二、贪心算法之区间调度问题
0.计算一个区间集合中无重复的区间的最大数量(模板)
public int intervalSchedule(int[][] intvs) {if (intvs.length == 0) return 0;// 按 end 升序排序Arrays.sort(intvs, (a, b) -> Integer.compare(a[1], b[1]));// 至少有一个区间不相交int count = 1;// 排序后,第一个区间就是 xint x_end = intvs[0][1];for (int[] interval : intvs) {int start = interval[0];if (start >= x_end) {// 找到下一个选择的区间了count++;x_end = interval[1];}}return count;
}1.435无重叠区间
class Solution {public int eraseOverlapIntervals(int[][] intervals) {int n = intervals.length;if (n == 0) return 0;// 按 end 升序排序Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> Integer.compare(a[1], b[1]));// 至少有一个区间不相交int count = 1;// 排序后,第一个区间就是 xint x_end = intervals[0][1];for (int[] interval : intervals) {int start = interval[0];if (start >= x_end) {// 找到下一个选择的区间了count++;x_end = interval[1];}}//count为最多的互不相交的区间,n - count就为最少的需要去除的区间数量count = n - count;return count;}
}
2.452.用最少的箭射爆气球
与模板不同点是在 intervalSchedule 算法中,如果两个区间的边界触碰,不算重叠;而按照这道题目的描述,箭头如果碰到气球的边界气球也会爆炸,所以说相当于区间的边界触碰也算重叠
将不重叠区间的条件 从 >= 改为 > 即可
class Solution {public int findMinArrowShots(int[][] points) {if (points.length == 0) return 0;// 按 end 升序排序Arrays.sort(points, (a, b) -> Integer.compare(a[1], b[1]));// 至少有一个区间不相交int count = 1;// 排序后,第一个区间就是 xint x_end = points[0][1];for (int[] interval : points) {int start = interval[0];if (start > x_end) {// 找到下一个选择的区间了count++;x_end = interval[1];}}return count;}
}
三、一个方法解决三道区间题
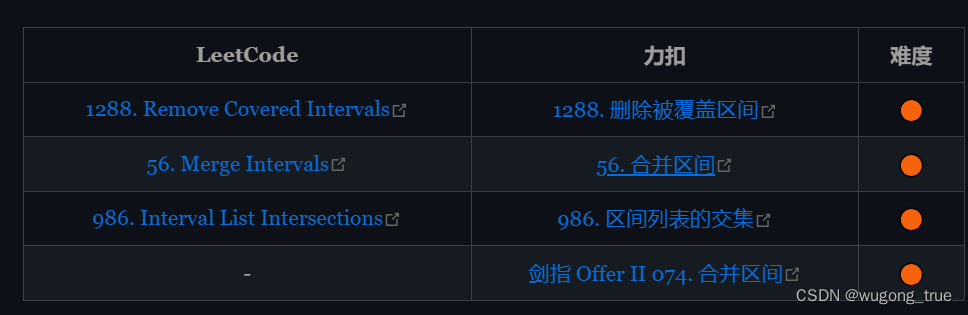
1.区间覆盖问题
1288删除被覆盖区间,返回剩余区间的数量
int removeCoveredIntervals(int[][] intvs) {// 按照起点升序排列,起点相同时降序排列Arrays.sort(intvs, (a, b) -> {if (a[0] == b[0]) {return b[1] - a[1];}return a[0] - b[0]; });// 记录合并区间的起点和终点int left = intvs[0][0];int right = intvs[0][1];int res = 0;for (int i = 1; i < intvs.length; i++) {int[] intv = intvs[i];// 情况一,找到覆盖区间if (left <= intv[0] && right >= intv[1]) {res++;}// 情况二,找到相交区间,合并if (right >= intv[0] && right <= intv[1]) {right = intv[1];}// 情况三,完全不相交,更新起点和终点if (right < intv[0]) {left = intv[0];right = intv[1];}}//总数量减去合并后剩余的区间数量就是被删除的区间数量return intvs.length - res;
}2.区间合并问题
class Solution {public int[][] merge(int[][] intervals) {if(intervals == null || intervals.length == 0) return new int[][]{};// 按区间的 start 升序排列Arrays.sort(intervals, Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0]));List<int[]> res = new ArrayList<>();//将第一个元素加入到res中res.add(intervals[0]);// 注意从1开始for(int i=1; i<intervals.length; i++){int[] curr = intervals[i];// res 中最后一个元素的引用int[] last = res.get(res.size()-1);if(curr[0] <= last[1]){ //当前的起始 < 上一个结束,表示相交// 找到最大的 endlast[1] = Math.max(last[1], curr[1]);} else{ //否则不相交// 处理下一个待合并区间res.add(curr);}}return res.toArray(new int[res.size()][]);}
}
3.区间交集问题
三个关键点
- 两区间相交的条件
- 获取相交区间的左端点和右端点
- 两个指针什么情况下移动
class Solution {public int[][] intervalIntersection(int[][] firstList, int[][] secondList) {int i = 0, j = 0;List<int[]> res = new ArrayList<>();while (i < firstList.length && j < secondList.length) {//a1,b1 是 两个区间列表的左端点,a2,b2是对应的右端点int a1 = firstList[i][0], a2 = firstList[i][1];int b1 = secondList[j][0], b2 = secondList[j][1];// 两个区间存在交集,使用没有交集的对立条件推出存在交集的条件//if b2 < a1 or a2 < b1: [a1,a2] 和 [b1,b2] 无交集if (b2 >= a1 && a2 >= b1) {// 计算出交集,加入 res; 交集是左端点的最大值和右端点的最小值组成的res.add(new int[]{Math.max(a1, b1), Math.min(a2, b2)});}// 指针前进,取决于右端点的大小,谁小谁就向后遍历if (b2 < a2) {j++;} else {i++;}}return res.toArray(new int[res.size()][]);}
}
四、LRU缓存 && LFU缓存
这个算是我老朋友了,我窥觊它得一个月了,但实在太难,直到遇见labuladong,学的更轻松了,也算是激发了我学习热情,感谢dong哥
LRU 算法的核心数据结构是使用哈希链表 LinkedHashMap,首先借助链表的有序性使得链表元素维持插入顺序,同时借助哈希映射的快速访问能力使得我们可以在 O(1) 时间访问链表的任意元素
1.LRU缓存
-
使用哈希双端链表(Java中对应的是LinkedHashMap)
-
创建Node单个节点 -> 组成DoubleList双端链表
-
因为同时维护map的双端链表,需要抽象出来几个方法在对元素操作时同时操作map和DoubleList,防止漏掉操作,比如说删除某个
key时,在cache中删除了对应的Node,但是却忘记在map中删除key。解决这种问题的有效方法是:在这两种数据结构之上提供一层抽象 API。
说的有点玄幻,实际上很简单,就是尽量让 ==LRU 的主方法
get和put避免直接操作map和cache==的细节。我们可以先实现下面几个函数: -
get逻辑比较简单,这里阐述一下put的逻辑
- 若key已经存在,那么修改key对应的value
- 若key不存在,需要插入key
- 当容量满的时候,淘汰最久未使用的key
- 当容量没有满,直接执行c
- 插入key和val为最近使用的数据
class LRUCache {// key -> Node(key, val)private HashMap<Integer, Node> map;// Node(k1, v1) <-> Node(k2, v2)...private DoubleList cache;// 最大容量private int cap;public LRUCache(int capacity) {this.cap = capacity;map = new HashMap<>();cache = new DoubleList();}class Node {public int key, val;public Node next, prev;public Node(int k, int v) {this.key = k;this.val = v;}
}class DoubleList { // 头尾虚节点private Node head, tail; // 链表元素数private int size;public DoubleList() {// 初始化双向链表的数据head = new Node(0, 0);tail = new Node(0, 0);head.next = tail;tail.prev = head;size = 0;}// 在链表尾部添加节点 x,时间 O(1)public void addLast(Node x) {x.prev = tail.prev;x.next = tail;tail.prev.next = x;tail.prev = x;size++;}// 删除链表中的 x 节点(x 一定存在)// 由于是双链表且给的是目标 Node 节点,时间 O(1)public void remove(Node x) {x.prev.next = x.next;x.next.prev = x.prev;size--;}// 删除链表中第一个节点,并返回该节点,时间 O(1)public Node removeFirst() {if (head.next == tail)return null;Node first = head.next;remove(first);return first;}// 返回链表长度,时间 O(1)public int size() { return size; }}/* 将某个 key 提升为最近使用的 */private void makeRecently(int key) {Node x = map.get(key);// 先从链表中删除这个节点cache.remove(x);// 重新插到队尾cache.addLast(x);}/* 添加最近使用的元素 */private void addRecently(int key, int val) {Node x = new Node(key, val);// 链表尾部就是最近使用的元素cache.addLast(x);// 别忘了在 map 中添加 key 的映射map.put(key, x);}/* 删除某一个 key */private void deleteKey(int key) {Node x = map.get(key);// 从链表中删除cache.remove(x);// 从 map 中删除map.remove(key);}/* 删除最久未使用的元素 */private void removeLeastRecently() {// 链表头部的第一个元素就是最久未使用的Node deletedNode = cache.removeFirst();// 同时别忘了从 map 中删除它的 keyint deletedKey = deletedNode.key;map.remove(deletedKey);}public int get(int key) {if (!map.containsKey(key)) {return -1;}// 将该数据提升为最近使用的makeRecently(key);return map.get(key).val;}public void put(int key, int val) {if (map.containsKey(key)) {// 删除旧的数据deleteKey(key);// 新插入的数据为最近使用的数据addRecently(key, val);return;}if (cap == cache.size()) {// 删除最久未使用的元素removeLeastRecently();}// 添加为最近使用的元素addRecently(key, val);}}/*** Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:* LRUCache obj = new LRUCache(capacity);* int param_1 = obj.get(key);* obj.put(key,value);*/
2.LFU缓存
class LFUCache {// key 到 val 的映射,我们后文称为 KV 表HashMap<Integer, Integer> keyToVal;// key 到 freq 的映射,我们后文称为 KF 表HashMap<Integer, Integer> keyToFreq;// freq 到 key 列表的映射,我们后文称为 FK 表HashMap<Integer, LinkedHashSet<Integer>> freqToKeys;// 记录最小的频次int minFreq;// 记录 LFU 缓存的最大容量int cap;public LFUCache(int capacity) {keyToVal = new HashMap<>();keyToFreq = new HashMap<>();freqToKeys = new HashMap<>();this.cap = capacity;this.minFreq = 0;}public int get(int key) {if (!keyToVal.containsKey(key)) {return -1;}// 增加 key 对应的 freqincreaseFreq(key);return keyToVal.get(key);}public void put(int key, int val) {if (this.cap <= 0) return;/* 若 key 已存在,修改对应的 val 即可 */if (keyToVal.containsKey(key)) {keyToVal.put(key, val);// key 对应的 freq 加一increaseFreq(key);return;}/* key 不存在,需要插入 *//* 容量已满的话需要淘汰一个 freq 最小的 key */if (this.cap <= keyToVal.size()) {removeMinFreqKey();}/* 插入 key 和 val,对应的 freq 为 1 */// 插入 KV 表keyToVal.put(key, val);// 插入 KF 表keyToFreq.put(key, 1);// 插入 FK 表freqToKeys.putIfAbsent(1, new LinkedHashSet<>());freqToKeys.get(1).add(key);// 插入新 key 后最小的 freq 肯定是 1this.minFreq = 1;}private void removeMinFreqKey() {// freq 最小的 key 列表LinkedHashSet<Integer> keyList = freqToKeys.get(this.minFreq);// 其中最先被插入的那个 key 就是该被淘汰的 keyint deletedKey = keyList.iterator().next();/* 更新 FK 表 */keyList.remove(deletedKey);if (keyList.isEmpty()) {freqToKeys.remove(this.minFreq);// 问:这里需要更新 minFreq 的值吗?}/* 更新 KV 表 */keyToVal.remove(deletedKey);/* 更新 KF 表 */keyToFreq.remove(deletedKey);}private void increaseFreq(int key) {int freq = keyToFreq.get(key);/* 更新 KF 表 */keyToFreq.put(key, freq + 1);/* 更新 FK 表 */// 将 key 从 freq 对应的列表中删除freqToKeys.get(freq).remove(key);// 将 key 加入 freq + 1 对应的列表中freqToKeys.putIfAbsent(freq + 1, new LinkedHashSet<>());freqToKeys.get(freq + 1).add(key);// 如果 freq 对应的列表空了,移除这个 freqif (freqToKeys.get(freq).isEmpty()) {freqToKeys.remove(freq);// 如果这个 freq 恰好是 minFreq,更新 minFreqif (freq == this.minFreq) {this.minFreq++;}}}}