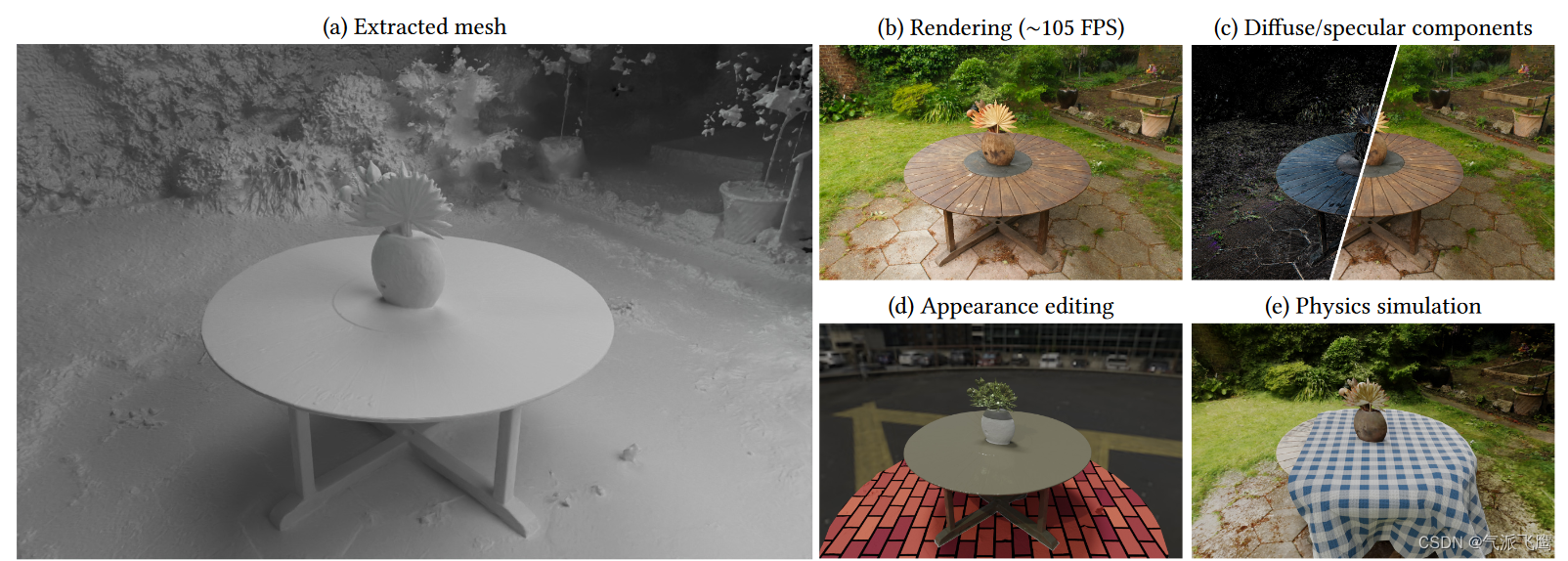
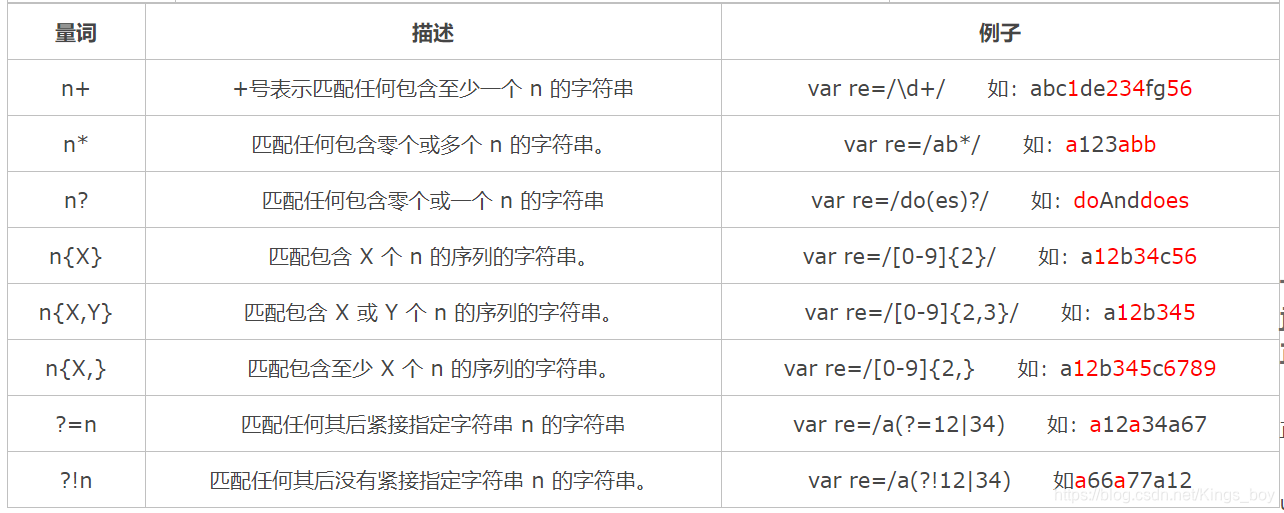
论文链接:https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content/CVPR2022/papers/An_Killing_Two_Birds_With_One_Stone_Efficient_and_Robust_Training_CVPR_2022_paper.pdf
代码链接:insightface/recognition/arcface_torch at master · deepinsight/insightface · GitHub
背景
使用基于百万规模的数据集和基于margin的softmax损失函数来学习区分性的embeddings是当前人脸识别的SOTA方法。然而,全连接层的内存和计算成本随着训练集中ID数量的增加而线性增加。此外,大规模训练数据存在类间冲突(同一个人被分成不同ID)和长尾分布的问题。
传统FC
将传统的FC层应用在大规模的数据集上时,存在以下缺陷:
1、gradient confusion under interclass conflict
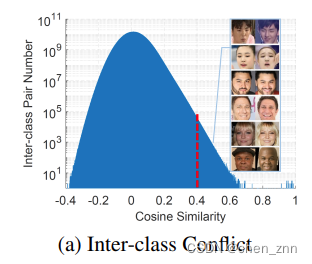
WebFace42M里有很多不同类别对之间的余弦相似度大于0.4,这表明类间冲突仍然存在于这些清洗过的数据集中。直接优化的话会导致gradient confusion(同一个人的特征非常相似却要掰成两个ID)
2、centers of tail classes undergo too many passive updates
每个iteration都优化图片数量很少的id,可能会导致负优化
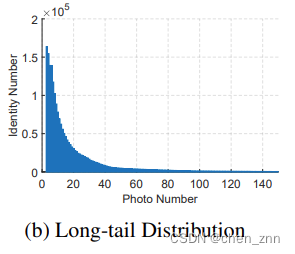
3、the storage and calculation of the FC layer can easily exceed current GPU capabilities
PartialFC
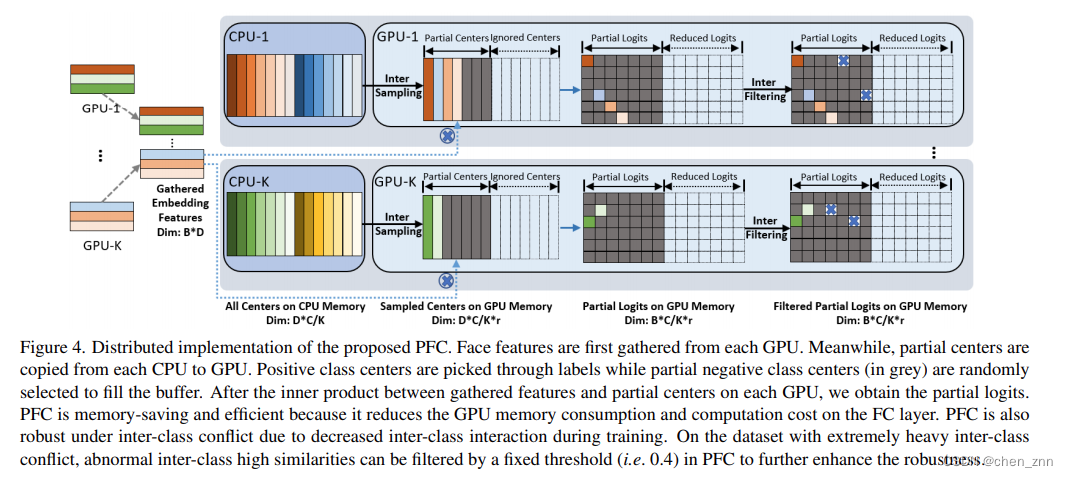
在训练期间仍然维护所有类别中心,但只随机采样一小部分负类别中心来计算基于margin的softmax损失,而不是在每次迭代中使用所有负类别中心。更具体地说,首先从每个GPU收集embeddings和标签,然后将组合的特征和标签分布到所有GPU。为了平衡每个GPU的内存使用和计算成本,为每个GPU设置了一个内存缓冲区(下面代码中的perm)。内存缓冲区的大小由类别总数和负类别中心的采样率决定。在每个GPU上,首先通过标签选择正类中心并放入缓冲区,然后随机选择一小部分负类中心(负类中心的数量为self.sample_rate * self.num_local)填充缓冲区的其余部分,
def sample(self, labels, index_positive):"""This functions will change the value of labelsParameters:-----------labels: torch.Tensorpassindex_positive: torch.Tensorpassoptimizer: torch.optim.Optimizerpass"""with torch.no_grad():positive = torch.unique(labels[index_positive], sorted=True).cuda()if self.num_sample - positive.size(0) >= 0:perm = torch.rand(size=[self.num_local]).cuda()perm[positive] = 2.0index = torch.topk(perm, k=self.num_sample)[1].cuda()index = index.sort()[0].cuda()else:index = positiveself.weight_index = indexlabels[index_positive] = torch.searchsorted(index, labels[index_positive])return self.weight[self.weight_index]随后,使用选出的样本中心去与特征相乘并计算基于margin的softmax损失。
PFC在DDP框架下的流程图如下图所示,
整体代码如下,
class PartialFC_V2(torch.nn.Module):"""https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.15565A distributed sparsely updating variant of the FC layer, named Partial FC (PFC).When sample rate less than 1, in each iteration, positive class centers and a random subset ofnegative class centers are selected to compute the margin-based softmax loss, all classcenters are still maintained throughout the whole training process, but only a subset isselected and updated in each iteration... note::When sample rate equal to 1, Partial FC is equal to model parallelism(default sample rate is 1).Example:-------->>> module_pfc = PartialFC(embedding_size=512, num_classes=8000000, sample_rate=0.2)>>> for img, labels in data_loader:>>> embeddings = net(img)>>> loss = module_pfc(embeddings, labels)>>> loss.backward()>>> optimizer.step()"""_version = 2def __init__(self,margin_loss: Callable,embedding_size: int,num_classes: int,sample_rate: float = 1.0,fp16: bool = False,):"""Paramenters:-----------embedding_size: intThe dimension of embedding, requirednum_classes: intTotal number of classes, requiredsample_rate: floatThe rate of negative centers participating in the calculation, default is 1.0."""super(PartialFC_V2, self).__init__()assert (distributed.is_initialized()), "must initialize distributed before create this"self.rank = distributed.get_rank()self.world_size = distributed.get_world_size()self.dist_cross_entropy = DistCrossEntropy()self.embedding_size = embedding_sizeself.sample_rate: float = sample_rateself.fp16 = fp16self.num_local: int = num_classes // self.world_size + int(self.rank < num_classes % self.world_size)self.class_start: int = num_classes // self.world_size * self.rank + min(self.rank, num_classes % self.world_size)self.num_sample: int = int(self.sample_rate * self.num_local)self.last_batch_size: int = 0self.is_updated: bool = Trueself.init_weight_update: bool = Trueself.weight = torch.nn.Parameter(torch.normal(0, 0.01, (self.num_local, embedding_size)))# margin_lossif isinstance(margin_loss, Callable):self.margin_softmax = margin_losselse:raisedef sample(self, labels, index_positive):"""This functions will change the value of labelsParameters:-----------labels: torch.Tensorpassindex_positive: torch.Tensorpassoptimizer: torch.optim.Optimizerpass"""with torch.no_grad():positive = torch.unique(labels[index_positive], sorted=True).cuda()if self.num_sample - positive.size(0) >= 0:perm = torch.rand(size=[self.num_local]).cuda()perm[positive] = 2.0index = torch.topk(perm, k=self.num_sample)[1].cuda()index = index.sort()[0].cuda()else:index = positiveself.weight_index = indexlabels[index_positive] = torch.searchsorted(index, labels[index_positive])return self.weight[self.weight_index]def forward(self,local_embeddings: torch.Tensor,local_labels: torch.Tensor,):"""Parameters:----------local_embeddings: torch.Tensorfeature embeddings on each GPU(Rank).local_labels: torch.Tensorlabels on each GPU(Rank).Returns:-------loss: torch.Tensorpass"""local_labels.squeeze_()local_labels = local_labels.long()batch_size = local_embeddings.size(0)if self.last_batch_size == 0:self.last_batch_size = batch_sizeassert self.last_batch_size == batch_size, (f"last batch size do not equal current batch size: {self.last_batch_size} vs {batch_size}")_gather_embeddings = [torch.zeros((batch_size, self.embedding_size)).cuda()for _ in range(self.world_size)]_gather_labels = [torch.zeros(batch_size).long().cuda() for _ in range(self.world_size)]_list_embeddings = AllGather(local_embeddings, *_gather_embeddings)distributed.all_gather(_gather_labels, local_labels)embeddings = torch.cat(_list_embeddings)labels = torch.cat(_gather_labels)## 选出落在本进程对应的类别范围内的数据labels = labels.view(-1, 1)index_positive = (self.class_start <= labels) & (labels < self.class_start + self.num_local)## 标签不在本类别段的, 将其类别标签设为-1labels[~index_positive] = -1## 将类别ID平移到原点(因为不同进程都会初始化对应的self.weight, 若不平移回去, 则label与self.weight中的index会对应不上)labels[index_positive] -= self.class_startif self.sample_rate < 1:weight = self.sample(labels, index_positive)else:weight = self.weightwith torch.cuda.amp.autocast(self.fp16):norm_embeddings = normalize(embeddings)norm_weight_activated = normalize(weight)logits = linear(norm_embeddings, norm_weight_activated)if self.fp16:logits = logits.float()logits = logits.clamp(-1, 1)logits = self.margin_softmax(logits, labels)loss = self.dist_cross_entropy(logits, labels)return loss实验结果
将PFC替换掉传统FC后,模型在WebFace(包括4m、12m、42m)上的性能会有所提升,
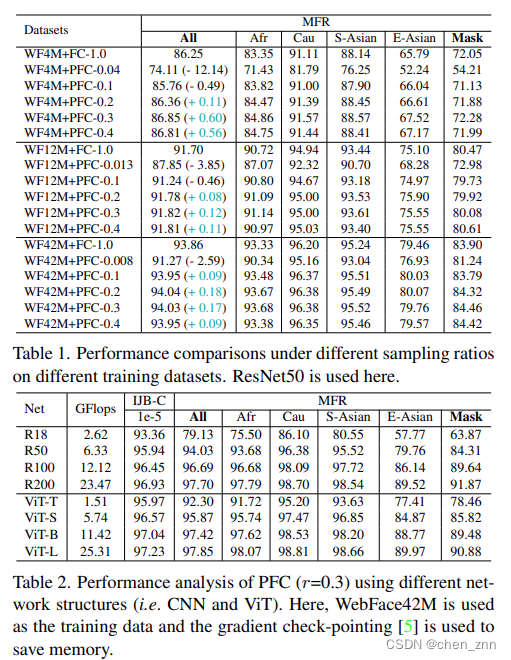

消融实验的结果如下,
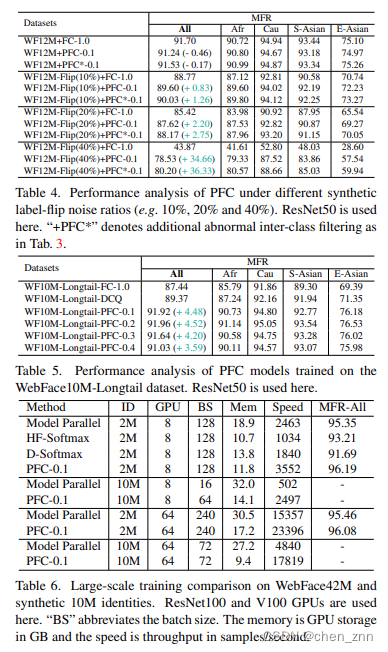
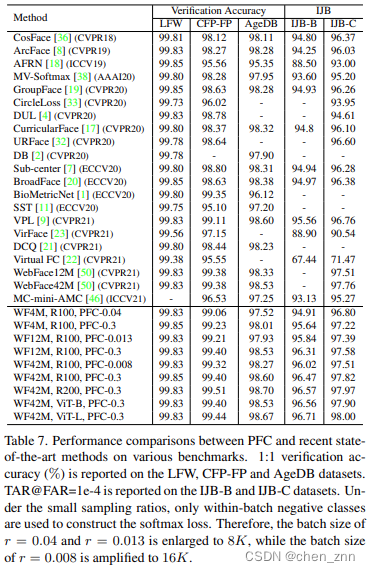
与SOTA方法的性能对比如下,
结论与讨论
结论
作者提出了一种用于在大规模数据集上训练人脸识别模型的方法——Partial FC (PFC)。在PFC的每次迭代中,仅选择一小部分类别中心来计算基于边际的softmax损失,这样可以显著减少类间冲突的概率、尾类中心的被动更新频率以及计算需求。通过广泛的实验,作者验证了所提出的PFC的有效性、鲁棒性和高效性。
局限性
尽管在WebFace上训练的PFC模型在高质量测试集上取得了不错的结果,但在人脸分辨率较低或低光照条件下拍摄的人脸上,PFC模型的表现可能较差。