🔥个人主页: Forcible Bug Maker
🔥专栏: STL || C++
目录
- 前言
- 🔥字符串操作(String operations)
- ==c_str==
- ==data==
- ==get_allocator==
- ==copy==
- ==find==
- ==rfind==
- ==find_first_of==
- ==find_last_of==
- ==find_first_not_of==
- ==find_last_not_of==
- ==substr==
- ==compare==
- 🔥常量成员(Member constants)
- ==npos==
- 结语
前言
本篇博客主要内容:STL库中string的字符串操作(String operations)和常量成员(Member constants)。
来到string类的使用第四篇,继续我们的内容,本篇博客将着重介绍如何使用string类提供的接口函数去查找和获取字符串的内容;同时还会讲一个定义在string类中的常量成员(npos)。
本篇也将是string类使用的收尾篇。
🔥字符串操作(String operations)
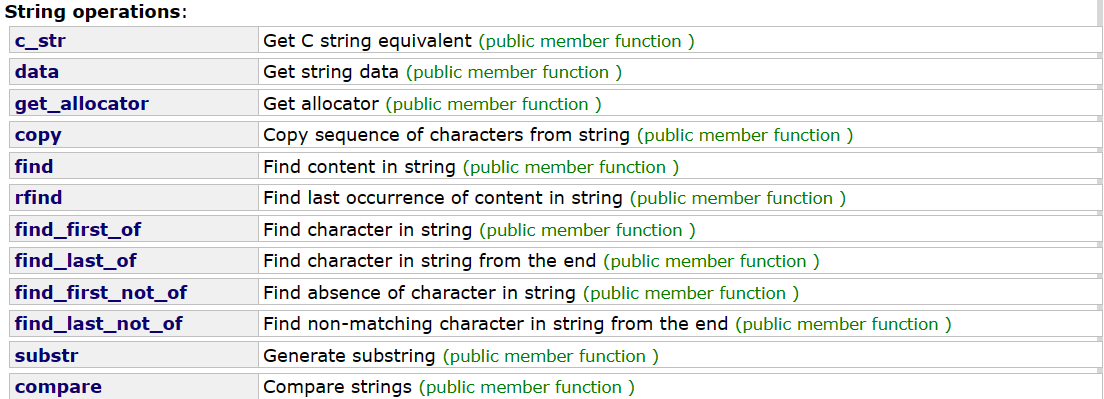
这些接口函数提供的是一些查找和获取string串内容的功能。
c_str

const char* c_str() const;
返回一个指向字符串数组(以'\0'结尾)的指针,代表当前string串的内容。
同时返回指针指向的字符串中的内容也是不可修改的。
使用案例:
// strings and c-strings
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{std::string str("hello world!");char* cstr = new char[str.length() + 1];strcpy(cstr, str.c_str());printf("%s\n", str.c_str());printf("%s\n", cstr);return 0;
}
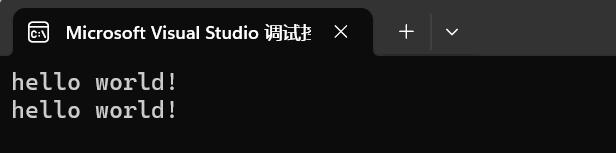
简单来说c_str就是获取一个字符串指针,指向的就是string对量串中的内容。
data

const char* data() const;
返回一个指向数组的指针。(该数组与string串构成字符相同,不保证字符串数组以'\0'结尾。c_str能保证)
使用案例:
// string::data
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
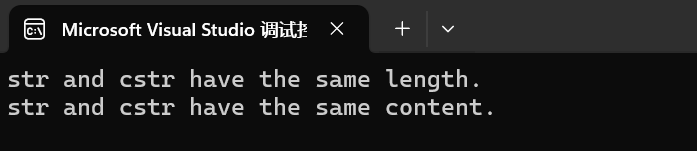
int main()
{int length;std::string str = "Test string";const char* cstr = "Test string";if (str.length() == strlen(cstr)){cout << "str and cstr have the same length.\n";if (memcmp(cstr, str.data(), str.length()) == 0)cout << "str and cstr have the same content.\n";}return 0;
}
get_allocator

allocator_type get_allocator() const;
此函数接口返回一个引用到该字符对象的内存分配器(alloctor)的副本。这个分配器用于管理std::string内部数据的内存分配和释放。
通常,你不需要使用此函数,编译器能帮你很好的管理好STL库中内存的分配与释放,除非你需要进行一些高级的,与内存管理相关的操作。
实际中并不常用,故不做过多讲解。
copy

size_t copy (char* s, size_t len, size_t pos = 0) const;
将一个string串从pos位置开始跨越len个长度的子串内容拷贝到s指向的数组中(子串len的长度包括pos位置的字符)。
返回值:从string串中拷贝到s中字符的个数,这个数字可以等于len或length()-pos(如果string对象串的长度小于pos+len)。
注:这个接口函数**
不会在拷贝完的字符串结尾自动加’\0’**。
使用案例:
// string::copy
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
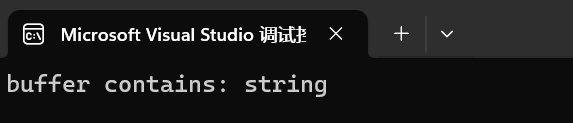
int main()
{char buffer[20];string str("Test string...");size_t length = str.copy(buffer, 6, 5);buffer[length] = '\0';cout << "buffer contains: " << buffer << '\n';return 0;
}
find

提供了在string串中按顺序查找某字符和某子串的功能。
(1) string
size_t find (const string& str, size_t pos = 0) const;
从pos位置开始查找string串中是否包含str串。如果有,返回匹配上的下标位置;如果没有,则返回常量成员npos(可以看作是一个很大的值,可以提前看下文末的常量成员内容)。
(2) c-string
size_t find (const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const;
从pos位置开始查找string串中是否包含字符串s。如果有,返回匹配上的下标位置;如果没有,则返回常量成员npos。
(3) buffer
size_t find (const char* s, size_t pos, size_t n) const;
从pos位置开始查找string串中是否包含字符串s的前n个字符组成的子串。如果有,返回匹配上的下标位置;如果没有,则返回常量成员npos。
(4) character
size_t find (char c, size_t pos = 0) const;
从pos位置开始查找string串中是否包字符c。如果有,返回匹配上的下标位置;如果没有,则返回常量成员npos。
使用案例:
// string::find
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <string> // std::string
using namespace std;
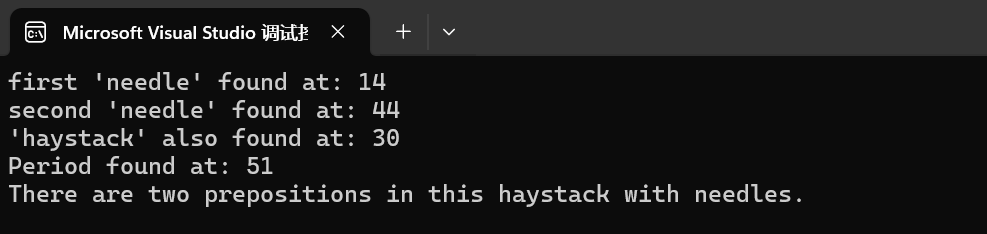
int main()
{string str("There are two needles in this haystack with needles.");string str2("needle");// different member versions of find in the same order as above:size_t found = str.find(str2);if (found != string::npos)cout << "first 'needle' found at: " << found << '\n';found = str.find("needles are small", found + 1, 6);if (found != string::npos)cout << "second 'needle' found at: " << found << '\n';found = str.find("haystack");if (found != string::npos)cout << "'haystack' also found at: " << found << '\n';found = str.find('.');if (found != string::npos)cout << "Period found at: " << found << '\n';// let's replace the first needle:str.replace(str.find(str2), str2.length(), "preposition");cout << str << '\n';return 0;
}
rfind

这个函数就是从后往前找的find,功能我就不多做赘述了。
(1) string
size_t rfind (const string& str, size_t pos = npos) const;
(2) c-string
size_t rfind (const char* s, size_t pos = npos) const;
(3) buffer
size_t rfind (const char* s, size_t pos, size_t n) const;
(4) character
size_t rfind (char c, size_t pos = npos) const;
注:当pos被确定时,rfind会忽略任何在pos之后的字符。
使用案例:
// string::rfind
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstddef>
using namespace std;
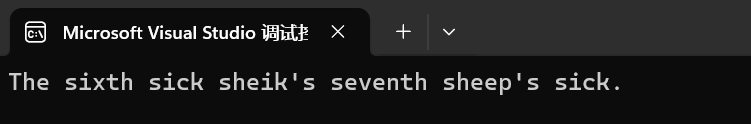
int main()
{string str("The sixth sick sheik's sixth sheep's sick.");string key("sixth");size_t found = str.rfind(key);if (found != string::npos)str.replace(found, key.length(), "seventh");cout << str << '\n';return 0;
}
find_first_of

从前往后查找在string串中任何存在于某字符或字符串中的字符。
(1) string
size_t find_first_of (const string& str, size_t pos = 0) const;
从pos位置开始查找string串的字符是否存在于str串中。如果存在,返回匹配上的下标位置;如果找到string串的末尾也没有,则返回常量成员npos(可以看作是一个很大的值,可以提前看下文末的常量成员内容)。
(2) c-string
size_t find_first_of (const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const;
从pos位置开始查找string串的字符是否存在于字符串s中。如果存在,返回匹配上的下标位置;如果找到string串的末尾也没有,则返回常量成员npos。
(3) buffer
size_t find_first_of (const char* s, size_t pos, size_t n) const;
从pos位置开始查找string串的字符是否存在于字符串s前n个字符组成的子串中。如果存在,返回匹配上的下标位置;如果找到string串的末尾也没有,则返回常量成员npos。
(4) character
size_t find_first_of (char c, size_t pos = 0) const;
从pos位置开始查找string串的字符是否为字符c。如果存在,返回匹配上的下标位置;如果找到string串的末尾也没有,则返回常量成员npos。
使用案例:
// string::find_first_of
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <string> // std::string
#include <cstddef> // std::size_t
using namespace std;
int main()
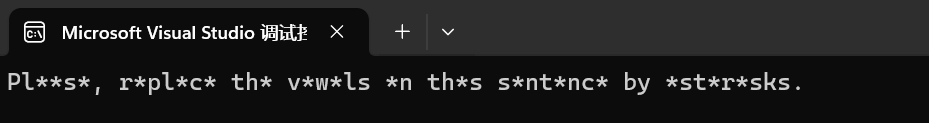
{// 将句子中的元音字母转换成星号(*)string str("Please, replace the vowels in this sentence by asterisks.");size_t found = str.find_first_of("aeiou");while (found != string::npos){str[found] = '*';found = str.find_first_of("aeiou", found + 1);}cout << str << '\n';return 0;
}
find_last_of

和find_first_of的功能及其相似,不过此函数是从后往前找。
(1) string
size_t find_last_of (const string& str, size_t pos = npos) const;
(2) c-string
size_t find_last_of (const char* s, size_t pos = npos) const;
(3) buffer
size_t find_last_of (const char* s, size_t pos, size_t n) const;
(4) character
size_t find_last_of (char c, size_t pos = npos) const;
使用案例:
// string::find_last_of
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <string> // std::string
#include <cstddef> // std::size_t
using namespace std;void SplitFilename(const std::string& str)
{cout << "Splitting: " << str << '\n';size_t found = str.find_last_of("/\\");cout << " path: " << str.substr(0, found) << '\n';cout << " file: " << str.substr(found + 1) << '\n';
}int main()
{string str1("/usr/bin/man");string str2("c:\\windows\\winhelp.exe");SplitFilename(str1);SplitFilename(str2);return 0;
}

find_first_not_of

在之前find_first_of的基础上,这个看名字似乎就能理解其功能了。没错这个就是从前往后找string串中任何不存在于某字符或字符串中的字符。
string (1)
size_t find_first_not_of (const string& str, size_t pos = 0) const;
c-string (2)
size_t find_first_not_of (const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const;
buffer (3)
size_t find_first_not_of (const char* s, size_t pos, size_t n) const;
character (4)
size_t find_first_not_of (char c, size_t pos = 0) const;
使用案例:
// string::find_first_not_of
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <string> // std::string
#include <cstddef> // std::size_t
using namespace std;
int main()
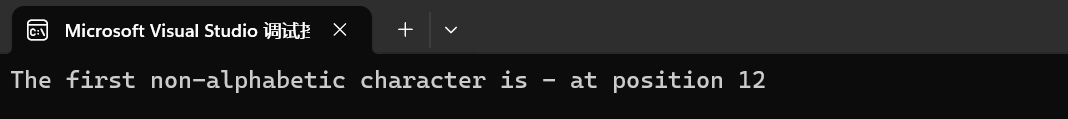
{string str("look for non-alphabetic characters...");size_t found = str.find_first_not_of("abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz ");if (found != string::npos){cout << "The first non-alphabetic character is " << str[found];cout << " at position " << found << '\n';}return 0;
}
find_last_not_of

从后往前找string串中任何不存在于某字符或字符串中的字符。
string (1)
size_t find_last_not_of (const string& str, size_t pos = npos) const;
c-string (2)
size_t find_last_not_of (const char* s, size_t pos = npos) const;
buffer (3)
size_t find_last_not_of (const char* s, size_t pos, size_t n) const;
character (4)
size_t find_last_not_of (char c, size_t pos = npos) const;
使用案例:
// string::find_last_not_of
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <string> // std::string
#include <cstddef> // std::size_t
using namespace std;
int main()
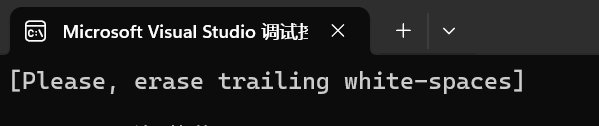
{string str("Please, erase trailing white-spaces \n");string whitespaces(" \t\f\v\n\r");size_t found = str.find_last_not_of(whitespaces);if (found != string::npos)str.erase(found + 1);elsestr.clear(); // str对象串中全为空白cout << '[' << str << "]\n";return 0;
}
substr

string substr (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos) const;
返回一个由string串pos位置开始跨越len个字符(len过大时就取到string对象末尾)创建的子对象(也是string类型)。
使用案例:
// string::substr
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main ()
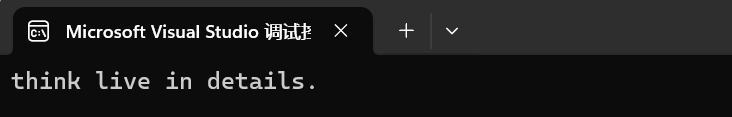
{string str="We think in generalities, but we live in details.";// (quoting Alfred N. Whitehead)string str2 = str.substr (3,5); // "think"size_t pos = str.find("live"); // 取"live"在str对象中的位置string str3 = str.substr (pos); // 取从"live"开始到整个str结尾构造字串给str3cout << str2 << ' ' << str3 << '\n';return 0;
}
compare
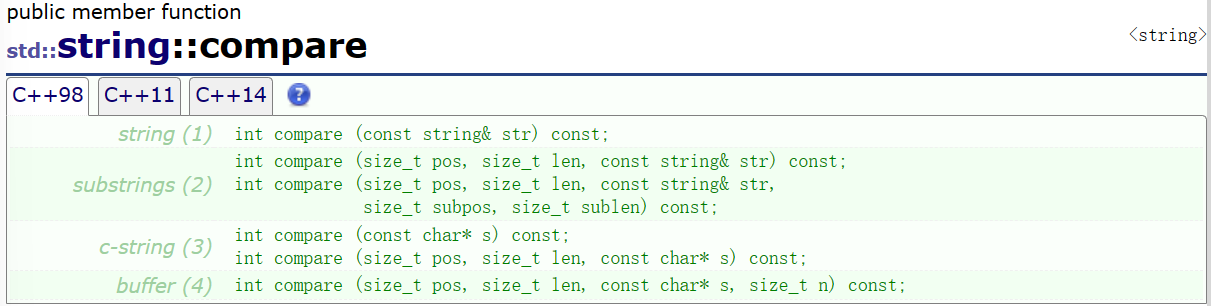
按字典序规则将string对象(或其字串)和别的字符序列进行比较。和之前非成员函数重载的比较运算符很相似,但其功能更全一些,可以直接进行子串之间的比较。
string (1)
int compare (const string& str) const;
substrings (2)
int compare (size_t pos, size_t len, const string& str) const;
int compare (size_t pos, size_t len, const string& str, size_t subpos, size_t sublen) const;
c-string (3)
int compare (const char* s) const;
int compare (size_t pos, size_t len, const char* s) const;
buffer (4)
int compare (size_t pos, size_t len, const char* s, size_t n) const;
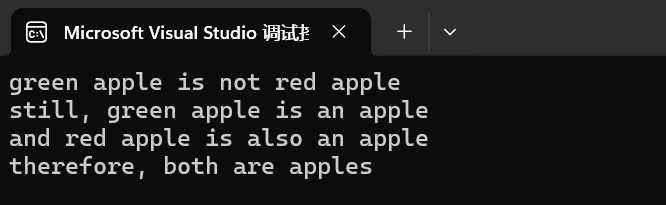
直接上代码案例吧,其实也好懂:
// comparing apples with apples
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string str1("green apple");string str2("red apple");if (str1.compare(str2) != 0)cout << str1 << " is not " << str2 << '\n';if (str1.compare(6, 5, "apple") == 0)cout << "still, " << str1 << " is an apple\n";if (str2.compare(str2.size() - 5, 5, "apple") == 0)cout << "and " << str2 << " is also an apple\n";if (str1.compare(6, 5, str2, 4, 5) == 0)cout << "therefore, both are apples\n";return 0;
}
🔥常量成员(Member constants)

npos

static const size_t npos = -1;
npos是一个const类型的静态成员常量,表示size_t类型的数据可能取到的最大值。
可以通过string::npos获取其值,在上面的很多代码案例中都有用到。
整个值,常被当作缺省参数用在string的很多成员函数中(如len,sublen等),表示取到string对象的末尾。
当它作为返回值被返回时,常被用于表示无匹配项。
这个常数被赋值为-1,是因为size_t是一个无符号整型,-1代表的就是无符号整型(size_t)可能取到的最大值。
结语
本篇博客,介绍了关于string的字符串操作,可以查找和获取字符串的相关内容;以及常量成员,表示size_t可能取到的最大值,作为返回值返回时常用于表示无匹配项。
string的使用系列到这里就结束了。博主后续还会分享string类的模拟实现以及STL更多的内容,感谢大家的支持。♥