 路径 -> Article 组件// 通过 children 配置项,可以配置嵌套路由// 1. 在 children 配置项中,配规则// 2. 准备二级路由出口routes: [{path: '/',component: Layout,children: [{path: '/article',component: Article,},{path: '/collect',component: Collect,},{path: '/like',component: Like,},{path: '/user',component: User,},]},{path: '/detail',component: ArticleDetail}] })export default routerLayout.vie
<template><div class="h5-wrapper"><div class="content"><!-- 二级路由出口,匹配到的二级路由组件就会展示 --><router-view></router-view></div><nav class="tabbar"><a href="#/article">面经</a><a href="#/collect">收藏</a><a href="#/like">喜欢</a><a href="#/user">我的</a></nav></div> </template><script> export default {name: "LayoutPage", } </script><style> body {margin: 0;padding: 0; } </style> <style lang="less" scoped> .h5-wrapper {.content {margin-bottom: 51px;}.tabbar {position: fixed;left: 0;bottom: 0;width: 100%;height: 50px;line-height: 50px;text-align: center;display: flex;background: #fff;border-top: 1px solid #e4e4e4;a {flex: 1;text-decoration: none;font-size: 14px;color: #333;-webkit-tap-highlight-color: transparent;}} } </style>
二级导航高亮
实现思路
- 将a标签替换成 组件,配置to属性,不用加 #
- 结合高亮类名实现高亮效果 (推荐模糊匹配:router-link-active)
代码实现
Layout.vue
<nav class="tabbar"><router-link to="/article">面经</router-link><router-link to="/collect">收藏</router-link><router-link to="/like">喜欢</router-link><router-link to="/user">我的</router-link>
</nav>---------------------------a.router-link-active {color: orange
}
-
Code:
<template><div class="h5-wrapper"><div class="content"><!-- 二级路由出口,匹配到的二级路由组件就会展示 --><router-view></router-view></div><nav class="tabbar"><router-link to="/article">面经</router-link><router-link to="/collect">收藏</router-link><router-link to="/like">喜欢</router-link><router-link to="/user">我的</router-link></nav></div> </template><script> export default {name: "LayoutPage", } </script><style> body {margin: 0;padding: 0; } </style> <style lang="less" scoped> .h5-wrapper {.content {margin-bottom: 51px;}.tabbar {position: fixed;left: 0;bottom: 0;width: 100%;height: 50px;line-height: 50px;text-align: center;display: flex;background: #fff;border-top: 1px solid #e4e4e4;a {flex: 1;text-decoration: none;font-size: 14px;color: #333;-webkit-tap-highlight-color: transparent;}a.router-link-active {color: orange}} } </style>
首页请求渲染
1.步骤分析
1.安装axios
2.看接口文档,确认请求方式,请求地址,请求参数
3.created中发送请求,获取数据,存储到data中
4.页面动态渲染
2.代码实现
1.安装axios
yarn add axios npm i axios
2.接口文档
请求地址: https://mock.boxuegu.com/mock/3083/articles
请求方式: get
3.created中发送请求,获取数据,存储到data中
data() {return {articelList: [],}
},
async created() {const { data: { result: { rows } }} = await axios.get('https://mock.boxuegu.com/mock/3083/articles')this.articelList = rows
},
4.页面动态渲染
<template><div class="article-page"><div class="article-item" v-for="item in articelList" :key="item.id"><div class="head"><img :src="item.creatorAvatar" alt="" /><div class="con"><p class="title">{{ item.stem }}</p><p class="other">{{ item.creatorName }} | {{ item.createdAt }}</p></div></div><div class="body">{{item.content}}</div><div class="foot">点赞 {{item.likeCount}} | 浏览 {{item.views}}</div></div></div>
</template>
查询参数传参
1.说明
跳转详情页需要把当前点击的文章id传给详情页,获取数据
- 查询参数传参 this.$router.push(‘/detail?参数1=参数值&参数2=参数值’)
- 动态路由传参 先改造路由 在传参 this.$router.push(‘/detail/参数值’)
2.查询参数传参实现
关键点:
1-点击跳转文章详情
Article.vue
@click="$router.push(`/detail?id=${item.id}`)"
2-实现返回上一级:采用 $router.back()

ArticleDetail.vue
<nav class="nav"><span @click="$router.back()" class="back"><</span> 面经详情</nav>
动态路由传参
1.实现步骤
- 改造路由
- 动态传参
- 在详情页获取参数
2.代码实现
改造路由
router/index.js
3.额外优化功能点-点击回退跳转到上一页
详情页渲染
1.实现步骤分析
- 导入axios
- 查看接口文档
- 在created中发送请求
- 页面动态渲染
2.代码实现
接口文档
请求地址: https://mock.boxuegu.com/mock/3083/articles/:id
请求方式: get
这里id走的是动态参数
关键:
优化空白界面:
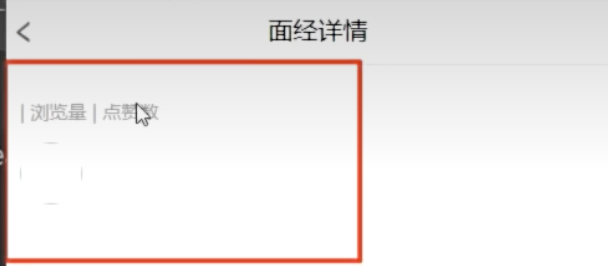
问题:在跳转页面的过程中,有空白浏览量和点赞等空白界面
原理:在请求和响应中间,不让template先去加载空的article对象
解决方案:
在 article.id 存在之后,再去做页面渲染
<div class="article-detail-page" v-if="article.id">-----------------------------------------------------data() {return {article: {},}
},
-
Code:
ArticleDetail.vue
<template><div class="article-detail-page" v-if="article.id"><nav class="nav"><span @click="$router.back()" class="back"><</span> 面经详情</nav><header class="header"><h1>{{ this.article.stem }}</h1><p>{{ this.article.createdAt }} | {{ this.article.views }} 浏览量 | {{ this.article.likeCount }} 点赞数</p><p><img:src=this.article.creatorAvataralt=""/><span>{{ this.article.creatorName }}</span></p></header><main class="body">{{ this.article.content }}</main></div> </template><script> import axios from 'axios' // 请求地址: https://mock.boxuegu.com/mock/3083/articles/:id // 请求方式: get export default {name: "ArticleDetailPage",data() {return {article: {},}},async created() {const id = this.$route.query.idconst { data } = await axios.get(`https://mock.boxuegu.com/mock/3083/articles/${id}`)// console.log(data);this.article = data.result}, } </script><style lang="less" scoped> .article-detail-page {.nav {height: 44px;border-bottom: 1px solid #e4e4e4;line-height: 44px;text-align: center;.back {font-size: 18px;color: #666;position: absolute;left: 10px;top: 0;transform: scale(1, 1.5);}}.header {padding: 0 15px;p {color: #999;font-size: 12px;display: flex;align-items: center;}img {width: 40px;height: 40px;border-radius: 50%;overflow: hidden;}}.body {padding: 0 15px;} } </style>
缓存组件
问题:
从面经列表 点到 详情页,又点返回,数据重新加载了 → 希望回到原来的位置

原因:
当路由被跳转后,原来所看到的组件就被销毁了(会执行组件内的beforeDestroy和destroyed生命周期钩子),重新返回后组件又被重新创建了(会执行组件内的beforeCreate,created,beforeMount,Mounted生命周期钩子),所以数据被加载了
**解决方案:**利用keep-alive把原来的组件给缓存下来
keep-alive
概念:它是 Vue 的内置组件,当它包裹动态组件时,会缓存不活动的组件实例,而不是销毁它们。
keep-alive 是一个抽象组件:它自身不会渲染成一个 DOM 元素,也不会出现在父组件中。
优点:
在组件切换过程中把切换出去的组件保留在内存中,防止重复渲染DOM,
减少加载时间及性能消耗,提高用户体验性。
keep-alive的三个属性
① include : 组件名数组,只有匹配的组件会被缓存
② exclude : 组件名数组,任何匹配的组件都不会被缓存
③ max : 最多可以缓存多少组件实例
案例:
对Layout页面进行缓存

如右边红框所示,当我们拉到这个位置时,再点击‘前端小白’这篇文章,然后退回来,会发现拖动条仍然在这个位置。

原理:被缓存的组件会多两个生命周期
额外的两个生命周期钩子:keep-alive的使用会触发两个生命周期函数
activated 当组件被激活(使用)的时候触发 → 进入这个页面的时候触发
deactivated 当组件不被使用的时候触发 → 离开这个页面的时候触发
组件缓存后就不会执行组件的created, mounted, destroyed 等钩子了
所以其提供了actived 和deactived钩子,帮我们实现业务需求。
理解:
如下图所示:当我们为 Layout 组件的生命周期钩子绑定输出函数,但是他们只会执行一次,之后尽管我们切换页面到 ArticleDetail 中再切回去,也不会再触发生命周期函数。
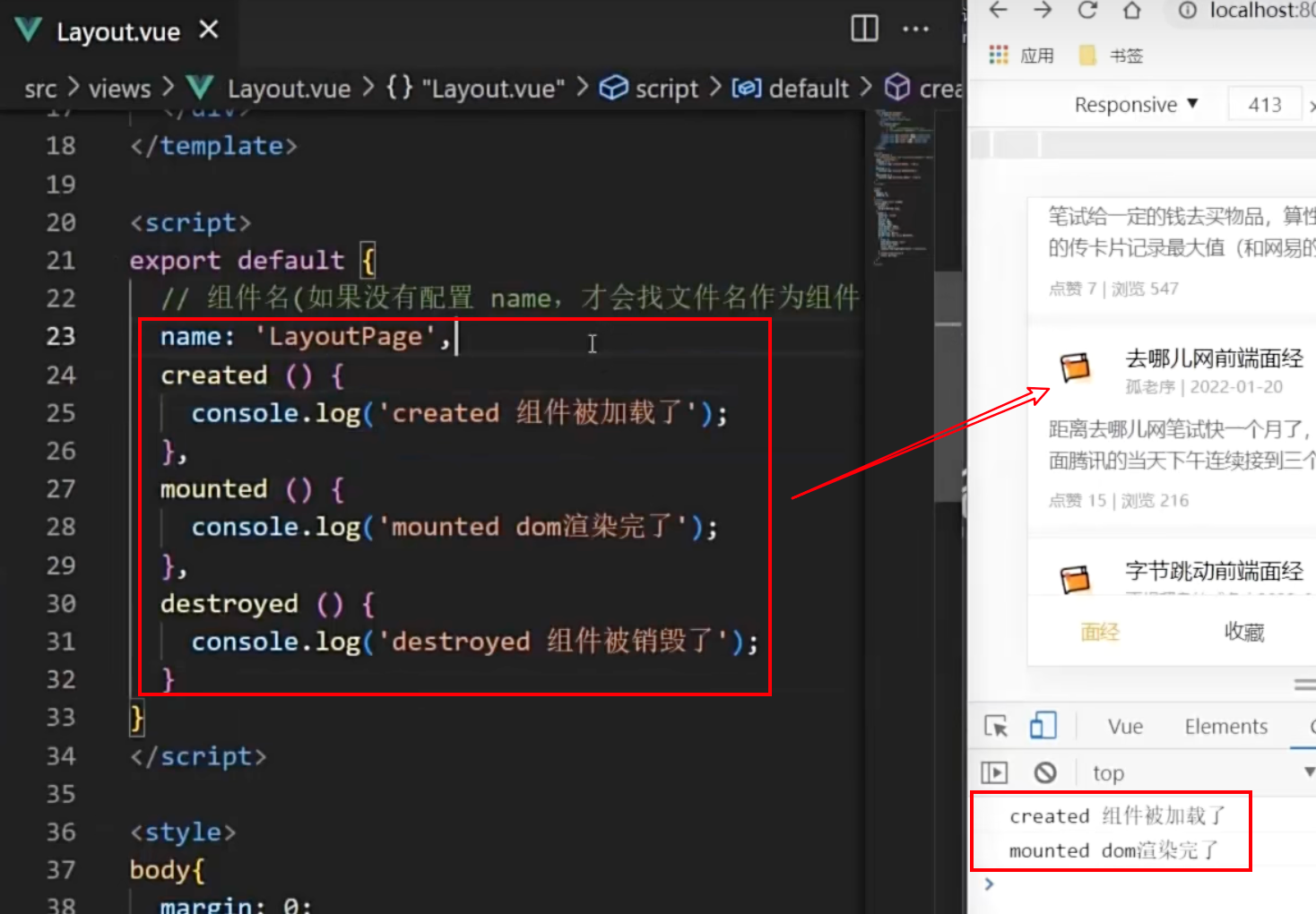
为了弥补无法使用之前生命函数的问题,Vue提供了 activated 和 deactivated 两个函数
如图,当我们第一次加载页面时,就会有 created mounted activated 三个函数被触发
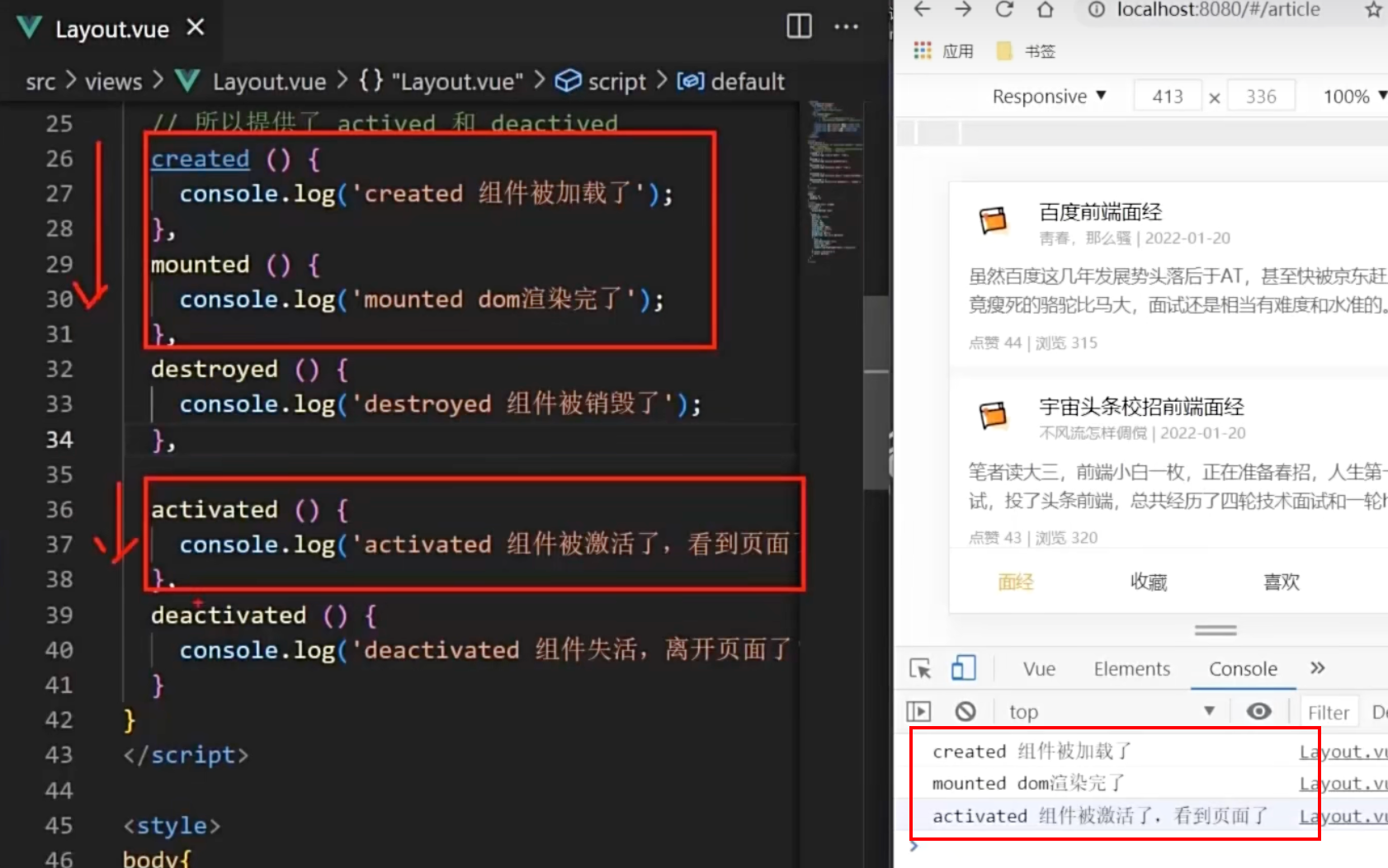
当我们切换到 ArticleDetail 时,就会触发deactivated函数
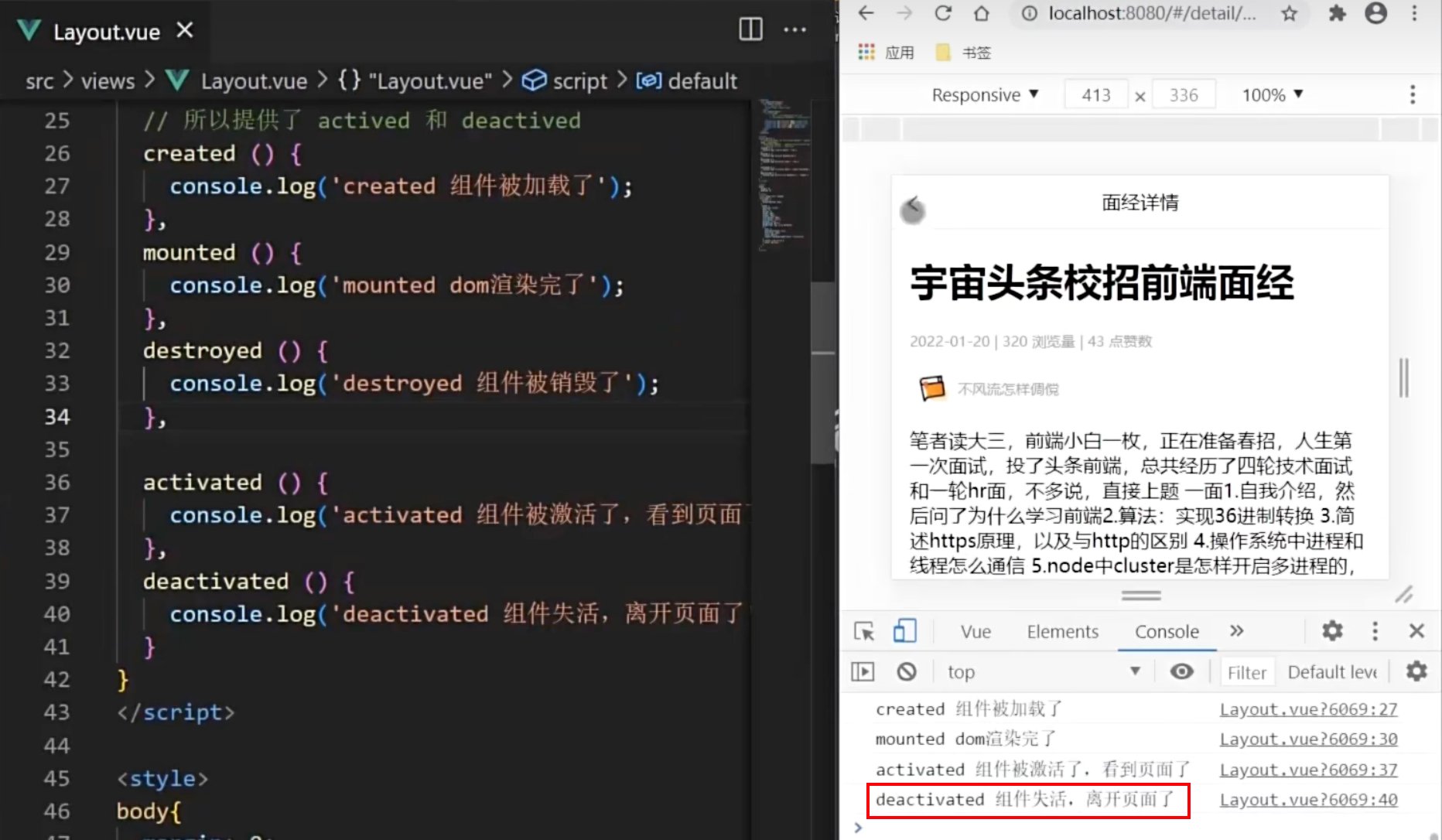
总结:
- keep-alive是什么
vue 的内置组件,包裹动态组件时,可以缓存 - keep-alive的优点
组件切换过程中 把切换出去的组件保留在内存中(提升性能) - keep-alive的三个属性(了解)
1-include:组件名数组,只有匹配的组件会被缓存
2-exclude :组件名数组,任何匹配的组件都不会被缓存
3-max:最多可以缓存多少组件实例 - keep-alive的使用会触发两个生命周期函数(了解)
activated 当组件被激活(使用)的时候触发 → 进入页面触发
deactivated 当组件不被使用的时候触发 → 离开页面触发
面经总结:

vue-router 的高级用法(参考21版Vue)
路由重定向
路由重定向指的是:用户在访问地址 A 的时候,强制用户跳转到地址 C ,从而展示特定的组件页面。通过路由规则的 redirect 属性,指定一个新的路由地址,可以很方便地设置路由的重定向:
const router = createRouter({// 3.1 通过 history 属性指定路由的工作模式history: createWebHashHistory(),// 3.2 通过 routes 数组,指定路由规则routes: [// path 是 hash 地址, component 是要展示的组件{ path: '/', redirect: '/home' },{ path: '/home', component: MyHome },{ path: '/movie', component: MyMovie },{ path: '/about', component: MyAbout },]
})
路由高亮
可以通过如下的两种方式,将激活的路由链接进行高亮显示:
① 使用默认的高亮 class 类 ② 自定义路由高亮的 class 类
2.1 默认的高亮 class 类
被激活的路由链接,默认会应用一个叫做 router-link-active 的类名。开发者可以使用此类名选择器,为激活的路由链接设置高亮的样式:
/* 在 index.css 全局样式表中,重新 router-link-active 的样式 */
.router-link-active {background-color: red;color: white;font-weight: bold;
}
效果:

2.2 自定义路由高亮的 class 类
在创建路由的实例对象时,开发者可以基于 linkActiveClass 属性,自定义路由链接被激活时所应用的类名:
// 3. 创建路由实例对象
const router = createRouter({// 3.1 通过 history 属性指定路由的工作模式history: createWebHashHistory(),// 指定被激活的路由链接,会应用 router-active 这个类名// 默认的 router-link-active 类名会被覆盖掉linkActiveClass: 'router-active',// 3.2 通过 routes 数组,指定路由规则routes: [// 其中,path 表示需要被重定向的“原地址”,redirect表示将要被重定向到的“新地址”{ path: '/', redirect: '/movie' },// path 是 hash 地址, component 是要展示的组件{ path: '/home', component: MyHome },{ path: '/movie', component: MyMovie },{ path: '/about', component: MyAbout },]
})
嵌套路由
通过路由实现组件的嵌套展示,叫做嵌套路由。
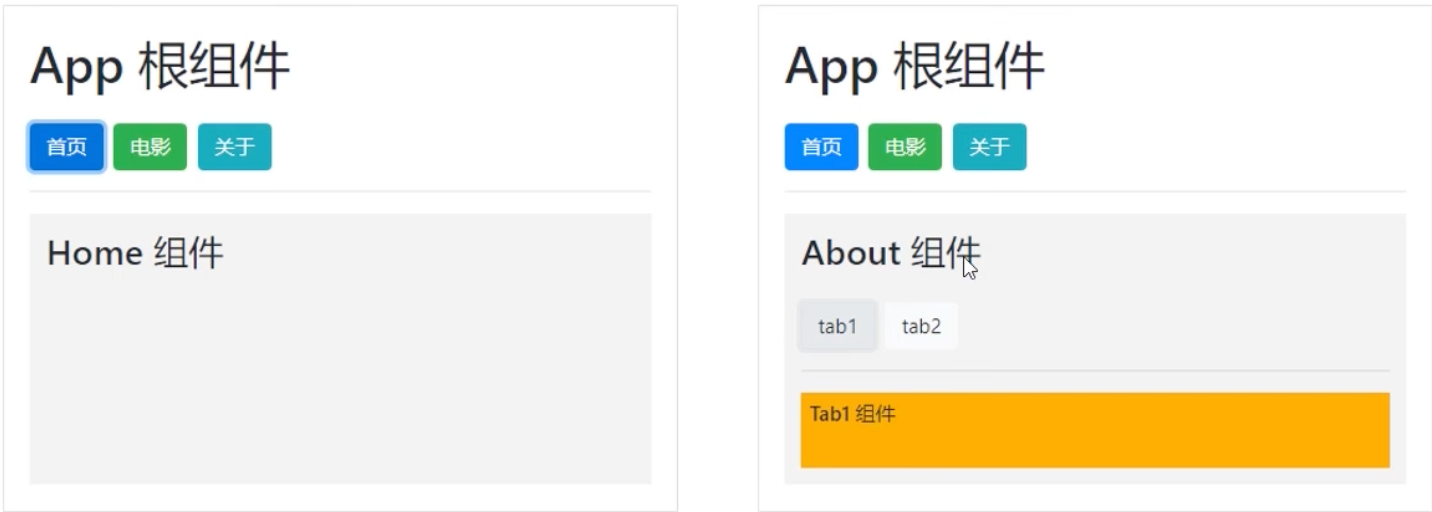
① 声明子路由链接和子路由占位符
② 在父路由规则中,通过 children 属性嵌套声明子路由规则
3.1 声明子路由链接和子路由占位符
在 About.vue 组件中,声明 tab1 和 tab2 的子路由链接以及子路由占位符。示例代码如下:
<template><div><h1>MyApp</h1><!-- 在关于页面中,声明两个子路由链接 --><router-link to="/about/tab1">Tab1</router-link> <router-link to="/about/tab2">Tab2</router-link> <router-link to="/about/tab3">Tab3</router-link><hr /><!-- 在关于页面中,声明 tab1 和 tab2 的路由占位符 --><router-view></router-view></div>
</template>
3.2 通过 children 属性声明子路由规则
在 router.js 路由模块中,导入需要的组件,并使用 children 属性声明子路由规则。示例代码如下:
import Tab1 from './tabs/MyTab1.vue'
import Tab2 from './tabs/MyTab2.vue'// 创建路由对象
const router = createRouter({// 指定路由的工作模式history: createWebHashHistory(),// 自定义路由高亮的 class 类linkActiveClass: 'active-router',// 声明路由的匹配规则routes: [{ path: '/', redirect: '/home'},{ path: '/home', component: Home },{ path: '/movie', component: Movie },{ path: '/about', component: About, children: [// 通过 children 属性嵌套子级路由规则{ path: 'tab1', component: Tab1 }, // 访问 /about/tab1 时, 展示 Tab1 组件{ path: 'tab2', component: Tab2 }, // 访问 /about/tab2 时,展示 Tab2 组件] },]
})
注意:子路由规则的 path 不要以 / 开头!
3.3 子路由重定向
当我们点击‘关于’时,可以直接显示出Tab1中的内容:
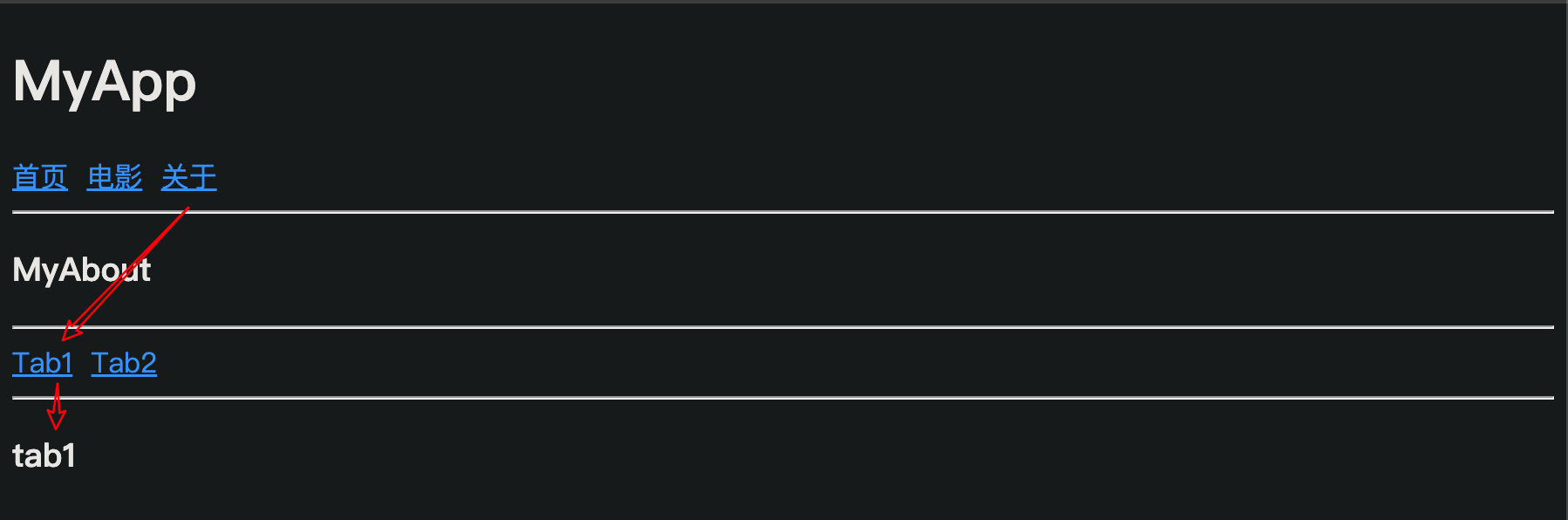
routes: [// 其中,path 表示需要被重定向的“原地址”,redirect表示将要被重定向到的“新地址”{ path: '/', redirect: '/movie' },// path 是 hash 地址, component 是要展示的组件{ path: '/home', component: MyHome },{ path: '/movie', component: MyMovie },{ path: '/about', component: MyAbout , redirect: '/about/tab1',children: [{ path: 'tab1', component: Tab1 },{ path: 'tab2', component: Tab2 },]},
]
动态路由匹配
思考:有如下 3 个路由链接:
<router-link to="/movie/1">电影1</router-link>
<router-link to="/movie/2">电影2</router-link>
<router-link to="/movie/3">电影3</router-link>
定义如下 3 个路由规则,是否可行???
{ path: '/movie/1', component: Movie },
{ path: '/movie/2', component: Movie },
{ path: '/movie/3', component: Movie },
缺点:路由规则的复用性差。
4.1 动态路由的概念
动态路由指的是:把 Hash 地址中可变的部分定义为参数项,从而提高路由规则的复用性。在 vue-router 中使用英文的冒号(:)来定义路由的参数项。
示例代码如下:
// 路由中的动态参数以:进行声明,冒号后面的是动态参数的名称
{ path: '/movie/:id', component: Movie },// 将以下3个路由规划,合并成了一个,提高了路由规划的复用性
{ path: '/movie/1', component: Movie }
{ path: '/movie/2', component: Movie }
{ path: '/movie/3', component: Movie }
4.2 $route.params 参数对象
通过动态路由匹配的方式渲染出来的组件中,可以使用 $route.params 对象访问到动态匹配的参数值。
<template><!-- $route.params 是路由的“参数对象” --><h3>MyMoive --- {{ $route.params.id }}</h3>
</template><script>
export default {name: 'MyMovie'
}
</script>
4.3 使用 props 接收路由参数
为了简化路由参数的获取形式,vue-router 允许在路由规则中开启 props 传参。示例代码如下:
// 在定义路由规则时,声明 props: true 选项// 即可在 Movie 组件中,以 props 的形式接收到路由规则匹配到的参数项
{ path: '/movie/:id', component: MyMovie , props: true},<template><!-- 3.直接使用 props 中接收路由参数 --><h3>MyMoive --- {{ id }}</h3>
</template><script>
export default {name: 'MyMovie',props: ['id'] // 2. 使用 props 接收路由规则中匹配到的参数项
}
</script>
编程式导航
通过调用 API 实现导航的方式,叫做编程式导航。与之对应的,通过点击链接实现导航的方式,叫做声明式导航。例如:
普通网页中点击链接、vue 项目中点击 都属于声明式导航
普通网页中调用 location.href 跳转到新页面的方式,属于编程式导航
5.1 vue-router 中的编程式导航 API
vue-router 提供了许多编程式导航的 API,其中最常用的两个 API 分别是:
① this.$router.push(‘hash 地址’)
跳转到指定 Hash 地址,从而展示对应的组件
② this.$router.go(数值 n)
实现导航历史的前进、后退
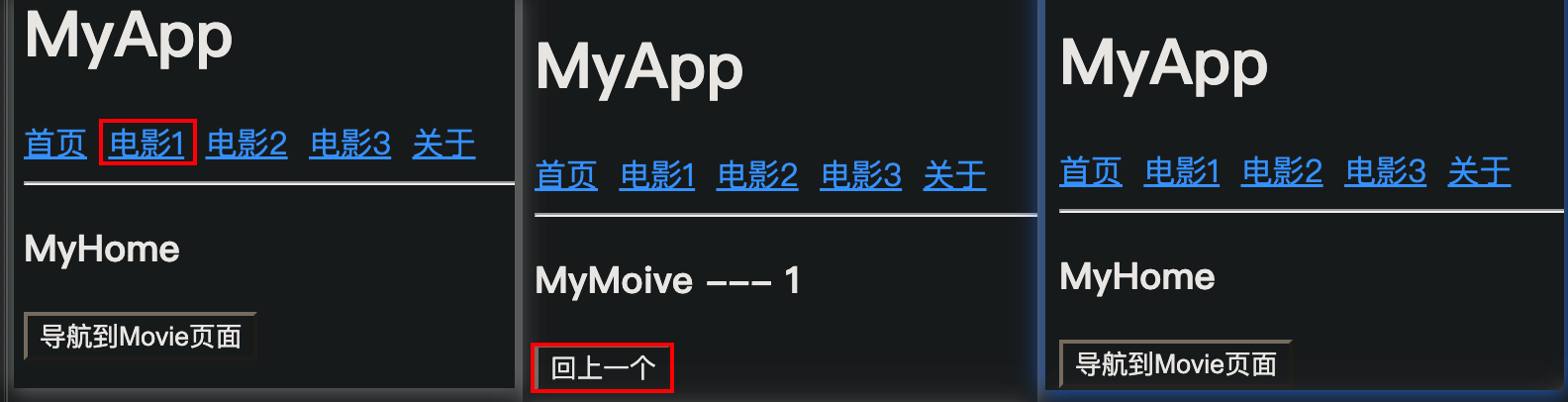
**5.2 r o u t e r . p u s h ∗ ∗ 调用 t h i s . router.push** 调用 this. router.push∗∗调用this.router.push() 方法,可以跳转到指定的 hash 地址,从而展示对应的组件页面。示例代码如下:
<template><h3>MyHome</h3><button @click="goToMovie(3)">导航到Movie页面</button>
</template><script>
export default {name: 'MyHome',methods: {goToMovie(id) {this.$router.push('/movie/' + id)// this.$router.push(`/movie/${id}`)}}
}
</script>
5.2 $router.go
调用 this.$router.go() 方法,可以在浏览历史中进行前进和后退。示例代码如下:
<template><!-- 3.直接使用 props 中接收路由参数 --><h3>MyMoive --- {{ id }}</h3><button @click="goBack()">回上一个</button>
</template><script>
export default {name: 'MyMovie' ,props: ['id'] ,// 2. 使用 props 接收路由规则中匹配到的参数项methods: {goBack() {this.$router.go(-1)}}
}
</script>
效果:
总结:
使用对应的API来实现导航跳转,就叫做编程式导航。
命名路由
通过 name 属性为路由规则定义名称的方式,叫做命名路由。示例代码如下:
{ // 使用 name 属性为当前的路由规则定义一个“名称”name: 'mov', path: '/movie/:id', component: MyMovie ,props: true,
},
注意:命名路由的 name 值不能重复,必须保证唯一性!
6.1 使用命名路由实现声明式导航
为 标签动态绑定 to 属性的值,并通过 name 属性指定要跳转到的路由规则。期间还可以用params 属性指定跳转期间要携带的路由参数。示例代码 如下:
<template><h3>MyHome</h3><router-link :to="{ name: 'mov' , params: {id: 3}}">go to Movie</router-link>
</template><script>
export default {name: 'MyHome'
}
</script>
6.2 使用命名路由实现编程式导航
调用 push 函数期间指定一个配置对象,name 是要跳转到的路由规则、params 是携带的路由参数:
<template><div><h3>MyHome</h3><router-link :to="{ name: 'mov' , params: {id: 3}}">go to Movie</router-link><button @click="goToMovie(1)"> go to movie </button></div>
</template><script>
export default {name: 'MyHome',methods: {goToMovie(id) {this.$router.push({name: 'mov',params: {id: id,}})}}
}
</script>
总结:
如果在实际项目中,哈希地址比较长的话,建议采用name来进行命名跳转
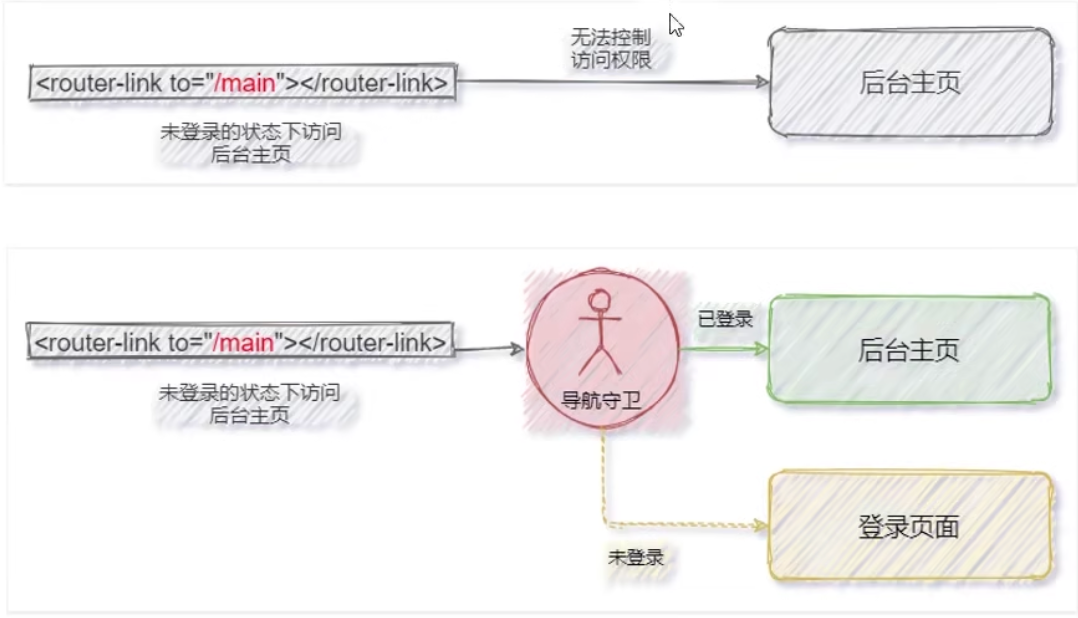
导航守卫
导航守卫可以控制路由的访问权限。示意图如下:
7.1 如何声明全局导航守卫
全局导航守卫会拦截每个路由规则,从而对每个路由进行访问权限的控制。可以按照如下的方式定义全局导航守卫:
// 创建路由实例对象
const router = createRouter({ ... })// 声明全局的导航守卫// 调用路由实例对象的 beforeEach 函数,声明 "全局前置守卫"// fn 必须是一个函数,每次拦截到路由的请求,都会调用 fn 进行处理// 因此 fn 叫做 “守卫方法”
router.beforeEach(fn)
也可以是箭头函数:
router.beforeEach(() => {console.log('ok');
})
7.2 守卫方法的 3 个形参
全局导航守卫的守卫方法中接收 3 个形参,格式为:
// 创建路由实例对象
const router = createRouter({ ... })// 全局前置守卫
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {// to 目标路由对象// from 当前导航正要离开的路由对象// next 是一个函数,表示放行
})
注意:
① 在守卫方法中如果不声明 next 形参,则默认允许用户访问每一个路由!
② 在守卫方法中如果声明了 next 形参,则必须调用 next() 函数,否则不允许用户访问任何一个路由!
7.3 next 函数的 3 种调用方式
参考示意图,分析 next 函数的 3 种调用方式最终导致的结果:
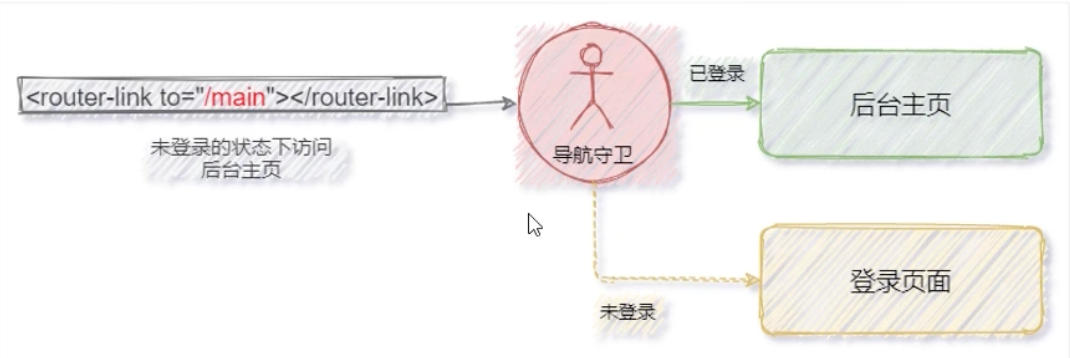
直接放行:next()
案例:
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {if(to.path === '/main') {// 证明用户要访问后台 主页next()} else {// 访问的不是后台主页next()}
})
强制其停留在当前页面:next(false)
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {if(to.path === '/main') {// 证明用户要访问后台 主页next(false)} else {// 访问的不是后台主页next()}
})
强制其跳转到登录页面:next(‘/login’)
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {if(to.path === '/main') {// 证明用户要访问后台 主页next('/login')} else {// 访问的不是后台主页next()}
})
7.4 结合 token 控制后台主页的访问权限
目的:通过token来控制后台主页的访问权限
我们先通过localStorage来获取token值,再判断目的地址是否为main以及token值是否存在,
如果用户的token值存在且目的地址为main,则让用户通过,否则让用户进入登陆页面。
这里我通过在Application中设置假token来进入网站:
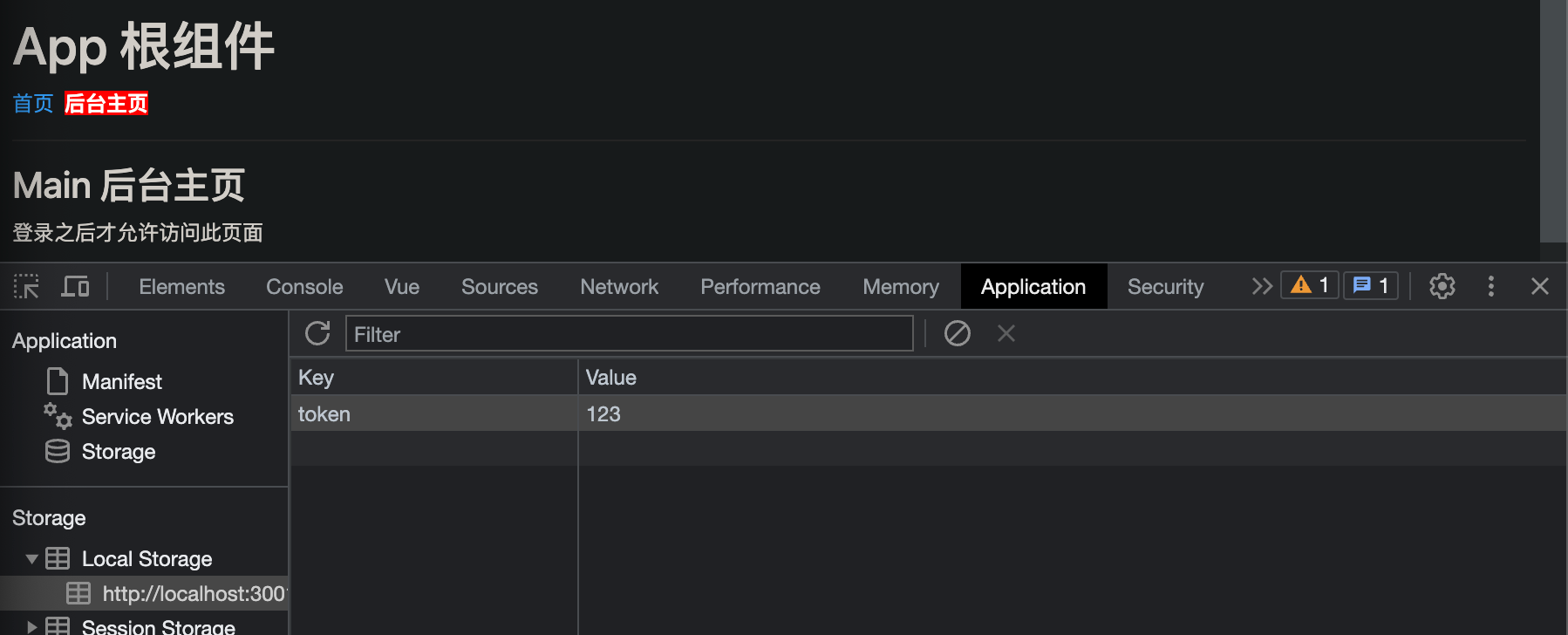
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {const tokenStr = localStorage.getItem('token') // 1. 获取 tokenif(to.path === '/main' && !token) { // 2. 想要访问“后台主页”,且token值不存在// next(false) // 3.1 不允许跳转next('/login') // 3.2 强制跳转到"登陆页面"} else {next() // 3.3 直接放行,允许访问“后台主页”}
})
理解:从localstorage值获取token值,并且根据访问路径以及token值是否存在来进行下面的逻辑处理
VueCli 自定义创建项目
创建步骤:
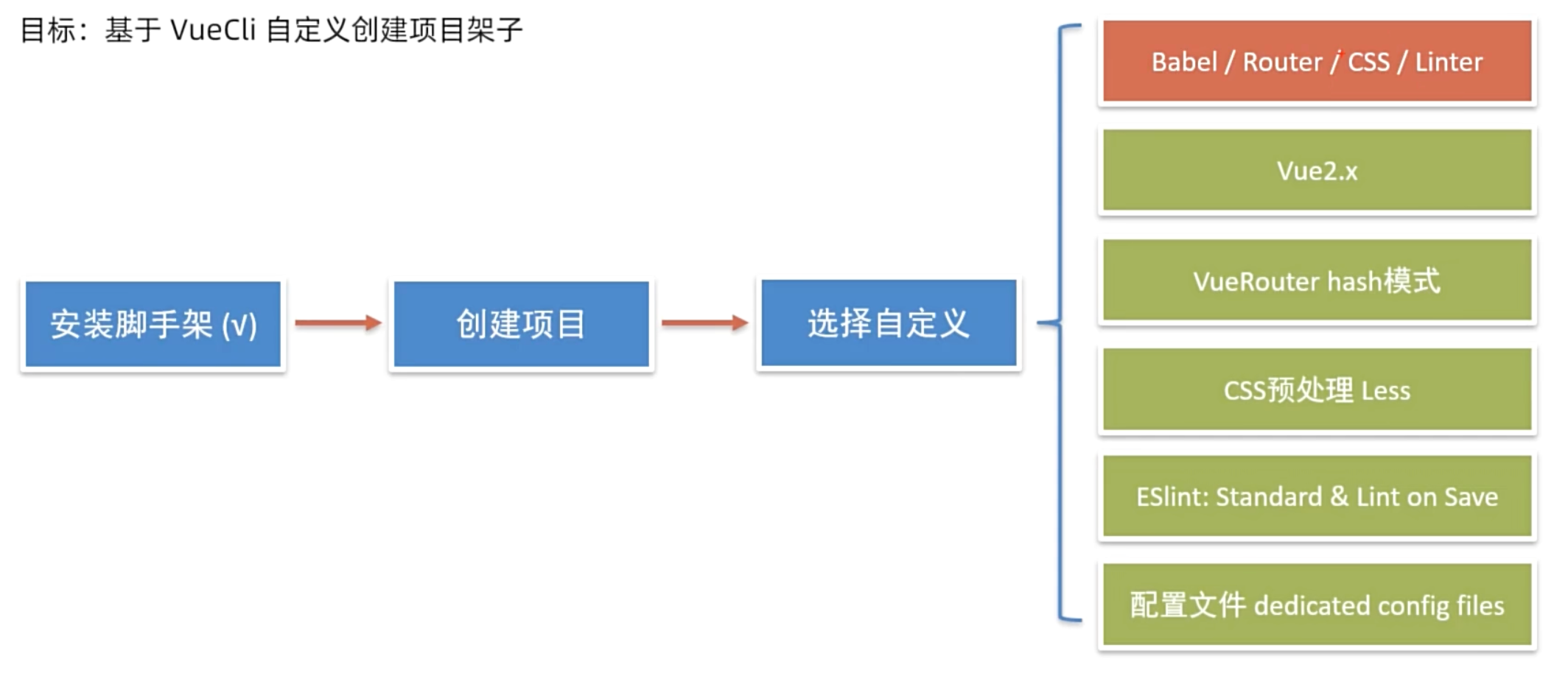
1.安装脚手架 (已安装)
npm i @vue/cli -g
2.创建项目
vue create hm-exp-mobile
- 选项
Vue CLI v5.0.8
? Please pick a preset:Default ([Vue 3] babel, eslint)Default ([Vue 2] babel, eslint)
> Manually select features 选自定义
- 手动选择功能

- 选择vue的版本
3.x
> 2.x
- 是否使用history模式

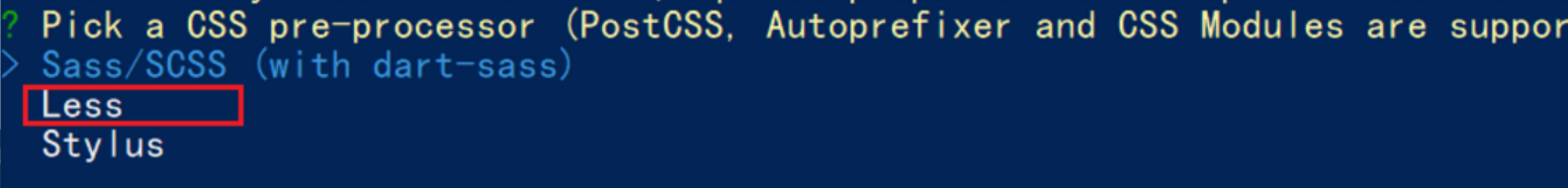
- 选择css预处理
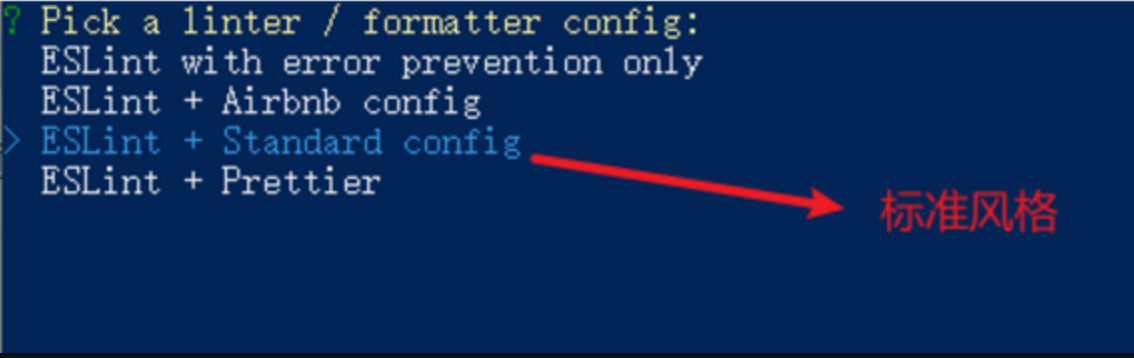
- 选择eslint的风格 (eslint 代码规范的检验工具,检验代码是否符合规范)
- 比如:const age = 18; => 报错!多加了分号!后面有工具,一保存,全部格式化成最规范的样子
- 选择校验的时机 (直接回车)
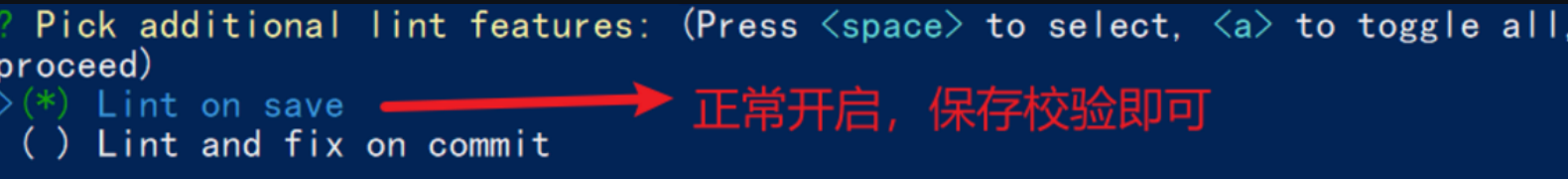
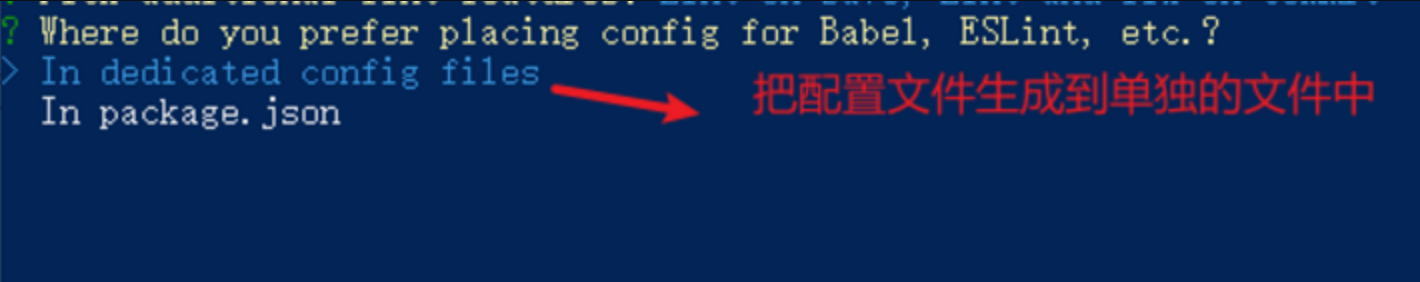
- 选择配置文件的生成方式 (直接回车)
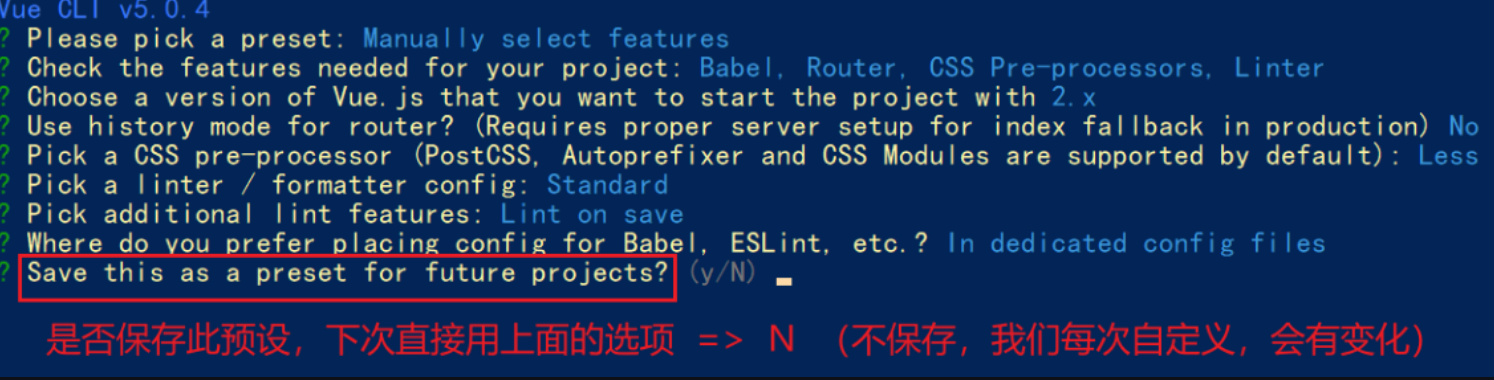
- 是否保存预设,下次直接使用? => 不保存,输入 N
- 等待安装,项目初始化完成
- 启动项目
npm run serve
ESlint代码规范及手动修复
代码规范:一套写代码的约定规则。
例如:赋值符号的左右是否需要空格?一句结束是否是要加;?…
没有规矩不成方圆
ESLint:是一个代码检查工具,用来检查你的代码是否符合指定的规则(你和你的团队可以自行约定一套规则)。在创建项目时,我们使用的是 JavaScript Standard Style 代码风格的规则。
1.JavaScript Standard Style 规范说明
建议把:https://standardjs.com/rules-zhcn.html 看一遍,然后在写的时候, 遇到错误就查询解决。
下面是这份规则中的一小部分:
- 字符串使用单引号 – 需要转义的地方除外
- 无分号 – 这没什么不好。不骗你!
- 关键字后加空格
if (condition) { ... } - 函数名后加空格
function name (arg) { ... } - 坚持使用全等
===摒弃==一但在需要检查null || undefined时可以使用obj == null - …
2.代码规范错误
如果你的代码不符合standard的要求,eslint会跳出来刀子嘴,豆腐心地提示你。
下面我们在main.js中随意做一些改动:添加一些空行,空格。
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'import './styles/index.less'
import router from './router'
Vue.config.productionTip = falsenew Vue ( {render: h => h(App),router
}).$mount('#app')
按下保存代码之后:
你将会看在控制台中输出如下错误:
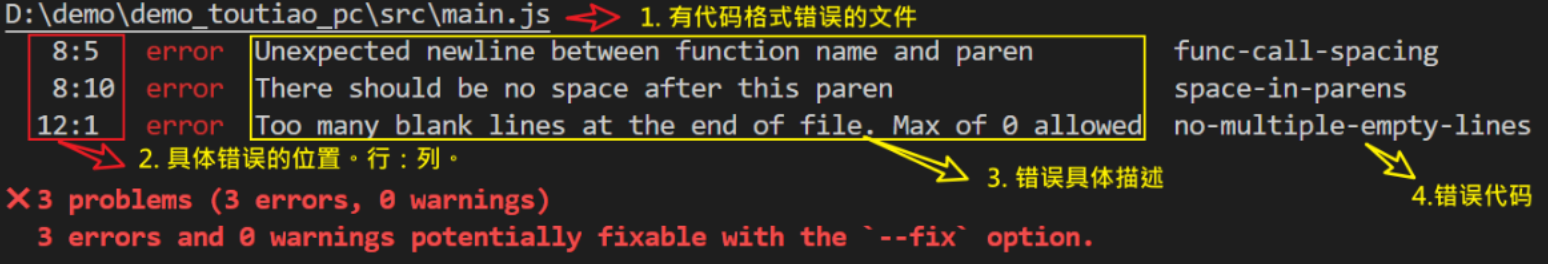
eslint 是来帮助你的。心态要好,有错,就改。
3.手动修正
根据错误提示来一项一项手动修正。
如果你不认识命令行中的语法报错是什么意思,你可以根据错误代码(func-call-spacing, space-in-parens,…)去 ESLint 规则列表中查找其具体含义。
打开 ESLint 规则表,使用页面搜索(Ctrl + F)这个代码,查找对该规则的一个释义。
通过eslint插件来实现自动修正
eslint会自动高亮错误显示
通过配置,eslint会自动帮助我们修复错误
- 如何安装

- 如何配置
// 当保存的时候,eslint自动帮我们修复错误
"editor.codeActionsOnSave": {"source.fixAll": true
},
// 保存代码,不自动格式化
"editor.formatOnSave": false
注意:eslint的配置文件必须在根目录下,这个插件才能才能生效。打开项目必须以根目录打开,一次打开一个项目
注意:使用了eslint校验之后,把vscode带的那些格式化工具全禁用了 Beatify
settings.json 参考
{"window.zoomLevel": 2,"workbench.iconTheme": "vscode-icons","editor.tabSize": 2,"emmet.triggerExpansionOnTab": true,// 当保存的时候,eslint自动帮我们修复错误"editor.codeActionsOnSave": {"source.fixAll": true},// 保存代码,不自动格式化"editor.formatOnSave": false
}