61. 旋转链表
给你一个链表的头节点 head ,旋转链表,将链表每个节点向右移动 k 个位置。
示例 1:

输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 输出:[4,5,1,2,3]
示例 2:

输入:head = [0,1,2], k = 4 输出:[2,0,1]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目在范围
[0, 500]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 1000 <= k <= 2 * 10^9
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;struct ListNode {int val;ListNode *next;ListNode() : val(0), next(NULL) {}ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};class Solution {public:ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k) {if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL || k == 0) {return head;}int length = 1;ListNode *tail = head;while(tail->next != NULL) {tail = tail->next;length++;}tail->next = head; // 将链表头尾相连,形成环k = k % length;int steps = length - k;ListNode *newTail = head;for(int i = 1; i < steps; i++) {newTail = newTail->next;} ListNode *newHead = newTail->next;newTail->next = NULL;return newHead;}
};ListNode* createList() {ListNode *head = NULL;ListNode *current = NULL;int val;while(cin >> val) {ListNode *newNode = new ListNode(val);if(head == NULL) {head = newNode;current = newNode;} else {current->next = newNode;current = current->next;}if(cin.get() == '\n') {break;}}return head;
}void printList(ListNode *head) {ListNode *current = head;while(current != NULL) {cout << current->val << " ";current = current->next;}
}int main() {ListNode *head = createList();int k;cin >> k;Solution solution;ListNode *res = solution.rotateRight(head, k);printList(res);return 0;
}62. 不同路径
一个机器人位于一个 m x n 网格的左上角 (起始点在下图中标记为 “Start” )。
机器人每次只能向下或者向右移动一步。机器人试图达到网格的右下角(在下图中标记为 “Finish”)。
问总共有多少条不同的路径?
示例 1:

输入:m = 3, n = 7 输出:28
示例 2:
输入:m = 3, n = 2 输出:3 解释: 从左上角开始,总共有 3 条路径可以到达右下角。 1. 向右 -> 向下 -> 向下 2. 向下 -> 向下 -> 向右 3. 向下 -> 向右 -> 向下
示例 3:
输入:m = 7, n = 3 输出:28
示例 4:
输入:m = 3, n = 3 输出:6
提示:
1 <= m, n <= 100- 题目数据保证答案小于等于
2 * 10^9
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:
// int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
// if(m == 1 || n == 1) {
// return 1;
// }
//
// if(m == 2 && n == 2) {
// return 2;
// }
//
// return uniquePaths(m - 1, n) + uniquePaths(m, n - 1);
// }int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {vector<vector<int>> dp(m, vector<int>(n, 0));// 初始化边界条件for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {dp[i][0] = 1; // 第一列的路径数量都为1,因为只能向下移动 } for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {dp[0][j] = 1; // 第一行的路径数量都为1,只能只能向右移动 }// 动态规划计算不同路径数量for(int i = 1; i < m; i++) {for(int j = 1; j < n; j++) {dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - 1];}} return dp[m - 1][n - 1];}
};int main() {int m, n;cin >> m >> n;Solution solution;cout << solution.uniquePaths(m, n);return 0;
}63. 不同路径Ⅱ
一个机器人位于一个 m x n 网格的左上角 (起始点在下图中标记为 “Start” )。
机器人每次只能向下或者向右移动一步。机器人试图达到网格的右下角(在下图中标记为 “Finish”)。
现在考虑网格中有障碍物。那么从左上角到右下角将会有多少条不同的路径?
网格中的障碍物和空位置分别用 1 和 0 来表示。
示例 1:

输入:obstacleGrid = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]] 输出:2 解释:3x3 网格的正中间有一个障碍物。 从左上角到右下角一共有 2条不同的路径: 1. 向右 -> 向右 -> 向下 -> 向下 2. 向下 -> 向下 -> 向右 -> 向右
示例 2:

输入:obstacleGrid = [[0,1],[0,0]] 输出:1
提示:
m == obstacleGrid.lengthn == obstacleGrid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 100obstacleGrid[i][j]为0或1
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:int uniquePathsWishObstacles(vector<vector<int>>& obstacleGrid) {int m = obstacleGrid.size();int n = obstacleGrid[0].size();// 创建一个二维数组dp,dp[i][j]表示从起始点到网络(i, j)的不同路径数量vector<vector<long>> dp(m, vector<long>(n, 0));// 处理起始点的障碍物情况dp[0][0] = (obstacleGrid[0][0] == 1) ? 0 : 1;// 初始化第一列的路径数量for(int i = 1; i < m; i++) {dp[i][0] = (obstacleGrid[i][0] == 1) ? 0 : dp[i - 1][0];} // 初始化第一行的路径数量for(int j = 1; j < n; j++) {dp[0][j] = (obstacleGrid[0][j] == 1) ? 0 : dp[0][j - 1];} // 动态规划计算不同路径数量for(int i = 1; i < m; i++) {for(int j = 1; j < n; j++) {if(obstacleGrid[i][j] == 1) {dp[i][j] = 0; // 遇到障碍物,路径数量为0 } else {dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - 1]; } }} return dp[m - 1][n - 1];}
};int main() {int m, n;cin >> m >> n;vector<vector<int>> grid(m, vector<int>(n, 0));for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {cin >> grid[i][j];}}Solution solution;cout << solution.uniquePathsWishObstacles(grid);return 0;
}64. 最小路径和
给定一个包含非负整数的 m x n 网格 grid ,请找出一条从左上角到右下角的路径,使得路径上的数字总和为最小。
说明:每次只能向下或者向右移动一步。
示例 1:
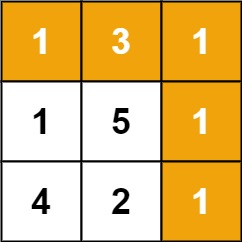
输入:grid = [[1,3,1],[1,5,1],[4,2,1]] 输出:7 解释:因为路径 1→3→1→1→1 的总和最小。
示例 2:
输入:grid = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6]] 输出:12
提示:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 2000 <= grid[i][j] <= 200
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:int minPathSum(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();vector<vector<int>> dp(m, vector<int>(n, 0));dp[0][0] = grid[0][0];// 初始化第一行for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) {dp[0][i] = dp[0][i - 1] + grid[0][i];} // 初始化第一列for(int i = 1; i < m; i++) {dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][0] + grid[i][0];} for(int i = 1; i < m; i++) {for(int j = 1; j < n; j++) {dp[i][j] = min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]) + grid[i][j];}}return dp[m - 1][n - 1];}
};int main() {int m, n;cin >> m >> n;vector<vector<int>> grid(m, vector<int>(n, 0));for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {cin >> grid[i][j];}}Solution solution;cout << solution.minPathSum(grid);return 0;
}65. 有效数字
有效数字(按顺序)可以分成以下几个部分:
- 一个 小数 或者 整数
- (可选)一个
'e'或'E',后面跟着一个 整数
小数(按顺序)可以分成以下几个部分:
- (可选)一个符号字符(
'+'或'-') - 下述格式之一:
- 至少一位数字,后面跟着一个点
'.' - 至少一位数字,后面跟着一个点
'.',后面再跟着至少一位数字 - 一个点
'.',后面跟着至少一位数字
- 至少一位数字,后面跟着一个点
整数(按顺序)可以分成以下几个部分:
- (可选)一个符号字符(
'+'或'-') - 至少一位数字
部分有效数字列举如下:["2", "0089", "-0.1", "+3.14", "4.", "-.9", "2e10", "-90E3", "3e+7", "+6e-1", "53.5e93", "-123.456e789"]
部分无效数字列举如下:["abc", "1a", "1e", "e3", "99e2.5", "--6", "-+3", "95a54e53"]
给你一个字符串 s ,如果 s 是一个 有效数字 ,请返回 true 。
示例 1:
输入:s = "0" 输出:true
示例 2:
输入:s = "e" 输出:false
示例 3:
输入:s = "." 输出:false
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 20s仅含英文字母(大写和小写),数字(0-9),加号'+',减号'-',或者点'.'。
#include<iostream>
#include<cctype>
#include<string>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:bool isNumber(string s) {int valid = 0;int hasE = -1;int hasPoint = -1;int hasDigit = -1;for(auto c : s) {switch(c) {case '+':case '-':if(valid == 0 || hasE + 1 == valid) {valid++;continue;}return false;case 'E':case 'e':if(hasE < 0 && hasDigit >= 0) {hasE = valid;valid++;continue;}return false;case '.':if(hasPoint < 0 && hasE < 0) {hasPoint = valid;valid++;continue;}return false;default:if(isdigit(c)) {hasDigit = valid;valid++;continue;}return false;}}return hasDigit >= 0 && hasDigit > hasE;}
};int main() {string s;cin >> s;Solution solution;cout << boolalpha << solution.isNumber(s);return 0;
}66. 加一
给定一个由 整数 组成的 非空 数组所表示的非负整数,在该数的基础上加一。
最高位数字存放在数组的首位, 数组中每个元素只存储单个数字。
你可以假设除了整数 0 之外,这个整数不会以零开头。
示例 1:
输入:digits = [1,2,3] 输出:[1,2,4] 解释:输入数组表示数字 123。
示例 2:
输入:digits = [4,3,2,1] 输出:[4,3,2,2] 解释:输入数组表示数字 4321。
示例 3:
输入:digits = [0] 输出:[1]
提示:
1 <= digits.length <= 1000 <= digits[i] <= 9
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:vector<int> plusOne(vector<int>& digits) {int n = digits.size();for(int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {if(digits[i] < 9) {digits[i]++;return digits;}digits[i] = 0; // 进1 }digits.insert(digits.begin(), 1); // 增加一位,如9999 return digits;}
};int main() {int temp;vector<int> digits;while(cin >> temp) {digits.push_back(temp);if(cin.get() == '\n')break;}Solution solution;solution.plusOne(digits);for(int i = 0; i < digits.size(); i++)cout << digits[i] << " ";return 0;
} 67. 二进制求和
给你两个二进制字符串 a 和 b ,以二进制字符串的形式返回它们的和。
示例 1:
输入:a = "11", b = "1" 输出:"100"
示例 2:
输入:a = "1010", b = "1011" 输出:"10101"
提示:
1 <= a.length, b.length <= 104a和b仅由字符'0'或'1'组成- 字符串如果不是
"0",就不含前导零
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:string addBinary(string a, string b) {int i = a.size(), j = b.size();while(i < j) { // 两个字符不等长时 a = '0' + a;++i;}while(i > j) {b = '0' + b;++j;}for(int n = a.size() - 1; n > 0; --n) { // 从后到前遍历所有的位数(第0位除外),同位相加 a[n] = a[n] - '0' + b[n];if(a[n] >= '2') { // 若大于等于字符'2',进一 a[n] = (a[n] - '0') % 2 + '0';a[n - 1] = a[n - 1] + 1;}}a[0] = a[0] - '0' + b[0]; // 将a b的第0位相加 if(a[0] >= '2') { // 第一位大于等于2, 进一 a[0] = (a[0] - '0') % 2 + '0';a = '1' + a;}return a;}
};int main() {string a, b;cin >> a >> b;Solution solution;string result = solution.addBinary(a, b);cout << result;return 0;
} 68. 文本左右对齐
给定一个单词数组 words 和一个长度 maxWidth ,重新排版单词,使其成为每行恰好有 maxWidth 个字符,且左右两端对齐的文本。
你应该使用 “贪心算法” 来放置给定的单词;也就是说,尽可能多地往每行中放置单词。必要时可用空格 ' ' 填充,使得每行恰好有 maxWidth 个字符。
要求尽可能均匀分配单词间的空格数量。如果某一行单词间的空格不能均匀分配,则左侧放置的空格数要多于右侧的空格数。
文本的最后一行应为左对齐,且单词之间不插入额外的空格。
注意:
- 单词是指由非空格字符组成的字符序列。
- 每个单词的长度大于 0,小于等于 maxWidth。
- 输入单词数组
words至少包含一个单词。
示例 1:
输入: words = ["This", "is", "an", "example", "of", "text", "justification."], maxWidth = 16 输出: ["This is an","example of text","justification. " ]
示例 2:
输入:words = ["What","must","be","acknowledgment","shall","be"], maxWidth = 16 输出: ["What must be","acknowledgment ","shall be " ] 解释: 注意最后一行的格式应为 "shall be " 而不是 "shall be",因为最后一行应为左对齐,而不是左右两端对齐。 第二行同样为左对齐,这是因为这行只包含一个单词。
示例 3:
输入:words = ["Science","is","what","we","understand","well","enough","to","explain","to","a","computer.","Art","is","everything","else","we","do"],maxWidth = 20 输出: ["Science is what we","understand well","enough to explain to","a computer. Art is","everything else we","do " ]
提示:
1 <= words.length <= 3001 <= words[i].length <= 20words[i]由小写英文字母和符号组成1 <= maxWidth <= 100words[i].length <= maxWidth
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:vector<string> fullJustify(vector<string>& words, int maxWidth) {vector<string> result;int n = words.size();int i = 0;while (i < n) {int start = i;int sum = 0;// 计算当前行可以容纳的单词总长度while (i < n && sum + words[i].size() + i - start <= maxWidth) {sum += words[i].size();i++;}int spaces = maxWidth - sum;int gaps = i - start - 1;string line = words[start];if (i == n || gaps == 0) { // 最后一行或者只有一个单词for (int j = start + 1; j < i; j++) {line += " " + words[j];}line += string(maxWidth - line.size(), ' '); // 补充空格} else {int spacesBetweenWords = gaps > 0 ? spaces / gaps : 0;int extraSpaces = gaps > 0 ? spaces % gaps : 0;for (int j = start + 1; j < i; j++) {line += string(spacesBetweenWords + (extraSpaces-- > 0 ? 1 : 0), ' ') + words[j];}}result.push_back(line);}return result;}
};//作者:清秋几许
//链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/text-justification/solutions/2680668/xian-suan-xing-shu-zai-zhu-xing-gou-zao-1jtqs/int main() {vector<string> words;string tmp;int maxWidth;while(cin >> tmp) {words.push_back(tmp);if(cin.get() == '\n')break;}cin >> maxWidth;Solution solution;vector<string> result = solution.fullJustify(words, maxWidth);cout << "[" << endl;for(int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {if(i == result.size() - 1) {cout << "\"" << result[i] << "\"" << endl;} else {cout << "\"" << result[i] << "\"," << endl;}}cout << "]";return 0;
}69. x的平方根
给你一个非负整数 x ,计算并返回 x 的 算术平方根 。
由于返回类型是整数,结果只保留 整数部分 ,小数部分将被 舍去 。
注意:不允许使用任何内置指数函数和算符,例如 pow(x, 0.5) 或者 x ** 0.5 。
示例 1:
输入:x = 4 输出:2
示例 2:
输入:x = 8 输出:2 解释:8 的算术平方根是 2.82842..., 由于返回类型是整数,小数部分将被舍去。
提示:
0 <= x <= 2^31 - 1
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:int mySqrt(int x) {if(x == 1) return 1;int min = 0;int max = x;while(max - min > 1) {int m = (max + min) / 2; // 二分查找法 if(x / m < m) // 平方根落在m的左侧,更新max max = m;else // 平方根落在m的右侧,更新min min = m;}return min;}
};int main() {int x;cin >> x;Solution solution;cout << solution.mySqrt(x);return 0;
} 70. 爬楼梯
假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶。
每次你可以爬 1 或 2 个台阶。你有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶呢?
示例 1:
输入:n = 2 输出:2 解释:有两种方法可以爬到楼顶。 1. 1 阶 + 1 阶 2. 2 阶
示例 2:
输入:n = 3 输出:3 解释:有三种方法可以爬到楼顶。 1. 1 阶 + 1 阶 + 1 阶 2. 1 阶 + 2 阶 3. 2 阶 + 1 阶
提示:
1 <= n <= 45
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:int climbStairs(int n) {if(n == 1) return 1;if(n == 2) return 2;int prev = 1;int current = 2;for(int i = 3; i <= n; i++) { // 保存前两个台阶的爬楼方式数int temp = current;current = prev + current;prev = temp;}return current;}
};int main() {int n;cin >> n;Solution solution;cout << solution.climbStairs(n);return 0;
} 71. 简化路径
给你一个字符串 path ,表示指向某一文件或目录的 Unix 风格 绝对路径 (以 '/' 开头),请你将其转化为更加简洁的规范路径。
在 Unix 风格的文件系统中,一个点(.)表示当前目录本身;此外,两个点 (..) 表示将目录切换到上一级(指向父目录);两者都可以是复杂相对路径的组成部分。任意多个连续的斜杠(即,'//')都被视为单个斜杠 '/' 。 对于此问题,任何其他格式的点(例如,'...')均被视为文件/目录名称。
请注意,返回的 规范路径 必须遵循下述格式:
- 始终以斜杠
'/'开头。 - 两个目录名之间必须只有一个斜杠
'/'。 - 最后一个目录名(如果存在)不能 以
'/'结尾。 - 此外,路径仅包含从根目录到目标文件或目录的路径上的目录(即,不含
'.'或'..')。
返回简化后得到的 规范路径 。
示例 1:
输入:path = "/home/" 输出:"/home" 解释:注意,最后一个目录名后面没有斜杠。
示例 2:
输入:path = "/../" 输出:"/" 解释:从根目录向上一级是不可行的,因为根目录是你可以到达的最高级。
示例 3:
输入:path = "/home//foo/" 输出:"/home/foo" 解释:在规范路径中,多个连续斜杠需要用一个斜杠替换。
示例 4:
输入:path = "/a/./b/../../c/" 输出:"/c"
提示:
1 <= path.length <= 3000path由英文字母,数字,'.','/'或'_'组成。path是一个有效的 Unix 风格绝对路径。
#include<iostream>
#include<sstream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:string simplifyPath(string path) {stringstream ss(path);vector<string> tokens;string token;while(getline(ss, token, '/')) { // 按'/'分割 if(token == "" || token == ".") {continue;} else if(token == "..") {if(!tokens.empty()) {tokens.pop_back();} } else {tokens.push_back(token);}}string simplifiedPath = "";for(string dir : tokens) {simplifiedPath += "/" + dir;}return simplifiedPath.empty() ? "/" : simplifiedPath;}
};int main() {string path;cin >> path;Solution solution;cout << solution.simplifyPath(path) << endl;return 0;
}72. 编辑距离
给你两个单词 word1 和 word2, 请返回将 word1 转换成 word2 所使用的最少操作数 。
你可以对一个单词进行如下三种操作:
- 插入一个字符
- 删除一个字符
- 替换一个字符
示例 1:
输入:word1 = "horse", word2 = "ros" 输出:3 解释: horse -> rorse (将 'h' 替换为 'r') rorse -> rose (删除 'r') rose -> ros (删除 'e')
示例 2:
输入:word1 = "intention", word2 = "execution" 输出:5 解释: intention -> inention (删除 't') inention -> enention (将 'i' 替换为 'e') enention -> exention (将 'n' 替换为 'x') exention -> exection (将 'n' 替换为 'c') exection -> execution (插入 'u')
提示:
0 <= word1.length, word2.length <= 500word1和word2由小写英文字母组成
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:int minDistance(string word1, string word2) {int m = word1.size();int n = word2.size();vector<vector<int>> dp(m + 1, vector<int>(n + 1, 0));for(int i = 0; i <= m; i++) {dp[i][0] = i; // 初始化第一列 }for(int j = 0; j <= n; j++) {dp[0][j] = j; // 初始化第一行 }// 动态规划 for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {if(word1[i - 1] == word2[j - 1]) { // 当前字符相等,不需要进行任何操作 dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];} else { // 分别对应替换、删除、插入操作 dp[i][j] = 1 + min(dp[i- 1][j - 1], min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]));}}}return dp[m][n];}
}; int main() {string word1, word2;cin >> word1 >> word2;Solution solution;cout << solution.minDistance(word1, word2) << endl;return 0;
} 73. 矩阵置零
给定一个 m x n 的矩阵,如果一个元素为 0 ,则将其所在行和列的所有元素都设为 0 。请使用 原地 算法。
示例 1:
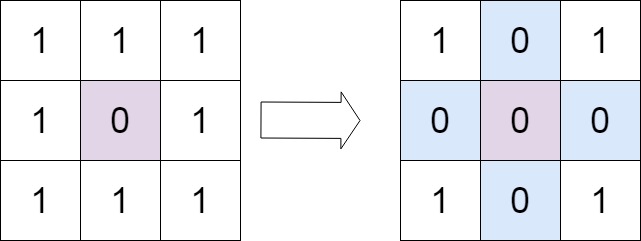
输入:matrix = [[1,1,1],[1,0,1],[1,1,1]] 输出:[[1,0,1],[0,0,0],[1,0,1]]
示例 2:
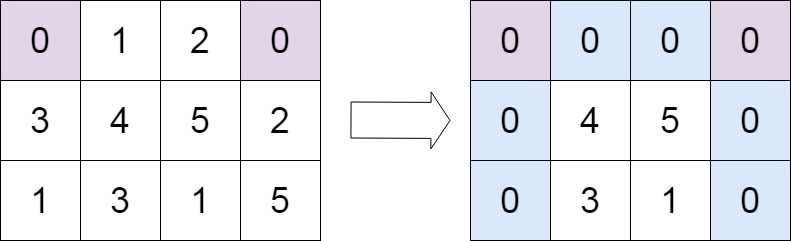
输入:matrix = [[0,1,2,0],[3,4,5,2],[1,3,1,5]] 输出:[[0,0,0,0],[0,4,5,0],[0,3,1,0]]
提示:
m == matrix.lengthn == matrix[0].length1 <= m, n <= 200-231 <= matrix[i][j] <= 231 - 1
进阶:
- 一个直观的解决方案是使用
O(mn)的额外空间,但这并不是一个好的解决方案。 - 一个简单的改进方案是使用
O(m + n)的额外空间,但这仍然不是最好的解决方案。 - 你能想出一个仅使用常量空间的解决方案吗?
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:void setZeroes(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {int row = matrix.size();int col = matrix[0].size();vector<vector<int>> cor; // 用来记录0出现位置的下标for(int i = 0; i < row; i++) {for(int j = 0; j < col; j++) {if(matrix[i][j] == 0) {cor.push_back({i, j});}}} for(auto c : cor) {// 将所在行置为0for(int j = 0; j < col; j++) {matrix[c[0]][j] = 0;}// 将所在列置为0for(int i = 0; i < row; i++) {matrix[i][c[1]] = 0;} }return;}
};int main() {int m, n;cin >> m >> n;vector<vector<int>> matrix(m, vector<int>(n, 0));for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {cin >> matrix[i][j];}}Solution solution;solution.setZeroes(matrix);for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {cout << matrix[i][j] << " ";}cout << endl;}return 0;
} 74. 搜索二维矩阵
给你一个满足下述两条属性的 m x n 整数矩阵:
- 每行中的整数从左到右按非严格递增顺序排列。
- 每行的第一个整数大于前一行的最后一个整数。
给你一个整数 target ,如果 target 在矩阵中,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
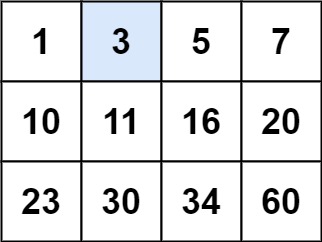
输入:matrix = [[1,3,5,7],[10,11,16,20],[23,30,34,60]], target = 3 输出:true
示例 2:
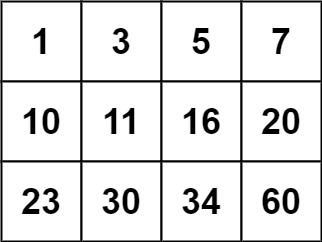
输入:matrix = [[1,3,5,7],[10,11,16,20],[23,30,34,60]], target = 13 输出:false
提示:
m == matrix.lengthn == matrix[i].length1 <= m, n <= 100-10^4 <= matrix[i][j], target <= 10^4
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:bool searchMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target) {int m = matrix.size();int n = matrix[0].size();int index = -1; // 记录target所在行的下标 for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {if(target <= matrix[i][n - 1]) // 每一行的最后一个{index = i;break;} }if(index == -1) {return false;}for(int j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--) {if(matrix[index][j] == target) {return true;}}return false;}
};int main() {int m, n;cin >> m >> n;int target;vector<vector<int>> matrix(m, vector<int>(n, 0));for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {cin >> matrix[i][j];}}cin >> target;Solution solution;cout << boolalpha << solution.searchMatrix(matrix, target);return 0;
}#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:void sortColors(vector<int>& nums) {int n = nums.size();if(n < 2) {return;}int zero = 0, two = n, i = 0;while(i < two) {if(nums[i] == 0) {swap(nums[zero], nums[i]);zero++;i++;} else if(nums[i] == 1) {i++;} else {two--;swap(nums[i], nums[two]);}}}
};int main() {vector<int> nums;int tmp;while(cin >> tmp) {nums.push_back(tmp);if(cin.get() == '\n') {break;}}Solution solution;solution.sortColors(nums);for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {cout << nums[i] << " ";}return 0;
}75. 颜色分类
给定一个包含红色、白色和蓝色、共 n 个元素的数组 nums ,原地对它们进行排序,使得相同颜色的元素相邻,并按照红色、白色、蓝色顺序排列。
我们使用整数 0、 1 和 2 分别表示红色、白色和蓝色。
必须在不使用库内置的 sort 函数的情况下解决这个问题。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [2,0,2,1,1,0] 输出:[0,0,1,1,2,2]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [2,0,1] 输出:[0,1,2]
提示:
n == nums.length1 <= n <= 300nums[i]为0、1或2
进阶:
- 你能想出一个仅使用常数空间的一趟扫描算法吗?
解法一:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:void sortColors(vector<int>& nums) {int n = nums.size();if(n < 2) {return;}int zero = 0, two = n, i = 0;while(i < two) {if(nums[i] == 0) {swap(nums[zero], nums[i]);zero++;i++;} else if(nums[i] == 1) {i++;} else {two--;swap(nums[i], nums[two]);}}}
};int main() {vector<int> nums;int tmp;while(cin >> tmp) {nums.push_back(tmp);if(cin.get() == '\n') {break;}}Solution solution;solution.sortColors(nums);for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {cout << nums[i] << " ";}return 0;
}解法二:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:
// void sortColors(vector<int>& nums) {
// int n = nums.size();
// if(n < 2) {
// return;
// }
//
// int zero = 0, two = n, i = 0;
// while(i < two) {
// if(nums[i] == 0) {
// swap(nums[zero], nums[i]);
// zero++;
// i++;
// } else if(nums[i] == 1) {
// i++;
// } else {
// two--;
// swap(nums[i], nums[two]);
// }
// }
// }void sortColors(vector<int>& nums) {int n = nums.size();int start = 0;for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {if(nums[i] == 0) {swap(nums[i], nums[start++]);}}for(int i = start; i < n; i++) {if(nums[i] == 1) {swap(nums[i], nums[start++]);}}}
};int main() {vector<int> nums;int tmp;while(cin >> tmp) {nums.push_back(tmp);if(cin.get() == '\n') {break;}}Solution solution;solution.sortColors(nums);for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {cout << nums[i] << " ";}return 0;
}76. 最小覆盖子串
给你一个字符串 s 、一个字符串 t 。返回 s 中涵盖 t 所有字符的最小子串。如果 s 中不存在涵盖 t 所有字符的子串,则返回空字符串 "" 。
注意:
- 对于
t中重复字符,我们寻找的子字符串中该字符数量必须不少于t中该字符数量。 - 如果
s中存在这样的子串,我们保证它是唯一的答案。
示例 1:
输入:s = "ADOBECODEBANC", t = "ABC" 输出:"BANC" 解释:最小覆盖子串 "BANC" 包含来自字符串 t 的 'A'、'B' 和 'C'。
示例 2:
输入:s = "a", t = "a" 输出:"a" 解释:整个字符串 s 是最小覆盖子串。
示例 3:
输入: s = "a", t = "aa" 输出: "" 解释: t 中两个字符 'a' 均应包含在 s 的子串中, 因此没有符合条件的子字符串,返回空字符串。
提示:
m == s.lengthn == t.length1 <= m, n <= 10^5s和t由英文字母组成
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:string minWindow(string s, string t) {unordered_map<char, int> targetFreq, windowFreq;for(char c : t) {targetFreq[c]++;}int left = 0, right = 0;int minLen = INT_MAX;int valid = 0;int start = 0;// 滑动窗口while(right < s.size()) {char c = s[right];right++;if(targetFreq.count(c)) {windowFreq[c]++;if(windowFreq[c] == targetFreq[c]) {valid++;}}while(valid == targetFreq.size()) {if(right - left < minLen) {start = left;minLen = right - left;}char d = s[left];left++;if(targetFreq.count(d)) {if(windowFreq[d] == targetFreq[d]) {valid--;}windowFreq[d]--;}}}return minLen == INT_MAX ? "" : s.substr(start, minLen);}
};int main() {string s, t;cin >> s >> t;Solution solution;cout << solution.minWindow(s, t) << endl;return 0;
}77. 组合
给定两个整数 n 和 k,返回范围 [1, n] 中所有可能的 k 个数的组合。
你可以按 任何顺序 返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:n = 4, k = 2 输出: [[2,4],[3,4],[2,3],[1,2],[1,3],[1,4], ]
示例 2:
输入:n = 1, k = 1 输出:[[1]]
提示:
1 <= n <= 201 <= k <= n
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:vector<vector<int>> combine(int n, int k) {vector<vector<int>> result;vector<int> path;backtrack(result, path, 1, n, k);return result;}void backtrack(vector<vector<int>>& result, vector<int>& path, int start, int n, int k) {if(k == 0) {result.push_back(path);return;}for(int i = start; i <= n; i++) {path.push_back(i);backtrack(result, path, i + 1, n, k - 1);path.pop_back();}}
};int main() {int n, k;cin >> n >> k;Solution solution;vector<vector<int>> result = solution.combine(n, k);cout << "[";for(int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {cout << "[";for(int j = 0; j < result[i].size(); j++) {if(j == result[i].size() - 1) {cout << result[i][j];} else {cout << result[i][j] << ", ";}}if(i == result.size() - 1) {cout << "]";} else {cout << "]" << ", ";}}cout << "]" << endl;return 0;
}78. 子集
给你一个整数数组 nums ,数组中的元素 互不相同 。返回该数组所有可能的
子集
(幂集)。
解集 不能 包含重复的子集。你可以按 任意顺序 返回解集。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,3] 输出:[[],[1],[2],[1,2],[3],[1,3],[2,3],[1,2,3]]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0] 输出:[[],[0]]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 10-10 <= nums[i] <= 10nums中的所有元素 互不相同
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:vector<vector<int>> subsets(vector<int>& nums) {vector<vector<int>> result;vector<int> subset;backtrack(result, subset, nums, 0);return result;}void backtrack(vector<vector<int>>& result, vector<int>& subset, vector<int>& nums, int start) {result.push_back(subset);for(int i = start; i < nums.size(); i++) {subset.push_back(nums[i]);backtrack(result, subset, nums, i + 1);subset.pop_back();}}
};int main() {vector<int> nums;int tmp;while(cin >> tmp) {nums.push_back(tmp);if(cin.get() == '\n') {break;}}Solution solution;vector<vector<int>> result = solution.subsets(nums);cout << "[";for(int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {cout << "[";for(int j = 0; j < result[i].size(); j++) {if(j == result[i].size() - 1) {cout << result[i][j];} else {cout << result[i][j] << ", ";}}if(i == result.size() - 1) {cout << "]";} else {cout << "]" << ", ";}}cout << "]" << endl;
}79. 单词搜索
给定一个 m x n 二维字符网格 board 和一个字符串单词 word 。如果 word 存在于网格中,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
单词必须按照字母顺序,通过相邻的单元格内的字母构成,其中“相邻”单元格是那些水平相邻或垂直相邻的单元格。同一个单元格内的字母不允许被重复使用。
示例 1:

输入:board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCCED" 输出:true
示例 2:
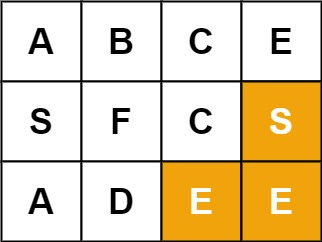
输入:board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "SEE" 输出:true
示例 3:

输入:board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCB" 输出:false
提示:
m == board.lengthn = board[i].length1 <= m, n <= 61 <= word.length <= 15board和word仅由大小写英文字母组成
进阶:你可以使用搜索剪枝的技术来优化解决方案,使其在 board 更大的情况下可以更快解决问题?
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:bool exist(vector<vector<char>>& board, string word) {if(board.empty() || board[0].empty() || word.empty()) {return false;}int m = board.size();int n = board[0].size();vector<vector<bool>> visited(m, vector<bool>(n, false));for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {if(dfs(board, word, visited, i, j, 0)) {return true;}}}return false;}bool dfs(vector<vector<char>>& board, string& word, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int i, int j, int index) {if(index == word.length()) {return true;}if(i < 0 || i >= board.size() || j < 0 || j >= board[0].size() || visited[i][j] || board[i][j] != word[index]) {return false;}visited[i][j] = true;bool result = dfs(board, word, visited, i + 1, j, index + 1) || dfs(board, word, visited, i, j + 1, index + 1) ||dfs(board, word, visited, i - 1, j, index + 1) ||dfs(board, word, visited, i, j - 1, index + 1);visited[i][j] = false;return result;}
};int main() {int m, n;cin >> m >> n;string word;vector<vector<char>> board(m, vector<char>(n));for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {cin >> board[i][j];}}cin >> word;Solution solution;cout << boolalpha << solution.exist(board, word) << endl;return 0;
}80. 删除有序数组中的重复项Ⅱ
给你一个有序数组 nums ,请你 原地 删除重复出现的元素,使得出现次数超过两次的元素只出现两次 ,返回删除后数组的新长度。
不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须在 原地 修改输入数组 并在使用 O(1) 额外空间的条件下完成。
说明:
为什么返回数值是整数,但输出的答案是数组呢?
请注意,输入数组是以「引用」方式传递的,这意味着在函数里修改输入数组对于调用者是可见的。
你可以想象内部操作如下:
// nums 是以“引用”方式传递的。也就是说,不对实参做任何拷贝
int len = removeDuplicates(nums);// 在函数里修改输入数组对于调用者是可见的。
// 根据你的函数返回的长度, 它会打印出数组中 该长度范围内 的所有元素。
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {print(nums[i]);
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3] 输出:5, nums = [1,1,2,2,3] 解释:函数应返回新长度 length = 5, 并且原数组的前五个元素被修改为 1, 1, 2, 2, 3。 不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0,0,1,1,1,1,2,3,3] 输出:7, nums = [0,0,1,1,2,3,3] 解释:函数应返回新长度 length = 7, 并且原数组的前七个元素被修改为 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 3。不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 3 * 10^4-10^4 <= nums[i] <= 10^4nums已按升序排列
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:int removeDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) {if(nums.size() <= 2) {return nums.size();}int index = 2; // 从第3个元素开始检查for(int i = 2; i < nums.size(); i++) {if(nums[i] != nums[index - 2]) { // 有序数组 nums[index] = nums[i];++index;}} return index;}
}; int main() {vector<int> nums;int temp;while(cin >> temp) {nums.push_back(temp);if(cin.get() == '\n')break;}Solution solution;int n = solution.removeDuplicates(nums);cout << n << endl;cout << "[";for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {cout << nums[i] << " ";}cout << "]";return 0;
}81. 搜索旋转排序数组Ⅱ
已知存在一个按非降序排列的整数数组 nums ,数组中的值不必互不相同。
在传递给函数之前,nums 在预先未知的某个下标 k(0 <= k < nums.length)上进行了 旋转 ,使数组变为 [nums[k], nums[k+1], ..., nums[n-1], nums[0], nums[1], ..., nums[k-1]](下标 从 0 开始 计数)。例如, [0,1,2,4,4,4,5,6,6,7] 在下标 5 处经旋转后可能变为 [4,5,6,6,7,0,1,2,4,4] 。
给你 旋转后 的数组 nums 和一个整数 target ,请你编写一个函数来判断给定的目标值是否存在于数组中。如果 nums 中存在这个目标值 target ,则返回 true ,否则返回 false 。
你必须尽可能减少整个操作步骤。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [2,5,6,0,0,1,2], target = 0 输出:true
示例 2:
输入:nums = [2,5,6,0,0,1,2], target = 3 输出:false
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 5000-10^4 <= nums[i] <= 10^4- 题目数据保证
nums在预先未知的某个下标上进行了旋转 -10^4 <= target <= 10^4
进阶:
- 这是 搜索旋转排序数组 的延伸题目,本题中的
nums可能包含重复元素。 - 这会影响到程序的时间复杂度吗?会有怎样的影响,为什么?
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:bool search(vector<int>& nums, int target) {int left = 0, right = nums.size() - 1;while(left <= right) {int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;if(nums[mid] == target) {return true;}if(nums[left] == nums[mid] && nums[mid] == nums[right]) {// 如果左指针指向的元素、中间元素和右指针指向的元素相等,// 则将左指针右移一位,右指针左移一位(处理重复元素的情况)left++;right--;} else if(nums[left] <= nums[mid]) {if(nums[left] <= target && target < nums[right]) {// 如果左指针指向的元素小于等于中间元素,则判断目标值是否在左半部分,更新左右指针right = mid - 1;} else {left = mid + 1;}} else {if(nums[mid] < target && target <= nums[right]) {// 如果左指针指向的元素大于中间元素,则判断目标值是否在右半部分,更新左右指针left = mid + 1;} else {right = mid - 1;}}}return false; }
};int main() {int temp, target;vector<int> nums;while(cin >> temp) {nums.push_back(temp);if(cin.get() == '\n')break;}cin >> target;Solution solution;cout << boolalpha << solution.search(nums, target);return 0;
} 82. 删除排序链表中的重复元素Ⅱ
给定一个已排序的链表的头 head , 删除原始链表中所有重复数字的节点,只留下不同的数字 。返回 已排序的链表 。
示例 1:

输入:head = [1,2,3,3,4,4,5] 输出:[1,2,5]
示例 2:
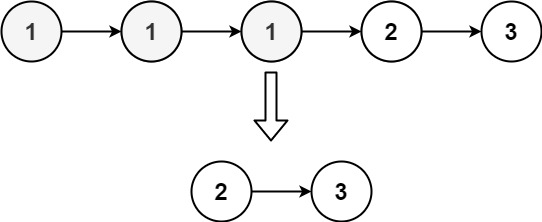
输入:head = [1,1,1,2,3] 输出:[2,3]
提示:
- 链表中节点数目在范围
[0, 300]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100- 题目数据保证链表已经按升序 排列
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;// Definition for singly-linked list
struct ListNode {int val;ListNode *next;ListNode() : val(0), next(NULL) {}ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};class Solution {public:ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL) {return head;}ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);dummy->next = head;ListNode* prev = dummy;while(head != NULL) {if(head->next != NULL && head->val == head->next->val) {// 如果当前节点的值与下一个节点的值相同,则循环遍历直到找到不同的节点,并将prev指针指向不同的节点while(head->next != NULL && head->val == head->next->val) {head = head->next;}prev->next = head->next;} else {// 如果当前节点的值与下一个节点的值不同,则更新prev指针为当前节点,并继续遍历下一个节点prev = prev->next;}head = head->next;}return dummy->next;}
};ListNode* createList() {ListNode* head = NULL;ListNode* current = NULL;int val;while(cin >> val) {ListNode* newNode = new ListNode(val);if(head == NULL) {head = newNode;current = newNode;} else {current->next = newNode;current = newNode;}if(cin.get() == '\n')break;}return head;
}void printList(ListNode* head) {ListNode* current = head;while(current != NULL) {cout << current->val << " ";current = current->next;}
}int main() {ListNode* head = createList();Solution solution;head = solution.deleteDuplicates(head);printList(head);return 0;
}83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素
给定一个已排序的链表的头 head , 删除所有重复的元素,使每个元素只出现一次 。返回 已排序的链表 。
示例 1:

输入:head = [1,1,2] 输出:[1,2]
示例 2:
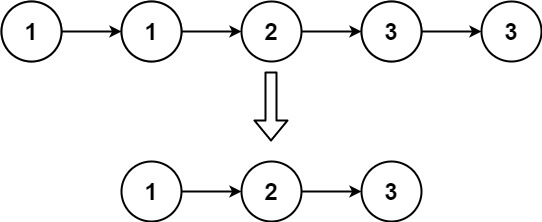
输入:head = [1,1,2,3,3] 输出:[1,2,3]
提示:
- 链表中节点数目在范围
[0, 300]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100- 题目数据保证链表已经按升序 排列
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;struct ListNode {int val;ListNode *next;ListNode() : val(0), next(NULL) {}ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};class Solution {public:ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {ListNode* current = head;while(current != NULL && current->next != NULL) {if(current->val == current->next->val) {ListNode* temp = current->next;current->next = current->next->next;delete temp;} else {current = current->next;}}return head;}
};ListNode* createList() {ListNode* head = NULL;ListNode* current = NULL;int val;while(cin >> val) {ListNode* newNode = new ListNode(val);if(head == NULL) {head = newNode;current = newNode;} else {current->next = newNode;current = newNode;}if(cin.get() == '\n')break;}return head;
}void printList(ListNode* head) {ListNode* current = head;while(current != NULL) {cout << current->val << " ";current = current->next;}
}int main() {ListNode* head = createList();Solution solution;head = solution.deleteDuplicates(head);printList(head);return 0;
}84. 柱形图中最大的矩形
给定 n 个非负整数,用来表示柱状图中各个柱子的高度。每个柱子彼此相邻,且宽度为 1 。
求在该柱状图中,能够勾勒出来的矩形的最大面积。
示例 1:

输入:heights = [2,1,5,6,2,3] 输出:10 解释:最大的矩形为图中红色区域,面积为 10
示例 2:

输入: heights = [2,4] 输出: 4
提示:
1 <= heights.length <=10^50 <= heights[i] <= 10^4
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {stack<int> s;heights.push_back(0);// 在输入数组末尾添加一个高度为0的柱子,以处理所有柱子都比栈中柱子高的情况int maxArea = 0;for(int i = 0; i < heights.size(); i++) {// 遍历数组,如果当前柱子的高度小于栈顶柱子的高度,则计算以栈顶柱子为高度的矩形面积,并更新最大面积while(!s.empty() && heights[i] < heights[s.top()]) {int h = heights[s.top()];s.pop();int left = s.empty() ? -1 : s.top();maxArea = max(maxArea, h * (i - 1- left));}s.push(i);}return maxArea;}
};int main() {vector<int> heights;int temp;while(cin >> temp) {heights.push_back(temp);if(cin.get() == '\n')break;}Solution solution;cout << solution.largestRectangleArea(heights);return 0;
}85. 最大矩形
给定一个仅包含 0 和 1 、大小为 rows x cols 的二维二进制矩阵,找出只包含 1 的最大矩形,并返回其面积。
示例 1:
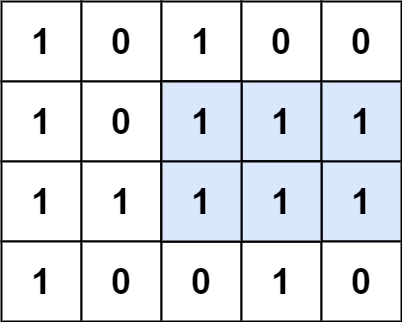
输入:matrix = [["1","0","1","0","0"],["1","0","1","1","1"],["1","1","1","1","1"],["1","0","0","1","0"]] 输出:6 解释:最大矩形如上图所示。
示例 2:
输入:matrix = [["0"]] 输出:0
示例 3:
输入:matrix = [["1"]] 输出:1
提示:
rows == matrix.lengthcols == matrix[0].length1 <= row, cols <= 200matrix[i][j]为'0'或'1'
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include <algorithm>using namespace std;class Solution {public:int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {if(matrix.empty() || matrix[0].empty()) {return 0;}int rows = matrix.size();int cols = matrix[0].size();// 从当前位置向上连续的1的个数vector<vector<int>> heights(rows, vector<int>(cols, 0));int maxArea = 0;for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {if(matrix[i][j] == '1') {heights[i][j] = (i == 0) ? 1 : heights[i - 1][j] + 1;}}}for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {stack<int> s;vector<int> left(cols), right(cols, cols);// 对于每一行,使用栈来计算每个位置的左边界和右边界,进而计算最大矩形面积for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {while(!s.empty() && heights[i][j] < heights[i][s.top()]) {right[s.top()] = j;s.pop();}left[j] = s.empty() ? -1 : s.top();s.push(j);}for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {maxArea = max(maxArea, heights[i][j] * (right[j] - left[j] - 1));}}return maxArea;}
};int main() {int rows, cols;cin >> rows >> cols;vector<vector<char>> matrix(rows, vector<char>(cols));for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {cin >> matrix[i][j];}}Solution solution;cout << solution.maximalRectangle(matrix);return 0;
}
86. 分隔链表
给你一个链表的头节点 head 和一个特定值 x ,请你对链表进行分隔,使得所有 小于 x 的节点都出现在 大于或等于 x 的节点之前。
你应当 保留 两个分区中每个节点的初始相对位置。
示例 1:
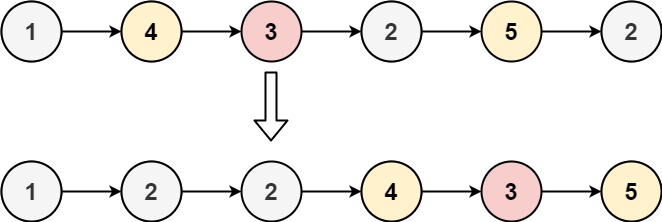
输入:head = [1,4,3,2,5,2], x = 3 输出:[1,2,2,4,3,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [2,1], x = 2 输出:[1,2]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目在范围
[0, 200]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100-200 <= x <= 200
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;// Definition for singly-linked list
struct ListNode {int val;ListNode *next;ListNode() : val(0), next(NULL) {}ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};class Solution {public:ListNode* partition(ListNode* head, int x) {ListNode less_head(0);ListNode greater_head(0);ListNode *less_ptr = &less_head;ListNode *greater_ptr = &greater_head;while(head) {if(head->val < x) {less_ptr->next = head;less_ptr = less_ptr->next;} else {greater_ptr->next = head;greater_ptr = greater_ptr->next;}head = head->next;}less_ptr->next = greater_head.next;greater_ptr->next = NULL;return less_head.next;}
};ListNode* createList() {ListNode* head = NULL;ListNode* current = NULL;int val;while(cin >> val) {ListNode* newNode = new ListNode(val);if(head == NULL) {head = newNode;current = newNode;} else {current->next = newNode;current = newNode;}if(cin.get() == '\n')break;}return head;
}void printList(ListNode* head) {ListNode* current = head;while(current != NULL) {cout << current->val << " ";current = current->next;}
}int main() {ListNode* head = createList();int x;cin >> x;Solution solution;ListNode* result = solution.partition(head, x);printList(result);return 0;
}87. 扰乱字符串
使用下面描述的算法可以扰乱字符串 s 得到字符串 t :
- 如果字符串的长度为 1 ,算法停止
- 如果字符串的长度 > 1 ,执行下述步骤:
- 在一个随机下标处将字符串分割成两个非空的子字符串。即,如果已知字符串
s,则可以将其分成两个子字符串x和y,且满足s = x + y。 - 随机 决定是要「交换两个子字符串」还是要「保持这两个子字符串的顺序不变」。即,在执行这一步骤之后,
s可能是s = x + y或者s = y + x。 - 在
x和y这两个子字符串上继续从步骤 1 开始递归执行此算法。
- 在一个随机下标处将字符串分割成两个非空的子字符串。即,如果已知字符串
给你两个 长度相等 的字符串 s1 和 s2,判断 s2 是否是 s1 的扰乱字符串。如果是,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
输入:s1 = "great", s2 = "rgeat" 输出:true 解释:s1 上可能发生的一种情形是: "great" --> "gr/eat" // 在一个随机下标处分割得到两个子字符串 "gr/eat" --> "gr/eat" // 随机决定:「保持这两个子字符串的顺序不变」 "gr/eat" --> "g/r / e/at" // 在子字符串上递归执行此算法。两个子字符串分别在随机下标处进行一轮分割 "g/r / e/at" --> "r/g / e/at" // 随机决定:第一组「交换两个子字符串」,第二组「保持这两个子字符串的顺序不变」 "r/g / e/at" --> "r/g / e/ a/t" // 继续递归执行此算法,将 "at" 分割得到 "a/t" "r/g / e/ a/t" --> "r/g / e/ a/t" // 随机决定:「保持这两个子字符串的顺序不变」 算法终止,结果字符串和 s2 相同,都是 "rgeat" 这是一种能够扰乱 s1 得到 s2 的情形,可以认为 s2 是 s1 的扰乱字符串,返回 true
示例 2:
输入:s1 = "abcde", s2 = "caebd" 输出:false
示例 3:
输入:s1 = "a", s2 = "a" 输出:true
提示:
s1.length == s2.length1 <= s1.length <= 30s1和s2由小写英文字母组成
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<unordered_map>using namespace std;class Solution {public:bool isScramble(string s1, string s2) {if(s1 == s2) {return true;}int n = s1.length();if(n != s2.length()) {return false;}unordered_map<string, bool> memo;return isScrambleHelper(s1, s2, memo);}bool isScrambleHelper(string s1, string s2, unordered_map<string, bool>& memo) {string key = s1 + "#" + s2;if(memo.find(key) != memo.end()) {return memo[key];}int n = s1.length();if(n != s2.length()) {return false;}if(s1 == s2) {return true;}string sorted_s1 = s1;string sorted_s2 = s2;sort(sorted_s1.begin(), sorted_s1.end());sort(sorted_s2.begin(), sorted_s2.end());if(sorted_s1 != sorted_s2) {memo[key] = false;return false;}for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) {if ((isScrambleHelper(s1.substr(0, i), s2.substr(0, i), memo) && isScrambleHelper(s1.substr(i), s2.substr(i), memo)) ||(isScrambleHelper(s1.substr(0, i), s2.substr(n - i), memo) && isScrambleHelper(s1.substr(i), s2.substr(0, n - i), memo))) {memo[key] = true;return true;}}memo[key] = false;return false;}
};int main() {string s1, s2;cin >> s1 >> s2;Solution solution;cout << boolalpha << solution.isScramble(s1, s2);return 0;
}88. 合并两个有序数组
给你两个按 非递减顺序 排列的整数数组 nums1 和 nums2,另有两个整数 m 和 n ,分别表示 nums1 和 nums2 中的元素数目。
请你 合并 nums2 到 nums1 中,使合并后的数组同样按 非递减顺序 排列。
注意:最终,合并后数组不应由函数返回,而是存储在数组 nums1 中。为了应对这种情况,nums1 的初始长度为 m + n,其中前 m 个元素表示应合并的元素,后 n 个元素为 0 ,应忽略。nums2 的长度为 n 。
示例 1:
输入:nums1 = [1,2,3,0,0,0], m = 3, nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3 输出:[1,2,2,3,5,6] 解释:需要合并 [1,2,3] 和 [2,5,6] 。 合并结果是 [1,2,2,3,5,6] ,其中斜体加粗标注的为 nums1 中的元素。
示例 2:
输入:nums1 = [1], m = 1, nums2 = [], n = 0 输出:[1] 解释:需要合并 [1] 和 [] 。 合并结果是 [1] 。
示例 3:
输入:nums1 = [0], m = 0, nums2 = [1], n = 1 输出:[1] 解释:需要合并的数组是 [] 和 [1] 。 合并结果是 [1] 。 注意,因为 m = 0 ,所以 nums1 中没有元素。nums1 中仅存的 0 仅仅是为了确保合并结果可以顺利存放到 nums1 中。
提示:
nums1.length == m + nnums2.length == n0 <= m, n <= 2001 <= m + n <= 200-10^9 <= nums1[i], nums2[j] <= 10^9
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:void merge(vector<int>& nums1, int m, vector<int>&nums2, int n) {int i = m + n - 1;m--;n--;while(n >= 0) {if(m >= 0 && nums1[m] > nums2[n]) { // 从后往前比较大小swap(nums1[i--], nums1[m--]);} else {swap(nums1[i--], nums2[n--]);}}}
};int main() {vector<int> nums1, nums2;int m, n;int temp;while(cin >> temp) {nums1.push_back(temp);if(cin.get() == '\n') break;}cin >> m;while(cin >> temp) {nums2.push_back(temp);if(cin.get() == '\n')break;}cin >> n;Solution solution;solution.merge(nums1, m, nums2, n);for(int i = 0; i < m + n; i++)cout << nums1[i] << " ";return 0;
}89. 格雷编码
n 位格雷码序列 是一个由 2n 个整数组成的序列,其中:
- 每个整数都在范围
[0, 2n - 1]内(含0和2n - 1) - 第一个整数是
0 - 一个整数在序列中出现 不超过一次
- 每对 相邻 整数的二进制表示 恰好一位不同 ,且
- 第一个 和 最后一个 整数的二进制表示 恰好一位不同
给你一个整数 n ,返回任一有效的 n 位格雷码序列 。
示例 1:
输入:n = 2 输出:[0,1,3,2] 解释: [0,1,3,2] 的二进制表示是 [00,01,11,10] 。 - 00 和 01 有一位不同 - 01 和 11 有一位不同 - 11 和 10 有一位不同 - 10 和 00 有一位不同 [0,2,3,1] 也是一个有效的格雷码序列,其二进制表示是 [00,10,11,01] 。 - 00 和 10 有一位不同 - 10 和 11 有一位不同 - 11 和 01 有一位不同 - 01 和 00 有一位不同
示例 2:
输入:n = 1 输出:[0,1]
提示:
1 <= n <= 16
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:vector<int>grayCode(int n) {vector<int> result;for(int i = 0; i < (1 << n); i++) {result.push_back(i ^ (i >> 1)); // 异或运算}return result;}
};int main() {int n;cin >> n;Solution solution;vector<int> result = solution.grayCode(n);for(int num : result) {cout << num << " ";}return 0;
}90. 子集Ⅱ
给你一个整数数组 nums ,其中可能包含重复元素,请你返回该数组所有可能的
子集
(幂集)。
解集 不能 包含重复的子集。返回的解集中,子集可以按 任意顺序 排列。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,2] 输出:[[],[1],[1,2],[1,2,2],[2],[2,2]]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0] 输出:[[],[0]]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 10-10 <= nums[i] <= 10
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;class Solution {public:vector<vector<int>> subsetsWithDup(vector<int>& nums) {vector<vector<int>> subsets;vector<int> subset;sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());backtrack(subsets, nums, subset, 0);return subsets;}void backtrack(vector<vector<int>>& subsets, vector<int>& nums, vector<int>& subset, int start) {subsets.push_back(subset);for(int i = start; i < nums.size(); i++) {if(i > start && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) {continue;}subset.push_back(nums[i]);backtrack(subsets, nums, subset, i + 1);subset.pop_back();}}
}; int main() {vector<int> nums;int temp;while(cin >> temp) {nums.push_back(temp);if(cin.get() == '\n')break;}Solution solution;vector<vector<int>> result = solution.subsetsWithDup(nums);cout << "[";for(int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {cout << "[";for(int j = 0; j < result[i].size(); j++) {if(j == result[i].size() - 1) {cout << result[i][j];} else {cout << result[i][j] << ", ";}}if(i == result.size() - 1) {cout << "]";} else {cout << "]" << ", ";}}cout << "]" << endl;return 0;
}