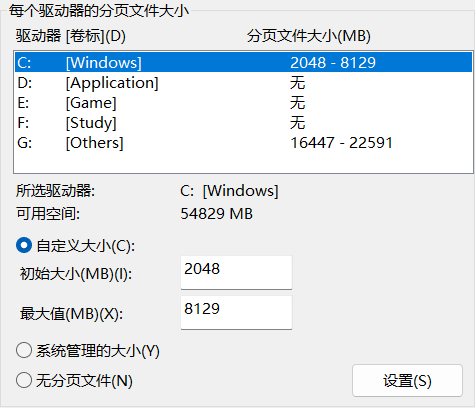
A.小W与伙伴招募
考虑贪心,可以发现,每一天只需要优先选择价值低的即可
这种贪心思路有一个错误的扩展,就是先把 \(m\) 天的货一次性补齐再一次性买,这样做的问题在于有可能买到次日的货,而这样做是不被允许的
考虑放到线段树上,维护 “节点能够提供的钻石数量” 和 “节点花费” 两个值,只要我们保证价格在线段树上递增排列(这是很好做到的,排序再建树即可),那么我们就可以通过和平衡树类似的二分来向下递归
- 如果左子树满足当前要求,直接在左子树里买
- 否则,先把左子树买完,再在右子树里买
然后考虑怎么维护这两个值
每次补货只能单点修改,复杂度显然太高了,因此,我们设计节点数量 \(t=kb_i+s\),其中 \(b_i\) 为 \(i\) 的每日补货数量,这样我们在每一天新开始的时候,只需要让所有的 \(k\) 都增加 \(1\) 就可以了,而这在线段树上是容易实现的
介于我们并不能同时维护加和乘,所以开两棵线段树(当然也可以合成一颗,不过两者的维护是完全没有关系的),然后在父结点上维护子节点权值和即可
还有问题就是怎么在补货之后比较快地实现 pushdown,可以在外面开两个前缀和来实现(分别对应两颗线段树)
然后是 lazytag,针对本题需要开两个 tag,一个维护补货时候的 k 增量,一个维护买了东西以后的整体清空,执行的时候先清空再增,注意顺序
\(-1\) 直接赋成 \(1e6\) 就行了
另外需要注意的就是,不要直接对 \(m\) 建树,可以考虑微调一下 sort,让价值相同的中,数量最多的排在前面,然后你只要遇到一个 \(-1\) 就说明你一直买这个就行了(后面的都更贵),因此直接对此时的 \(i\) 建树就行了
不过我不明白为啥对 \(m\) 建树会导致答案错掉
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
template<typename T>
void read(T& x){x=0;bool sym=0;char c=getchar();while(!isdigit(c)){sym^=(c=='-');c=getchar();}while(isdigit(c)){x=x*10+c-48;c=getchar();}if(sym)x=-x;
}
template<typename T,typename... Args>
void read(T& x,Args&... args){read(x);read(args...);
}
#define int long long
struct tree{int l,r;int tot_sum,cost_sum;int lazy_cover,lazy_k;
}t[200001*4];
int tot_sum[200001],cost_sum[200001];
struct item{int a,b;bool operator <(const item &A)const{if(a==A.a) return b>A.b;return a<A.a;}
}w[200001];
#ifndef TOOL_H
#define TOOL_H
#endif
template<typename T>
T floor_sqrt(T x,T l=1,T r=-1){if(r==-1) r=x;int ans=-1;while(l<=r){int mid=(l+r)/2;if(mid*mid<=x){l=mid+1;ans=mid;}else{r=mid-1;}}return ans;
}
void print(__int128 x,bool first=true){if(x<0){putchar('-');print(-x,false);return;}if(x==0){if(first) putchar('0');return;}print(x/10,false);putchar((int)(x%10)+'0');
}
template<typename T>
std::string to_string(T x){std::string res;bool f=false;if(x<0){f=true;x*=-1;}while(x){res.push_back((int)(x%10)+'0');x/=10;}reverse(res.begin(),res.end());if(f) res.push_back('-');if(res.empty()) res.push_back('0');return res;
}
long long to_number(std::string x){long long res=0;bool f=false;for(int i=0;i<=(int)x.length()-1;++i){if(x[i]=='-'){f=true;}else{res=res*10+x[i]-'0';}}return res*(f?-1:1);
}
/*------TOOL_H------*/
#define tol (id*2)
#define tor (id*2+1)
#define mid(l,r) mid=((l)+(r))/2
void build(int id,int l,int r){t[id].l=l;t[id].r=r;if(l==r) return;int mid(l,r);build(tol,l,mid);build(tor,mid+1,r);
}
void update(int id){t[id].tot_sum=t[tol].tot_sum+t[tor].tot_sum;t[id].cost_sum=t[tol].cost_sum+t[tor].cost_sum;
}
void pushdown_cover(int id){if(t[id].lazy_cover){t[tol].tot_sum=t[tol].cost_sum=0;t[tor].tot_sum=t[tor].cost_sum=0;t[tol].lazy_k=t[tor].lazy_k=0;t[tol].lazy_cover=t[tor].lazy_cover=1;t[id].lazy_cover=0;}
}
void pushdown_k(int id){if(t[id].lazy_k){t[tol].tot_sum+=t[id].lazy_k*(tot_sum[t[tol].r]-tot_sum[t[tol].l-1]);t[tor].tot_sum+=t[id].lazy_k*(tot_sum[t[tor].r]-tot_sum[t[tor].l-1]);t[tol].cost_sum+=t[id].lazy_k*(cost_sum[t[tol].r]-cost_sum[t[tol].l-1]);t[tor].cost_sum+=t[id].lazy_k*(cost_sum[t[tor].r]-cost_sum[t[tor].l-1]);t[tol].lazy_k+=t[id].lazy_k;t[tor].lazy_k+=t[id].lazy_k;t[id].lazy_k=0;}
}
void change(int id,int k){if(k>0){t[id].tot_sum+=(tot_sum[t[id].r]-tot_sum[t[id].l-1]);t[id].cost_sum+=(cost_sum[t[id].r]-cost_sum[t[id].l-1]);t[id].lazy_k+=k;}else{t[id].tot_sum=0;t[id].cost_sum=0;t[id].lazy_k=0;t[id].lazy_cover=1;}
}
int ask(int id,int k){if(t[id].l==t[id].r){t[id].tot_sum-=k;t[id].cost_sum-=w[t[id].l].a*k;return w[t[id].l].a*k;}pushdown_cover(id);pushdown_k(id);int res=0;if(k<=t[tol].tot_sum){res=ask(tol,k);}else{res=t[tol].cost_sum+ask(tor,k-t[tol].tot_sum);change(tol,-1);}update(id);return res;
}
int n,m;
int c[200001];
const int inf=1e6;
signed main(){freopen("a.in","r",stdin);freopen("a.out","w",stdout);read(n,m);for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){read(c[i]);}for(int i=1;i<=m;++i){read(w[i].a,w[i].b);if(w[i].b==-1) w[i].b=inf;}sort(w+1,w+m+1);for(int i=1;i<=m;++i){tot_sum[i]=tot_sum[i-1]+w[i].b;cost_sum[i]=cost_sum[i-1]+w[i].a*w[i].b;if(w[i].b==inf){build(1,1,i);break;}}int ans=0;for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){change(1,1);ans+=ask(1,c[i]);}print(ans);
}
B.小W与制胡串谜题
[](string a,string b){return a+b<b+a;}