我们之前讨论并实践过通过常规的函数调用来实现 AI Agent 的设计和实现。但是,有一个关键点我之前并没有详细讲解。今天我们就来讨论一下,如何让大模型只决定是否调用某个函数,但是Spring AI 不会在内部处理函数调用,而是将其代理到客户端。然后,客户端负责处理函数调用,将其分派到相应的函数并返回结果。
好的,我们开始。
函数调用
核心代码
函数调用是开发AI Agent的关键组成部分,它使得AI能够与外部系统、数据库或其他服务进行交互,从而提升了其功能性和灵活性。所以开发必须要适用于支持函数调用的聊天模型,在Spring AI中处理函数调用也仅仅是一行代码,核心代码如下,我们看下:
if (!isProxyToolCalls(prompt, this.defaultOptions)&& isToolCall(response, Set.of(OpenAiApi.ChatCompletionFinishReason.TOOL_CALLS.name(),OpenAiApi.ChatCompletionFinishReason.STOP.name()))) {var toolCallConversation = handleToolCalls(prompt, response);return this.internalCall(new Prompt(toolCallConversation, prompt.getOptions()), response);
}
假设我们已经开发并集成了一个天气查询函数,当我们向大模型提出类似“长春天气咋样”这样的请求时,大模型会自动识别并选择调用相应的函数。在这个过程中,handleToolCalls 方法通过反射机制来动态地调用正确的天气查询方法,接着该方法会递归调用 internalCall 方法,继续处理后续的逻辑。需要注意的是,关于反射机制和递归调用的具体实现细节,在前文中已经有所说明,因此此处不再赘述。
判断是否是函数
protected boolean isToolCall(Generation generation, Set<String> toolCallFinishReasons) {var finishReason = (generation.getMetadata().getFinishReason() != null)? generation.getMetadata().getFinishReason() : "";return generation.getOutput().hasToolCalls() && toolCallFinishReasons.stream().map(s -> s.toLowerCase()).toList().contains(finishReason.toLowerCase());
}
isToolCall的核心逻辑就是要判断大模型返回的信息是否正确,OpenAI的API文档如下:
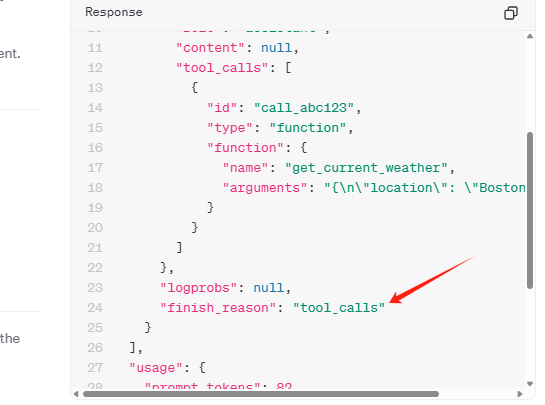
重写判断
如果你的大模型返回的格式不一样,那么重写方法即可,比如minimax就重写了,我们看下:
protected boolean isToolCall(Generation generation, Set<String> toolCallFinishReasons) {if (!super.isToolCall(generation, toolCallFinishReasons)) {return false;}return generation.getOutput().getToolCalls().stream().anyMatch(toolCall -> org.springframework.ai.minimax.api.MiniMaxApiConstants.TOOL_CALL_FUNCTION_TYPE.equals(toolCall.type()));
}
他在原有的基础上又再次判断了一下toolCall.type是否为function,因为minimax不仅支持function类型的type,还支持web_search,看下官方文档,如图所示:
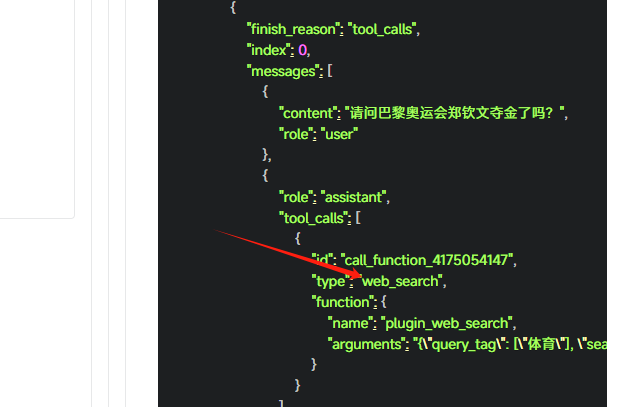
不要细究为什么他会有这个类型,只需要明白你可以根据不同大模型接口重写isToolCall方法判断即可!
函数自动调用开关
前面提到之所以会默认调用函数并再次进行大模型调用以进行润色并返回参考结果,关键原因在于 isProxyToolCalls 参数默认设置为 false。这个参数充当了一个控制开关,用来决定是由用户自行处理相关逻辑,还是由 Spring AI 自动进行处理并进行润色。
具体而言,用户可以通过设置该开关来选择是手动管理流程,还是让系统自动完成这一过程。以下是该控制开关的核心代码示例:
OpenAiChatOptions openAiChatOptions = OpenAiChatOptions.builder().withProxyToolCalls(true).build();
此时一旦你打开此开关,你就需要自己进行处理本次结果了。大模型将仅返回调用的参数以及其思考过程的输出,具体内容如下所示:
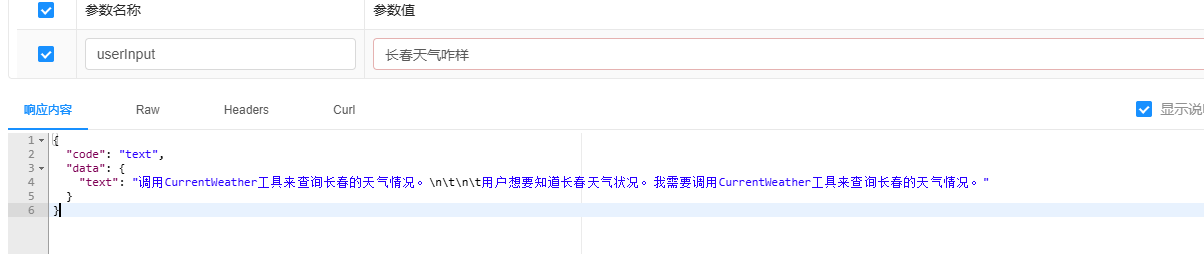
没返回参数等信息,是因为我把其他信息丢弃了,你可以这样写:
ChatResponse content = this.chatClient.prompt(systemPrompt).user(userInput).options(openAiChatOptions).advisors(messageChatMemoryAdvisor,myLoggerAdvisor).functions("CurrentWeather","TravelPlanning","toDoListFunctionWithContext","myWorkFlowServiceCall").call();// .content();这里只返回string,也就是思考结果
好的。一旦你获得了 ChatResponse 类的实例后,你就可以根据需要自由地操作该对象,并调用其中的各种函数了。你不必从头编写所有的代码,实际上,你可以参考 OpenAI 提供的测试样例,这样会大大简化你的开发过程。以下是一个参考示例:
FunctionCallback functionDefinition = new FunctionCallingHelper.FunctionDefinition("getWeatherInLocation","Get the weather in location", """{"type": "object","properties": {"location": {"type": "string","description": "The city and state e.g. San Francisco, CA"},"unit": {"type": "string","enum": ["C", "F"]}},"required": ["location", "unit"]}""");@Autowired
private OpenAiChatModel chatModel;private FunctionCallingHelper functionCallingHelper = new FunctionCallingHelper();@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private static Map<String, String> getFunctionArguments(String functionArguments) {try {return new ObjectMapper().readValue(functionArguments, Map.class);}catch (JsonProcessingException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}
}// Function which will be called by the AI model.
private String getWeatherInLocation(String location, String unit) {double temperature = 0;if (location.contains("Paris")) {temperature = 15;}else if (location.contains("Tokyo")) {temperature = 10;}else if (location.contains("San Francisco")) {temperature = 30;}return String.format("The weather in %s is %s%s", location, temperature, unit);
}void functionCall() throws JsonMappingException, JsonProcessingException {List<Message> messages = List.of(new UserMessage("What's the weather like in San Francisco, Tokyo, and Paris?"));var promptOptions = OpenAiChatOptions.builder().functionCallbacks(List.of(this.functionDefinition)).build();var prompt = new Prompt(messages, promptOptions);boolean isToolCall = false;ChatResponse chatResponse = null;do {chatResponse = this.chatModel.call(prompt);isToolCall = this.functionCallingHelper.isToolCall(chatResponse,Set.of(OpenAiApi.ChatCompletionFinishReason.TOOL_CALLS.name(),OpenAiApi.ChatCompletionFinishReason.STOP.name()));if (isToolCall) {Optional<Generation> toolCallGeneration = chatResponse.getResults().stream().filter(g -> !CollectionUtils.isEmpty(g.getOutput().getToolCalls())).findFirst();AssistantMessage assistantMessage = toolCallGeneration.get().getOutput();List<ToolResponseMessage.ToolResponse> toolResponses = new ArrayList<>();for (AssistantMessage.ToolCall toolCall : assistantMessage.getToolCalls()) {var functionName = toolCall.name();String functionArguments = toolCall.arguments();@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")Map<String, String> argumentsMap = new ObjectMapper().readValue(functionArguments, Map.class);String functionResponse = getWeatherInLocation(argumentsMap.get("location").toString(),argumentsMap.get("unit").toString());toolResponses.add(new ToolResponseMessage.ToolResponse(toolCall.id(), functionName,ModelOptionsUtils.toJsonString(functionResponse)));}ToolResponseMessage toolMessageResponse = new ToolResponseMessage(toolResponses, Map.of());List<Message> toolCallConversation = this.functionCallingHelper.buildToolCallConversation(prompt.getInstructions(), assistantMessage, toolMessageResponse);prompt = new Prompt(toolCallConversation, prompt.getOptions());}}while (isToolCall);logger.info("Response: {}", chatResponse);assertThat(chatResponse.getResult().getOutput().getText()).contains("30", "10", "15");
}
这段代码采用了 while 循环来实现默认情况下调用大模型进行润色的逻辑。你可以选择去掉这一部分逻辑,改为直接调用你自己定义的函数,这样就可以绕过大模型的润色过程,直接将结果返回给客户端。通过这种方式,你能够轻松实现类似市面上大多数智能体平台所提供的功能:即在不同场景下,可以选择是否使用固定格式的回答,或是直接采用大模型的回答。
聊天记录维护
这里有几个需要特别注意的关键点。首先,你必须将每次调用后的结果主动封装并更新到历史聊天记录中。如果不这样做,一旦信息顺序或格式出现混乱,系统会直接报错。因此,确保按正确的顺序进行操作是至关重要的。正常的操作流程应遵循如下顺序:

你可以看到测试样例中是有这一步操作的,在这一行代码buildToolCallConversation,代码追到后面就是这样的核心逻辑,代码如下:
protected List<Message> buildToolCallConversation(List<Message> previousMessages, AssistantMessage assistantMessage,ToolResponseMessage toolResponseMessage) {List<Message> messages = new ArrayList<>(previousMessages);messages.add(assistantMessage);messages.add(toolResponseMessage);return messages;
}
总结
通过今天的讨论,我们首先了解了如何实现函数调用的基础机制,通过核心代码示例展示了如何在Spring AI中进行函数的动态调用。在此过程中,关键的isToolCall方法和函数自动调用开关的使用,确保了我们可以根据具体需求调整函数调用的方式,甚至完全由客户端来接管函数执行。此外,通过维护聊天记录并精心管理工具调用的顺序,我们能确保AI的行为更为可控和稳定。
总的来说,今天的分享为大家提供了一种新的思路,使得在开发AI Agent时,我们不仅仅依赖大模型的内建能力,还可以通过客户端控制函数的调用和返回结果,从而打造更加灵活和高效的智能系统。这种方式无疑为开发者提供了更多定制化的选择,提升了开发过程的自由度和效率。
我是努力的小雨,一个正经的 Java 东北服务端开发,整天琢磨着 AI 技术这块儿的奥秘。特爱跟人交流技术,喜欢把自己的心得和大家分享。还当上了腾讯云创作之星,阿里云专家博主,华为云云享专家,掘金优秀作者。各种征文、开源比赛的牌子也拿了。
💡 想把我在技术路上走过的弯路和经验全都分享出来,给你们的学习和成长带来点启发,帮一把。
🌟 欢迎关注努力的小雨,咱一块儿进步!🌟