目录
- 1 树
- 1.1 认识树
- 1.2 树的相关概念
- 1.3 树的表示
- 孩子兄弟表示法
- 2 二叉树
- 2.1 概念
- 2. 2 特殊二叉树
- 2.3 二叉树的性质
- 2.4 二叉树的存储结构
- 3 堆 — 完全二叉树的顺序结构实现
- 3.1 堆的概念
- 3.2 核心代码
- 3.3 堆应用
- 1 堆排序
- 2 TOP-K问题
- 4 二叉树的链式存储
- 4.1 二叉链结构与初始化
- 4.2 核心代码
- 5 二叉搜索树
- 5.1 概念
- 5.2 结构与代码实现
- 5.3 复杂度与缺陷
- 6 AVL树
- 6.1 概念
- 6.2 旋转核心代码与思想
- 6.3 插入
- 6.4 验证平衡
- 7 红黑树
- 7.1 红黑树的概念
- 7.2 红黑树的性质
- 7.3 插入
- 插入思想
- 核心代码
- 7.4 验证红黑树
1 树
1.1 认识树
树是一种非线性的数据结构,它是由n(n>=0)个有限结点组成一个具有层次关系的集合。
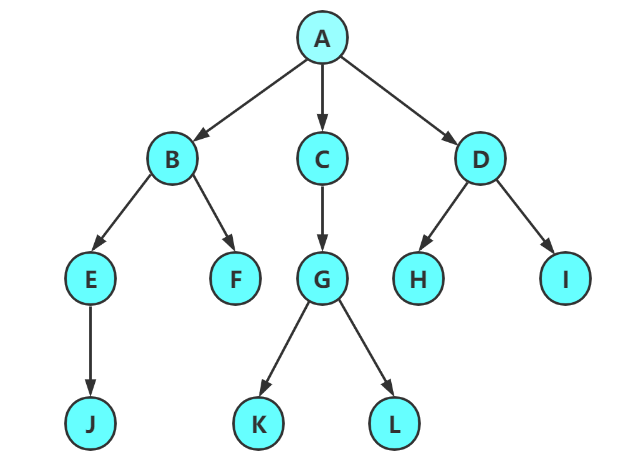
- 有一个特殊的结点,称为根结点,根节点没有前驱结点
- 除根节点外,其余结点被分成M(M>0)个互不相交的集合T1、T2、……、Tm,其中每一个集合Ti(1<= i<= m)又是一棵结构与树类似的子树。每棵子树的根结点有且只有一个前驱,可以有0个或多个后继。
- 因此,树是递归定义的。
- 注意:树形结构中
- 子树之间不能有交集,否则就不是树形结构
- 除了根节点外,每个结点有且仅有一个父结点
- 一颗N各结点的树有N-1条边
1.2 树的相关概念
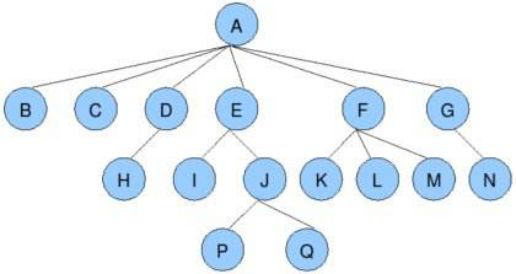
- 节点的度:一个节点含有的子树的个数称为该节点的度; 如上图:A的为6
- 叶节点或终端节点:度为0的节点称为叶节点; 如上图:B、C、H、I…等节点为叶节点
- 非终端节点或分支节点:度不为0的节点; 如上图:D、E、F、G…等节点为分支节点
- 双亲节点或父节点:若一个节点含有子节点,则这个节点称为其子节点的父节点; 如上图:A是B的父节点
- 孩子节点或子节点:一个节点含有的子树的根节点称为该节点的子节点; 如上图:B是A的孩子节点
- 兄弟节点:具有相同父节点的节点互称为兄弟节点; 如上图:B、C是兄弟节点
- 树的度:一棵树中,最大的节点的度称为树的度; 如上图:树的度为6
- 节点的层次:从根开始定义起,根为第1层,根的子节点为第2层,以此类推;
- 树的高度或深度:树中节点的最大层次; 如上图:树的高度为4
- 堂兄弟节点:双亲在同一层的节点互为堂兄弟;如上图:H、I互为兄弟节点
- 节点的祖先:从根到该节点所经分支上的所有节点;如上图:A是所有节点的祖先
- 子孙:以某节点为根的子树中任一节点都称为该节点的子孙。如上图:所有节点都是A的子孙
- 森林:由m(m>0)棵互不相交的树的集合称为森林;
1.3 树的表示
孩子兄弟表示法
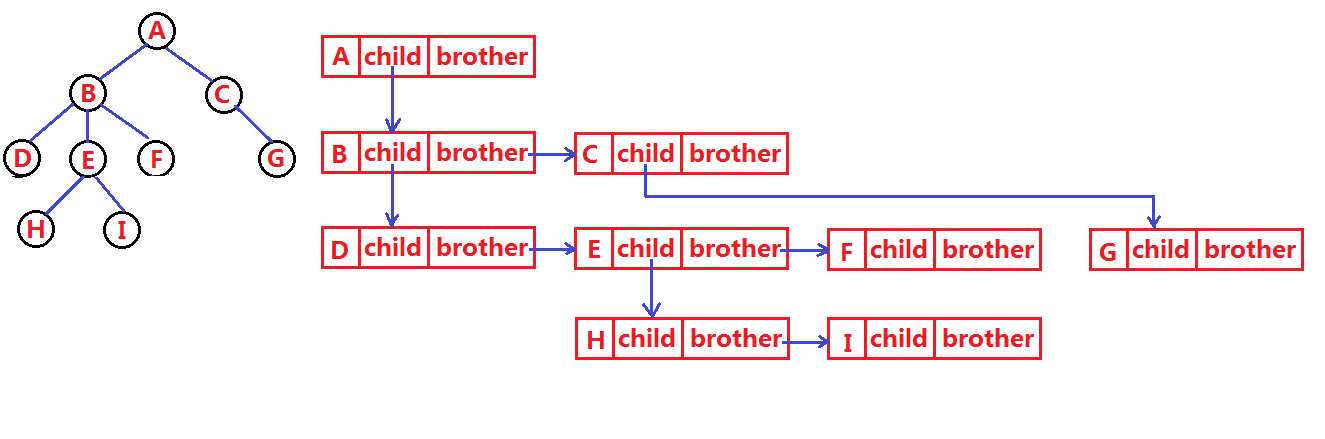
typedef int DataType;
struct TreeNode {struct TreeNode* _firstChild1; //第一个孩子结点struct Node* _pNextBrother; //指向其下一个兄弟结点DataType _data; //结点中的数据域
};
2 二叉树
2.1 概念
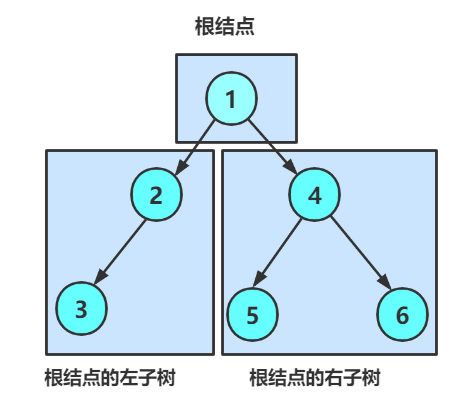
一棵二叉树是结点的一个有限集合,该集合:
- 或者为空
- 或者,由一个根节点加上两颗别称为左子树和右子树的二叉树组成
注意:
二叉树不存在度大于2的结点
二叉树的子树有左右之分,次序不能颠倒,因此二叉树是有序树
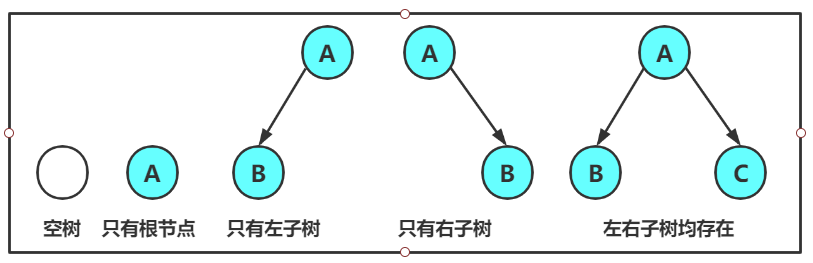
任意二叉树都是由以下几种情况复合而成
2. 2 特殊二叉树
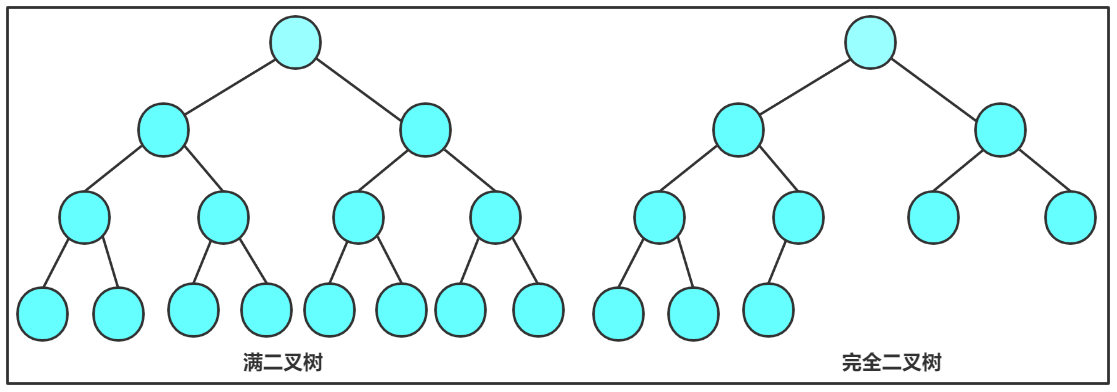
满二叉树:
- 每一层节点数达到最大值,即第k层结点总数为2(k-1)。
- 通过等比数列运算,满二叉树总结点数为2k - 1。
完全二叉树:
- 对于深度为k的完全二叉树,则前k-1层是满的
- 最后一层从左到右是连续的
2.3 二叉树的性质
若规定根节点的层数为1,则一棵非空二叉树的第i层上最多有2(i-1)个结点.
若规定根节点的层数为1,则深度为h的二叉树的最大结点数是2h - 1.
对任何一棵二叉树,如果度为0其叶结点个数为n0,度为2的分支结点个数为n2 ,则有n0= n2+1
若规定根节点的层数为1,具有n个结点的满二叉树的深度,h = log2(n+1)
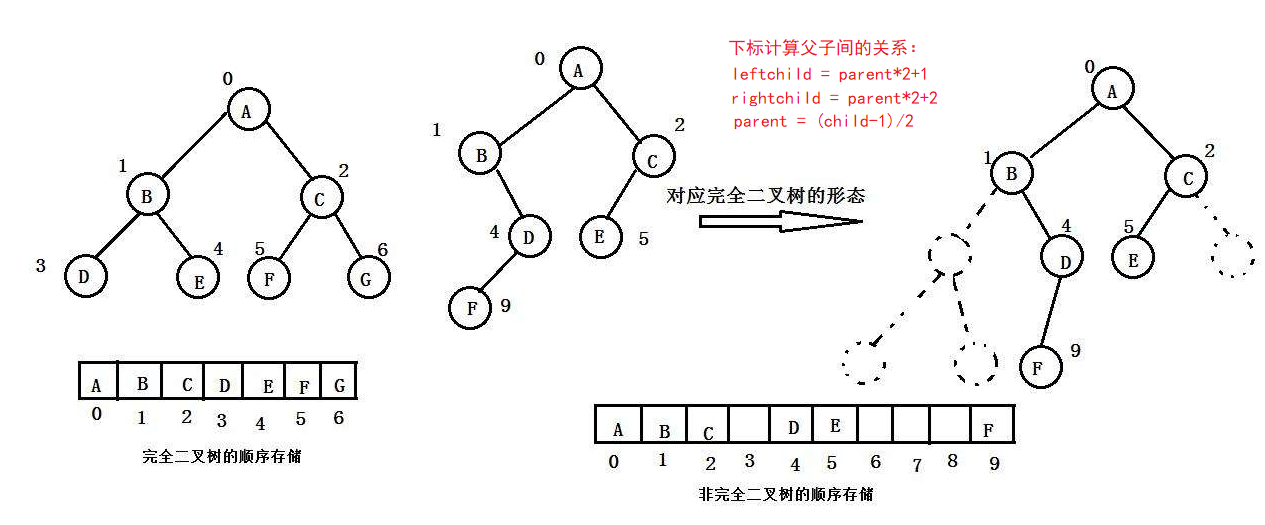
对于具有n个结点的完全二叉树,如果按照从上至下从左至右的数组顺序对所有节点从0开始编号,则对
于序号为i的结点有:
2.4 二叉树的存储结构
二叉树一般有两种结构存储,一种顺序结构,一种链式结构
顺序结构
适合满二叉树和完全二叉树,其他二叉树会造成空间浪费。
链式结构
- 二叉链
typedef int BTDataType; // 二叉链 struct BinaryTreeNode {struct BinTreeNode* _pLeft; // 指向当前节点左孩子struct BinTreeNode* _pRight; // 指向当前节点右孩子BTDataType _data; // 当前节点值域 };
- 三叉链
// 三叉链 struct BinaryTreeNode {struct BinTreeNode* _pParent; // 指向当前节点的双亲struct BinTreeNode* _pLeft; // 指向当前节点左孩子struct BinTreeNode* _pRight; // 指向当前节点右孩子BTDataType _data; // 当前节点值域 };
3 堆 — 完全二叉树的顺序结构实现
3.1 堆的概念
完全二叉树
- 小根堆:树中所有的父亲都是小于等于孩子
- 大根堆:树中所有的父亲都是大于等于孩子
3.2 核心代码
- 插入时向上调整
typedef int HPDataType;
typedef struct Heap {HPDataType* a;int size;int capacity;
}HP;
//向上调整
void AdjustUp(HPDataType* a, int child) {int parent = (child - 1) / 2;while (child > 0) {// if (a[child] > a[parent]) //大根堆if (a[child] < a[parent]) {Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);child = parent;parent = (child - 1) / 2;}else {break;}}
}
void HeapPush(HP* php, HPDataType x) {assert(php);if (php->size == php->capacity) {//扩容int newcapacity = php->capacity == 0 ? 4 : php->capacity * 2;HPDataType* tmp = (HPDataType*)realloc(php->a, sizeof(HPDataType)*newcapacity);if (tmp == NULL) {printf("realloc fail\n");exit(-1);}php->a = tmp;php->capacity = newcapacity;}php->a[php->size] = x;php->size++;AdjustUp(php->a, php->size - 1);}
- 删除时向下调整
//向下调整
void AdjustDown(HPDataType* a, int size, int parent) {int child = parent * 2 + 1;while(child < size){// if (child+1 < size && a[child + 1] > a[child]) //大根堆if (child+1 < size && a[child + 1] < a[child]) {++child;}// if (a[child] > a[parent]) //大根堆if (a[child] < a[parent]) {Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);parent = child;child = parent * 2 + 1;}else{break;}}}
void HeapPop(HP* php) {assert(php);assert(php->size > 0);Swap(php->a[0], php->a[php->size - 1]);php->size--;AdjustDown(php->a, php->size, 0);}
3.3 堆应用
1 堆排序
升序排序使用大根堆,降序排序使用小根堆
核心代码
void HeapSort(int* a, int n) {// 向下调整建堆 O(N)for (int i = (n - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; --i) {AdjustDown(a, n, i);}int end = n - 1;// O(N * logN) while (end > 0){Swap(&a[0], &a[end]);AdjustDown(a, end, 0);--end;}}
时间复杂度
O(N*logN)
2 TOP-K问题
求大数据量大的前K个最大或最小元素。
- 直接堆排序 O(N*logN)
- 当数据量不是非常大时,建N个数的大堆,Top/Pop K次, O(N + logN*K)
- 当N非常大(100亿),K比较小(100)
- 前K个数建立小堆
- 剩下的N-K个一次跟堆顶数据比较,如果比堆顶数据大,就替换堆顶数据进队
- 走完以后,堆里面的K个数,就是最大的前K个
核心代码
//模拟实现
void PrintTopK(int* a, int n, int k)
{// 1. 建堆--用a中前k个元素建堆int* kMinHeap = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * k);assert(kMinHeap);for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {kMinHeap[i] = a[i];}for (int i = (k - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; --i) {AdjustDown(kMinHeap, k, i);}// 2. 将剩余n-k个元素依次与堆顶元素交换,不满则则替换for (int j = k; j < n; ++j) {if (a[j] > kMinHeap[0]) {kMinHeap[0] = a[j];AdjustDown(kMinHeap, k, 0);}}for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {printf("%d ", kMinHeap[i]);}printf("\n");
}
void TestTopk()
{int n = 10000;int* a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);srand(time(0));for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){a[i] = rand() % 1000000;}a[5] = 1000000 + 1;a[1231] = 1000000 + 2;a[531] = 1000000 + 3;a[5121] = 1000000 + 4;a[115] = 1000000 + 5;a[2335] = 1000000 + 6;a[9999] = 1000000 + 7;a[76] = 1000000 + 8;a[423] = 1000000 + 9;a[3144] = 1000000 + 10;PrintTopK(a, n, 10);
}
4 二叉树的链式存储
二叉树的链式存储结构是指,用链表来表示一棵二叉树,即用链来指示元素的逻辑关系。 通常的方法是链表中每个结点由三个域组成,数据域和左右指针域,左右指针分别用来给出该结点左孩子和右孩子所在的链结点的存储地址 。
链式结构又分为二叉链和三叉链,三叉链比二叉链多一个parent指针。
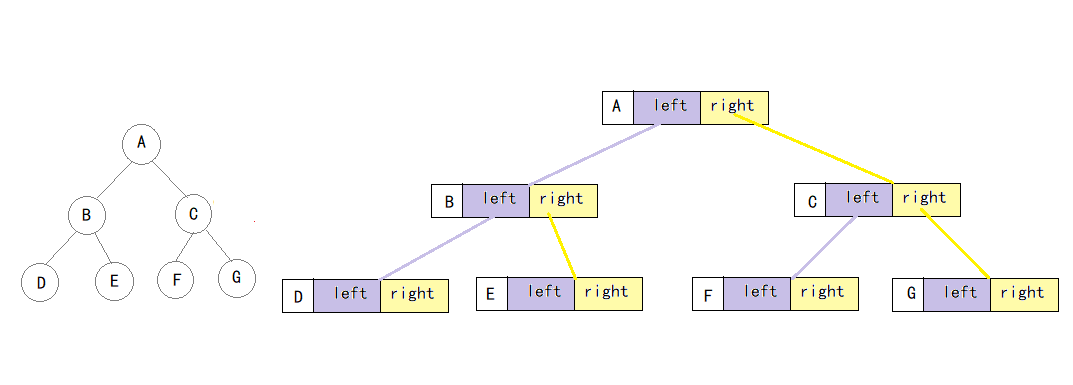
4.1 二叉链结构与初始化
typedef int BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode {struct BinaryTreeNode* left;struct BinaryTreeNode* right;BTDataType data;
}BTNode;BTNode* BuyNode(BTDataType x) {BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));assert(node);node->data = x;node->left = NULL;node->right = NULL;return node;
}
4.2 核心代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "Queue.h"
typedef int BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode {struct BinaryTreeNode* left;struct BinaryTreeNode* right;BTDataType data;
}BTNode;BTNode* BuyNode(BTDataType x) {BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));assert(node);node->data = x;node->left = NULL;node->right = NULL;return node;
}
BTNode* CreatBinaryTree()
{BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);node1->left = node2;node1->right = node4;node2->left = node3;node4->left = node5;node4->right = node6;return node1;
}
// 前序遍历 分治
void PreOrder(BTNode* root) {if (root == NULL) {printf("# ");return;}printf("%d ", root->data);PreOrder(root->left);PreOrder(root->right);
}
// 中序遍历
void InOrder(BTNode* root) {if (root == NULL) {printf("# ");return;}PreOrder(root->left);printf("%d ", root->data);PreOrder(root->right);
}// 后序遍历
void PostOrder(BTNode* root) {if (root == NULL) {printf("# ");return;}PreOrder(root->left);PreOrder(root->right);printf("%d ", root->data);}
int count = 0;
void TreeSize(BTNode* root) {if (root == NULL) {return;}++count;TreeSize(root->left);TreeSize(root->right);
}
// 分而治之
int TreeSize2(BTNode* root) {return root == NULL ? 0 :TreeSize2(root->left) + TreeSize2(root->right) + 1;
}int TreeLeafSize2(BTNode* root) {if (root == NULL)return 0;else if(root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL){return 1;}else {return TreeLeafSize2(root->left) + TreeLeafSize2(root->right);}
}
// 求第K层结点数
int TreeKLevel(BTNode* root, int k) {assert(k >= 1);if (root == NULL) {return 0;}if (k == 1) {return 1;}return TreeKLevel(root->left, k - 1) + TreeKLevel(root->right, k - 1);
}
// 求二叉树深度
int TreePath(BTNode* root) {if (root == NULL) {return 0;}else {int leftDepth = TreePath(root->left);int rightDepth = TreePath(root->right);return (leftDepth > rightDepth) ? (leftDepth + 1) : (rightDepth + 1);}
}// 二叉树查找值为x的结点
BTNode* TreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x) {if (root == NULL)return NULL;if (root->data == x) {return root;}BTNode* ret1 = TreeFind(root->left, x);if (ret1)return ret1;BTNode* ret2 = TreeFind(root->left, x);if (ret2)return ret2;return NULL;
}void TreeDestroy(BTNode* root) {if (root == NULL) {return;}TreeDestroy(root->left);TreeDestroy(root->right);printf("%p:%d\n", root, root->data);free(root);}//层序遍历 一种广度优先遍历 借助队列
void LevelOrder(BTNode* root) {Queue q;QueueInit(&q);if (root) {QueuePush(&q, root);}while (!QueueEmpty(&q)){BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);printf("%d ", front->data);QueuePop(&q);if (front->left) {QueuePush(&q, front->left);}if (front->right) {QueuePush(&q, front->right);}}printf("\n");QueueDestroy(&q);
}// 判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树 借助队列
bool TreeComplete(BTNode* root) {Queue q;QueueInit(&q);if (root) {QueuePush(&q, root);}while (!QueueEmpty(&q)){BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);QueuePop(&q);if (front) {QueuePush(&q, front->left);QueuePush(&q, front->right);}else {//遇到空以后,则跳出层序遍历break;}}//1、如果后面全是空,则是完全二叉树//2、如果空后面还有非空,则不是完全二叉树while (!QueueEmpty(&q)){BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);QueuePop(&q);if (front) {QueueDestroy(&q);return false;}}QueueDestroy(&q);return true;
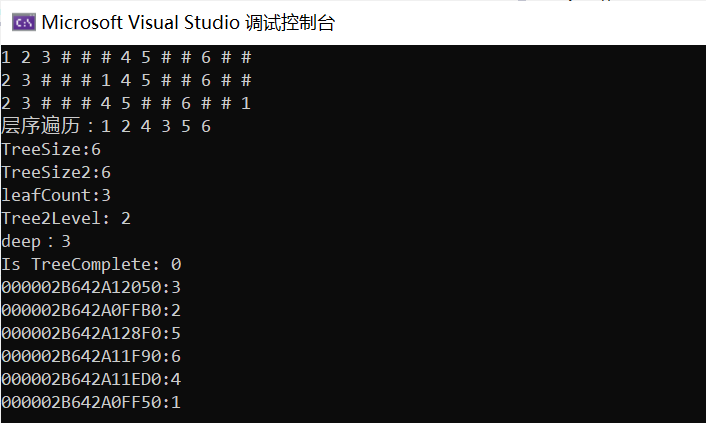
}int main() {BTNode* root = CreatBinaryTree();PreOrder(root);printf("\n");InOrder(root);printf("\n");PostOrder(root);printf("\n");printf("层序遍历:");LevelOrder(root);TreeSize(root);printf("TreeSize:%d\n", count);printf("TreeSize2:%d\n", TreeSize2(root));printf("leafCount:%d\n", TreeLeafSize2(root));printf("Tree2Level: %d\n", TreeKLevel(root, 2));printf("deep:%d\n", TreePath(root));printf("Is TreeComplete: %d\n", TreeComplete(root)); TreeDestroy(root);root = NULL;return 0;
}
5 二叉搜索树
5.1 概念
二叉搜索树又称二叉排序树,它是一棵空树或者具有以下性质的非空二叉树:
- 若左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值
- 若右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值
- 搜索二叉树的左右子树也分别为二叉搜索树
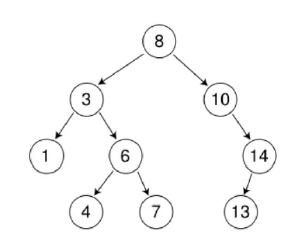
因其以上特性,使用搜索二叉树查找时,最多查找次数等于其高度。
对二叉搜索树进行中序遍历,可得到一个升序排序的数值。
5.2 结构与代码实现
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <class K>
struct BSTreeNode {BSTreeNode<K>* _left;BSTreeNode<K>* _right;K _key;BSTreeNode(const K& key): _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _key(key){}
};//class BinarySearchTree {
template<class K>
class BSTree{typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
public:bool Insert(const K& key) {if (_root == nullptr) {_root = new Node(key);return true;}Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_key < key) {parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (cur->_key > key){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else {return false;}}cur = new Node(key);if (parent->_key < key) {parent->_right = cur;}else {parent->_left = cur;}return true;}bool Find(const K& key) {Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_key < key) {parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (cur->_key > key){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else {return true;}}return false;}bool Erase(const K& key) { Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_key < key) {parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (cur->_key > key) {parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else {// 开始删除//1. 左为空//2. 右为空//3. 左右都不为空if (cur->_left == nullptr) {if (cur == _root) {_root = cur->_right;}else {if (cur == parent->_left) {parent->_left = cur->_right;}else {parent->_right = cur->_right;}}delete cur;cur = nullptr;}else if (cur->_right == nullptr) {if (_root == cur) {_root = cur->_left;}else {if (cur == parent->_left) {parent->_left = cur->_left;}else {parent->_right = cur->_left;}}delete cur;cur = nullptr;}else {//替换法删除Node* minParent = cur;Node* min = cur->_right;while (min->_left){minParent = min;min = min->_left;}//cur->_key = min->_key;swap(cur->_key, min->_key);if (minParent->_left == min){minParent->_left = min->_right;}else {minParent->_right = min->_right;}delete min;}return true;}}return false;}void InOrder() {_InOrder(_root);cout << endl;}/*---------------------利用递归实现操作-------------------------------*/bool FindR(const K& key) {return _FindR(_root, key);}bool InsertR(const K& key) {return _InsertR(_root, key);}bool EraseR(const K& key) {return _EraseR(_root, key);}~BSTree() {_Destory(_root);}// c++11的用法,强制编译器生成默认的构造BSTree() = default;BSTree(const BSTree<K>& t) {_root = _Copy(t._root);}BSTree<K>& operator=(BSTree<K> t) {swap(_root, t._root);return *this;}
private:Node* _Copy(Node* root) {if (root == nullptr) {return nullptr;}Node* copyRoot = new Node(root->_key);copyRoot->_left = _Copy(root->_left);copyRoot->_right = _Copy(root->_right);return copyRoot;}void _Destory(Node*& root) {if (root == nullptr) {return;}_Destory(root->_left);_Destory(root->_right);delete root;root = nullptr;}bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key) {if (root == nullptr) {return false;}if (root->_key < key) {return _EraseR(root->_right, key);}else if (root->_key > key) {return _EraseR(root->_left, key);}else {Node* del = root;if (root->_left == nullptr) {root = root->_right;}else if (root->_right == nullptr) {root = root->_left;}else {// 找右树的最左节点Node* min = root->_right;while (min->_left) {min = min->_left;}swap(root->_key, min->_key);return _EraseR(root->_right, key);}delete del;return true;}}bool _InsertR(Node* &root, const K& key) {if (root == nullptr) {root = new Node(key);return true;}if (root->_key < key) {return _InsertR(root->_right, key);}else if (root->_key > key) {return _InsertR(root->_left, key);}else {return false;}}bool _FindR(Node* root, const K& key) {if (root == nullptr) {return false;}if (root->_key < key) {return _FindR(root->_right);}else if (root->_key > key) {return _FindR(root->_left, key);}else {return true;}}void _InOrder(Node* root) {if (root == nullptr) {return;}_InOrder(root->_left);cout << root->_key << " ";_InOrder(root->_right);}
private:Node* _root = nullptr;};
void TestBSTree1() {BSTree<int> t;int a[] = { 8, 3, 1, 10, 6, 4, 7, 14, 13 };for (auto e : a) {t.Insert(e);}// 排序+去重t.InOrder();t.EraseR(3);t.InOrder();t.EraseR(8);t.InOrder();for (auto e : a) {t.EraseR(e);t.InOrder();}
}
void TestBSTree3() {BSTree<int> t;int a[] = { 8, 3, 1, 10, 6, 4, 7, 14, 13 };for (auto e : a) { t.InsertR(e);}BSTree<int> copy = t;copy.InOrder();t.InOrder();BSTree<int> t1;t1.Insert(2);t1.Insert(1);t1.Insert(3);copy = t1;copy.InOrder();t1.InOrder();
}
5.3 复杂度与缺陷
二叉搜索树的增删查的时间复杂度为O(h),h为树的高度。当key值的插入接近有序时,h最坏情况下等于N。此时增删查时间复杂度过高。
平衡树(AVL树)改善了此处的缺陷。
6 AVL树
6.1 概念
当向二叉搜索树中插入新结点后,如果能保证每个结点的左右子树高度之差的绝对值不超过1(需要对树中的结点进行调整),即可降低树的高度,从而减少平均搜索长度。
AVL树,或者是颗空树,或者是具有下列性质的二叉搜索树:
- 左右子树都是AVL树
- 左右子树高度之差(简称平衡因子)的绝对值不超过1(-1/0/1)
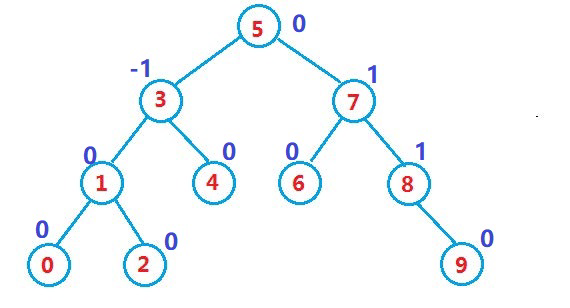
6.2 旋转核心代码与思想
单旋:
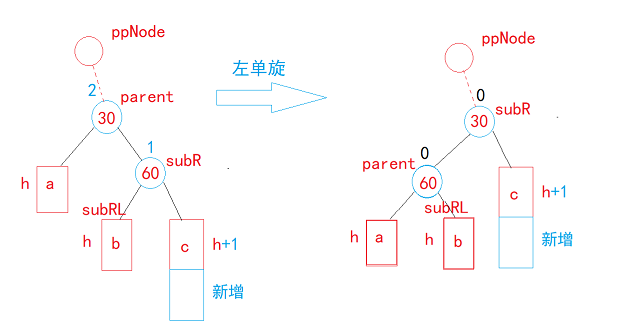
//左单旋
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;parent->_right = subRL;if (subRL)subRL->_parent = parent;Node* ppNode = parent->_parent;subR->_left = parent;parent->_parent = subR;if (_root == parent){_root = subR;subR->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (ppNode->_left == parent){ppNode->_left = subR;}else{ppNode->_right = subR;}subR->_parent = ppNode;}subR->_bf = parent->_bf = 0;
}
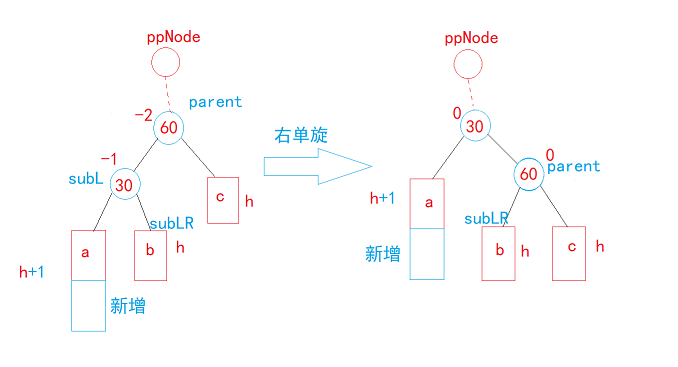
//右单旋
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;parent->_left = subLR;if (subLR){subLR->_parent = parent;}Node* ppNode = parent->_parent;subL->_right = parent;parent->_parent = subL;if (_root == parent){_root = subL;subL->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (ppNode->_left == parent){ppNode->_left = subL;}else{ppNode->_right = subL;}subL->_parent = ppNode;}subL->_bf = parent->_bf = 0;
}
左右双旋:
- b插入新增,引发双旋
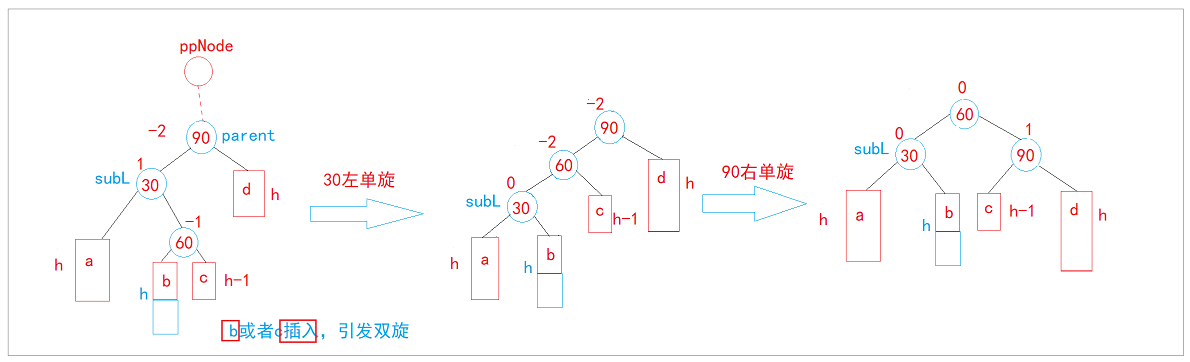
- c插入新增,引发双旋
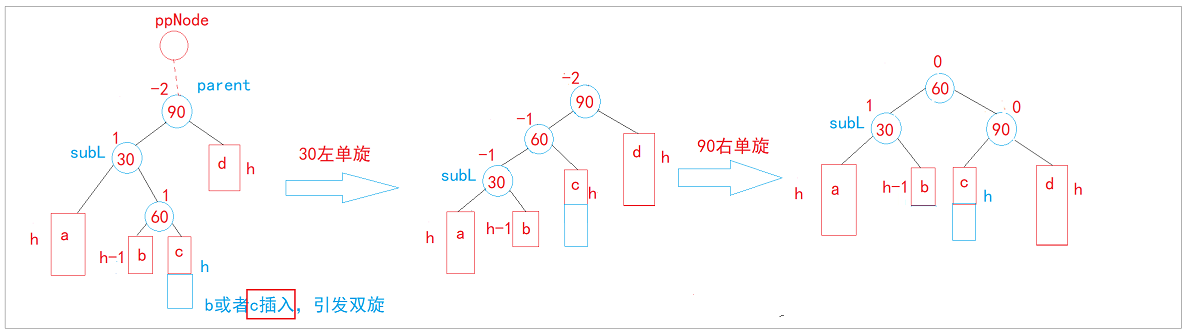
- a/b/c/d是空树,60是新增,引发双旋
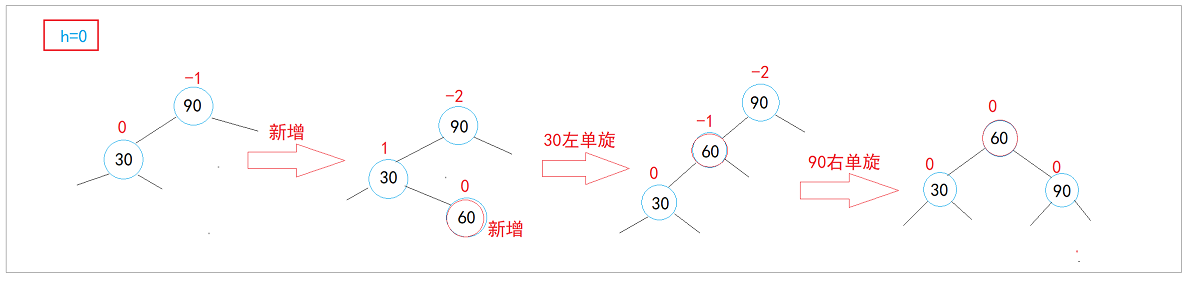
void RotateLR(Node* parent)
{Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;int bf = subLR->_bf;RotateL(parent->_left);RotateR(parent);subLR->_bf = 0;if (bf == 1){parent->_bf = 0;subL->_bf = -1;}else if (bf == -1){parent->_bf = 1;subL->_bf = 0;}else if (bf == 0){parent->_bf = 0;subL->_bf = 0;}else{assert(false);}
}
//右左双旋,与左右双旋相似,图略
void RotateRL(Node* parent)
{Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;int bf = subRL->_bf;RotateR(parent->_right);RotateL(parent);subRL->_bf = 0;if (bf == 1){subR->_bf = 0;parent->_bf = -1;}else if (bf == -1){subR->_bf = 1;parent->_bf = 0;}else if (bf == 0){parent->_bf = 0;subR->_bf = 0;}else{assert(false);}
}
旋转的价值和意义:
- 平衡
- 降高度(高度恢复到插入之前的样子)
6.3 插入
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(kv);return true;}Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_kv.first < kv.first){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (cur->_kv.first > kv.first){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else{return false;}}cur = new Node(kv);if (parent->_kv.first < kv.first){parent->_right = cur;}else{parent->_left = cur;}cur->_parent = parent;// 控制平衡// 1、更新平衡因子while (parent){if (cur == parent->_right){parent->_bf++;}else{parent->_bf--;}if (parent->_bf == 0){break;}else if (abs(parent->_bf) == 1){parent = parent->_parent;cur = cur->_parent;}else if (abs(parent->_bf) == 2){// 说明parent所在子树已经不平衡了,需要旋转处理if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == 1){RotateL(parent);}else if ((parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == -1)){RotateR(parent);}else if (parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == 1){RotateLR(parent);}else if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == -1){RotateRL(parent);}else{assert(false);}break;}else{assert(false);}}return true;
}
6.4 验证平衡
bool _IsBanlance(Node* root) {if (root == nullptr) {return true;}int leftHT = Height(root->_left);int rightHT = Height(root->_right);int diff = rightHT - leftHT;return abs(diff) < 2&& _IsBanlance(root->_left)&& _IsBanlance(root->_right);
}
int Height(Node* root) {if (root == nullptr)return 0;return max(Height(root->_left), Height(root->_right)) + 1;
}
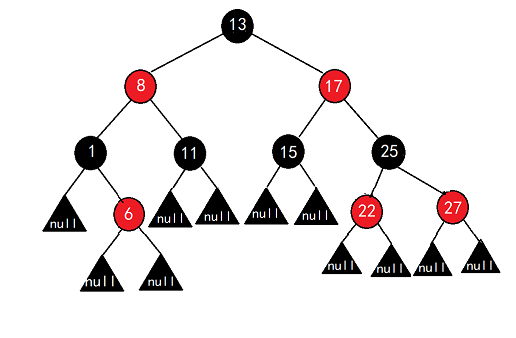
7 红黑树
7.1 红黑树的概念
红黑树,是一种二叉搜索树,但在每个结点上增加一个存储位表示结点的颜色,可以是Red或Black。 通过对任何一条从根到叶子的路径上各个结点着色方式的限制,红黑树确保没有一条路径会比其他路径长出俩倍,即最长路径不超过最短路径的2倍,因而是接近平衡的。
效果:相对而言,插入同样的数据,AVL树旋转更多,红黑树旋转更少
7.2 红黑树的性质
- 每个节点不是红色就是黑色
- 根节点是黑色的
- 如果一个节点是红色的,则它的两个孩子节点是黑色的(树中没有连续的红色节点)
- 对于每个节点,从该节点到其所有后代节点的简单路径上,均包含相同数目的黑色节点(每条路径黑色节点数量相等)
- 每个叶子节点都是黑色的(此处的叶子节点指的是空节点)
由以上性质可知,一棵树内极限最短为全黑,极限最长为一黑一红,因此最长路径中节点个数不会超过最短路径节点个数的两倍。
7.3 插入
插入思想
-
cur->_parent为黑,插入成功
-
cur->_parent为红,分情况进行调整:
-
情况一:cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u存在且为红:
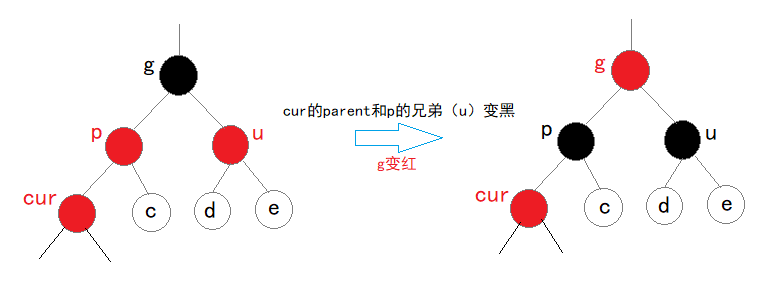
调整后,若g为根节点,此时只需将g变为黑色即可调整完毕。
调整后,若g不为根节点,且g的父结点为黑色则调整完毕;若g的父结点为红色,则将g作为当前节点继续根据情况调整。
-
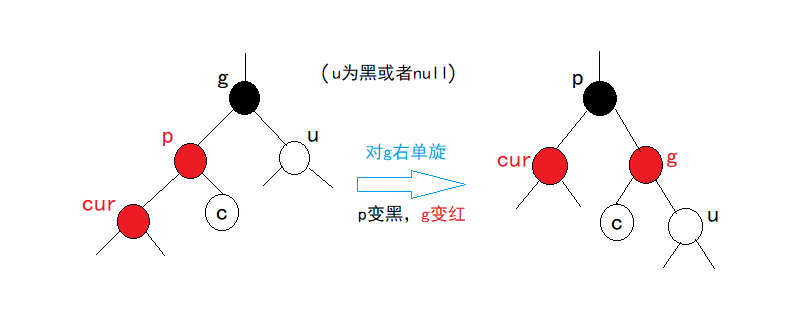
情况二:cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u不存在/u存在且为黑
cur和p都是他们的父结点的左孩子,对g进行右单旋,p变黑,g变红,则调整完毕:
cur和p都是他们的父结点的右孩子,对g进行左单旋,p变黑,g变红,则调整完毕:
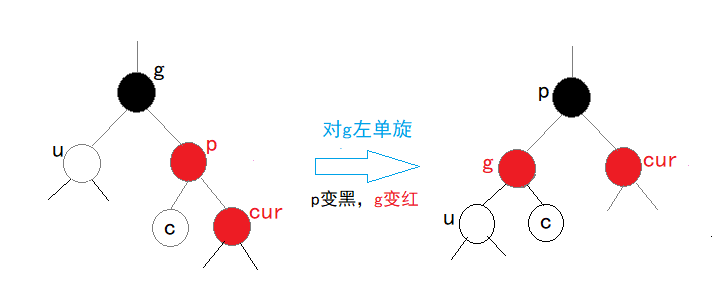
-
情况三:cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u不存在/u存在且为黑
p为g的左孩子,cur为p的右孩子,则针对p做左单旋,则可转为情况二继续调整:
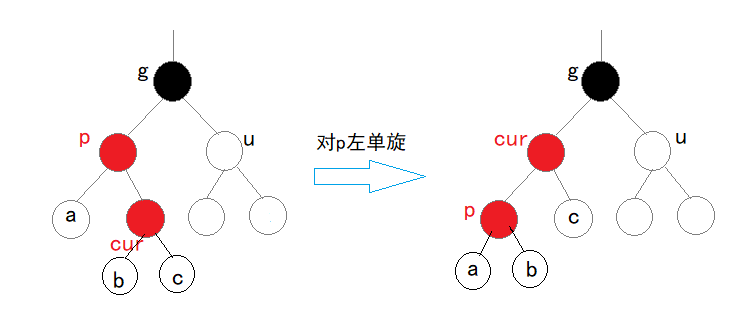
p为g的右孩子,cur为p的左孩子,则针对p做右单旋,则可转为情况二继续调整:
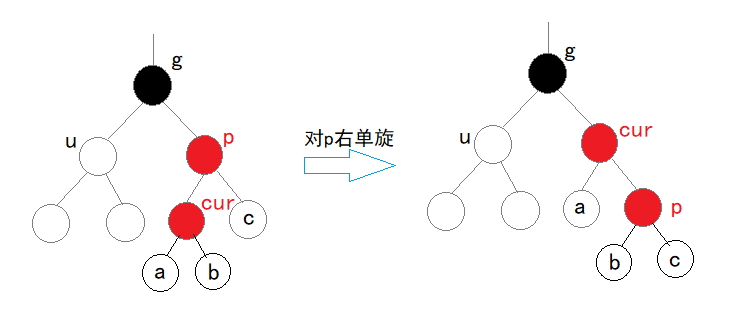
则情况三中,无论是上述哪两种小情况,都需要进行一次单旋后转为情况二继续调整,那么情况三总的调整也就是双旋后进行变色(单旋+情况二的单旋+变色)。
-
红黑树的的关键是看叔叔。
核心代码
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(kv);_root->_col = BLACK;return true;}Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_kv.first < kv.first){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (cur->_kv.first > kv.first){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else{return false;}}cur = new Node(kv);cur->_col = RED;if (parent->_kv.first < kv.first){parent->_right = cur;}else{parent->_left = cur;}cur->_parent = parent;while (parent && parent->_col == RED){Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;assert(grandfather);assert(grandfather->_col == BLACK);// 关键看叔叔if (parent == grandfather->_left){Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;// 情况一:uncle存在且为红,变色+继续往上处理if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;// 继续将grandfather作为current进行处理cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}// 情况二+三:uncle不存在或uncle存在为黑色else{// 情况二:单旋+变色// g// p u// cif (cur == parent->_left){RotateR(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else{// 情况三:左单旋+右单旋+变色// g// p u// cRotateL(parent);RotateR(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}else{Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;// 情况一:叔叔是红色if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;// 继续将grandfather作为current进行处理cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}// 情况二+三:uncle不存在或uncle存在为黑色else{// 情况二:单旋+变色// g// u p// cif (cur == parent->_right){RotateL(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else{// 情况三:右单旋+左单旋+变色// g// u p// cRotateR(parent);RotateL(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}}_root->_col = BLACK;return true;
}
7.4 验证红黑树
红黑树的检测分为两步:
- 检测其是否满足二叉搜索树(中序遍历是否为有序序列)
- 检测其是否满足红黑树的性质
bool IsBanlance()
{if (_root == nullptr){return true;}if (_root->_col == RED){cout << "根节点不是黑色" << endl;return false;}// 黑色节点数量基准值int benchmark = 0;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_col == BLACK) {++benchmark;}cur = cur->_left;}return PrevCheck(_root, 0, benchmark);
}
bool PrevCheck(Node* root, int blackNum, int benchmark)
{if (root == nullptr){/*cout << blackNum << endl;return;*/if (blackNum != benchmark){cout << "某条黑色节点的数量不相等" << endl;return false;}else {return true;}}if (root->_col == RED && root->_parent->_col == RED){cout << "存在红色的连续节点" << endl;return false;}if (root->_col == BLACK){++blackNum;}return PrevCheck(root->_left, blackNum, benchmark)&& PrevCheck(root->_right, blackNum, benchmark);
}